Introduction
In Japan, the number of patients who have received
radiotherapy for cancer has increased since 1995. With the rapidly
increasing number of patients with prostate cancer in their 50s and
older, as well as an aging society, radiotherapy is expected to be
one of the treatment methods used. There were 851 radiotherapy
facilities in Japan (1), with
intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT), a type of high-precision
radiotherapy, being the most commonly used for prostate cancer
cases, with over 320 facilities (1). In 2020, 423 facilities were equipped
to provide IMRT (2), making it
easier for patients to receive treatment. Conversely, for prostate
cancer, adverse events (AE) are a significant issue in external
beam radiotherapy. Acute AEs include diarrhea, proctitis, cystitis,
fatigue, and mild skin irritation, primarily in the gluteal fold
(3). Furthermore, the most recent
Japanese radiotherapeutic guideline (JASTRO Guidelines 2020)
identified dysentery, dermatitis around the anus, rectal bleeding,
and frequent urination as AEs (4).
Genitourinary toxicity, such as bladder spasms, cystitis,
genitourinary fistula, urinary incontinence, genitourinary leak,
genitourinary obstruction, genitourinary perforation, prolapse of
stoma, renal failure, stricture/stenosis, urinary electrolyte
wasting, urinary frequency/urgency, and urinary retention (5), is particularly associated with a
decrease in quality of life after treatment initiation. These
diagnoses are primarily made by interview and direct observation of
the patient. Therefore, no standard biomarkers are known for a
priori prediction of them.
A rough treatment plan is developed once the cancer
type and pathology are identified within the current radiotherapy
strategy. The patient's condition during treatment is monitored
through medical examination, blood and urine sampling, and
diagnostic imaging; however, little radiobiological information is
considered, making it difficult to predict AEs. Thus, there is no
definitive method for confirming the response of target tissue
cells or organs at risk in real time (6), and it is proposed to incorporate this
biological response into radiotherapy strategies.
A well-established theory in which 4R
radiobiological concepts are considered is fractionated
radiotherapy. Out of these concepts, only ‘repair’ is considered in
the linear-quadratic model (7,8). In
clinical practice, assessing the remaining reoxygenation,
redistribution, and repopulation (3Rs) in real time has proven
difficult. Recent technological advances in molecular biology, as
well as increased statistical analysis speed, have enabled more
detailed analysis of cancer cells. Furthermore, new theories have
emerged that challenge conventional theories of radiation biology.
Particularly, cancer cell metabolism remains largely unknown
because of the diversity of their characteristics.
Metabolome analysis, which has gained popularity in
recent years, can detect metabolite changes using mass spectrometry
with high qualitative and quantitative accuracy (9). In this study, metabolomics was
performed on urine samples from patients with localized prostate
cancer to identify biomarkers predictive of acute AEs.
The European Association of Urology now recommends
dose-escalated IMRT or volumetric-modulated arc therapy (VMAT) as
standard therapies for prostate carcinoma because of the lower
toxicity compared to 3D-conformal radiotherapy (3D-CRT) (10). VMAT may be the first option
(11) and is widely accepted as
the gold standard for prostate radiotherapy (12). With the use of modern RT (IMRT,
VMAT), greater precision was achieved when compared to conventional
RT (13). Various studies have
established IMRT as the standard of care for external beam RT for
prostate cancer, with a lower rate of acute and late RT-induced
toxicities compared to 3D-CRT (14). To optimize planning for VMAT, which
has fewer acute and late complications, the AUA/ASTRO guideline
2022 recommended the use of highly conformal radiotherapy such as
IMRT, VMAT, and stereotactic body radiotherapy, in conjunction with
published target and normal tissue dose objectives (15).
The high radiation dose rate causes DNA damage in
cancer cells as a direct or indirect reaction mediated by ROS. The
most serious damage is caused by DNA single-strand breaks and
double-strand breaks. Several AEs are caused by chronic oxidative
stress, which impairs the nuclear function of DNA repair mechanisms
(16). However, there are
different types of AEs based on symptoms, frequency, and
severity.
Identifying and predicting metabolites that respond
to acute AEs in external beam radiotherapy would help to maintain
radiotherapy safety and quality of life, as well as improve
treatment selection (i.e., optimization). This study sought to
identify a predictive biomarker from urinary metabolites for AEs
during VMAT in localized prostate cancer and to optimize this
radiotherapy in preparation for an increase in target patients.
Materials and methods
Study population
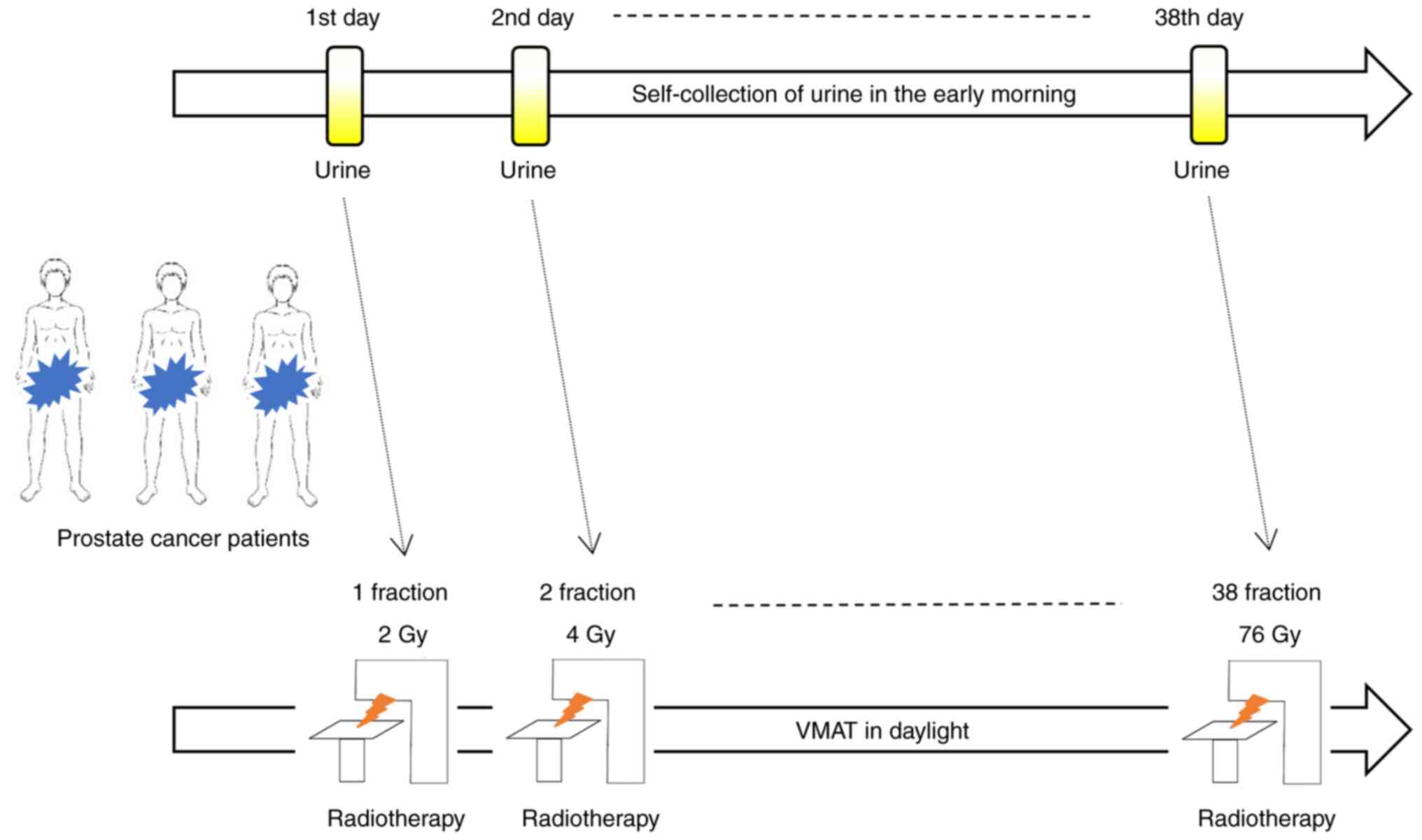
The current study included 11 patients with
localized prostate cancer who received VMAT at Hirosaki University
Hospital between June 2021 and March 2022 were enrolled (Fig. 1). All of the patients were Asians
from across eastern Japan. The key characteristics examined
included age, T stage, Gleason score, prostate-specific antigen
(PSA), National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) risk
classification, and fraction with acute AEs. The acute AEs
highlighted in this study were classified using the Common
Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events Version 5.0 from the U.S.
Department of Health and Human Services (https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/ctc.htm#ctc_50).
Patient urination
The participants were patients with localized
prostate cancer who underwent VMAT (76 Gy/38 fractions) at Hirosaki
University Hospital between June 2021 and March 2022. Urine was
self-collected using Uro Catch II (ATLETA Corp., Ltd., Osaka,
Japan) early in the morning at rest and via midstream catch (10
ml). Self-urination samples were collected daily from the first to
the last day of irradiation (Fig.
1). Urine samples were collected and stored in a freezer (MY
BIO VT-208HC, Nihon freezer Corp., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) at -80˚C, to
ensure metabolite stability until mass spectrometry analysis. Acute
AEs such as urinary frequency during the irradiation period were
documented during the patient's medical interview.
Metabolomics
Urine samples were thawed to room temperature. A
total of 630 metabolites from 14 small molecules and 12 different
lipid classes were analyzed using the MxP® Quant 500 kit
(Biocrates Life Sciences AG, Innsbruck, Austria) according to the
manufacturer's instructions. Approximately 10 µl of urine was
pipetted on a 96-well plate with internal standards and dried under
a nitrogen stream using a positive-pressure manifold (Biotage AB,
Uppsala, Sweden). Then, 50 µl of 5% phenyl isothiocyanate solution
was added to each well to derivatize amino acids and biogenic
amines. After 1 h of incubation at room temperature, the plate was
dried again. To extract metabolites, 300 µl of 5-mM ammonium
acetate in methanol was pipetted into each filter and incubated for
30 min. The extract was eluted into a new 96-well plate via a
positive-pressure manifold. To conduct further LC-MS/MS analyses,
the 150-µl extract was diluted with an equal volume of water. For
FIA-MS/MS analyses, a 10-µl extract was diluted with 490-µl FIA
solvent (Biocrates). LC-MS/MS and FIA-MS/MS measurements were
performed following dilution. For chromatographic separation, an
ExionLC AD (AB SCIEX, Framingham, Massachusetts, USA) system was
connected to a SCIEX QTRAP 6500+ mass spectrometry system in
electrospray ionization mode. Data were generated using the Analyst
(AB SCIEX) software suite and transferred to the MetIDQ software
(using the Recipe Urine QC), where they were further processed and
analyzed. All metabolites were identified using isotopically
labeled internal standards and multiple reaction monitoring through
optimized MS conditions provided by Biocrates. For quantification,
a seven-point calibration curve or one-point calibration was used
depending on the metabolite class. Urine samples were processed
with no prior preparation. Furthermore, in each well (except for
the blank), an internal standard (creatinine) was added before
urine was pipetted onto the plate. Metabolite concentrations were
adjusted for creatinine content. Biologically and clinically
relevant 293 metabolic indices were determined using the
MetaboINDICATOR tool (Biocrates). Each metabolite was given
absolute quantitative values. The collected metabolome data was
registered to the integrated metabolome data repository
(MetaboBank; MTBKS242 and MTBKS243),
Statistical analysis
Using R (Ver. 4.2.0), statistical analysis was
conducted, as well as correlation analysis (Spearman's rank
correlation) was performed between these metabolic indices and
acute AEs or metabolic indices and fraction (physical quantity).
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were produced using
MetaboAnalyst (17) on metabolic
indices that showed a significant correlation with the number of
irradiations. The paired samples Student's t-test was run on
fractions ranging from 0 to 29 to look for metabolites associated
with various metabolic indicators with and without AEs. P<0.05
was considered to indicate a statistically significant
difference.
Results
Patient characteristics
We identified 11 patients who had localized prostate
cancer and underwent VMAT. Four patients (median age, 69 years) had
no confirmed AEs, while the remaining seven patients (71 years)
experienced genitourinary toxicity (GU, Grade 1). The clinical
characteristics of the study population are shown in Table I. With a median PSA of 7.23 ng/ml,
T2b-T3b of 72.7%, and a median total Gleason score of 7 (6-9),
NCCN high-risk constituted 54.5% (n=6) of the study population.
 | Table IClinical characteristics of the study
population. |
Table I
Clinical characteristics of the study
population.
| Characteristic | Adverse event (-)
(n=4) | Adverse event (+)
(n=7) |
|---|
| Age, years | | |
|
Range | 59.0-73.0 | 61.0-75.0 |
|
Median
(IQR) | 69.0 (65.8-70.8) | 71 (69.0-71.5) |
| T stage | | |
|
cT1c | 2 | 1 |
|
cT2a | 1 | 0 |
|
cT2b | 1 | 2 |
|
cT3 | 0 | 3 |
|
cT3a | 0 | 1 |
| Gleason score | | |
|
3+3 | 2 | 0 |
|
3+4 | 1 | 1 |
|
4+3 | 0 | 2 |
|
4+4 | 1 | 0 |
|
4+5 | 0 | 1 |
|
5+3 | 0 | 1 |
|
5+4 | 0 | 2 |
| PSA, ng/ml | | |
|
Range | 4.4-27.2 | 4.4-26.4 |
|
Median
(IQR) | 7.1 (6.3-12.2) | 12.1
(4.8-21.1) |
| NCCN risk
classification | | |
|
Low-risk | 1 | 0 |
|
Intermediate-risk | 2 | 2 |
|
High-risk | 1 | 5 |
| Fraction with
adverse event | | |
|
Median
(IQR) | - | 29 (21.5-30.5) |
| Ethnicity | Asian
(Japanese) | Asian
(Japanese) |
Indicator of lipid metabolism
It has been reported that the phospholipase A2
activity (PLA2 activity) in healthy adults is approximately
1.21(18). This was higher values
than the fraction zero (F=0) of AEs (0.48±0.18) and F=0 of non-AEs
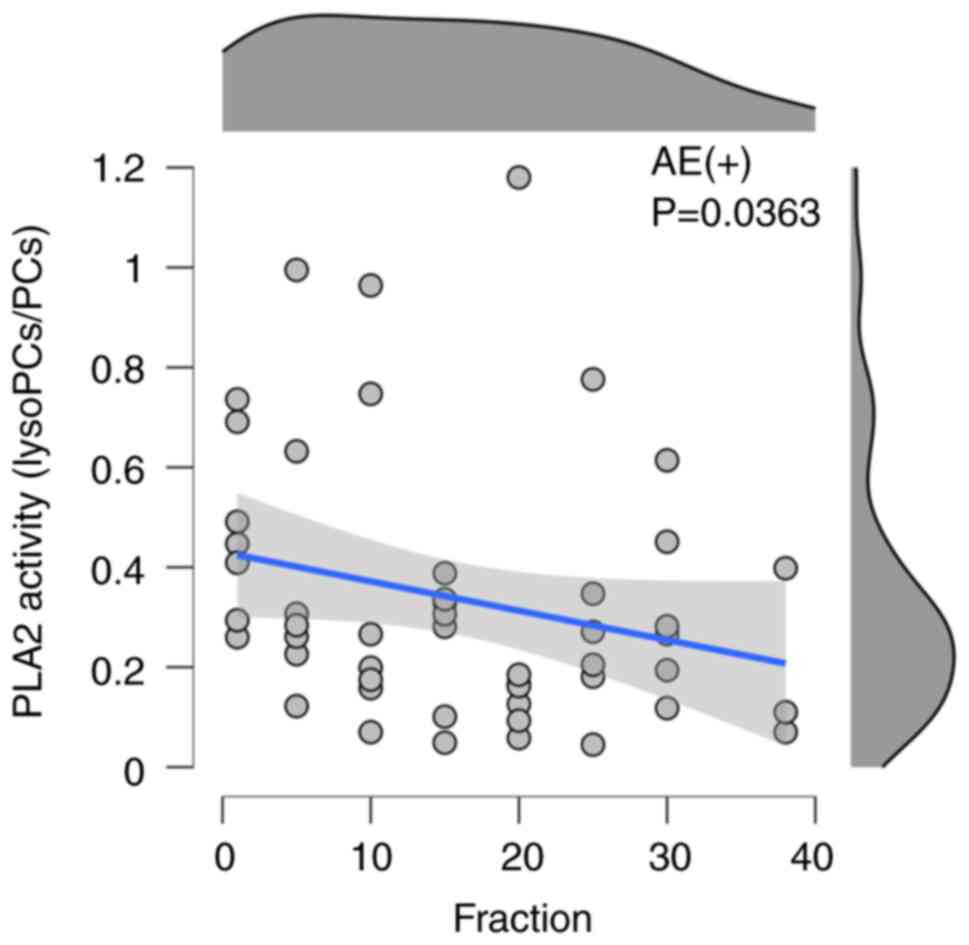
(0.58±0.38) in the current data. In seven patients with acute
AE(+), Spearman's rank correlation revealed a significant
correlation between the fraction and the PLA2 activity index
(rs=-0.297, P<0.05) in Fig. 2
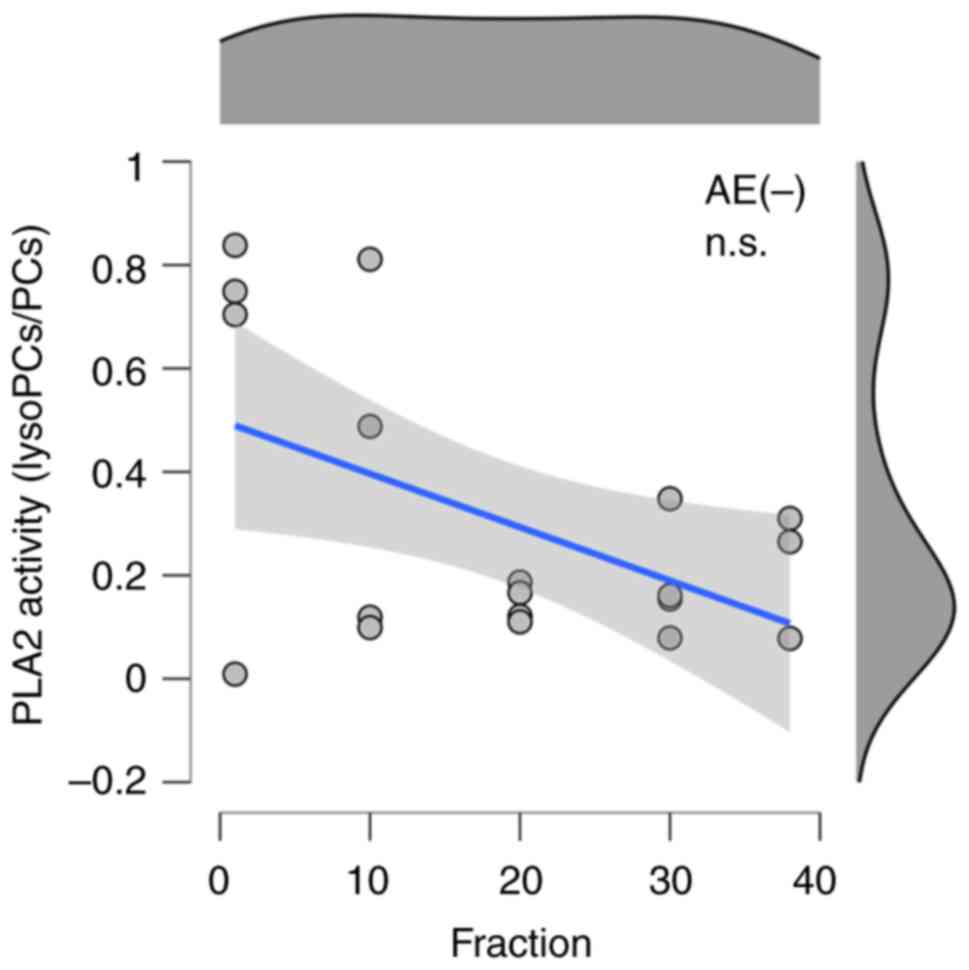
and Table II. There was no
significant correlation found with the absence of AEs (Fig. 3 and Table II). Because PLA2 activity is
represented in the MetaboINDICATOR as lysoPC a Cxx:x/PC ax Cxx:x,
we chose to focus on lysophosphatidylcholine (lysoPC) and
phosphatidylcholine (PC) as metabolites linked to radiation-induced
AEs.
 | Table IISpearman rank correlation between
fraction and PLA2 activity in with/without AE groups. |
Table II
Spearman rank correlation between
fraction and PLA2 activity in with/without AE groups.
| AE group | Lower confidence
limit | rs-value | Upper confidence
limit | P-value |
|---|
| AE(+) | -0.531 | -0.297 | -0.0202 | 0.0363 |
| AE(-) | -0.658 | -0.291 | 0.188 | 0.227 |
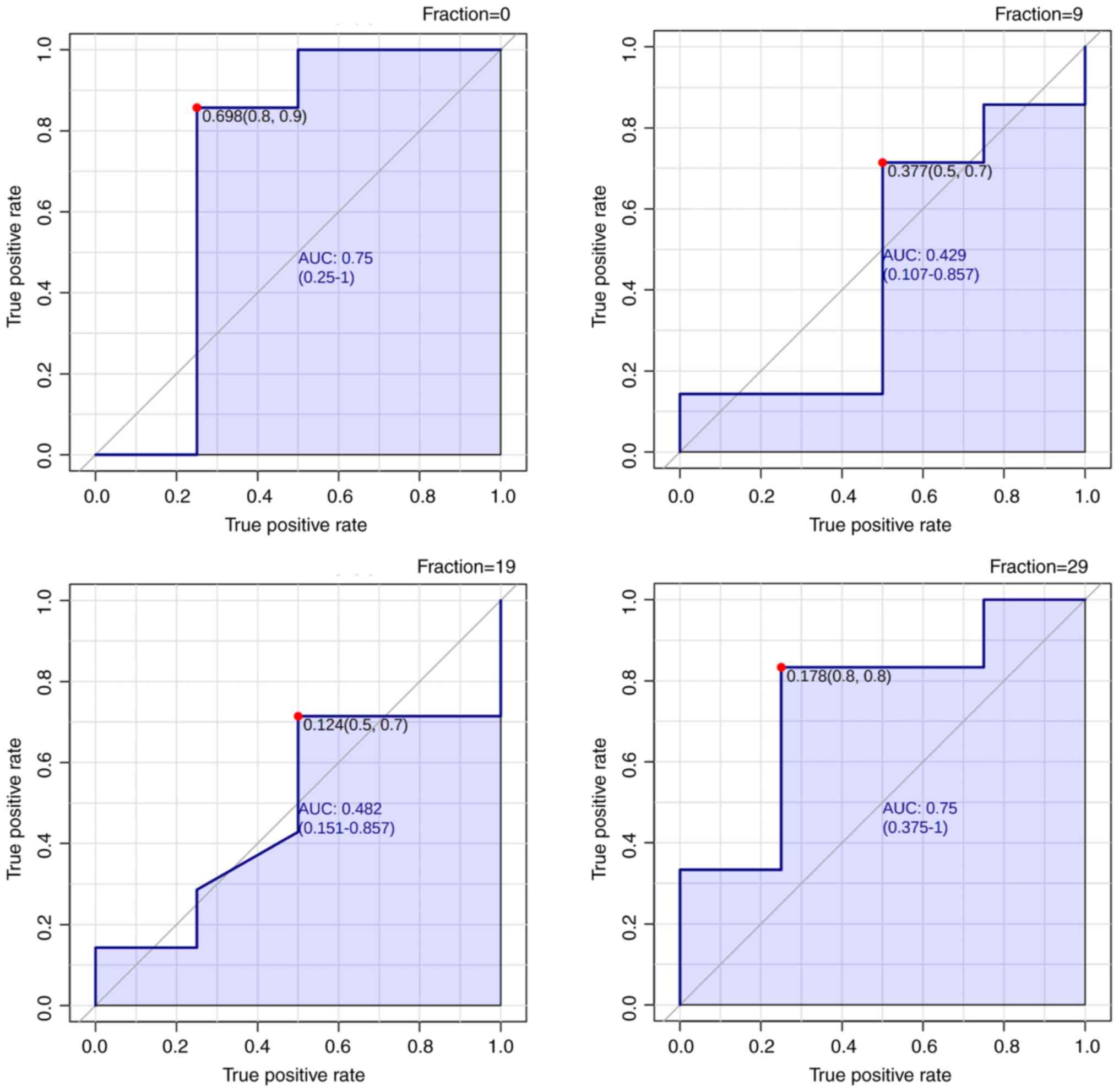
ROC analysis of metabolic
indicators
The ROC curves for the PLA2 activity index in each
fraction are shown in Fig. 4 and
Table III. The cutoff value of
the PLA2 Activity index was 0.178 in 29 fractions, resulting in an
area under the curve (AUC) of 0.75. Fraction 0 also had a high AUC
of 0.75; however, fractions 9 and 19 did not have an AUC greater
than 0.5, indicating a random prediction. Thus, the PLA2 activity
index demonstrated high specificity and sensitivity as a biomarker
in fractions 0 and 29 for predicting the occurrence of AEs.
 | Table IIIReceiver operating characteristic
analysis between fraction and PLA2 activity. |
Table III
Receiver operating characteristic
analysis between fraction and PLA2 activity.
| Fraction | AUC | Cut-off | Specificity | Sensitivity |
|---|
| F0 | 0.75 | 0.698 | 0.8 | 0.9 |
| F9 | 0.429 | 0.377 | 0.5 | 0.7 |
| F19 | 0.482 | 0.124 | 0.5 | 0.7 |
| F29 | 0.75 | 0.178 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
Lipid evaluation classification in
metabolomics
PLA2 activity was found to be correlated with
fractions through correlation analysis. The use of this index as a
biomarker necessitates measuring the entire series of lysoPCs and
PCs. Thus, we explored surrogate markers for PLA2 activity by
performing paired samples Student's t-test for metabolites
associated with the PLA2 activity index. Phosphatidylcholine with
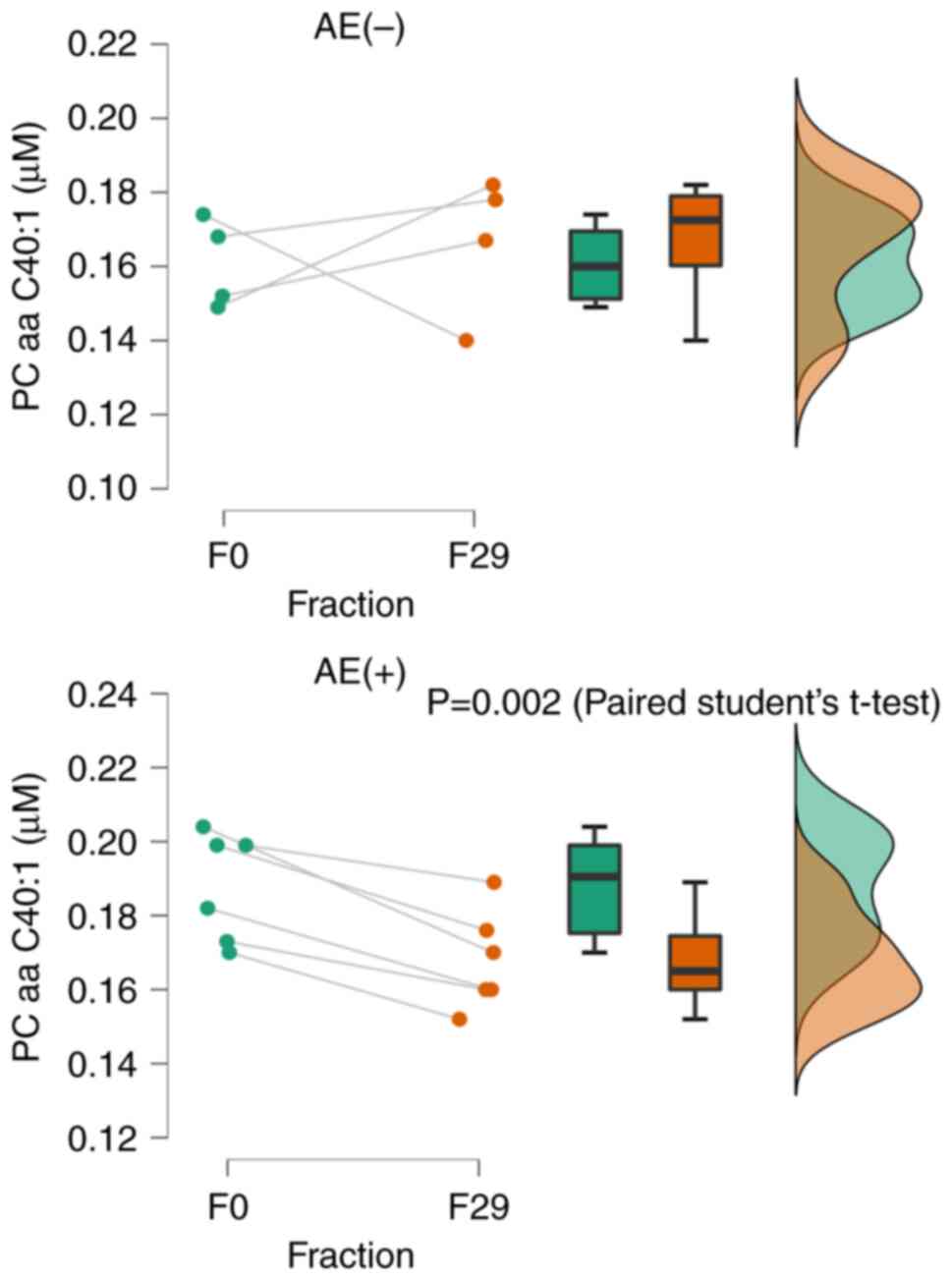
diacyl residue sum C40:1 (PC aa C40:1) was significantly reduced in
the presence of AEs (P<0.01). However, there was no significant
difference without AEs (Fig. 5).
This suggests that a reduction in PC aa C40:1 at 29 fractions is
indicative of an AE. In the post-treatment serum data, PSA could be
used as a known indicator of tumor activity. PSA levels in the
AE(+) population decreased after radiotherapy (Table IV).
 | Table IVThe relationship between adverse
events and serum PSA in each patient. |
Table IV
The relationship between adverse
events and serum PSA in each patient.
| Variable | Pt.1 | Pt.2 | Pt.3 | Pt.4 | Pt.5 | Pt.6 | Pt.7 | Percentage |
|---|
| Urinary
frequency/urgency | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 100.0 |
| Urethritis | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | 14.3 |
| Urodynia | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 100.0 |
| Slow stream | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 100.0 |
| PSA, ng/ml | | | | | | | | |
|
Pre-RT | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.024 | 4.4 | |
|
Post-RT | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.1 | |
Discussion
This study aimed to explore metabolites that predict
acute AEs in patients with localized prostate cancer who underwent
VMAT with urine. Patient analysis of acute AE was conducted at
every outpatient visit during the VMAT course for approximately 2
months. While numerous urinary toxicity biomarkers have been
reported, we discovered a specific parameter for the detection of
AE: the PLA2 activity index, which reacts during the phase of 30
fractions (60 Gy as cumulative dose) in the VMAT course (6 and 7
weeks from initial fraction) (Figs.
2, 3, and 5). In this study, radiotherapy was
performed according to JASTRO Guidelines (4), and urine samples were collected at
regular intervals. This type of analysis has not been reported, but
post-treatment serum data (PSA) can be used as a known indicator of
tumor activity. PSA levels decreased after radiotherapy, indicating
an antitumor effect. It is critical to monitor PSA concentrations
in peripheral blood, but invasive blood sampling is difficult to
perform frequently. Therefore, urine has the advantage of being
simple to collect and useful for tracking markers over time during
treatment. PLA2 activity is calculated using the lysoPCs to PCs
ratio, and Zhai et al found that PLA2 activity upregulation
is associated with both inflammatory and noninflammatory types of
osteoarthritis (19). According to
reports dating back more than 30 years, extracellular phospholipase
A2 expression has been linked to inflammation-related diseases
(20). In this study, we
discovered for the first time a negative correlation between Grade
1 AE by VMAT and PLA2 activity. LysoPC and PC are produced by
various metabolic pathways and degraded by enzymes. AE can reflect
these metabolites directly or indirectly. Wegener et al
reported the highest acute GU toxicity with grades 1 and 2 in weeks
7 and 8 of radiotherapy (21).
Spratt et al found that the GI and GU scores in grades 2 and
3 gradually increased during treatment, plateauing after 5 weeks
and peaking at 7 weeks (22).
According to the reports of these radiotherapy-related AEs, we
believe that the significant decrease in the maximum GU score and
PLA2 activity in fraction 30 is accurately reflected. The AUC
calculated from the ROC generated by the current predictors is a
measure of their accuracy. According to the AUC values, test
accuracy can be classified as perfect (AUC=1), highly accurate
(AUC=0.9-1), moderately accurate (AUC=0.7-0.9), less accurate
(AUC=0.5-0.7), and noninformative (AUC=0.5) (23). According to this AUC guideline, the
predictors developed in the current study for investigating
predictive molecules of AE events were moderately accurate
(Fig. 4). Alicikus et al
found that when using IMRT to localize prostate cancer, the
presence of acute Grade >2 GU toxicity predicted the development
of late Grade >2 GU toxicity using a multivariate analysis
(24). Zelefsky et al found
that the presence of acute gastrointestinal (GI) and GU symptoms
during treatment conferred a 5-fold and 3-fold increase in the risk
of late GI and GU toxicities, respectively, in 1,571 prostate
cancer patients who had a long follow-up after receiving
three-dimensional, conformal radiotherapy or IMRT (25). In contrast, our findings for GU
toxicity clearly revealed that manifesting GU symptoms prior to
radiotherapy initiation is a strong predictor of acute GU toxicity,
as 94% of patients with a Grade 2 before radiotherapy also scored a
Grade 2 as the maximum acute GU score (26).
Both the preRT baseline IPSS score of >15
(P<0.001) and acute GU toxicity (P<0.001) predicted late GU
toxicity. The RTOG study 94-06 showed an excellent toxicity profile
with a dose escalation of up to 79.2 Gy, with the use of 3D-CRT,
with ≤3% of patients experiencing a Grade 3 GI or GU acute
toxicity, and 85% of patients experiencing no late toxicity or
Grade 1 toxicity (22). According
to the above reports, the discovery of a biomarker that predicts
Grade 1 AEs based on PLA2 activity is extremely important because
it allows us to prepare for severe AEs of Grade 2 or higher. This
marker can be used to reconsider treatment regimens to prevent AEs
when there is a negative correlation in the number of fractions vs.
PLA2 activity with continued urine collection. According to a
recent paper, hyperbaric oxygen therapy can be used to prevent AEs
during radiotherapy (27).
Combining these can be considered a new measure against AEs. The
limitation of this study is the small sample size used to analyze
the prediction of acute AE in other grades (more than 2) (28,29),
and lack of healthy group as control. However, it is encouraging
that despite the small sample size, the predictor of treatment
delay was moderately accurate. Future studies with larger sample
sizes may enable the identification of predictive molecules for
acute AEs. Detection of PLA2 activity is associated with
inflammatory diseases. Kartikasari et al explained that the
tumor microenvironment is an environment of chronic inflammation
(30). Interestingly, Zhao et
al reported that plasma LysoPC [20:2] and LysoPC [20:3]
decrease depending on radiation exposure doses and suggested that
it is involved apoptosis (31). It
is suggested that there are two regulation pathways by lysoPCs
production, one is inflammatory pathway, the other is radiation
induces apoptotic pathway. These may be involved in the increase or
decrease in LysoPCs and AE, which determines PLA2 activity levels,
but the details remain unknown. There is currently no information
the relationship between these pathways, metabolites and impact of
genitourinary toxicity (Grade 1). Furthermore, the analysis of the
biological function, these pathways associated with the identified
metabolites, and their relationship to genitourinary toxicity will
be clarified by basic experiments using a cell line model.
In conclusion, this study demonstrated the
significance of genitourinary metabolite biomarkers in predicting
radiotherapy toxicity using urine metabolomics. In patients
undergoing VMAT for localized prostate cancer, the surrogate marker
PC aa C40:1 for PLA2 activity was found to predict genitourinary
(Grade 1) acute AEs at approximately 30 fractions. Larger sample
sizes are expected to improve accuracy even more in future
validation studies.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Ms. Miyu Miyazaki
(Center for Scientific Equipment Management, Hirosaki University
Graduate School of Medicine) for her help with the LC-MS/MS
analysis.
Funding
Funding: This work was supported by KAKENHI, Grant-in-Aid for
Early-Career Scientists (grant no. 20K16685, Hideki Obara),
Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) (grant no. 21H02861,
Satoru Monzen) and Grant-in-Aid for Challenging Research
(Exploratory) (grant no. 19K22731, Satoru Monzen). The funders had
no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision
to publish, or manuscript preparation.
Availability of data and materials
The metabolomics data generated in the present study
may be found in the MetaboBank under accession numbers MTBKS242 and
MTBKS243 or at the following URLs: https://mb2.ddbj.nig.ac.jp/study/MTBKS242.html and
https://mb2.ddbj.nig.ac.jp/study/MTBKS243.html.
Authors' contributions
HO, SaM, and YT designed the study, prepared the
manuscript draft and substantively participated in the manuscript
revision. ShM, HY, NK, MS, FK, MN, YH and MA analyzed both the
patient and biological data. SaM and MA supervised the study,
critically reviewed the manuscript, and provided final approval for
the version to be submitted and published. All authors have read
and approved the final version of the manuscript. HO, YT and SaM
confirmed the authenticity of all the raw data.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
This study was approved by the Medical Ethics
Committee of Hirosaki University Graduate School of Medicine
(Hirosaki, Japan; approval no. 2020-075) to ensure the welfare and
privacy of the donors. Following a detailed verbal explanation
regarding the content of this study, written informed consent was
obtained.
Patient consent for publication
All patients and their families provided both
written and oral informed consent for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Numasaki H, Nakada Y, Ohba H and Nakamura
K: Japanese Structure Survey of Radiation Oncology in 2019 (First
Report): Japanese Society for Radiation Oncology; JASTRO Database
Committee, 2022. https://www.jastro.or.jp/medicalpersonnel/data_center/JASTRO_NSS_2019-01.pdf,
Accessed July 7, 2024 (In Japanese).
|
|
2
|
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare:
Summary of Static/Dynamic Surveys of Medical Institutions and
Hospital Report in 2020. https://www.mhlw.go.jp/english/database/db-hss/mih_report_2020.html.
Accessed February 28, 2024 (In Japanese).
|
|
3
|
Iwamoto RR and Maher KE: Radiation therapy
for prostate cancer. Semin Oncol Nurs. 17:90–100. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Japanese Society for Radiation Oncology:
JASTRO Guidelines 2020 for Radiotherapy Treatment Planning. 5th
edition. Kanehara & Co. Ltd., 2020 (In Japanese).
|
|
5
|
David RV, Kahokehr AA, Lee J, Watson DI,
Leung J and O'Callaghan ME: Incidence of genitourinary
complications following radiation therapy for localized prostate
cancer. World J Urol. 40:2411–2422. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Monzen S, Tatsuya Ueno, Mitsuru Chiba and
Yasushi Mariya: Exploratory study of biomarkers for radiation
exposure adverse events. Nihon Hoshasen Gijutsu Gakkai Zasshi.
75:480–85. 2019.(In Japanese).
|
|
7
|
Franken NA, Oei AL, Kok HP, Rodermond HM,
Sminia P, Crezee J, Stalpers LJ and Barendsen GW: Cell survival and
radiosensitisation: Modulation of the linear and quadratic
parameters of the LQ model (Review). Int J Oncol. 42:1501–1515.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Annede P, Cosset JM, Van Limbergen E,
Deutsch E, Haie-Meder C and Chargari C: Radiobiology: Foundation
and new insights in modeling brachytherapy effects. Semin Radiat
Oncol. 30:4–15. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Meng W, Pan H, Sha Y, Zhai X, Xing A,
Lingampelly SS, Sripathi SR, Wang Y and Li K: Metabolic connectome
and its role in the prediction, diagnosis, and treatment of complex
diseases. Metabolites. 14(93)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Mottet N, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Briers E,
Cumberbatch MG, De Santis M, Fossati N, Gross T, Henry AM, Joniau
S, et al: EAU-ESTRO-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer. Part 1:
Screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent. Eur
Urol. 71:618–629. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Tøndel H, Lund JÅ, Lydersen S, Wanderås
AD, Aksnessæther B, Jensen CA, Kaasa S and Solberg A: Radiotherapy
for prostate cancer-does daily image guidance with tighter margins
improve patient reported outcomes compared to weekly orthogonal
verified irradiation? Results from a randomized controlled trial.
Radiother Oncol. 126:229–235. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hunte SO, Clark CH, Zyuzikov N and Nisbet
A: Volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT): A review of clinical
outcomes-what is the clinical evidence for the most effective
implementation? Br J Radiol. 95(20201289)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Halperin EC, Wazer DE, Perez CA and Brady
LW: Perez and Brady's principles and practice of radiation
oncology. 7th edition. Wolters Kluwer, PA, 2018.
|
|
14
|
Ghanem AI, Elsaid AA, Elshaikh MA and
Khedr GA: Volumetric-modulated arc radiotherapy with daily
image-guidance carries better toxicity profile for higher risk
prostate cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 22:61–68. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Eastham JA, Auffenberg GB, Barocas DA,
Chou R, Crispino T, Davis JW, Eggener S, Horwitz EM, Kane CJ,
Kirkby E, et al: Clinically localized prostate cancer: AUA/ASTRO
guideline. Part Ⅲ: Principles of radiation and future directions. J
Urol. 208:26–33. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hubenak JR, Zhang Q, Branch CD and
Kronowitz SJ: Mechanisms of injury to normal tissue after
radiotherapy: A review. Plast Reconstr Surg. 133:49e–56e.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Pang Z, Chong J, Zhou G, de Lima Morais
DA, Chang L, Barrette M, Gauthier C, Jacques PÉ, Li S and Xia J:
MetaboAnalyst 5.0: Narrowing the gap between raw spectra and
functional insights. Nucleic Acids Res. 49(W1):W388–W396.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Erben V, Poschet G, Schrotz-King P and
Brenner H: Comparing metabolomics profiles in various types of
liquid biopsies among screening participants with and without
advanced colorectal neoplasms. Diagnostics (Basel).
11(561)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhai G, Pelletier JP, Liu M, Aitken D,
Randell E, Rahman P, Jones G and Martel-Pelletier J: Activation of
the phosphatidylcholine to lysophosphatidylcholine pathway is
associated with osteoarthritis knee cartilage volume loss over
time. Sci Rep. 9(9648)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Vadas P, Browning J, Edelson J and
Pruzanski W: Extracellular phospholipase A2 expression and
inflammation: The relationship with associated disease states. J
Lipid Mediat. 8:1–30. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wegener D, Berger B, Outtagarts Z, Zips D,
Paulsen F, Bleif M, Thorwarth D, Alber M, Dohm O and Müller AC:
Prospective evaluation of probabilistic dose-escalated IMRT in
prostate cancer. Radiol Oncol. 55:88–96. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Spratt DE, Pei X, Yamada J, Kollmeier MA,
Cox B and Zelefsky MJ: Long-term survival and toxicity in patients
treated with high-dose intensity modulated radiation therapy for
localized prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
85:686–692. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Greiner M, Pfeiffer D and Smith RD:
Principles and practical application of the receiver-operating
characteristic analysis for diagnostic tests. Prev Vet Med.
45:23–41. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Alicikus ZA, Yamada Y, Zhang Z, Pei X,
Hunt M, Kollmeier M, Cox B and Zelefsky MJ: Ten-year outcomes of
high-dose, intensity-modulated radiotherapy for localized prostate
cancer. Cancer. 117:1429–1437. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zelefsky MJ, Levin EJ, Hunt M, Yamada Y,
Shippy AM, Jackson A and Amols HI: Incidence of late rectal and
urinary toxicities after 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy and
intensity-modulated radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer. Int
J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 70:1124–1129. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Peeters ST, Heemsbergen WD, Van Putten WL,
Slot A, Tabak H, Mens JW, Lebesque JV and Koper PC: Acute and late
complications after radiotherapy for prostate cancer: Results of a
multicenter randomized trial comparing 68 Gy to 78 Gy. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 61:1019–1034. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Oscarsson N, Müller B, Rosén A, Lodding P,
Mölne J, Giglio D, Hjelle KM, Vaagbø G, Hyldegaard O, Vangedal M,
et al: Radiation-induced cystitis treated with hyperbaric oxygen
therapy (RICH-ART): A randomised, controlled, phase 2-3 trial.
Lancet Oncol. 20:1602–1614. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Dykstra MA, Switzer N, Eisner R, Tso V,
Foshaug R, Ismond K, Fedorak R and Wang H: Urine metabolomics as a
predictor of patient tolerance and response to adjuvant
chemotherapy in colorectal cancer. Mol Clin Oncol. 7:767–770.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Li X, Nakayama K, Goto T, kimura H,
Akamatsu S, Hayashi Y, Fujita K, Kobayashi T, Shimizu K, Nonomura
N, et al: High level of
phosphatidylcholines/lysophosphatidylcholine ratio in urine is
associated with prostate cancer. Cancer Sci. 112:4292–4302.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kartikasari AER, Huertas CS, Mitchell A
and Plebanski M: Tumor-Induced inflammatory cytokines and the
emerging diagnostic devices for cancer detection and prognosis.
Front Oncol. 11(692142)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhao H, Xi C, Tian M, Lu X, Cai TJ, Li S,
Tian XL, Gao L, Liu HX, Liu KH and Liu QJ: Identification of
potential radiation responsive metabolic biomarkers in plasma of
rats exposed to different doses of cobalt-60 gamma rays. Dose
Response. 18(1559325820979570)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|