|
1
|
Fotsing Yannick Stéphane F, Kezetas Jean
Jules B, El-Saber Batiha G, Ali I and Ndjakou Bruno L: Extraction
of bioactive compounds from medicinal plants and herbs. In:
El-Shemy HA (ed). Natural Medicinal Plants. IntechOpen; London, UK,
2022.
|
|
2
|
Balekundri A and Mannur V: Quality control
of the traditional herbs and herbal products: A review. Futur J
Pharm Sci. 6(67)2020.
|
|
3
|
Cione E, La Torre C, Cannataro R, Caroleo
MC, Plastina P and Gallelli L: Quercetin, epigallocatechin gallate,
curcumin, and resveratrol: from dietary sources to human MicroRNA
modulation. Molecules. 25(63)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lambert JD, Lee MJ, Lu H, Meng X, Hong JJ,
Seril DN, Sturgill MG and Yang CS: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate is
absorbed but extensively glucuronidated following oral
administration to mice. J Nutr. 133:4172–4177. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chunarkar-Patil P, Kaleem M, Mishra R, Ray
S, Ahmad A, Verma D, Bhayye S, Dubey R, Singh HN and Kumar S:
Anticancer Drug discovery based on natural products: From
computational approaches to clinical studies. Biomedicines.
12(201)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Pandey AK, Gulati S, Gupta A and Tripathi
YC: Variation in andrographolide content among different accessions
of Andrographis paniculata. Pharma Innov J. 8:140–144.
2019.
|
|
7
|
Liang D, Zhang WM, Liang X, Tian HY, Zhang
XM, Li X and Gao WY: A review on the extraction and separation of
andrographolide from Andrographis paniculata: Extraction
selectivity, current challenges and strategies. Tradit Med Res.
8(38)2023.
|
|
8
|
Sharma S, Sharma YP and Bhardwaj C: HPLC
quantification of andrographolide in different parts of
Andrographis paniculata (Burm.f.) Wall. ex Nees. J
Pharmacogn Phytochem. 7:168–171. 2018.
|
|
9
|
Kandanur SGS, Tamang N, Golakoti NR and
Nanduri S: Andrographolide: A natural product template for the
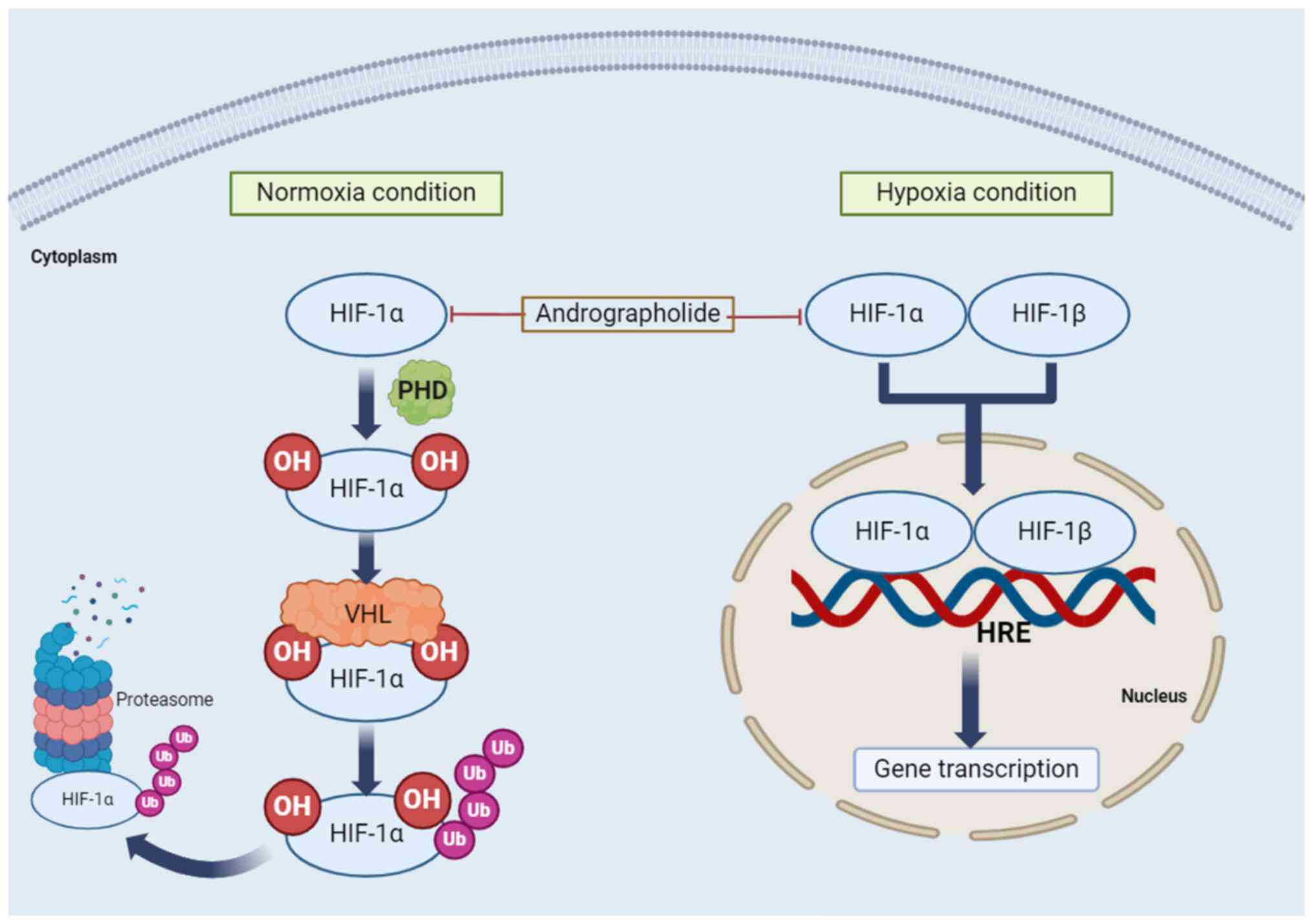
generation of structurally and biologically diverse diterpenes. Eur
J Med Chem. 176:513–533. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Tran QTN, Tan WSD, Wong WSF and Chai CLL:
Polypharmacology of andrographolide: Beyond one molecule one
target. Nat Prod Rep. 38:682–692. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Phunikom N, Boonmuen N, Kheolamai P,
Suksen K, Manochantr S, Tantrawatpan C and Tantikanlayaporn D:
Andrographolide promotes proliferative and osteogenic potentials of
human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells through the
activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther.
12(241)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Nair DS and Manjula S: Induction of root
endosymbiosis as a highly sustainable and efficient strategy for
overproduction of the medicinally important diterpenoid
lactone-andrographolide in Andrographis paniculata (Burm.
F.) Wall. ex Nees. Ind Crops Prod. 156(112835)2020.
|
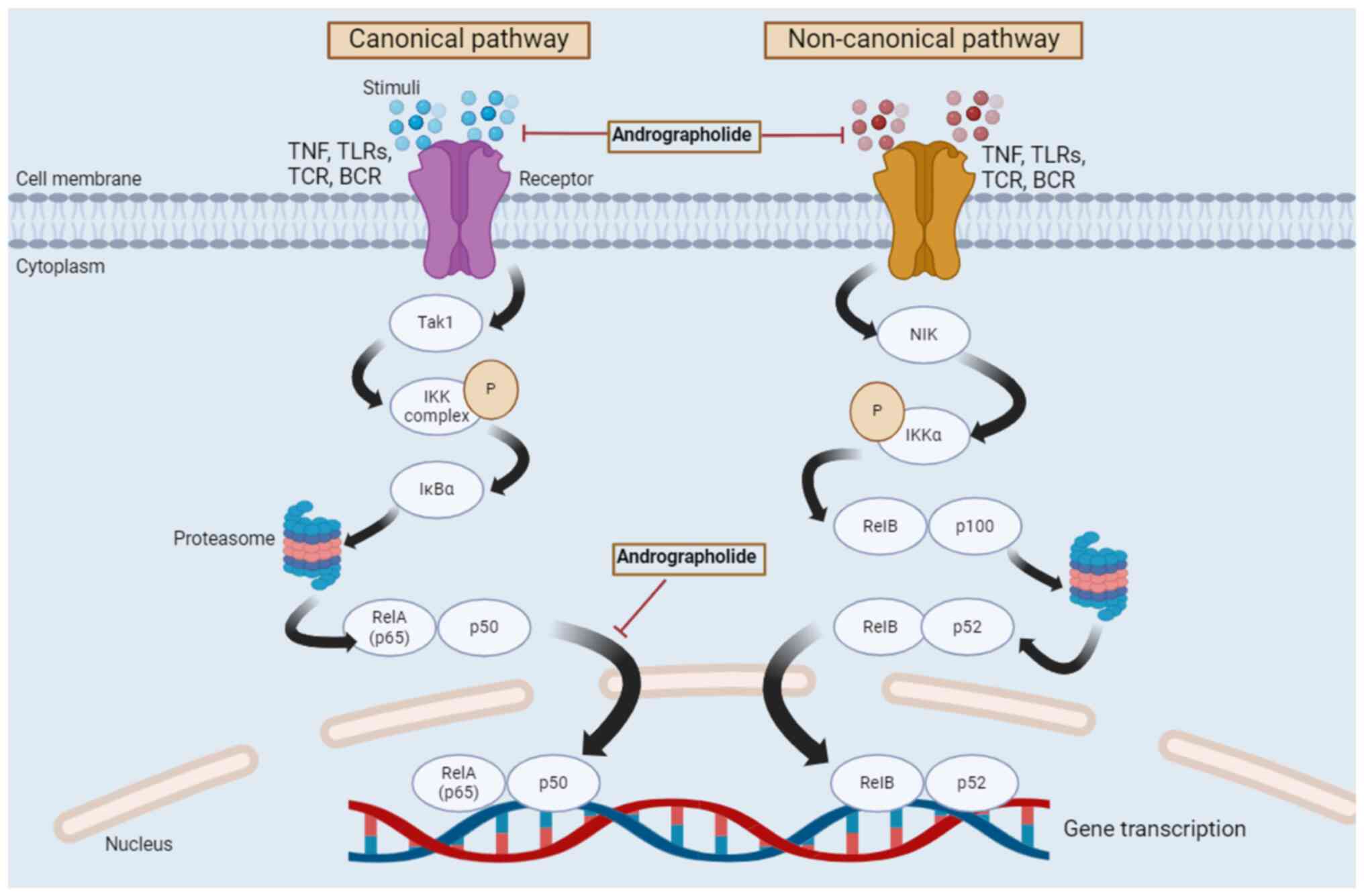
|
13
|
Dai Y, Chen SR, Chai L, Zhao J and Wang Y
and Wang Y: Overview of pharmacological activities of
Andrographis paniculata and its major compound
andrographolide. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 59 (Suppl 1):S17–S29.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tundis R, Patra JK, Bonesi M, Das S, Nath
R, Das Talukdar A, Das G and Loizzo MR: Anti-cancer agent: The
labdane diterpenoid-andrographolide. Plants (Basel).
12(1969)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Cai W, Li J, Chen C, Wu J, Li J and Xue X:
Design, synthesis, and anticancer evaluation of novel
andrographolide derivatives bearing an α,β-unsaturated ketone
moiety. Bioorg Chem. 112(104941)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Arsakhant P, Sirion U, Chairoungdua A,
Suksen K, Piyachaturawat P, Suksamrarn A and Saeeng R: Design and
synthesis of C-12 dithiocarbamate andrographolide analogues as an
anticancer agent. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 30(127263)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Cheng CR, Zheng Z, Liang RM, Li XF, Jiang
QQ, Yue L, Wang Q, Ding J and Liu Y: Preparation and cytotoxic
Activity of 3,19-analogues of 12-thioether andrographolide. Chem
Nat Compd. 56:264–269. 2020.
|
|
18
|
Beesetti SL, Jayadev M, Subhashini GV,
Mansour L, Alwasel S and Harrath AH: Andrographolide as a
therapeutic agent against breast and ovarian cancers. Open Life
Sci. 14:462–469. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
He X, Li J, Gao H, Qiu F, Hu K, Cui X and
Yao X: Identification of a rare sulfonic acid metabolite of
andrographolide in rats. Drug Metab Dispos. 31:983–985.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sa-ngiamsuntorn K, Suksatu A, Pewkliang Y,
Thongsri P, Kanjanasirirat P, Manopwisedjaroen S,
Charoensutthivarakul S, Wongtrakoongate P, Pitiporn S, Chaopreecha
J, et al: Anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity of Andrographis
paniculata extract and its major component andrographolide in
human lung epithelial cells and cytotoxicity evaluation in major
organ cell representatives. J Nat Prod. 84:1261–1270.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Banerjee M, Parai D, Chattopadhyay S and
Mukherjee SK: Andrographolide: Antibacterial activity against
common bacteria of human health concern and possible mechanism of
action. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 62:237–244. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Widyawaruyanti A, Asrory M, Ekasari W,
Setiawan D, Radjaram A, Tumewu L and Hafid AF: In vivo antimalarial
activity of Andrographis paniculata tablets. Procedia Chem.
13:101–104. 2014.
|
|
23
|
Yu Q, Shi Y, Shu C, Ding X, Zhu S, Shen Z
and Lou Y: Andrographolide inhibition of Th17-regulated cytokines
and JAK1/STAT3 signaling in OVA-stimulated asthma in mice. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021(6862073)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Astuti NT, Novitasari PR, Tjandrawinata R,
Nugroho AE and Pramono S: Anti-diabetic effect of andrographolide
from Sambiloto herbs (Andrographis paniculata (Burm.f.)
Nees) through the expression of PPARγ and GLUT-4 in adipocytes.
Indones J Biotechnol. 27(203)2022.
|
|
25
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Gadi VK and Davidson NE: Practical
approach to triple-negative breast cancer. J Oncol Pract.
13:293–300. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Li L, Yang LL, Yang SL, Wang RQ, Gao H,
Lin ZY, Zhao YY, Tang WW, Han R, Wang WJ, et al: Andrographolide
suppresses breast cancer progression by modulating tumor-associated
macrophage polarization through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Phyther
Res. 36:4587–4603. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Anand U, Dey A, Chandel AKS, Sanyal R,
Mishra A, Pandey DK, De Falco V, Upadhyay A, Kandimalla R,
Chaudhary A, et al: Cancer chemotherapy and beyond: Current status,
drug candidates, associated risks and progress in targeted
therapeutics. Genes Dis. 10:1367–1401. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Aggarwal S, Verma SS, Aggarwal S and Gupta
SC: Drug repurposing for breast cancer therapy: Old weapon for new
battle. Semin Cancer Biol. 68:8–20. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Hung Y, Leung S, Chiu SP, Li PY, Kan AC,
Lo CC, Wong SZ, Luk SL, Lai CC, El Helali A and Chan WW:
Perceptions about traditional Chinese medicine use among Chinese
breast cancer survivors: A qualitative study. Cancer Med.
12:1997–2007. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Cohen I, Tagliaferri M and Tripathy D:
Traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of breast cancer.
Semin Oncol. 29:563–574. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wang R, Wang Y, Fang L, Xie Y, Yang S, Liu
S, Fang Y and Zhang Y: Efficacy and safety of traditional Chinese
medicine in the treatment of menopause-like syndrome for breast
cancer survivors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC
Cancer. 24(42)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Shu J, Huang R, Tian Y, Liu Y, Zhu R and
Shi G: Andrographolide protects against endothelial dysfunction and
inflammatory response in rats with coronary heart disease by
regulating PPAR and NF-κB signaling pathways. Ann Palliat Med.
9:1965–1975. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Xia YF, Ye BQ, Li YD, Wang JG, He XJ, Lin
X, Yao X, Ma D, Slungaard A, Hebbel RP, et al: Andrographolide
attenuates inflammation by inhibition of NF-kappa B activation
through covalent modification of reduced cysteine 62 of p50. J
Immunol. 173:4207–4217. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Li Z and Wu JC, Sheikh AY, Kraft D, Cao F,
Xie X, Patel M, Gambhir SS, Robbins RC, Cooke JP and Wu JC:
Differentiation, survival, and function of embryonic stem cell
derived endothelial cells for ischemic heart disease. Circulation.
116 (11 Suppl):I46–I54. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Giordano SH: Breast cancer in men. N Engl
J Med. 378:2311–2320. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Sousa S, Brion R, Lintunen M, Kronqvist P,
Sandholm J, Mönkkönen J, Kellokumpu-Lehtinen PL, Lauttia S,
Tynninen O, Joensuu H, et al: Human breast cancer cells educate
macrophages toward the M2 activation status. Breast Cancer Res.
17(101)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Yang Q, Guo N, Zhou Y, Chen J, Wei Q and
Han M: The role of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in tumor
progression and relevant advance in targeted therapy. Acta Pharm
Sin B. 10:2156–2170. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Hagemann T, Lawrence T, McNeish I, Charles
KA, Kulbe H, Thompson RG, Robinson SC and Balkwill FR:
‘Re-educating’ tumor-associated macrophages by targeting NF-κB. J
Exp Med. 205:1261–1268. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Goding Sauer A,
Fedewa SA, Butterly LF, Anderson JC, Cercek A, Smith RA and Jemal
A: Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin.
70:145–164. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ohri A, Robinson A, Liu B, Bhuket T and
Wong R: Updated assessment of colorectal cancer incidence in the
U.S. by age, sex, and race/ethnicity. Dig Dis Sci. 65:1838–1849.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Eslami M, Yousefi B, Kokhaei P, Hemati M,
Nejad ZR, Arabkari V and Namdar A: Importance of probiotics in the
prevention and treatment of colorectal cancer. J Cell Physiol.
234:17127–17143. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Lai Y, Wang C, Civan JM, Palazzo JP, Ye Z,
Hyslop T, Lin J, Myers RE, Li B, Jiang B, et al: Effects of cancer
stage and treatment differences on racial disparities in survival
from colon cancer: A United States population-based study.
Gastroenterology. 150:1135–1146. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Xynos ID, Kavantzas N, Tsaousi S,
Zacharakis M, Agrogiannis G, Kosmas C, Lazaris A, Sarantonis J,
Sougioultzis S, Tzivras D, et al: Factors influencing survival in
stage IV colorectal cancer: The influence of DNA ploidy. ISRN
Gastroenterol. 2013(490578)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Xie YH, Chen YX and Fang JY: Comprehensive
review of targeted therapy for colorectal cancer. Signal Transduct
Target Ther. 5(22)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
García-Alfonso P, Muñoz Martín AJ, Ortega
Morán L, Soto Alsar J, Torres Pérez-Solero G, Blanco Codesido M,
Calvo Ferrandiz PA and Grasso Cicala S: Oral drugs in the treatment
of metastatic colorectal cancer. Ther Adv Med Oncol.
13(17588359211009001)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Van Cutsem E, Cervantes A, Adam R, Sobrero
A, Van Krieken JH, Aderka D, Aranda Aguilar E, Bardelli A, Benson
A, Bodoky G, et al: ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of
patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol.
27:1386–1422. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Feng X, Sureda A, Jafari S, Memariani Z,
Tewari D, Annunziata G, Barrea L, Hassan STS, Šmejkal K, Malaník M,
et al: Berberine in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases: From
mechanisms to therapeutics. Theranostics. 9:1923–1951.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Palmieri A, Scapoli L, Iapichino A,
Mercolini L, Mandrone M, Poli F, Giannì AB, Baserga C and
Martinelli M: Berberine and Tinospora cordifolia exert a potential
anticancer effect on colon cancer cells by acting on specific
pathways. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol.
33(2058738419855567)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Ranjan A, Ramachandran S, Gupta N, Kaushik
I, Wright S, Srivastava S, Das H, Srivastava S, Prasad S and
Srivastava SK: Role of phytochemicals in cancer prevention. Int J
Mol Sci. 20(4981)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Islam MT, Ali ES, Uddin SJ, Islam MA, Shaw
S, Khan IN, Saravi SSS, Ahmad S, Rehman S, Gupta VK, et al:
Andrographolide, a diterpene lactone from Andrographis
paniculata and its therapeutic promises in cancer. Cancer Lett.
420:129–145. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Shi MD, Lin HH, Lee YC, Chao JK, Lin RA
and Chen JH: Inhibition of cell-cycle progression in human
colorectal carcinoma Lovo cells by andrographolide. Chem Biol
Interact. 174:201–210. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Norouzi M and Hardy P: Clinical
applications of nanomedicines in lung cancer treatment. Acta
Biomater. 121:134–142. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Torre LA, Siegel RL and Jemal A: Lung
cancer statistics. Adv Exp Med Biol. 893:1–19. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Thandra KC and Barsouk A, Saginala K,
Aluru JS and Barsouk A: Epidemiology of lung cancer. Contemp Oncol
(Pozn). 25:45–52. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 70:7–30. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Commar A, Prasad V and D'Espaignet ET: WHO
global report on trends in prevalence of tobacco use 2000-2025,
2021. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/who-global-report-on-trends-in-prevalence-of-tobacco-use-2000-2025-third-edition.
|
|
58
|
Dougherty SM, Mazhawidza W, Bohn AR,
Robinson KA, Mattingly KA, Blankenship KA, Huff MO, McGregor WG and
Klinge CM: Gender difference in the activity but not expression of
estrogen receptors alpha and beta in human lung adenocarcinoma
cells. Endocr Relat Cancer. 13:113–134. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Landi MT, Chatterjee N, Yu K, Goldin LR,
Goldstein AM, Rotunno M, Mirabello L, Jacobs K, Wheeler W, Yeager
M, et al: A genome-wide association study of lung cancer identifies
a region of chromosome 5p15 associated with risk for
adenocarcinoma. Am J Hum Genet. 85:679–691. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Yokota J, Shiraishi K and Kohno T: Genetic
basis for susceptibility to lung cancer: Recent progress and future
directions. Adv Cancer Res. 109:51–72. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Thorgeirsson TE, Geller F, Sulem P, Rafnar
T, Wiste A, Magnusson KP, Manolescu A, Thorleifsson G, Stefansson
H, Ingason A, et al: A variant associated with nicotine dependence,
lung cancer and peripheral arterial disease. Nature. 452:638–642.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Hussain S: Nanomedicine for treatment of
lung cancer. In: Ahmad A, Gadgeel S (eds). Lung Cancer and
Personalized Medicine: Novel Therapies and Clinical Management.
Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Vol. 890. Springer,
Cham, pp137-147, 2016.
|
|
64
|
Sun A, Durocher-Allen LD, Ellis PM, Ung
YC, Goffin JR, Ramchandar K and Darling G: Initial management of
small-cell lung cancer (limited- and extensive-stage) and the role
of thoracic radiotherapy and first-line chemotherapy: A systematic
review. Curr Oncol. 26:e372–e384. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Bahman F, Elkaissi S, Greish K and Taurin
S: Polymeric micelles in management of lung cancer. In:
Nanotechnology-Based Targeted Drug Delivery Systems for Lung
Cancer. Elsevier, pp193-216, 2019.
|
|
66
|
Norouzi M, Amerian M, Amerian M and Atyabi
F: Clinical applications of nanomedicine in cancer therapy. Drug
Discov Today. 25:107–125. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Norouzi M, Yathindranath V, Thliveris JA
and Miller DW: Salinomycin-loaded iron oxide nanoparticles for
glioblastoma therapy. Nanomaterials (Basel). 10(477)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Ricciardi S, Tomao S and de Marinis F:
Toxicity of targeted therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer
management. Clin Lung Cancer. 10:28–35. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Su XL, Wang JW, Che H, Wang CF, Jiang H,
Lei X, Zhao W, Kuang HX and Wang QH: Clinical application and
mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine in treatment of lung
cancer. Chin Med J (Engl). 133:2987–2997. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Paul S, Roy D, Pati S and Sa G: The
adroitness of andrographolide as a natural weapon against
colorectal cancer. Front Pharmacol. 12(731492)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Lin HH, Tsai CW, Chou FP, Wang CJ, Hsuan
SW, Wang CK and Chen JH: Andrographolide down-regulates
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in human non-small cell lung cancer
A549 cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 250:336–345. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Jiaqi L, Siqing H, qin W, di Z, bei Z and
jialin Y: Andrographolide promoted ferroptosis to repress the
development of non-small cell lung cancer through activation of the
mitochondrial dysfunction. Phytomedicine.
109(154601)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Neamatallah T, Malebari AM, Alamoudi AJ,
Nazreen S, Alam MM, Bin-Melaih HH, Abuzinadah OA, Badr-Eldin SM,
Alhassani G, Makki L and Nasrullah MZ: Andrographolide
nanophytosomes exhibit enhanced cellular delivery and pro-apoptotic
activities in HepG2 liver cancer cells. Drug Deliv.
30(2174209)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Shannon AH, Ruff SM and Pawlik TM: Expert
insights on current treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma:
Clinical and molecular approaches and bottlenecks to progress. J
Hepatocell Carcinoma. 9:1247–1261. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Rimassa L and Gish GR: HCC in focus:
Current developments in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 14:542–544. 2018.
|
|
76
|
Xi SY and Minuk GY: Role of traditional
Chinese medicine in the management of patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma. World J Hepatol. 10:799–806. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:12–49.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Forestier-Román IS, López-Rivas A,
Sánchez-Vázquez MM, Rohena-Rivera K, Nieves-Burgos G, Ortiz-Zuazaga
H, Torres-Ramos CA and Martínez-Ferrer M: Andrographolide induces
DNA damage in prostate cancer cells. Oncotarget. 10:1085–1101.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Chen FZ and Zhao XK: Prostate cancer:
Current treatment and prevention strategies. Iran Red Crescent Med
J. 15:279–284. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Malinowski B, Wiciński M, Musiała N,
Osowska I and Szostak M: Previous, current, and future
pharmacotherapy and diagnosis of prostate cancer-a comprehensive
review. Diagnostics (Basel). 9(161)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Jiang J, Slivova V, Valachovicova T,
Harvey K and Sliva D: Ganoderma lucidum inhibits
proliferation and induces apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells
PC-3. Int J Oncol. 24:1093–1099. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Chun JY, Tummala R, Nadiminty N, Lou W,
Liu C, Yang J, Evans CP, Zhou Q and Gao AC: Andrographolide, an
herbal medicine, inhibits interleukin-6 expression and suppresses
prostate cancer cell growth. Genes Cancer. 1:868–876.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Munir AH and Khan MI: Pattern of basic
hematological parameters in acute and chronic leukemias. J Med Sci.
27:125–129. 2019.
|
|
84
|
Li X, Wu T, Chen W, Zhang J, Jiang Y, Deng
J, Long W, Qin X and Zhou Y: Andrographolide acts with
dexamethasone to inhibit the growth of acute lymphoblastic leukemia
CEM-C1 cells via the regulation of the autophagy-dependent
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Biomed Reports.
20(43)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Hunger SP and Mullighan CG: Acute
lymphoblastic leukemia in children. N Engl J Med. 373:1541–1552.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Samii B, Jafarian A, Rabbani M, Zolfaghari
B, Rahgozar S and Pouraboutaleb E: The effects of Astragalus
polysaccharides, tragacanthin, and bassorin on
methotrexate-resistant acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Res Pharm Sci.
18:381–391. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Follini E, Marchesini M and Roti G:
Strategies to overcome resistance mechanisms in T-cell acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Int J Mol Sci. 20(3021)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Wang YJ, Liao CC, Chen HJ, Hsieh CL and Li
TC: The effectiveness of traditional Chinese medicine in treating
patients with leukemia. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2016(8394850)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Yang T, Yao S, Zhang X and Guo Y:
Andrographolide inhibits growth of human T-cell acute lymphoblastic
leukemia Jurkat cells by downregulation of PI3K/AKT and
upregulation of p38 MAPK pathways. Drug Des Devel Ther.
10:1389–1397. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Cai Q, Zhang W, Sun Y, Xu L, Wang M, Wang
X, Wang S and Ni Z: Study on the mechanism of andrographolide
activation. Front Neurosci. 16(977376)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Li X, Yuan W, Wu J, Zhen J, Sun Q and Yu
M: Andrographolide, a natural anti-inflammatory agent: An update.
Front Pharmacol. 13(920435)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Harrington BS and Annunziata CM: NF-κB
signaling in ovarian cancer. Cancers (Basel).
11(1182)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Khan H, Ullah H, Castilho PCMF, Gomila AS,
D'Onofrio G, Filosa R, Wang F, Nabavi SM, Daglia M, Silva AS, et
al: Targeting NF-κB signaling pathway in cancer by dietary
polyphenols. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 60:2790–2800. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Yu H and Jove R: The STATs of cancer-new
molecular targets come of age. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:97–105.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase-AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Baldwin AS Jr: Series introduction: The
transcription factor NF-kappaB and human disease. J Clin Invest.
107:3–6. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Showalter A, Limaye A, Oyer JL, Igarashi
R, Kittipatarin C, Copik AJ and Khaled AR: Cytokines in immunogenic
cell death: Applications for cancer immunotherapy. Cytokine.
97:123–132. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Mirzaei S, Zarrabi A, Hashemi F, Zabolian
A, Saleki H, Ranjbar A, Seyed Saleh SH, Bagherian M, Sharifzadeh
SO, Hushmandi K, et al: Regulation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB)
signaling pathway by non-coding RNAs in cancer: Inhibiting or
promoting carcinogenesis? Cancer Lett. 509:63–80. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Singh V, Gupta D and Arora R: NF-kB as a
key player in regulation of cellular radiation responses and
identification of radiation countermeasures. Discoveries (Craiova).
3(e35)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Sun SC: The non-canonical NF-κB pathway in
immunity and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 17:545–558.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Kawai T and Akira S: The role of
pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: Update on
Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol. 11:373–384. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Lin L, Hu X, Zhang H and Hu H: Tertiary
lymphoid organs in cancer immunology: Mechanisms and the new
strategy for immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 10(1398)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Abramson J and Anderson G: Thymic
epithelial cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 35:85–118. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Serasanambati M and Chilakapati SR:
Function of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kB) in human diseases-a
review. South Indian J Biol Sci. 2(368)2016.
|
|
105
|
Ben Hamouda S and Essafi-Benkhadir K:
Interplay between signaling pathways and tumor microenvironment
components: A paradoxical role in colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
24(5600)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Sun SC: Non-canonical NF-κB signaling
pathway. Cell Res. 21:71–85. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Jost PJ and Ruland J: Aberrant NF-kappaB
signaling in lymphoma: Mechanisms, consequences, and therapeutic
implications. Blood. 109:2700–2707. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Zhang T, Ma C, Zhang Z, Zhang H and Hu H:
NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. MedComm (2020).
2:618–653. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Liu T, Zhang L, Joo D and Sun SC: NF-κB
signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
2(17023)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Oeckinghaus A and Ghosh S: The NF-kappaB
family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring
Harb Perspect Biol. 1(a000034)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Guan C, Zhou X, Li H, Ma X and Zhuang J:
NF-κB inhibitors gifted by nature: The anticancer promise of
polyphenol compounds. Biomed Pharmacother.
156(113951)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Zhang R, Zhao J, Xu J, Jiao DX, Wang J,
Gong ZQ and Jia JH: Andrographolide suppresses proliferation of
human colon cancer SW620 cells through the TLR4/NF-κB/MMP-9
signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 14:4305–4310. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Im NK, Jang WJ, Jeong CH and Jeong GS:
Delphinidin suppresses PMA-induced MMP-9 expression by blocking the
NF-κB activation through MAPK signaling pathways in MCF-7 human
breast carcinoma cells. J Med Food. 17:855–861. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Liu MY, Li HJ, Yang C, Zang WD, Liu ZD,
Zhang L, Li PH, Zhu YJ, Zhao YY, Liu RZ and Gao YZ: Insight into
the pharmacological effects of andrographolide in musculoskeletal
disorders. Biomed Pharmacother. 146(112583)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Oh A, Pardo M, Rodriguez A, Yu C, Nguyen
L, Liang O, Chorzalska A and Dubielecka PM: NF-κB signaling in
neoplastic transition from epithelial to mesenchymal phenotype.
Cell Commun Signal. 21(291)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Naserian S, Abdelgawad ME, Afshar Bakshloo
M, Ha G, Arouche N, Cohen JL, Salomon BL and Uzan G: The TNF/TNFR2
signaling pathway is a key regulatory factor in endothelial
progenitor cell immunosuppressive effect. Cell Commun Signal.
18(94)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Hoesel B and Schmid JA: The complexity of
NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol Cancer.
12(86)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Li Y, He S, Tang J, Ding N, Chu X, Cheng
L, Ding X, Liang T, Feng S, Rahman SU, et al: Andrographolide
inhibits inflammatory cytokines secretion in LPS-stimulated
RAW264.7 cells through suppression of NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017(8248142)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Li J, Huang L, He Z, Chen M, Ding Y, Yao
Y, Duan Y, Zixuan L, Qi C, Zheng L, et al: Andrographolide
suppresses the growth and metastasis of luminal-like breast cancer
by inhibiting the NF-κB/miR-21-5p/PDCD4 signaling pathway. Front
Cell Dev Biol. 9(643525)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Zou W, Xiao Z, Wen X, Luo J, Chen S, Cheng
Z, Xiang D, Hu J and He J: The anti-inflammatory effect of
Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) Nees on pelvic
inflammatory disease in rats through down-regulation of the NF-κB
pathway. BMC Complement Altern Med. 16(483)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Wang W, Mani AM and Wu ZH: DNA
damage-induced nuclear factor-kappa B activation and its roles in
cancer progression. J Cancer Metastasis Treat. 3:45–59.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Han S, Huang T, Li W, Liu S, Yang W, Shi
Q, Li H, Ren J and Hou F: Association between hypoxia-inducible
factor-2α (HIF-2α) expression and colorectal cancer and its
prognostic role: A systematic analysis. Cell Physiol Biochem.
48:516–527. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Masoud GN and Li W: HIF-1α pathway: Role,
regulation and intervention for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B.
5:378–389. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Walsh JC, Lebedev A, Aten E, Madsen K,
Marciano L and Kolb HC: The clinical importance of assessing tumor
hypoxia: Relationship of tumor hypoxia to prognosis and therapeutic
opportunities. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 21:1516–1554.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Cerychova R and Pavlinkova G: HIF-1,
metabolism, and diabetes in the embryonic and adult heart. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9(460)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Glaus Garzon JF, Pastrello C, Jurisica I,
Hottiger MO, Wenger RH and Borsig L: Tumor cell endogenous HIF-1α
activity induces aberrant angiogenesis and interacts with TRAF6
pathway required for colorectal cancer development. Neoplasia.
22:745–758. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Principles and
mechanisms of vessel normalization for cancer and other angiogenic
diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 10:417–427. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Li J, Zhang C, Jiang H and Cheng J:
Andrographolide inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1 through
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT pathway and suppresses breast
cancer growth. Onco Targets Ther. 8:427–435. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Kubaichuk K and Kietzmann T: USP10
contributes to colon carcinogenesis via mTOR/S6K mediated HIF-1α
but Not HIF-2α protein synthesis. Cells. 12(1585)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Shi L, Zhang G, Zheng Z, Lu B and Ji L:
Andrographolide reduced VEGFA expression in hepatoma cancer cells
by inactivating HIF-1α: The involvement of JNK and MTA1/HDCA. Chem
Biol Interact. 273:228–236. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Bose S, Banerjee S, Mondal A, Chakraborty
U, Pumarol J, Croley CR and Bishayee A: Targeting the JAK/STAT
signaling pathway using phytocompounds for cancer prevention and
therapy. Cells. 9(1451)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Firdous P, Nissar K, Sabba A, Hassan T and
Maqbool MT: Application of plasma membrane proteomics to identify
cancer biomarkers. In: Ali S, Majid S and Rehman MU (eds).
Proteomics: A Promising Approach for Cancer Research. Elsevier,
pp287-317, 2023.
|
|
133
|
Hu Q, Bian Q, Rong D, Wang L, Song J,
Huang HS, Zeng J, Mei J and Wang PY: JAK/STAT pathway:
Extracellular signals, diseases, immunity, and therapeutic
regimens. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 11(1110765)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Huang B, Lang X and Li X: The role of
IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in cancers. Front Oncol.
12(1023177)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Bao GQ, Shen BY, Pan CP, Zhang YJ, Shi MM
and Peng CH: Andrographolide causes apoptosis via inactivation of
STAT3 and Akt and potentiates antitumor activity of gemcitabine in
pancreatic cancer. Toxicol Lett. 222:23–35. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Wang XR, Jiang ZB, Xu C, Meng WY, Liu P,
Zhang YZ, Xie C, Xu JY, Xie YJ, Liang TL, et al: Andrographolide
suppresses non-small-cell lung cancer progression through induction
of autophagy and antitumor immune response. Pharmacol Res.
179(106198)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Zhou J, Ong CN, Hur GM and Shen HM:
Inhibition of the JAK-STAT3 pathway by andrographolide enhances
chemosensitivity of cancer cells to doxorubicin. Biochem Pharmacol.
79:1242–1250. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Chen SR, Li F, Ding MY, Wang D, Zhao Q and
Wang Y, Zhou GC and Wang Y: Andrographolide derivative as STAT3
inhibitor that protects acute liver damage in mice. Bioorg Med
Chem. 26:5053–5061. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Bousoik E and Montazeri Aliabadi H: ‘Do we
know Jack’ About JAK? A closer look at JAK/STAT signaling pathway.
Front Oncol. 8(287)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Lemmon MA and Schlessinger J: Cell
signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 141:1117–1134.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
141
|
Su YC, Lee WC, Wang CC, Yeh SA, Chen WH
and Chen PJ: Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway as a
radiosensitization in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Int J
Mol Sci. 23(15749)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
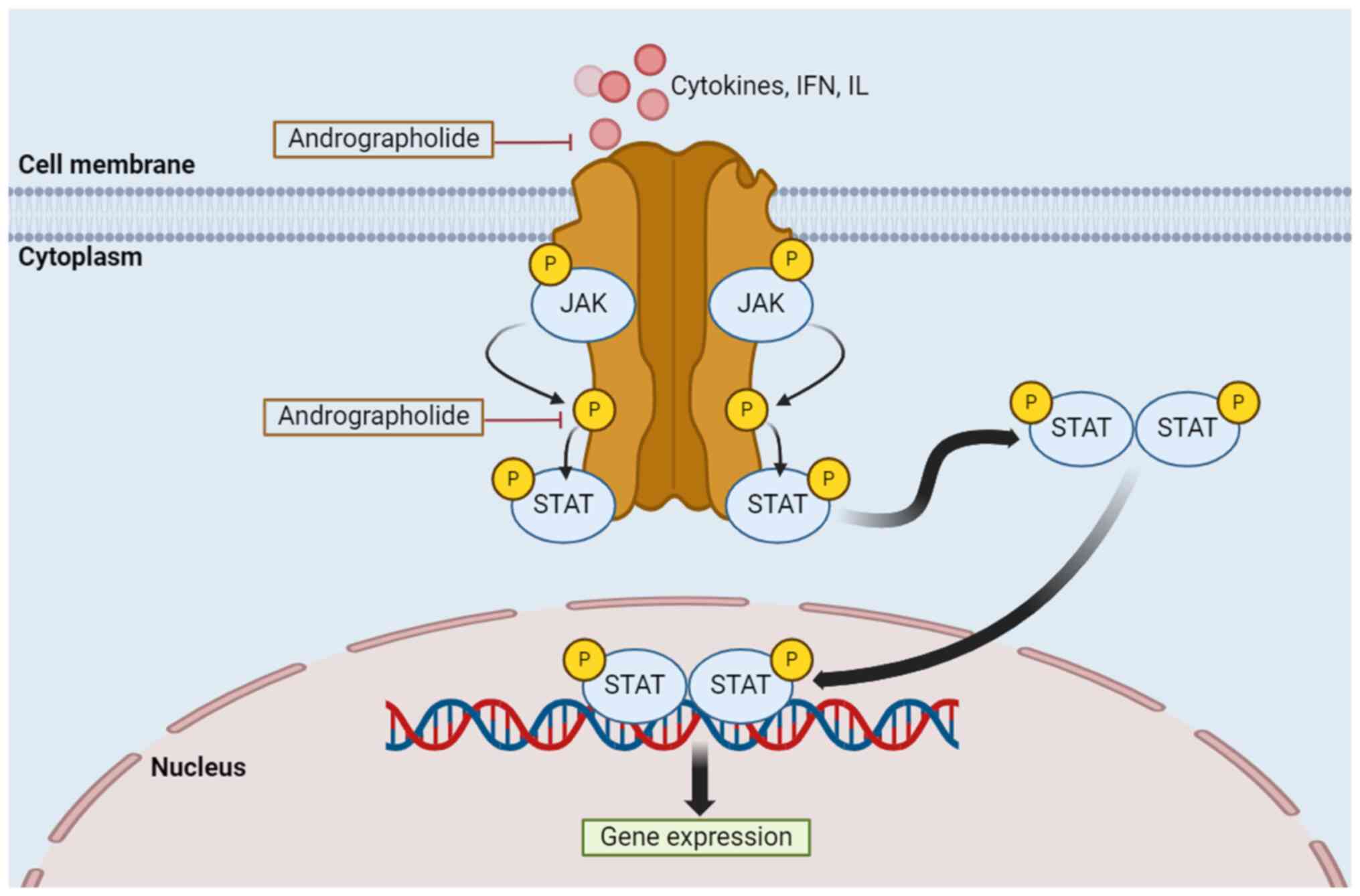
|
Tohkayomatee R, Reabroi S, Tungmunnithum
D, Parichatikanond W and Pinthong D: Andrographolide exhibits
anticancer activity against breast cancer cells (MCF-7 and
MDA-MB-231 cells) through suppressing cell proliferation and
inducing cell apoptosis via inactivation of ER-α receptor and
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling. Molecules. 27(3544)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
143
|
Weerackoon N, Gunawardhana KL and Mani A:
Wnt signaling cascades and their role in coronary artery health and
disease. J Cell Signal. 2:52–62. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Reyes M, Flores T, Betancur D,
Peña-Oyarzún D and Torres VA: Wnt/β-catenin signaling in oral
carcinogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 21(4682)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
145
|
MacDonald BT, Tamai K and He X:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases.
Dev Cell. 17:9–26. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
MacDonald BT and He X: Frizzled and LRP5/6
receptors for Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Cold Spring Harb Perspect
Biol. 4(a007880)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
147
|
Steinhart Z and Angers S: Wnt signaling in
development and tissue homeostasis. Development.
145(dev146589)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Chatterjee A, Paul S, Bisht B,
Bhattacharya S, Sivasubramaniam S and Paul MK: Advances in
targeting the WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway in cancer. Drug
Discov Today. 27:82–101. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
Jackstadt R, Hodder MC and Sansom OJ: WNT
and β-catenin in cancer: Genes and therapy. Annu Rev Cancer Biol.
4:177–196. 2020.
|
|
150
|
Liu J, Xiao Q, Xiao J, Niu C, Li Y, Zhang
X, Zhou Z, Shu G and Yin G: Wnt/β-catenin signalling: Function,
biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 7(3)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
151
|
Cruciat CM and Niehrs C: Secreted and
transmembrane Wnt inhibitors and activators. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 5(a015081)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
152
|
Skronska-Wasek W, Mutze K, Baarsma HA,
Bracke KR, Alsafadi HN, Lehmann M, Costa R, Stornaiuolo M,
Novellino E, Brusselle GG, et al: Reduced frizzled receptor 4
expression prevents WNT/β-catenin-driven alveolar lung repair in
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
196:172–185. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
153
|
Sharma P, Shimura T, Banwait JK and Goel
A: Andrographis-mediated chemosensitization through activation of
ferroptosis and suppression of β-catenin/Wnt-signaling pathways in
colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 41:1385–1394. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
154
|
Rubinfeld H and Seger R: The ERK cascade:
A prototype of MAPK signaling. Mol Biotechnol. 31:151–174.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
155
|
Karnoub AE and Weinberg RA: Ras oncogenes:
Split personalities. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:517–531.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
156
|
Zlobin A, Bloodworth JC and Osipo C:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling. In: Badve S,
Kumar G (eds). Predictive Biomarkers in Oncology. Springer, Cham,
pp213-221, 2019.
|
|
157
|
Guo YJ, Pan WW, Liu SB, Shen ZF, Xu Y and
Hu LL: ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp Ther Med.
19:1997–2007. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
158
|
Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O and Kolch W:
MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene. 26:3279–3290.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
159
|
Ballestín A, Armocida D, Ribecco V and
Seano G: Peritumoral brain zone in glioblastoma: Biological,
clinical and mechanical features. Front Immunol.
15(1347877)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
160
|
Yang SL, Kuo FH, Chen PN, Hsieh YH, Yu NY,
Yang WE, Hsieh MJ and Yang SF: Andrographolide suppresses the
migratory ability of human glioblastoma multiforme cells by
targeting ERK1/2-mediated matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression.
Oncotarget. 8:105860–105872. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
161
|
Zhang C, Yang C, Feldman MJ, Wang H, Pang
Y, Maggio DM, Zhu D, Nesvick CL, Dmitriev P, Bullova P, et al:
Vorinostat suppresses hypoxia signaling by modulating nuclear
translocation of hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha. Oncotarget.
8:56110–56125. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|