Introduction
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of
cancer-related mortality accounting for up to one-third of newly
diagnosed cancers in the women from USA (1). Despite the availability of advanced
surgical tools and chemo/radiation treatment, the long-term
therapeutic success of stage IV metastatic breast cancer is low
(2). This raises a need for
immune-targeted therapies that can provide improved long-term
response along with reduced treatment resistance and side-effect
profile. Advances in the understanding of tumor immunology enabled
the development of anticancer vaccines as a viable
immunotherapeutic approach (3).
Tumor-associated antigens (TAAs), either expressed exclusively in
the tumor tissue or selectively overexpressed by the oncogenes,
offer unique molecular targets that can be utilized for vaccine
development (4). Mammaglobin-A
(Mam-A), a 10-kDa human breast cancer-associated antigen almost
exclusively expressed in 40-80% of primary and metastatic breast
cancers, is an attractive vaccine target (5). There is conflicting literature
evidence on the correlation between MamA expression and hormonal
status (6). While some studies
have suggested a positive correlation between MamA expression and
estrogen receptor expression in breast tumors (7), other studies have revealed an
association between MamA expression and ER- breast tumors (8). The previous phase I clinical trials
performed by the authors have revealed that the MamA-based cDNA
vaccine was safe and could elicit modest CD8+ and
CD4+T lymphocyte immune responses in patients with
breast cancer (9). A previous
study by Jaramillo et al (10) investigated seven human leukocyte
antigen (HLA)-A2 restricted MamA immunodominant epitopes and
demonstrated that MamA2.1 (83-92 amino acid sequence of MamA)
induced highest cytotoxic CD8+T lymphocyte (CTL)
responses. Combination of MamA2.1 peptide vaccine with immune
adjuvants such as methylselenol or CpG oligodeoxy-nucleotides
(ODN2006 and M306) has further enhanced peptide-mediated CTL
responses, thus offering potential peptide-based cancer
immunotherapy against breast cancer (11,12).
Peptide vaccine-based active immunotherapy offers a
novel tool to combat cancer. In this form of vaccination,
immunodominant epitope sequences from TAAs are utilized to amplify
host antitumor adaptive immune responses. As cancer cells
selectively upregulate the expression of certain tumor-associated
and mutant proteins that are otherwise not expressed in normal
cells, these unique amino acid sequences could be utilized to
develop peptide vaccines (13).
Specificity, which is the hallmark of human adaptive immune
response, represents the ability of adaptive immune cells (CD8 and
CD4 T lymphocytes) to preferentially recognize TAAs on cancer cells
and destroy them. TAAs are generally presented by antigen
presentation molecules expressed on all nucleated cells to activate
CD8+T lymphocytes from naïve to cytotoxic phenotype by
the HLA class I pathway (14). It
has been revealed that in the HLA class I pathway the antigen TAA
is intracellularly processed by proteasome to 8-10 amino
acid-epitope for further presentation to CD8+T
lymphocytes (15).
The initial excitement in cancer vaccines is
significantly dampened by the minimal potency of this strategy to
elucidate anticancer CTL responses. This is particularly true with
peptide vaccines which have demonstrated poor uptake into the
lymphatics and eventual delivery to lymph nodes (16). Furthermore, peptides should be
actively transported (ATP-dependent) into the antigen-presenting
cells (APCs) for internalization and major histocompatibility
complex loading to be presented for priming of naïve
CD8+T lymphocytes to induce a cytotoxic anticancer
effect (17). However, this
challenge also offers new venues of research to explore
complementary strategies to enhance the efficacy of peptide
vaccines. Novel design of peptide antigens to enhance their
delivery through the hydrophobic cell membrane of APCs could
enhance the HLA class I presentation of this peptide to
CD8+T lymphocytes resulting in antitumor CTL responses
(18). Cell-penetrating peptides
(CPPs) are a unique class of delivery tools that aid with the
translocation of the macromolecular cargo bound to them (19). Previous studies have revealed that
the protein transduction domain of human immunodeficiency virus TAT
protein (Tat47-60) and S4 domain of Shaker-Potassium channel
protein (S4) interact with the cell membrane leading to
translocation through the hydrophobic core of the cell membrane in
an ATP energy-independent manner (20,21).
The ability of CPPs to translocate the peptide antigen target
could, in principle, cause enhanced intracellular delivery and
eventual downstream CTL responses. In the present study, the novel
applicability of the S4 protein transduction domain was reported as
a potent CPP conjugate for peptide vaccine delivery.
Materials and methods
Cell lines and reagents
The T2 cell line (HLA-A2+) and two human
breast cancer cell lines [MCF-7 (cat. no. HTB-22;
HLA-A2+/MamA-, ER+, PR+ and
HER2+/mild)] and AU565 (cat. no. CRL-2351;
HLA-A2+/MamA+, ER-, PR- and HER2+)
were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection. Pooled
primary human CD8+CD45RA+ naïve T lymphocytes
collected from healthy donors were obtained from StemCell
Technologies (cat. no. 70030). All cell cultures were performed
under aseptic conditions and as aforementioned (12). All cells were confirmed to be free
of mycoplasma contamination before experiments. The expression of
HLA-A2 and MamA was confirmed by mRNA analysis. All synthetic
peptides (Table I) were obtained
from Peptide2.0, Inc. and confirmed by the manufacturer to have
>95% purity. Unless mentioned otherwise, all other chemicals
were obtained either from MilliporeSigma or Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc. The present study was approved (approval no.
HS2018-4093) by the Tennessee State University (Nashvile, USA)
institutional review board.
 | Table IList of cell-penetrating peptides and
HLA-A2 restricted MamA epitopes. |
Table I
List of cell-penetrating peptides and
HLA-A2 restricted MamA epitopes.
| Peptide | Sequence |
|---|
| TAT | YGRKKRRQRRRPPQ |
| AntP |
RQIKIWFQNRRJKWKK |
| S4 |
RVIRLVRVFRIFKLSR |
| R8 | RRRRRRRRR |
| TP10 |
AGYLLGKINLKALAALAKKIL |
| MPG |
GLAFLGFLGAAGSTMGAWSQPKKKRKV |
| A9 | AAAAAAAAA (negative
control) |
| MamA2.1 | LIYDSSLCDL |
| MamA2.2 | KLLMVLMLA |
| MamA2.3 | LMVLMLAAL |
| MamA2.4 | FLNQTDETL |
| MamA2.5 | TLSNVEVFM |
| MamA2.6 | MQLIYDSSL |
| MamA2.7 | TINPQVSKT |
HLA-A2 membrane stabilization
assay
The peptide binding to HLA-A2 was assessed using
transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP)
protein-deficient T2 cells (22).
Towards this, T2 cells (0.5x105/ml) were incubated for
24 h in 96-well cell culture plates with 200 µl of complete
RPMI-1640 cell culture media (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) at
37˚C along with human β2-microglobulin (3 µg/ml) and various
individual peptides (50 µg/ml) mentioned below in the results
section (Fig. 1). The T2 cells
were then washed and incubated for 30 min at 4˚C with FITC labeled
BB7.2 anti-HLA-A2 monoclonal antibody (10 µg/ml; BioLegend, Inc.,
cat. no. 343304) and fixed with 0.5% paraformaldehyde (cat. no.
F8775; MilliporeSigma). FITC-labeled mouse monoclonal IgG2b/κ
(clone: MG2b-57; 1:20; cat. no. 401206; BioLegend, Inc.) was used
as an isotype control and stained at 4˚C. The cells were analyzed
with a FACS Calibur™/LSRII flow cytometer (Becton, Dickinson and
Company) and analyzed by FlowJo v10 software (FlowJo, LLC). Results
were expressed as the median channel fluorescence shift
corresponded to the difference between the median fluorescence
obtained with peptide-pulsed T2 cells and empty (no peptide) T2
cells.
Immunogenic peptide stimulation and
generation of MamA-specific CD8+T lymphocytes
The human naïve CD8+T lymphocytes
(0.5x105) were cultured in 2-ml complete RPMI-1640 media
in 6-well plates in the presence of irradiated (5,000 rads) peptide
loaded T2 cells (1x106, 20:1) in the presence of β2m (3
µg/ml), CD3 (500 ng/ml), CD28 mAb (500 ng/ml) and recombinant human
IL-2 (20 U/ml) for 5 days per stimulation cycle and repeated for
three stimulation cycles. Following this, the activated
CD8+T lymphocytes were isolated by immunomagnetic
separation (MACS® cell separation; Miltenyi Biotec,
Inc.) with >95% purity.
Cytotoxicity assay
The MamA-specific cytotoxicity of activated
CD8+T lymphocytes [referred to as effector cells (E)]
was analyzed by calorimetric lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release
assay (Abcam) following the manufacturer's protocol (23). The breast cancer cells
[1x104 cells, referred to as target cells (T)] were
co-cultured with activated CD8+T lymphocytes with an E:T
ratio of 20:1. The percentage specific lysis was calculated as
follows: [(experimental LDH release-spontaneous LDH
release)/(maximum LDH release-spontaneous LDH release)] x100.
Reverse transcription-quantitative
polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR)
Expression profiles of genes in the activated human
CD8+T lymphocytes were analyzed using the FAM-labeled
Taqman gene expression RT-qPCR primers (Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc.) for interferon-γ (IFNγ, Hs00989291_m1), granzyme B
(Hs00188051_m1), and β-actin (Hs01060665_g1) (12). The total RNA obtained by
TRIzol® extraction protocol was utilized to perform
RT-qPCR (iTaq one step kit; cat. no. 1725151; Bio-Rad Laboratories,
Inc.) with thermocycling conditions consisting of an initial
denaturation of 95˚C for 15 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95˚C for
30 sec, followed by 61˚C for 1 min; and analyzed by
2-ΔΔCq method in a final reaction volume of 50 µl using
Bio-Rad CFX connect system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.) (24).
Statistical analysis
Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM from four
independent studies. For multiple groups, significant differences
between the groups were assessed using Tukey HSD pair-wise
comparisons for two groups and one-way ANOVA for multiple
comparisons. For two groups, unpaired t-test was used. P<0.05
was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
All data analysis was carried out using GraphPad Prism 8 software
(Dotmatics) or SPSS software version 21 (IBM Corp.).
Results
Enhanced HLA-A2 membrane stabilization
of S4 conjugated MamA2.1 peptide
The T2 cells, due to their deficiency of TAP protein
cannot load peptides from endogenous proteasome processed external
antigenic proteins onto HLA-A2 molecules (22). This restricts the stable
translocation of peptide-loaded HLA-A2 to the extracellular surface
of cell membranes needed for eventual activation of naive
CD8+T lymphocytes to cytotoxic effector phenotype.
However, external peptides that can optimally bind to the
3-dimensional peptide binding groove structure of HLA-A2 will
circumvent the TAP-dependent pathway and induce stable membrane
expression of HLA-A2. Therefore, T2 cell lines are widely utilized
for peptide-HLA-A2 binding assay (25). To determine the HLA-A2 binding
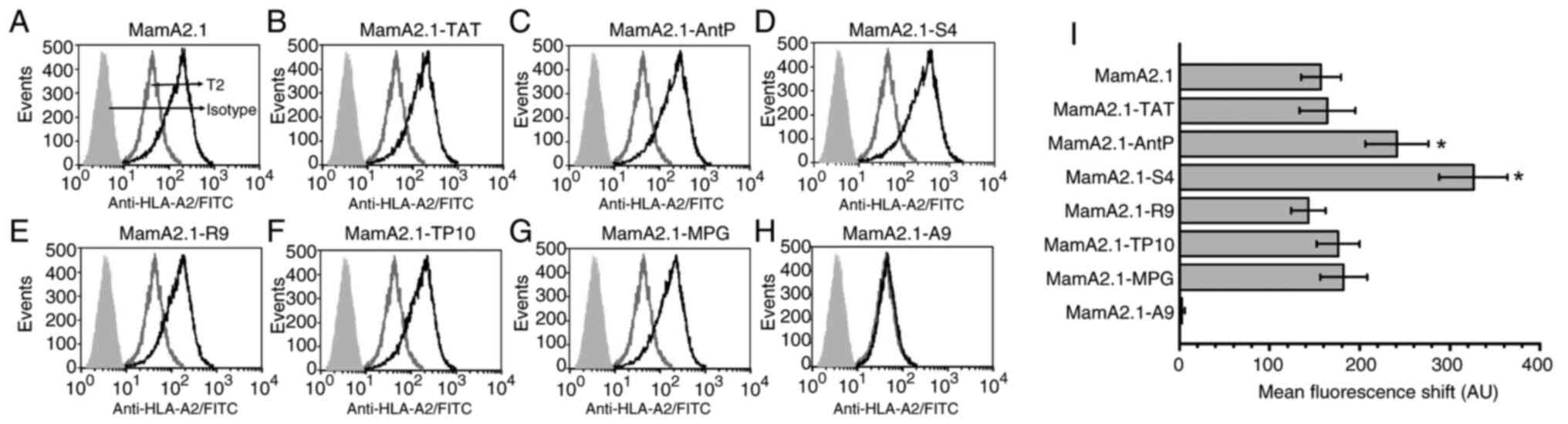
capability of CPP-conjugated MamA2.1 peptide (Fig. 1), membrane stabilization studies
were performed utilizing T2 cells. In order to achieve this, each
conjugated peptide (10 µg/ml) was incubated with T2 cells for 24 h,
following which, HLA-A2 membrane expression was analyzed by median
fluorescence channel shift (MFCS). As demonstrated in Fig. 1, MamA2.1 conjugated with AntP
(221±35 AU, P<0.05) and S4 (326±43 AU, P<0.05) peptides
demonstrated significantly increased MFCS as compared with
unconjugated MamA2.1 (157±22 AU). Understandably, polyalanine (A9)
conjugated MamA2.1 (MamA2.1-A9), negative control, did not induce
any surface expression of HLA-A2. All other conjugated peptides
demonstrated a similar MCFS as compared with unconjugated MamA2.1.
These data strongly suggested that S4-conjugated MamA2.1 induced
the highest surface expression of HLA-A2 with a possibly enhanced
potential to induce cytotoxic activation of naïve CD8+T
lymphocytes.
Cytotoxic efficiency of MamA2.1-S4
peptide-restricted CD8+T lymphocytes
Next, it was determined if S4 conjugated MamA2.1
peptide-pulsed T2 cells could activate naïve CD8+T
lymphocytes. Towards this, naïve CD8+T cells obtained
from HLA-A2+ healthy donors were stimulated in
vitro by various peptide-pulsed T2 cells for four cycles
followed by isolation of activated CD8+T cells by
magnetic beads. These HLA-A2 restricted and activated
CD8+T cells were co-cultured with human breast cancer
cells. Two breast cancer lines, UACC812
(HLA-A2+MamA+) and MCF7
(HLA-A2+MamA-), were utilized in the present
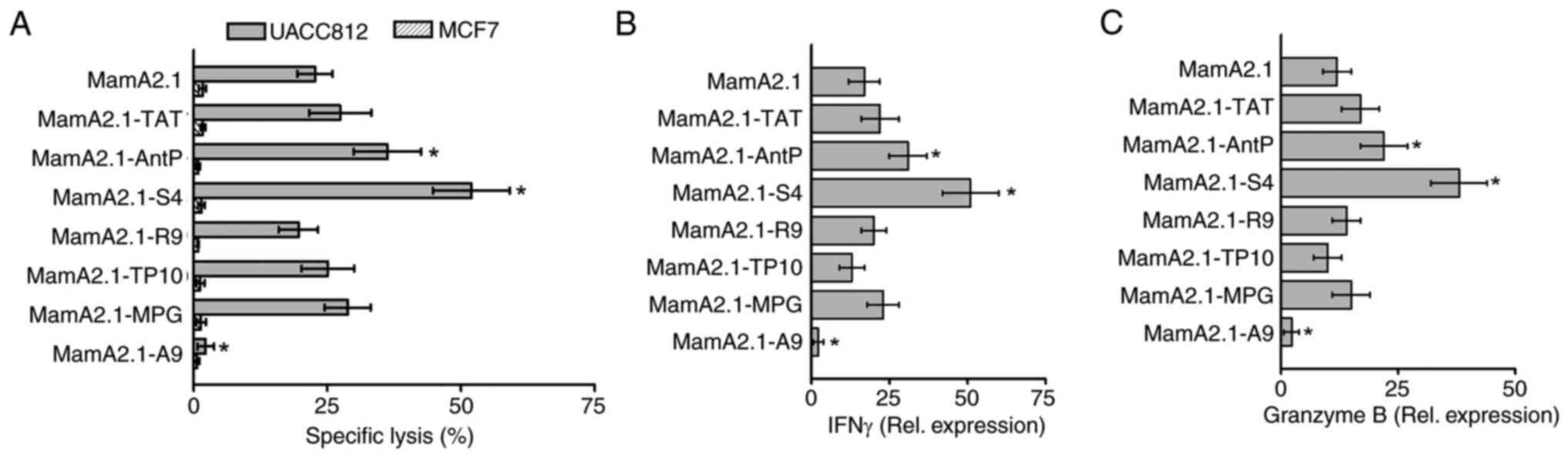
study. As demonstrated in Fig. 2A,
CD8+T cells activated by MamA2.1-S4-pulsed T2 cells
demonstrated highest cytotoxicity (51.9±7.2%, P<0.05) followed
by MamA2.1-AntP mediated activation (36.2±6.3%, P<0.05),
compared with unconjugated MamA2.1 peptide (22.7±3.4%). As
expected, no cytotoxicity was observed against the MCF7 breast
cancer cell line which does not express MamA protein. Gene
expression analysis of inflammatory cytokines (Fig. 2B and C) demonstrated enhanced expression of
IFNγ and granzyme B in CD8+T cells activated by
MamA2.1-S4 pulsed T2 cells. These data specifically indicate that
S4 conjugation of MamA2.1 peptide enhanced the potential vaccine
efficiency of HLA class I restricted anticancer activation of
CD8+T cells.
S4 conjugation enhances the
immunodominance of other HLA-A2 restricted MamA epitopes
A previous study by Jaramillo et al (10), have identified seven candidate
HLA-A2 restricted MamA epitopes (MamA2.1-2.7) based on an in
silico binding algorithm. S4 conjugation to these seven
epitopes was tested if it would enhance the immunodominance as
measured by membrane stabilization and CD8+T cell
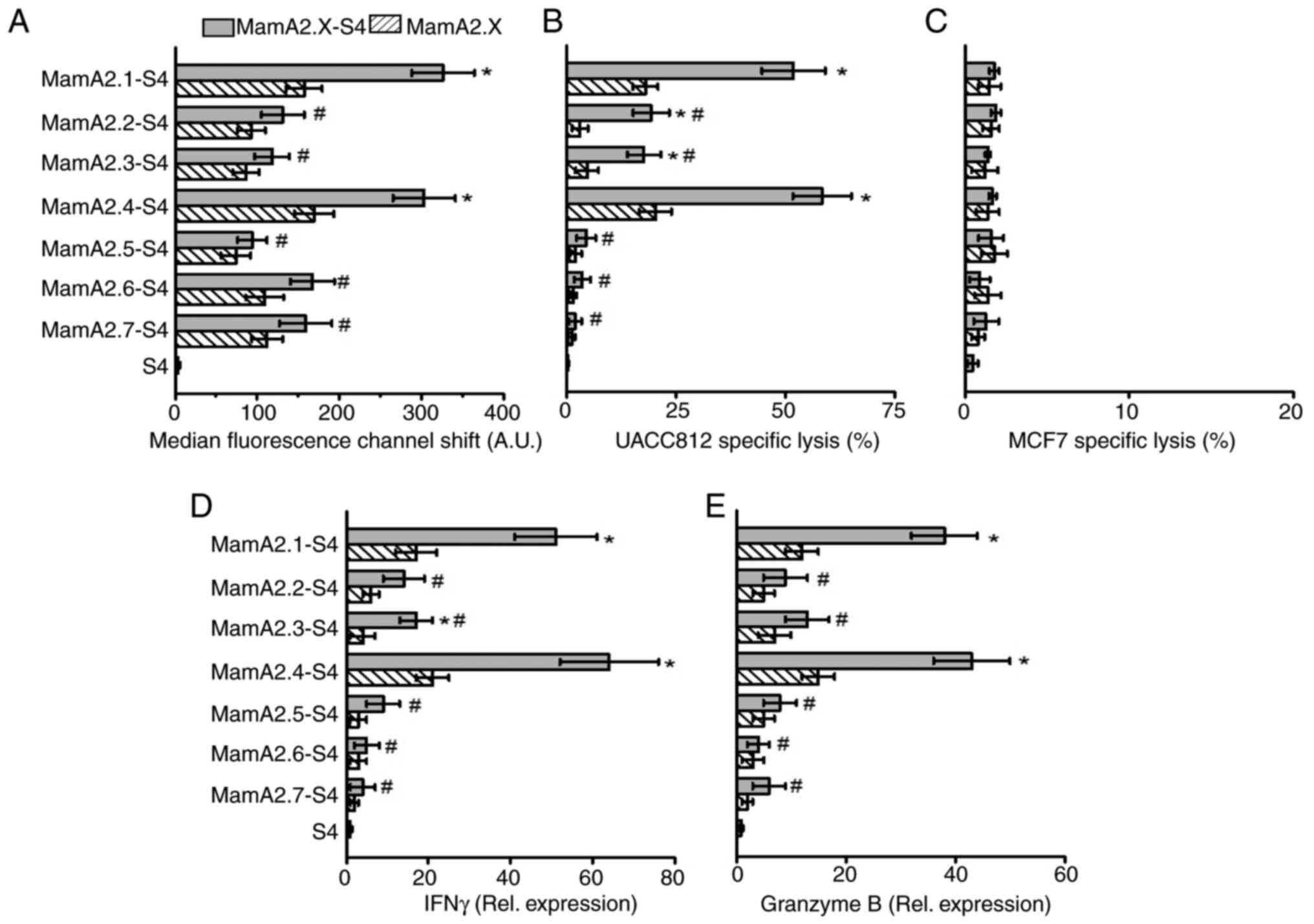
activation. As demonstrated in Fig.
3A, along with MamA2.1 (as aforementioned), S4 conjugation to
HLA-A2 restricted MamA epitopes and further enhanced the membrane
stabilization of MamA2.4 (303±38 AU, P<0.05), as compared with
unconjugated MamA2.4 (169±24 AU). The other five epitopes (namely,
MamA2.2, 2.3, 2.5, 2.6 and 2.7), while they demonstrated slightly
increased membrane stabilization, did not achieve statistical
significance (Fig. S1).
Similarly, stimulation of CD8+T cells by T2 cells pulsed
with S4 conjugated MamA2.4 (in addition to MamA2.1) enhanced the
cytotoxicity against UACC812 breast cancer cells (Fig. 3B). Furthermore, CD8+ T
cells stimulated by S4 conjugation of MamA2.2 and 2.3 epitopes also
demonstrated significant cytotoxicity. As expected, none of the
epitopes induced cytotoxicity of CD8+T cells against
MamA non-expressing MCF7 breast cancer cells (Fig. 3C). In line with membrane
stabilization and cytotoxicity data, CD8+T cells
stimulated by MamA2.4-S4 and 2.1-S4 have demonstrated the highest
expression of inflammatory cytokines IFNγ and granzyme B (Fig. 3D and E). Taken together, these data clearly
suggested that conjugation of MamA immunodominant epitopes with
S4-CPP, enhanced the cellular internalization and presentation of
the antigenic MamA immunodominant epitopes to CD8+T
cells, causing their inflammatory activation and anticancer
efficiency.
Conjugation of S4 at the C-terminus of
MamA2.1 enhanced its immunodominance
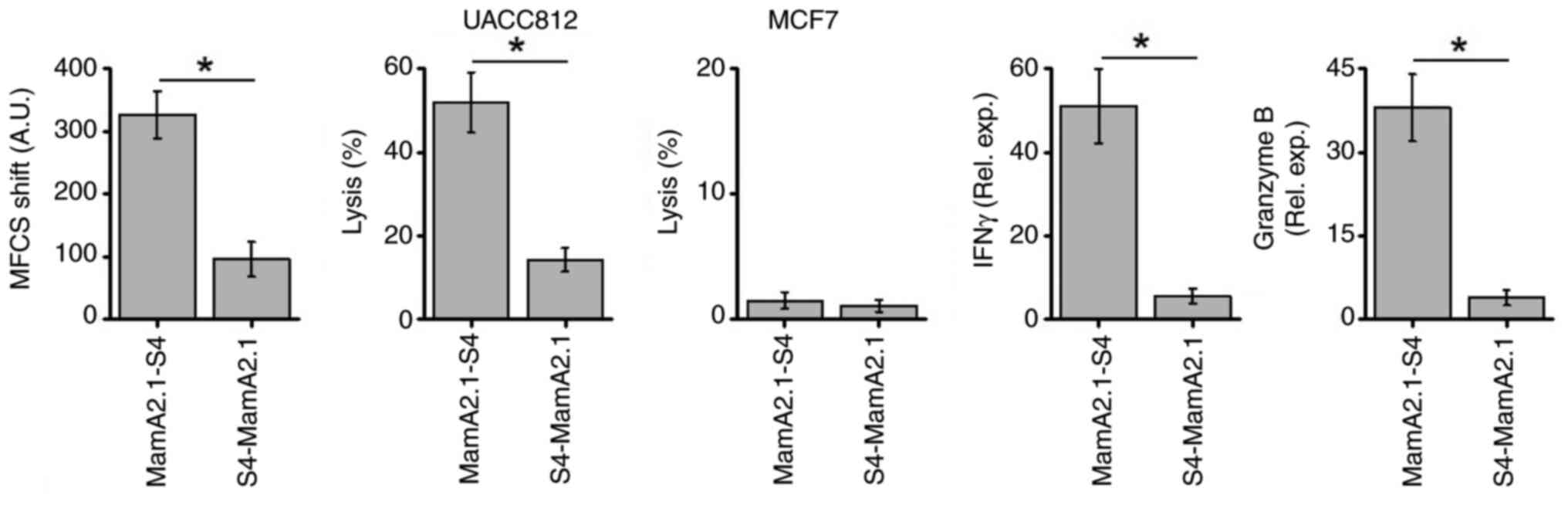
Next, it was verified whether immunodominance would
be impacted by the preferential conjugation of S4-CPP at the
N-terminus versus the C-terminus of the MamA2.1 epitope. As
demonstrated in Fig. 4,
conjugation of S4-CPP at the C-terminus over the N-terminus exerted
higher immunodominance as demonstrated by increased membrane
stabilization (Fig. S2), UACC
cytotoxicity and gene expression of inflammatory cytokines IFNγ and
granzyme B. These data demonstrated that the C-terminus conjugation
of S4-CPP to MamA2.1 epitope enhanced the cellular internalization
leading to the loading of this peptide to HLA-A2 and translocation
to the cell membrane. This caused efficient presentation of the
antigenic determinant to activate naïve CD8+T cells to
induce anticancer cytotoxicity.
Discussion
Compared with other vaccine and immunotherapeutic
strategies, peptide-based vaccination approaches offer major
advantages by their ability to selectively target cancer cells,
induce long-term memory CD8+T lymphocytes, minimal
side-effect profile, along with low manufacturing costs and easy
scalability (26). However,
limited efficacy of peptide vaccines in clinical trials could be
attributed to poor antigen presentation, low immunogenicity and
immune suppressive tumor microenvironment (27). Conjugation of antigenic epitopes
with CPPs has been considered to enhance the efficiency of peptide
vaccination. Various clinical trials (NCT01396239) have been
designed to study the application of CPPs as efficient peptide
vaccine delivery agents (28).
However, there has been significant debate regarding the universal
choice of a particular CPP for its efficient translocation through
the cell membrane for the eventual antigenic presentation of cancer
epitopes to induce immune responses. In the current study, six
different CPPs were tested for their ability to enhance the
immunogenicity of the MamA epitopes. While various CPPs have been
tested by several research groups (29), the CPP capability of S4 protein
transduction domain has not been reported.
The immunogenicity of peptide vaccines is dependent
upon the ability of this epitope to be loaded on HLA class I
molecules for its eventual presentation to CD8+T
lymphocytes (30). The present
study revealed that conjugation of MamA2.1 and MamA2.4 epitopes
with S4 domain enhances the stable membrane expression of HLA class
I molecule. The S4-CPP with its ability to pass through the cell
membrane, could enhance the cellular internalization of the HLA-A2
restricted MamA epitopes which in-turn enables the loading of this
epitope onto HLA-A2 molecules. However, it may be unlikely that
CPPs might impact other steps in antigen presentation, such as,
proteasome-mediated proteolytic processing for loading of epitopes
onto HLA class I molecules (31).
Enhanced fluorescence channel shift (Fig. 1) with CPP conjugated MamA2.1 and
MamA2.4 epitopes suggested that there was an increased number of
HLA-A2 molecules with stable membrane expression. Traditionally,
TAP-deficient T2 cells were used to verify the activation of
CD8+T lymphocytes following appropriate recognition of
antigenic determinants. The TAP protein is involved in
translocation of endogenously processed antigenic determinants to
endoplasmic reticulum for their eventual loading on HLA class I
molecules in Golgi apparatus. The TAP-deficient T2 cells do not
have stable surface membrane expression of HLA class I molecules.
The exogenous antigenic determinant-pulsed T2 cells enable
interaction of epitope-loaded HLA class I molecules to T-cell
receptor (TCR) of naïve CD8+T lymphocytes leading to
their antigen specific cytotoxic activation.
The ability of S4-conjugated MamA epitope-pulsed T2
cells to prime CD8 T lymphocytes to activate their cytotoxic
ability was identified (Fig. 2).
Furthermore, conjugation of the S4 domain to less immunogenic MamA
epitopes also revealed a marginal increase in HLA-A2 membrane
expression and downstream T-cell activation (Fig. 3) suggesting that CPPs generally
increase the final cytosolic availability of antigenic epitopes for
loading onto HLA class I presentation. While it may be reasonable
to expect that CPP-conjugation would directly increase the
internalization and cytosolic abundance of antigenic epitope,
studies by Backlund et al (32), revealed that enhanced
immunogenicity of CPP-conjugation to a melanoma-associated
antigenic epitope, gp100, requires Baft3-dependent cross
presentation by professional APCs and not by direct CPP-mediated
cytosolic internalization. They also revealed that enhanced
immunogenicity following CPP-conjugation in their murine
preclinical cancer model was dependent upon its ability to bind
with lymph-tracking lipoprotein. Similarly, peptide loading
capability of S4-conjugate epitopes to dendritic cells should be
tested in murine models following the aforementioned MamA peptide
vaccination. Therefore, future in vivo studies using
dendritic cells are needed to validate the findings of the present
study and to gain improved understanding of the molecular
mechanisms impacting the vaccination efficiency of the
S4-conjugated MamA epitopes. While the present study is limited to
HLA-A2 subtype, future studies are needed to characterize the
efficiency is the other HLA Class I subtypes for broader
application among diverse HLA profiles.
In summary, the present study indicated that
S4-domain conjugation enhances the anticancer immunogenicity of
MamA epitope-based peptide vaccination. The present study is
limited to assessing the in vitro efficiency of TAA-specific
activation of CD8+T lymphocytes. However, in vivo
molecular mechanisms of antigen presentation are dependent upon
vaccine bioavailability, tracking of vaccine to lymph nodes, cell
type specific differences between various APCs and ability of
T-cell receptor on CD8+ T lymphocyte's binding ability
to HLA molecules. Future studies are warranted in preclinical
animal models to develop a detailed understanding of the efficiency
of the S4-domain conjugation to immunodominant MamA epitopes. CPPs
were considered to act as adjuvants to further enhance vaccine
capability through binding with toll-like receptors (TLRs). The
role of TLRs in CPP-conjugated peptide vaccination should also be
analyzed. While the present study was designed to understand the
priming of CD8+T lymphocytes, future studies geared
towards understanding CD4+T lymphocyte adaptive immune
responses will enable future applicability of CPP-conjugation for
efficient peptide vaccination in cancer immunotherapy.
Supplementary Material
Membrane stabilization assay on T2
cells following treatment with various S4-conjugated MamA2.1-2.7
epitopes. (A-G) Representative flow cytometry results demonstrating
mean fluorescence channel shift. The membrane expression of HLA-A2
with S4-conjugated MamA epitopes is shown in unfilled bold black.
The isotype control antibody with no binding affinity to HLA-A2
molecules is demonstrated in a filled light grey histogram. The
HLA-A2 membrane expression on empty T2 cells untreated with the
aforementioned epitopes is demonstrated in unfilled light grey
histogram and with unconjugated MamA epitopes is demonstrated in
unfilled grey histograms. S4, shaker-potassium channel protein;
MamA2.1, mammaglobin-A; HLA, human leukocyte antigen.
Comparison of the membrane
stabilization efficiency between N-terminus versus C-terminus
conjugation of MamA epitope with S4-CPP domain. Representative flow
cytometry results demonstrating the mean fluorescence channel
shift. The membrane expression of HLA-A2 with S4-MamA2.1 epitope is
shown in unfilled bold black. The isotype control antibody with no
binding affinity to HLA-A2 molecules is shown in a filled light
grey histogram. The HLA-A2 membrane expression on empty T2 cells
untreated with aforementioned epitopes was shown in unfilled light
grey histogram and with MamA2.1-S4 epitope is shown in unfilled
grey histograms. S4, shaker-potassium channel protein; MamA2.1,
mammaglobin-A; HLA, human leukocyte antigen.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: The present study was supported by the National
Institutes of Health, USA (grant no. NIH-5U54CA163066).
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study are included
in the figures and/or tables of this article.
Authors' contributions
VT conceived the project and designed the
experiments. JAM, UA, SV and VT performed the experiments. JAM, UA,
SV, AYS and VT analyzed the data, and wrote and revised the paper.
AYS and VT confirm the authenticity of all the raw data. All
authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Healthy human tissue (including blood components)
were obtained from external sources and commercial vendors. The
present study was approved (approval no. HS2018-4093) by the
Tennessee State University (Nashvile, USA) institutional review
board.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:12–49.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Brufsky A, Kwan ML, Sandin R,
Stergiopoulos S, Karanth S, Cha-Silva AS, Makari D and Goyal RK:
Trends in HR+ metastatic breast cancer survival before and after
CDK4/6 inhibitor introduction in the United States: A SEER registry
analysis of patients with HER2- and HER2+ metastatic breast cancer.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 208:223–235. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Sotirov S and Dimitrov I: Tumor-derived
antigenic peptides as potential cancer vaccines. Int J Mol Sci.
25(4934)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Curigliano G, Bagnardi V, Ghioni M,
Louahed J, Brichard V, Lehmann FF, Marra A, Trapani D, Criscitiello
C and Viale G: Expression of tumor-associated antigens in breast
cancer subtypes. Breast. 49:202–209. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Liu Z, Yang X, Duan C, Li J, Tong R, Fan
Y, Feng J, Cao R, Zhong W, Feng X, et al: Identification and
characterization of mammaglobin-A epitope in heterogenous breast
cancers for enhancing tumor-targeting therapy. Signal Transduct
Target Ther. 5(82)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Milosevic B, Stojanovic B, Cvetkovic A,
Jovanovic I, Spasic M, Stojanovic MD, Stankovic V, Sekulic M,
Stojanovic BS, Zdravkovic N, et al: The enigma of mammaglobin:
Redefining the biomarker paradigm in breast carcinoma. Int J Mol
Sci. 24(13407)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Li G, Zhang J, Jin K, He K, Wang H, Lu H
and Teng L: Human mammaglobin: A superior marker for
reverse-transcriptase PCR in detecting circulating tumor cells in
breast cancer patients. Biomark Med. 5:249–260. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
O'Brien N, Maguire TM, O'Donovan N, Lynch
N, Hill AD, McDermott E, O'Higgins N and Duffy MJ: Mammaglobin a: A
promising marker for breast cancer. Clin Chem. 48:1362–1364.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tiriveedhi V, Tucker N, Herndon J, Li L,
Sturmoski M, Ellis M, Ma C, Naughton M, Lockhart AC, Gao F, et al:
Safety and preliminary evidence of biologic efficacy of a
mammaglobin-a DNA vaccine in patients with stable metastatic breast
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 20:5964–5975. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Jaramillo A, Narayanan K, Campbell LG,
Benshoff ND, Lybarger L, Hansen TH, Fleming TP, Dietz JR and
Mohanakumar T: Recognition of HLA-A2-restricted
mammaglobin-A-derived epitopes by CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes from
breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 88:29–41.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Babaer D, Amara S, McAdory BS, Johnson O,
Myles EL, Zent R, Rathmell JC and Tiriveedhi V:
Oligodeoxynucleotides ODN 2006 and M362 exert potent adjuvant
effect through TLR-9/-6 synergy to exaggerate mammaglobin-A peptide
specific cytotoxic CD8+T lymphocyte responses against breast cancer
cells. Cancers (Basel). 11(672)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Babaer D, Zheng M, Ivy MT, Zent R and
Tiriveedhi V: Methylselenol producing selenocompounds enhance the
efficiency of mammaglobin-A peptide vaccination against breast
cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 18:6891–6898. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Nelde A, Rammensee HG and Walz JS: The
peptide vaccine of the future. Mol Cell Proteomics.
20(100022)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Xie N, Shen G, Gao W, Huang Z, Huang C and
Fu L: Neoantigens: Promising targets for cancer therapy. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 8(9)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Nguyen AT, Szeto C and Gras S: The pockets
guide to HLA class I molecules. Biochem Soc Trans. 49:2319–2331.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Moynihan KD, Holden RL, Mehta NK, Wang C,
Karver MR, Dinter J, Liang S, Abraham W, Melo MB, Zhang AQ, et al:
Enhancement of peptide vaccine immunogenicity by increasing
lymphatic drainage and boosting serum stability. Cancer Immunol
Res. 6:1025–1038. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ding Y, Li Z, Jaklenec A and Hu Q: Vaccine
delivery systems toward lymph nodes. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.
179(113914)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kim CG, Kye YC and Yun CH: The role of
nanovaccine in cross-presentation of antigen-presenting cells for
the activation of CD8(+) T cell responses. Pharmaceutics.
11(612)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yang J, Luo Y, Shibu MA, Toth I and
Skwarczynskia M: Cell-penetrating peptides: Efficient vectors for
vaccine delivery. Curr Drug Deliv. 16:430–443. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Tiriveedhi V and Butko P: A fluorescence
spectroscopy study on the interactions of the TAT-PTD peptide with
model lipid membranes. Biochemistry. 46:3888–3895. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Tiriveedhi V, Miller M, Butko P and Li M:
Autonomous transmembrane segment S4 of the voltage sensor domain
partitions into the lipid membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1818:1698–1705. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Bossi G, Gerry AB, Paston SJ, Sutton DH,
Hassan NJ and Jakobsen BK: Examining the presentation of
tumor-associated antigens on peptide-pulsed T2 cells.
Oncoimmunology. 2(e26840)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Tiriveedhi V, Ivy MT, Myles EL, Zent R,
Rathmell JC and Titze J: Ex vivo high salt activated tumor-primed
CD4+T lymphocytes exert a potent anti-cancer response. Cancers
(Basel). 13(1690)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Luft T, Rizkalla M, Tai TY, Chen Q,
MacFarlan RI, Davis ID, Maraskovsky E and Cebon J: Exogenous
peptides presented by transporter associated with antigen
processing (TAP)-deficient and TAP-competent cells: Intracellular
loading and kinetics of presentation. J Immunol. 167:2529–2537.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zahedipour F, Jamialahmadi K, Zamani P and
Jaafari MR: Improving the efficacy of peptide vaccines in cancer
immunotherapy. Int Immunopharmacol. 123(110721)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Stephens AJ, Burgess-Brown NA and Jiang S:
Beyond just peptide antigens: The complex world of peptide-based
cancer vaccines. Front Immunol. 12(696791)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Bottens RA and Yamada T: Cell-Penetrating
peptides (CPPs) as therapeutic and diagnostic agents for cancer.
Cancers (Basel). 14(5546)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Hasannejad-Asl B, Pooresmaeil F, Takamoli
S, Dabiri M and Bolhassani A: Cell penetrating peptide: A potent
delivery system in vaccine development. Front Pharmacol.
13(1072685)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Buonaguro L and Tagliamonte M:
Peptide-based vaccine for cancer therapies. Front Immunol.
14(1210044)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wu X, Li T, Jiang R, Yang X, Guo H and
Yang R: Targeting MHC-I molecules for cancer: Function, mechanism,
and therapeutic prospects. Mol Cancer. 22(194)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Backlund CM, Holden RL, Moynihan KD,
Garafola D, Farquhar C, Mehta NK, Maiorino L, Pham S, Iorgulescu
JB, Reardon DA, et al: Cell-penetrating peptides enhance peptide
vaccine accumulation and persistence in lymph nodes to drive
immunogenicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
119(e2204078119)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|