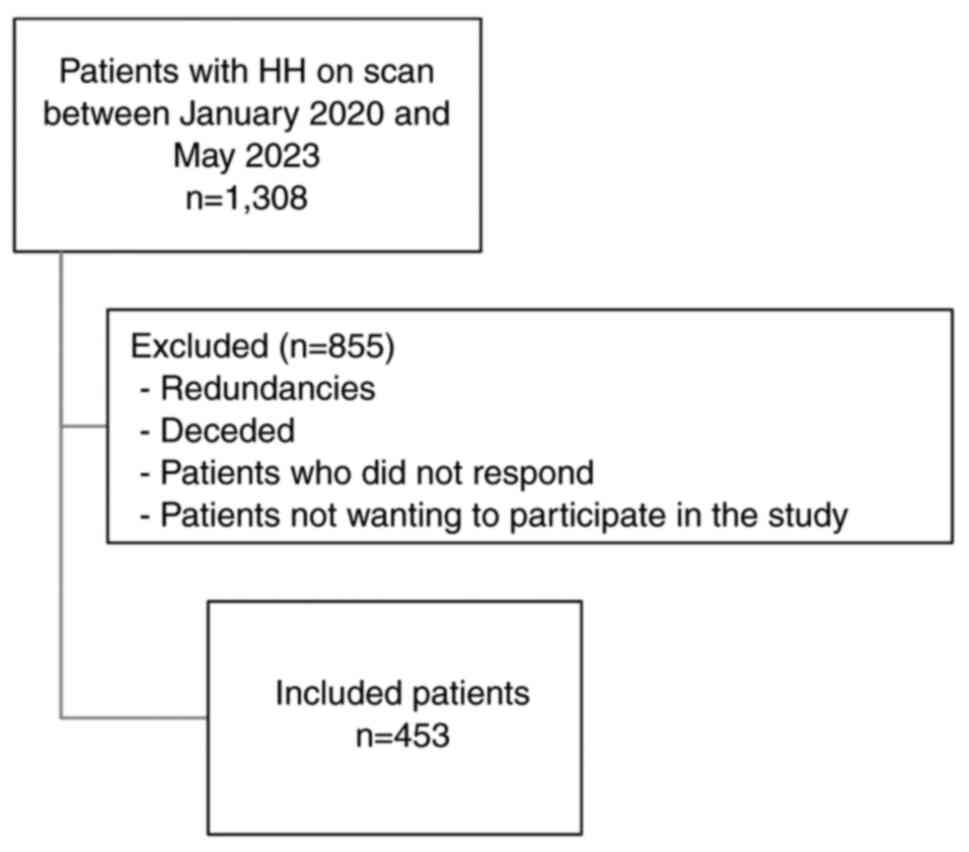
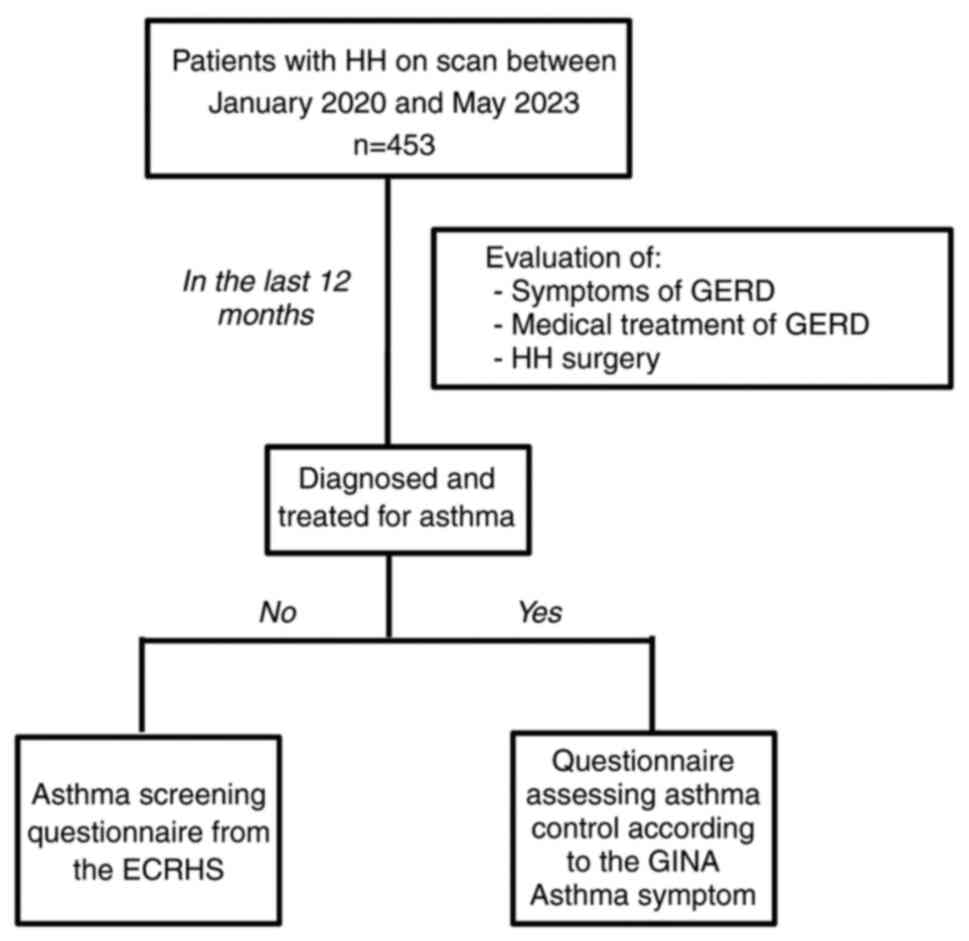
|
1
|
Oleynikov D and Jolley JM: Paraesophageal
hernia. Surg Clin North Am. 95:555–565. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Argyrou A, Legaki E, Koutserimpas C,
Gazouli M, Papaconstantinou I, Gkiokas G and Karamanolis G: Risk
factors for gastroesophageal reflux disease and analysis of genetic
contributors. World J Clin Cases. 6:176–182. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Sugimoto M, Uotani T, Ichikawa H, Andoh A
and Furuta T: Gastroesophageal Reflux disease in time covering
eradication for all patients infected with Helicobacter pylori in
Japan. Digestion. 93:24–31. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Patoulias D, Kalogirou M, Feidantsis T,
Kallergis I and Patoulias I: Paraesophageal hernia as a cause of
chronic asymptomatic anemia in a 6 years old boy; case report and
review of the literature. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 60:76–81.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Stein J, Connor S, Virgin G, Ong DEH and
Pereyra L: Anemia and iron deficiency in gastrointestinal and liver
conditions. World J Gastroenterol. 22:7908–1925. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kamarajah SK, Boyle C, Navidi M and
Phillips AW: Critical appraisal of the impact of surgical repair of
type II-IV paraoesophageal hernia (POH) on pulmonary improvement: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Surgeon. 18:365–374.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Dallemagne B, Kohnen L, Perretta S, Weerts
J, Markiewicz S and Jehaes C: Laparoscopic repair of paraesophageal
hernia. Long-term follow-up reveals good clinical outcome despite
high radiological recurrence rate. Ann Surg. 253:291–296.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hazebroek EJ, Gananadha S, Koak Y, Berry
H, Leibman S and Smith GS: Laparoscopic paraesophageal hernia
repair: Quality of life outcomes in the elderly. Dis Esophagus.
21:737–741. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tossier C, Dupin C, Plantier L, Leger J,
Flament T, Favelle O, Lecomte T, Diot P and Marchand-Adam S: Hiatal
hernia on thoracic computed tomography in pulmonary fibrosis. Eur
Respir J. 48:833–842. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Noth I, Zangan SM, Soares RV, Forsythe A,
Demchuk C, Takahashi SM, Patel SB, Strek ME, Krishnan JA, Patti MG
and Macmahon H: Prevalence of hiatal hernia by blinded
multidetector CT in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Eur Respir J. 39:344–351. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Du J, Lang HM, Ma Y, Chen AW, Qin YY,
Zhang XP and Huang CQ: Global trends in COVID-19 incidence and case
fatality rates (2019-2023): A retrospective analysis. Front Public
Health. 12(1355097)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mays EE, Dubois JJ and Hamilton GB:
Pulmonary fibrosis associated with tracheobronchial aspiration. A
study of the frequency of hiatal hernia and gastroesophageal reflux
in interstitial pulmonary fibrosis of obscure etiology. Chest.
69:512–515. 1976.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Raghu G and Meyer KC: Silent
gastro-oesophageal reflux and microaspiration in IPF: Mounting
evidence for anti-reflux therapy? Eur Respir J. 39:242–245.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Perdikis G, Hinder RA, Filipi CJ, Walenz
T, McBride PJ, Smith SL, Katada N and Klingler PJ: Laparoscopic
paraesophageal hernia repair. Arch Surg. 132:586–591.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Rahman U, Till B, Thosani DS, Ruane B,
Muse E, Barta J, Grenda T, Evans NR III and Okusanya OT: Prevalence
and management of hiatal hernia found on imaging during lung cancer
screening. Foregut. 3:166–171. 2023.
|
|
16
|
Menon S and Trudgill N: Risk factors in
the aetiology of hiatus hernia: a meta-analysis. Eur J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 23:133–138. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kim J, Hiura GT, Oelsner EC, Yin X, Barr
RG, Smith BM and Prince MR: Hiatal hernia prevalence and natural
history on non-contrast CT in the Multi-Ethnic Study of
Atherosclerosis (MESA). BMJ Open Gastroenterol.
8(e000565)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Dunn CP, Patel TA, Bildzukewicz NA,
Henning JR and Lipham JC: Which hiatal hernia's need to be fixed?
Large, small or none? Ann Laparosc Endosc Surg. 5(29)2020.
|
|
19
|
Hyun JJ and Bak YT: Clinical significance
of hiatal hernia. Gut Liver. 5:267–277. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kahrilas PJ: The role of hiatus hernia in
GERD. Yale J Biol Med. 72:101–111. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mattiuzzi C and Lippi G: Worldwide asthma
epidemiology: Insights from the global health data exchange
database. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 10:75–80. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Akiki Z, Saadeh D, Farah R, Hallit S,
Sacre H, Hosseini H and Salameh P: Asthma prevalence and associated
factors among lebanese adults: The first national survey. BMC Pulm
Med. 21(162)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Carmona-Sánchez R, Valdovinos-Díaz MA,
Facha MT, Aguilar L, Cachafeiro M, Solana S, Carrillo G, Chapela R,
Mejía M, Pérez-Chavira R and Salas J: Hiatal hernia in asthmatic
patients: Prevalence and its association with gastroesophageal
reflux. Rev Invest Clin. 51:215–220. 1999.PubMed/NCBI(In Spanish).
|
|
24
|
Zerbib F, Guisset O, Lamouliatte H,
Quinton A, Galmiche JP and Tunon-De-Lara JM: Effects of bronchial
obstruction on lower esophageal sphincter motility and
gastroesophageal reflux in patients with asthma. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 166:1206–1211. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Crowell MD, Zayat EN, Lacy BE,
Schettler-Duncan A and Liu MC: The effects of an inhaled
beta(2)-adrenergic agonist on lower esophageal function: A
dose-response study. Chest. 120:1184–1189. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Oue K, Mukaisho KI, Higo T, Araki Y,
Nishikawa M, Hattori T, Yamamoto G and Sugihara H: Histological
examination of the relationship between respiratory disorders and
repetitive microaspiration using a rat gastro-duodenal contents
reflux model. Exp Anim. 60:141–150. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Amarasiri DL, Pathmeswaran A, de Silva HJ
and Ranasinha CD: Response of the airways and autonomic nervous
system to acid perfusion of the esophagus in patients with asthma:
A laboratory study. BMC Pulm Med. 13(33)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Allegra L, Cremonesi G, Girbino G,
Ingrassia E, Marsico S, Nicolini G and Terzano C: PRISMA
(PRospectIve Study on asthMA control) Study Group. Real-life
prospective study on asthma control in Italy: Cross-sectional phase
results. Respir Med. 106:205–214. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Alghamdi M, Aljaafri ZA, Alhadlaq KH,
Alamro SA, Alfaryan SM, Al Swaidan O and Mohamud M: Association
between asthmatic patients' asthma control test score and the
number of exacerbations per year in king abdulaziz medical city,
Riyadh. Cureus. 14(e24001)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Demange V, Penven E, Paris C and Wild P:
Identification of asthma during the visit to the occupational
health service. Occupational Health References. 159:33–42.
2019.
|
|
31
|
el-Serag HB and Sonnenberg A: Comorbid
occurrence of laryngeal or pulmonary disease with esophagitis in
United States military veterans. Gastroenterology. 113:755–760.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wang YT, Tsai MC, Wang YH and Wei JCC:
Association between proton pump inhibitors and asthma: A
population-based cohort study. Front Pharmacol.
11(607)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhang GQ, Özuygur Ermis SS, Rådinger M,
Bossios A, Kankaanranta H and Nwaru B: Sex disparities in asthma
development and clinical outcomes: Implications for treatment
strategies. J Asthma Allergy. 15:231–247. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Dodge RR and Burrows B: The prevalence and
incidence of asthma and asthma-like symptoms in a general
population sample. Am Rev Respir Dis. 122:567–575. 1980.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Harju T, Keistinen T, Tuuponen T and
Kivelä SL: Hospital admissions of asthmatics by age and sex.
Allergy. 51:693–696. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|