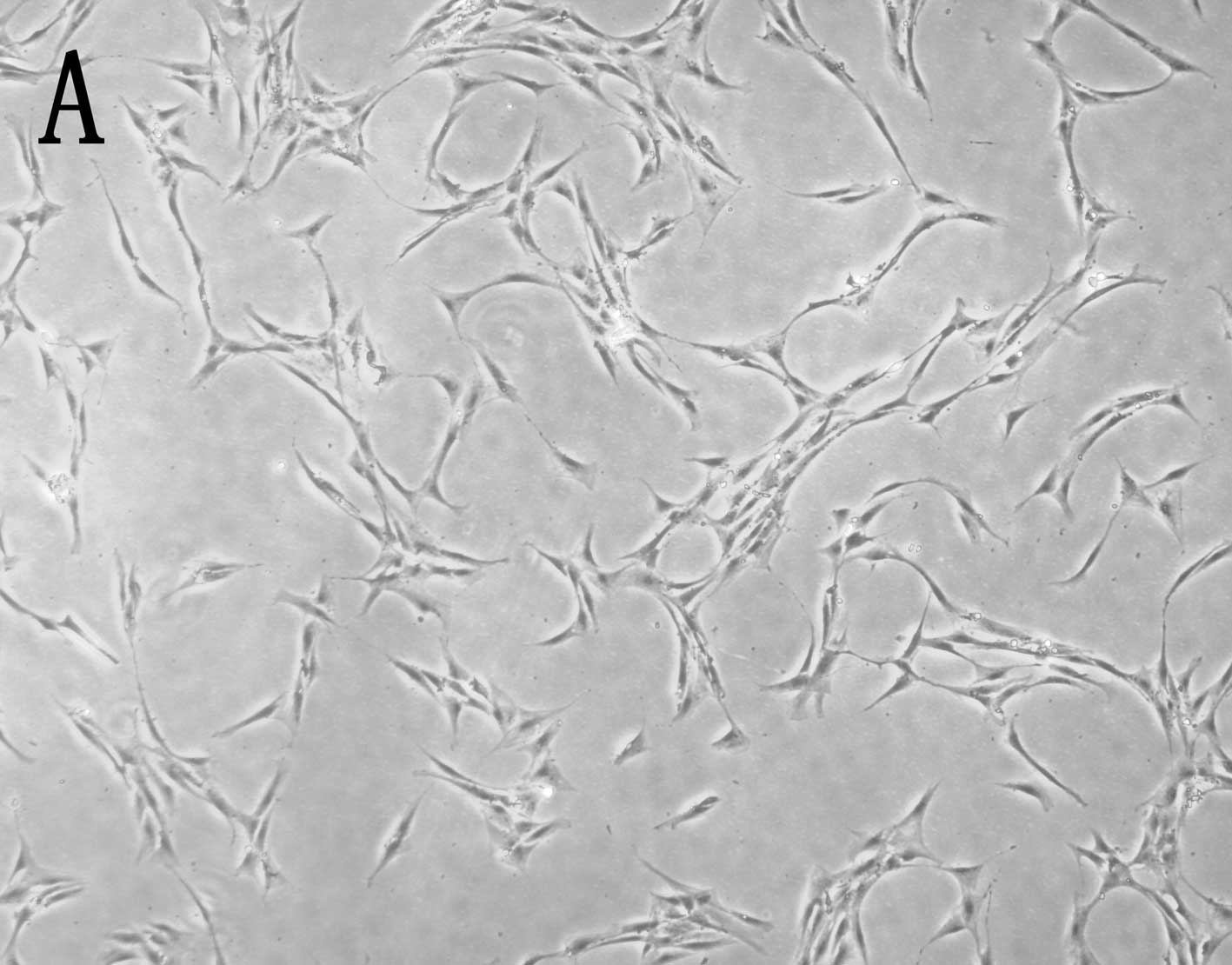
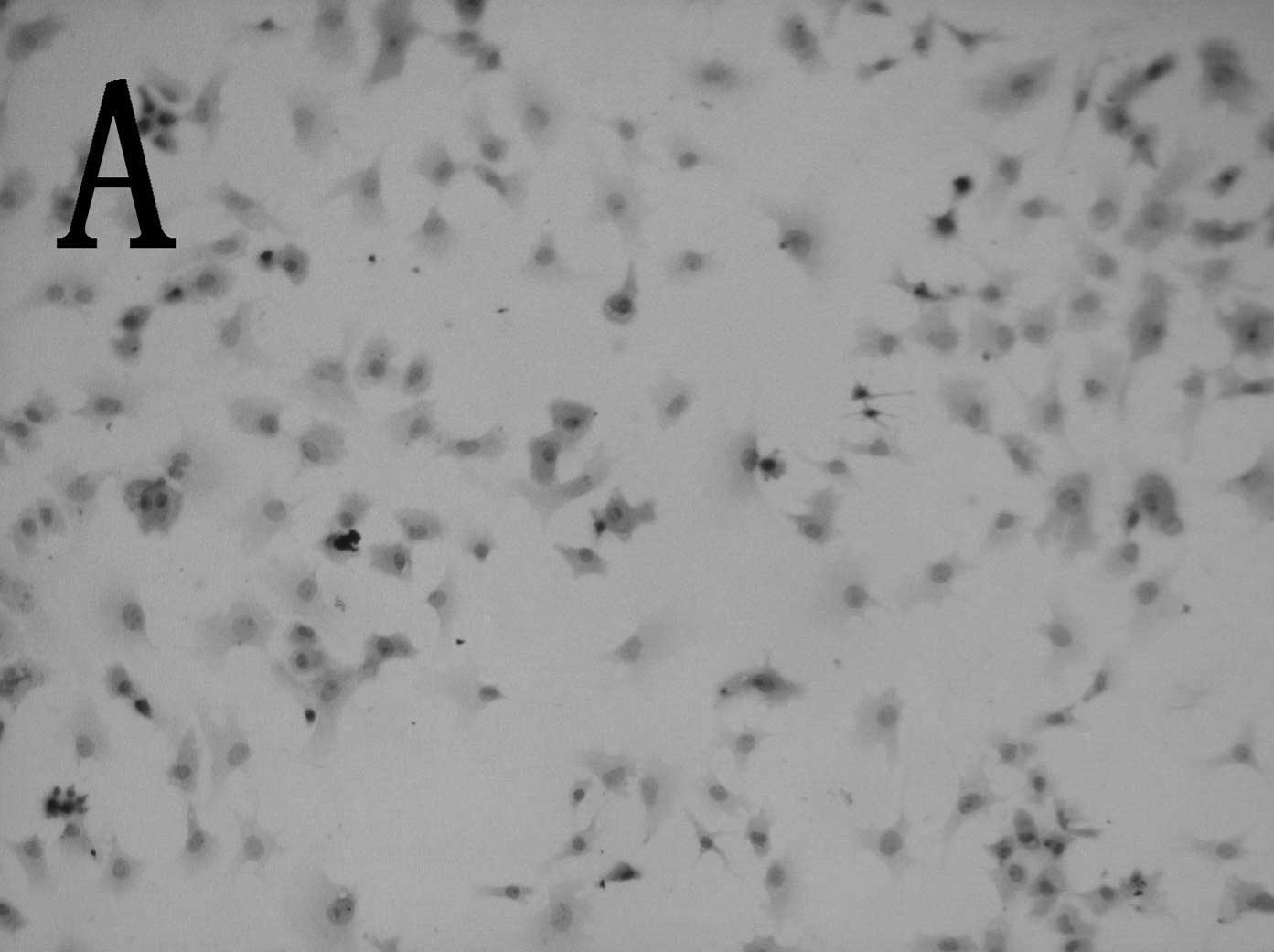
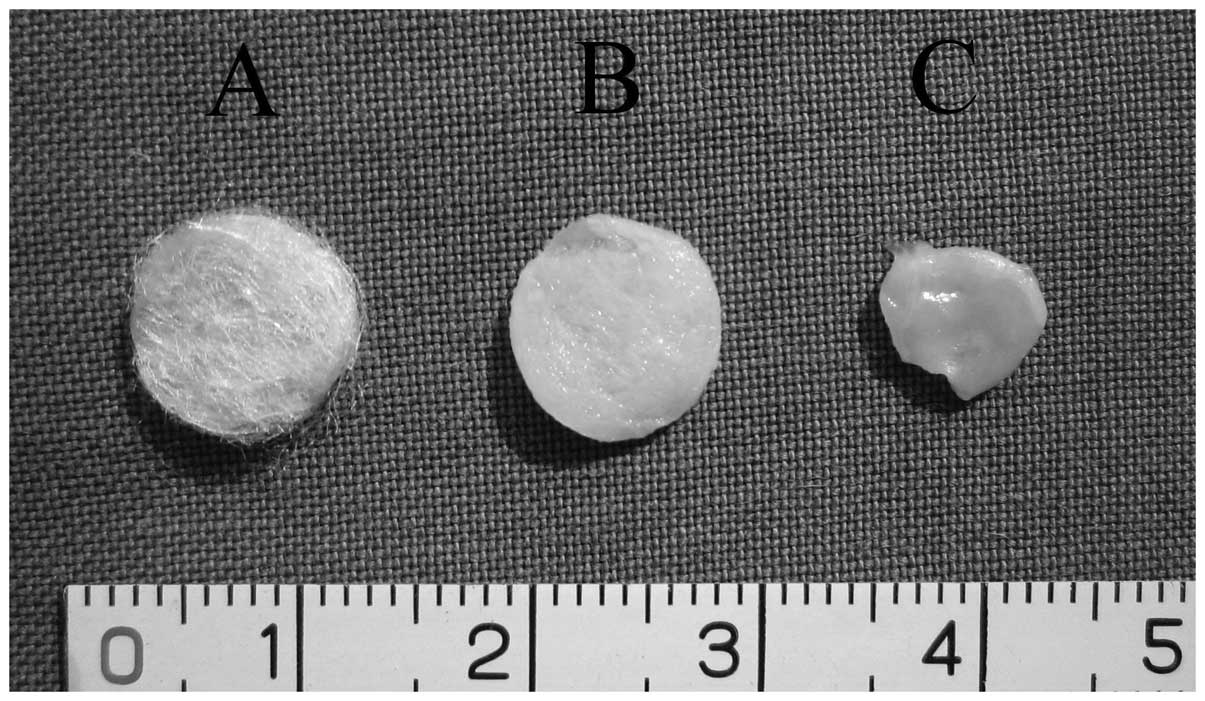
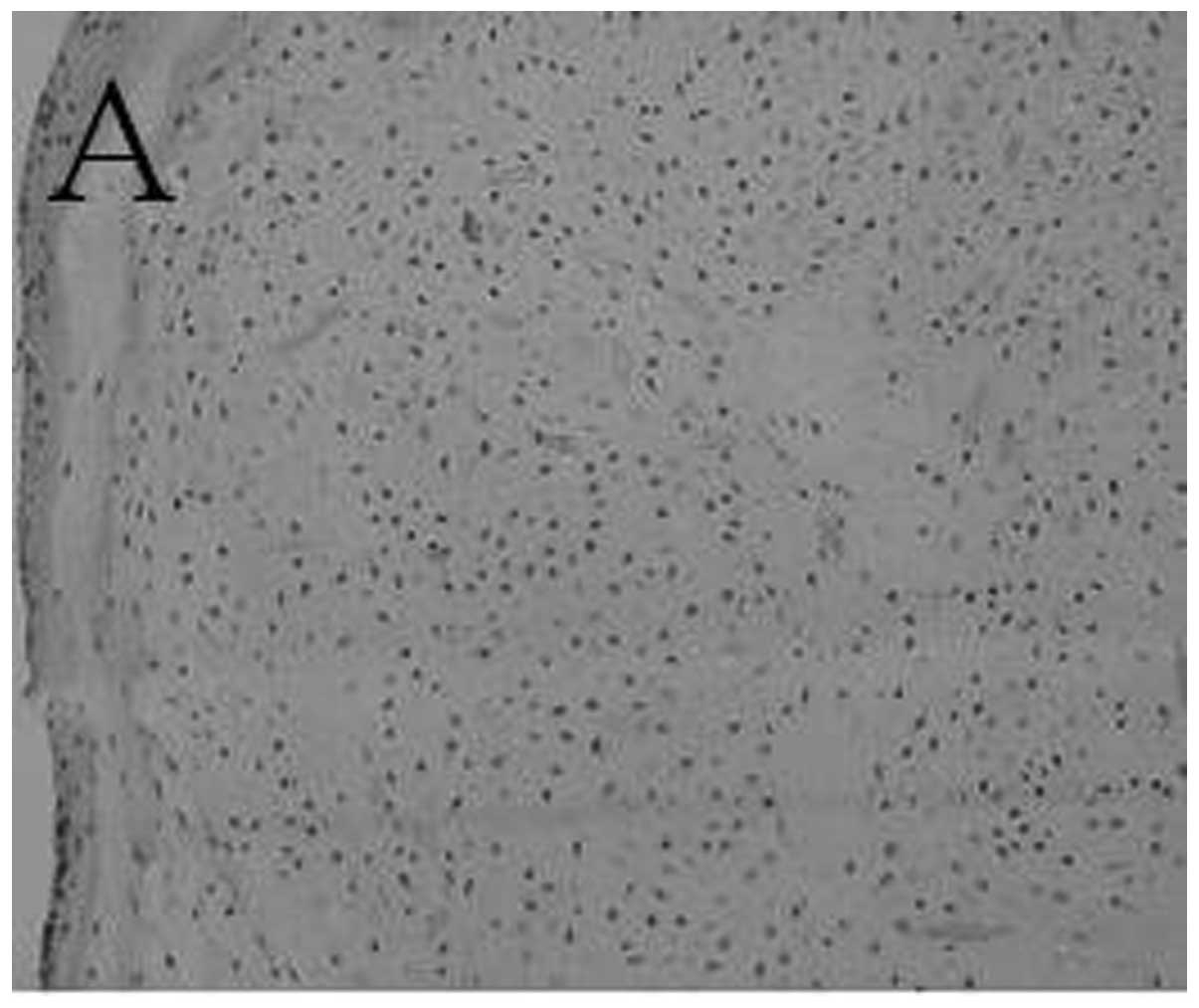
|
1
|
Hart R, Janecek M, Siska V, Kucera B and
Stipcák V: Correlation of long-term clinical and radiological
results after meniscectomies. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech.
72:304–307. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
van der Wal RJ, Thomassen BJ and van Arkel
ER: Long-term clinical outcome of open meniscal allograft
transplantation. Am J Sports Med. 37:2134–2139. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yamasaki T, Deie M, Shinomiya R, Yasunaga
Y, Yanada S and Ochi M: Transplantation of meniscus regenerated by
tissue engineering with a scaffold derived from a rat meniscus and
mesenchymal stromal cells derived from rat bone marrow. Artif
Organs. 32:519–524. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Webber RJ, York JL, Vanderschilden JL and
Hough AJ Jr: An organ culture model for assaying wound repair of
the fibrocartilaginous knee joint meniscus. Am J Sports Med.
17:393–400. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kang SW, Son SM, Lee JS, Lee ES, Lee KY,
Park SG, Park JH and Kim BS: Regeneration of whole meniscus using
meniscal cells and polymer scaffolds in a rabbit total meniscectomy
model. J Biomed Mater Res A. 78:659–671. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ishida K, Kuroda R, Miwa M, Tabata Y,
Hokugo A, Kawamoto T, Sasaki K, Doita M and Kurosaka M: The
regenerative effects of platelet-rich plasma on meniscal cells in
vitro and its in vivo application with biodegradable gelatin
hydrogel. Tissue Eng. 13:1103–1112. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Peretti GM, Gill TJ, Xu JW, Randolph MA,
Morse KR and Zaleske DJ: Cell-based therapy for meniscal repair: a
large animal study. Am J Sports Med. 32:146–158. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lu SH, Yang AH, Wei CF, Chiang HS and
Chancellor MB: Multi-potent differentiation of human purified
muscle-derived cells: potential for tissue regeneration. BJU Int.
105:1174–1180. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhou G, Liu W, Cui L, Wang X, Liu T and
Cao Y: Repair of porcine articular osteochondral defects in
non-weightbearing areas with autologous bone marrow stromal cells.
Tissue Eng. 12:3209–3221. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhu W, Wang Y, Qiu G and Chen B:
Characterization of the purification and primary culture of adult
canine myoblasts in vitro. Mol Med Report. 3:463–468.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gu YL and Wang YB: Treatment of meniscal
injury: a current concept review. Chin J Traumatol. 13:370–376.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gu Y, Wang Y, Dai H, Lu L, Cheng Y and Zhu
W: Chondrogenic differentiation of canine myoblasts induced by
cartilage-derived morphogenetic protein-2 and transforming growth
factor-β1 in vitro. Mol Med Report. 5:767–772.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Asakura A, Komaki M and Rudnicki M: Muscle
satellite cells are multipotential stem cells that exhibit
myogenic, osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation.
Differentiation. 68:245–253. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Matsushita T, Matsui N, Fujioka H, Kubo S,
Kuroda R, Kurosaka M and Yoshiya S: Expression of transcription
factor sox9 in rat L6 myoblastic cells. Connect Tissue Res.
45:164–173. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Goldring K, Partridge T and Watt D: Muscle
stem cells. J Pathol. 197:457–467. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Day CS, Kasemkijwattana C, Menetrey J,
Floyd SS Jr, Booth D, Moreland MS, Fu FH and Huard J:
Myoblast-mediated gene transfer to the joint. J Orthop Res.
15:894–903. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Koning M, Harmsen MC, van Luyn MJ and
Werker PM: Current opportunities and challenges in skeletal muscle
tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 3:407–415. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Singh D, Nayak V and Kumar A:
Proliferation of myoblast skeletal cells on three-dimensional
supermacroporous cryogels. Int J Biol Sci. 6:371–381. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Marsano A, Millward-Sadler SJ, Salter DM,
Adesida A, Hardingham T, Tognana E, Kon E, Chiari-Grisar C, Nehrer
S, Jakob M and Martin I: Differential cartilaginous tissue
formation by human synovial membrane, fat pad, meniscus cells and
articular chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 15:48–58. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Stern-Straeter J, Bran G, Riedel F, Sauter
A, Hörmann K and Goessler UR: Characterization of human myoblast
cultures for tissue engineering. Int J Mol Med. 21:49–56. 2008.
|
|
21
|
Moran JM, Pazzano D and Bonassar LJ:
Characterization of polylactic acid-polyglycolic acid composites
for cartilage tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. 9:63–70. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cui L, Wu Y, Cen L, Zhou H, Yin S, Liu G,
Liu W and Cao Y: Repair of articular cartilage defect in non-weight
bearing areas using adipose derived stem cells loaded polyglycolic
acid mesh. Biomaterials. 30:2683–2693. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zwingmann J, Mehlhorn AT, Südkamp N, Stark
B, Dauner M and Schmal H: Chondrogenic differentiation of human
articular chondrocytes differs in biodegradable PGA/PLA scaffolds.
Tissue Eng. 13:2335–2343. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|