|
1
|
Marks LB, Yu X, Vujaskovic Z, Small W Jr,
Folz R and Anscher MS: Radiation-induced lung injury. Semin Radiat
Oncol. 13:333–345. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mehta V: Radiation pneumonitis and
pulmonary fibrosis in non-small-cell lung cancer: pulmonary
function, prediction, and prevention. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
63:5–24. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kong FM, Hayman JA, Griffith KA,
Kalemkerian GP, Arenberg D, Lyons S, Turrisi A, Lichter A, Fraass
B, Eisbruch A, Lawrence TS and Ten Haken RK: Final toxicity results
of a radiation-dose escalation study in patients with
non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): predictors for radiation
pneumonitis and fibrosis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
65:1075–1086. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rübe CE, Wilfert F, Uthe D, Schmid KW,
Knoop R, Willich N, Schuck A and Rübe C: Modulation of
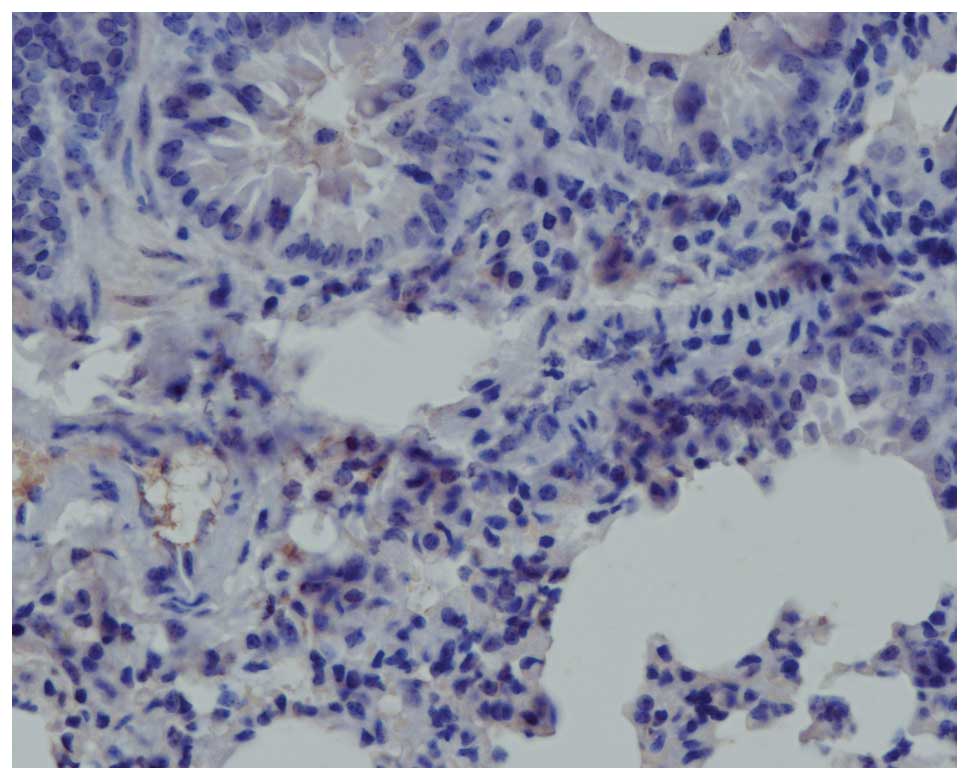
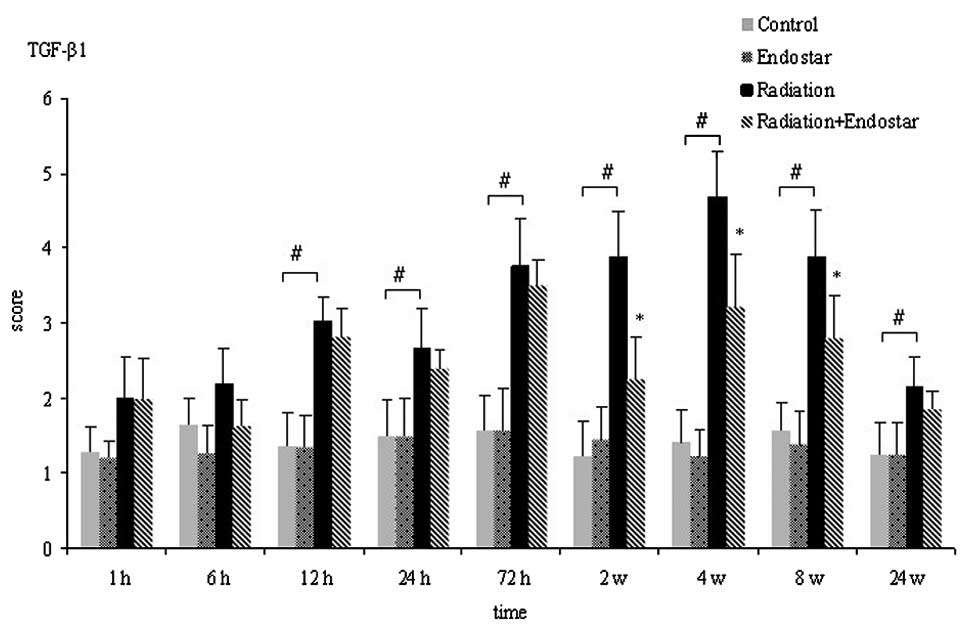
radiation-induced tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha)
expression in the lung tissue by pentoxifylline. Radiother Oncol.
64:177–187. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rübe CE, Uthe D, Schmid KW, Richter KD,
Wessel J, Schuck A, Willich N and Rübe C: Dose-dependent induction
of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) in the lung tissue of
fibrosis-prone mice after thoracic irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 47:1033–1042. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dong XR, Wang JN, Liu L, Chen X, Chen MS,
Chen J, Ren JH, Li Q and Han J: Modulation of radiation-induced
tumor necrosis factor-α and transforming growth factor β1
expression in the lung tissue by Shengqi Fuzheng injection. Mol Med
Report. 3:621–627. 2010.
|
|
7
|
Brush J, Lipnick SL, Phillips T, Sitko J,
McDonald JT and McBride WH: Molecular mechanisms of late normal
tissue injury. Semin Radiat Oncol. 17:121–130. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rübe CE, Uthe D, Wilfert F, Ludwig D, Yang
K, König J, Palm J, Schuck A, Willich N, Remberger K and Rübe C:
The bronchiolar epithelium as a prominent source of
pro-inflammatory cytokines after lung irradiation. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 61:1482–1492. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kong FM, Ao XP, Wang L and Lawrence TS:
The use of blood biomarkers to predict radiation lung toxicity: a
potential strategy to individualize thoracic radiation therapy.
Cancer Control. 15:140–150. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Novakova-Jiresova A, Van Gameren MM,
Coppes RP, Kampinga HH and Groen HJM: Transforming growth
factor-beta plasma dynamics and post-irradiation lung injury in
lung cancer patients. Radiother Oncol. 71:183–189. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ao XP, Zhao LJ, Davis MA, Lubman DM,
Lawrence TS and Kong FM: Radiation produces differential changes in
cytokine profiles in radiation lung fibrosis sensitive and
resistant mice. J Hematol Oncol. 2:62009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Munger JS, Huang X, Kawakatsu H, Griffiths
MJ, Dalton SL, Wu J, Pittet JF, Kaminski N, Garat C, Matthay MA,
Rifkin DB and Sheppard D: The integrin alpha v beta 6 binds and
activates latent TGF beta 1: a mechanism for regulating pulmonary
inflammation and fibrosis. Cell. 96:319–328. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Anscher MS, Thrasher B, Rabbani Z, Teicher
B and Vujaskovic Z: Antitransforming growth factor-beta antibody
1D11 ameliorates normal tissue damage caused by high-dose
radiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 65:876–881. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Anscher MS: Targeting the TGF-beta1
pathway to prevent normal tissue injury after cancer therapy.
Oncologist. 15:350–359. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sekine I, Sumi M, Ito Y, Nokihara H,
Yamamoto N, Kunitoh H, Ohe Y, Kodama T, Saijo N and Tamura T:
Retrospective analysis of steroid therapy for radiation-induced
lung injury in lung cancer patients. Radiother Oncol. 80:93–97.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
O’Reilly MS, Boehm T, Shing Y, Fukai N,
Vasios G, Lane WS, Flynn E, Birkhead JR, Olsen BR and Folkman J:
Endostatin: an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor
growth. Cell. 88:277–285. 1997.
|
|
17
|
Wang YS, Eichler W, Friedrichs U, Yafai Y,
Hoffmann S, Yasukawa T, Hui YN and Wiedemann P: Impact of
endostatin on bFGF-induced proliferation, migration, and matrix
metalloproteinase-2 expression/secretion of bovine choroidal
endothelial cells. Curr Eye Res. 30:479–489. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ling Y, Lu N, Gao Y, Chen Y, Wang S, Yang
Y and Guo QL: Endostar induces apoptotic effects in HUVECs through
activation of caspase-3 and decrease of Bcl-2. Anticancer Res.
29:411–417. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang L, Ge W, Hu K, Zhang YY, Li CH, Xu
XM, He D, Zhao ZY, Zhang JZ, Jie FF, Chen Y and Zheng YF: Endostar
down-regulates HIF-1 and VEGF expression and enhances the
radioresponse to human lung adenocarcinoma cancer cells. Mol Bio
Rep. 39:89–95. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jia H and Kling J: China offers
alternative gateway for experimental drugs. Nat Biotechnol.
24:117–118. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ling Y, Yang Y, Lu N, You QD, Wang S, Gao
Y, Chen Y and Guo QL: Endostar, a novel recombinant human
endostatin, exerts antiangiogenic blocking VEGF-induced tyrosine
phosphorylation of KDR/Flk-1 of endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 361:79–84. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Jiang XD, Dai P, Wu J, Song DA and Yu JM:
Inhibitory effect of radiotherapy combined with weekly recombinant
human endostatin on the human pulmonary adenocarcinoma A549
xenografts in nude mice. Lung Cancer. 72:165–171. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wen QL, Meng MB, Yang B, Tu LL, Jia L,
Zhou L, Xu Y and Lu Y: Endostar, a recombined humanized endostatin,
enhances the radioresponse for human nasopharyngeal carcinoma and
human lung adenocarcinoma xenografts in mice. Cancer Sci.
100:1510–1519. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Szapiel SV, Elson NA, Fulmer JD,
Hunninghake GW and Crystal RG: Bleomycin-induced interstitial
pulmonary disease in the nude, athymic mouse. Am Rev Respir Dis.
120:839–899. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Friedrichs K, Gluba S, Eidtmann H and
Jonat W: Overexpression of p53 and prognosis in breast cancer.
Cancer. 72:3641–3647. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jackson IL, Vujaskovic Z and Down JD: A
further comparison of pathologies after thoracic irradiation among
different mouse strains: finding the best preclinical model for
evaluating therapies directed against radiation-induced lung
damage. Radiat Res. 175:510–518. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Tsoutsou PG and Koukourakis MI: Radiation
pneumonitis and fibrosis: mechanisms underlying its pathogenesis
and implications for future research. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
66:1281–1293. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Liu L, Ding Q, Dai XF, Zhao YX, Ke Y and
Wu G: Study on the controlling effect of Shengqi Fuzheng injection
on plasma cytokine network in patients with thoracic tumor
undergoing radiotherapy. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi.
27:1082–1085. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
29
|
Haydont V, Mathé D, Bourgier C, Abdelali
J, Aigueperse J, Bourhis J and Vozenin-Brotons MC: Induction of
CTGF by TGF-beta1 in normal and radiation enteritis human smooth
muscle cells: Smad/Rho balance and therapeutic perspectives.
Radiother Oncol. 76:219–225. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Haydont V, Riser BL, Aigueperse J and
Vozenin-Brotons MC: Specific signals involved in the long-term
maintenance of radiation-induced fibrogenic differentiation: a role
for CCN2 and low concentration of TGF-beta1. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 294:C1332–C1341. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Franko AJ, Sharplin J, Ghahary A and
Barcellos-Hoff MH: Immunohistochemical localization of transforming
growth factor beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha in the lungs of
fibrosis-prone and ‘non-fibrosing’ mice during the latent period
and early phase after irradiation. Radiat Res. 147:245–256.
1997.
|
|
32
|
Chen L, Brizel DM, Rabbani ZN, Samulski
TV, Farrell CL, Larrier N, Anscher MS and Vujaskovic Z: The
protective effect of recombinant human keratinocyte growth factor
on radiation-induced pulmonary toxicity in rats. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 60:1520–1529. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Folkman J: Antiangiogenesis in cancer
therapy-endostatin and its mechanisms of action. Exp Cell Res.
312:594–607. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Itasaka S, Komaki R, Herbst RS, Shibuya K,
Shintani T, Hunter NR, Onn A, Bucana CD, Milas L, Ang KK and
O’Reilly MS: Endostatin improves radioresponse and blocks tumor
revascularization after radiation therapy for A431 xenografts in
mice. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 67:870–878. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tanabe K, Maeshima Y, Ichinose K, Kitayama
H, Takazawa Y, Hirokoshi K, Kinomura M, Sugiyama H and Makino H:
Endostatin peptide, an inhibitor of angiogenesis, prevents the
progression of peritoneal sclerosis in a mouse experimental model.
Kidney Int. 71:227–238. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vujaskovic Z, Anscher MS, Feng QF, Rabbani
ZN, Amin K, Samulski TS, Dewhirst MW and Haroon ZA:
Radiation-induced hypoxia may perpetuate late normal tissue injury.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 50:851–855. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gauter-Fleckenstein B, Fleckenstein K,
Owzar K, Jiang C, Rebouças JS, Batinic-Haberle I and Vujaskovic Z:
Early and late administration of MnTE-2-PyP5+ in
mitigation and treatment of radiation-induced lung damage. Free
Radic Biol Med. 48:1034–1043. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jackson IL, Chen L, Batinic-Haberle I and
Vujaskovic Z: Superoxide dismutase mimetic reduces hypoxia-induced
O2*−, TGF-beta, and VEGF production by
macrophages. Free Radic Res. 41:8–14. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|