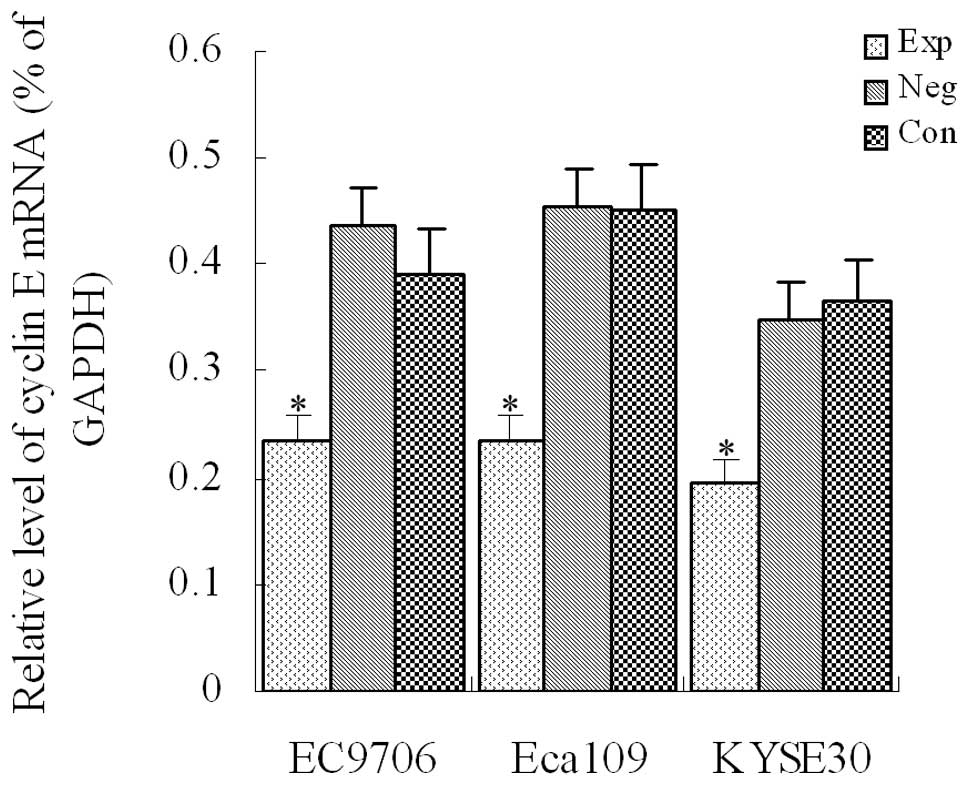
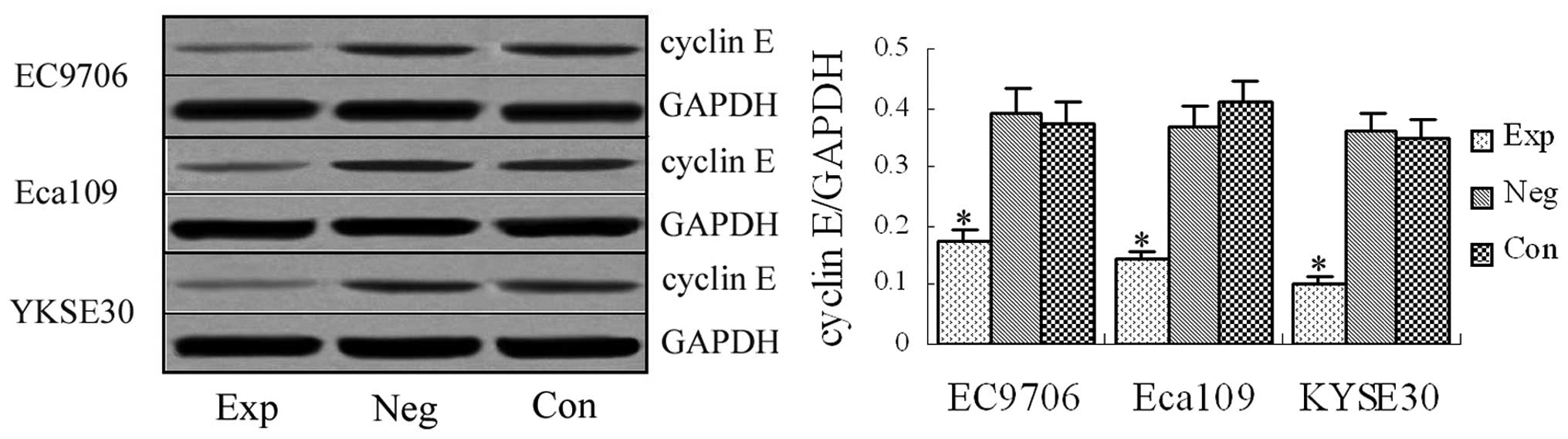
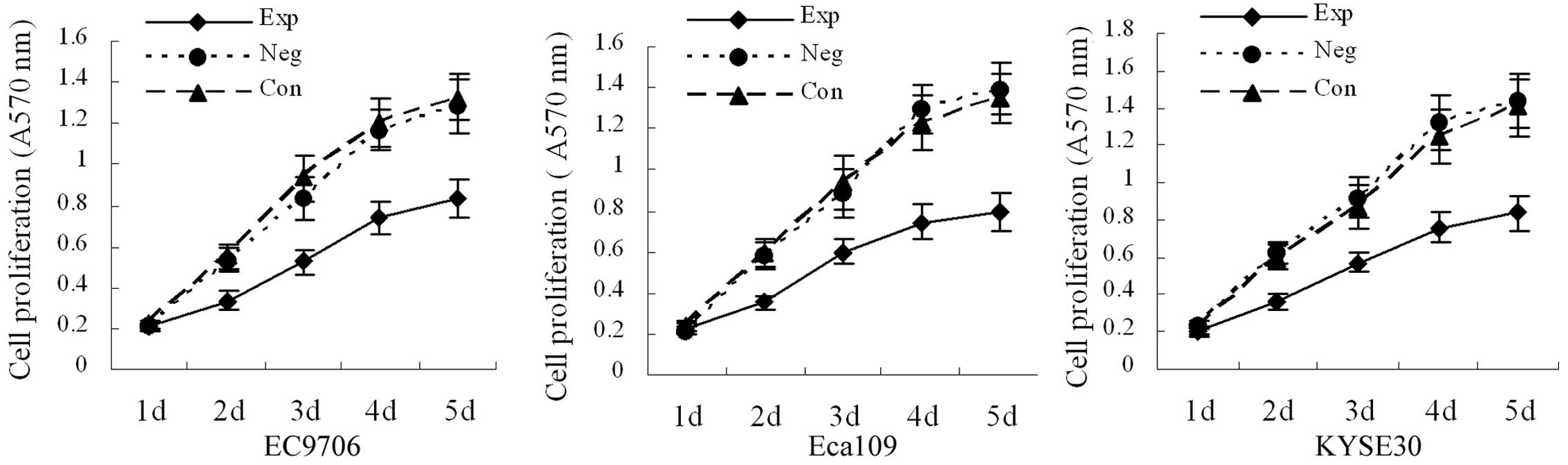
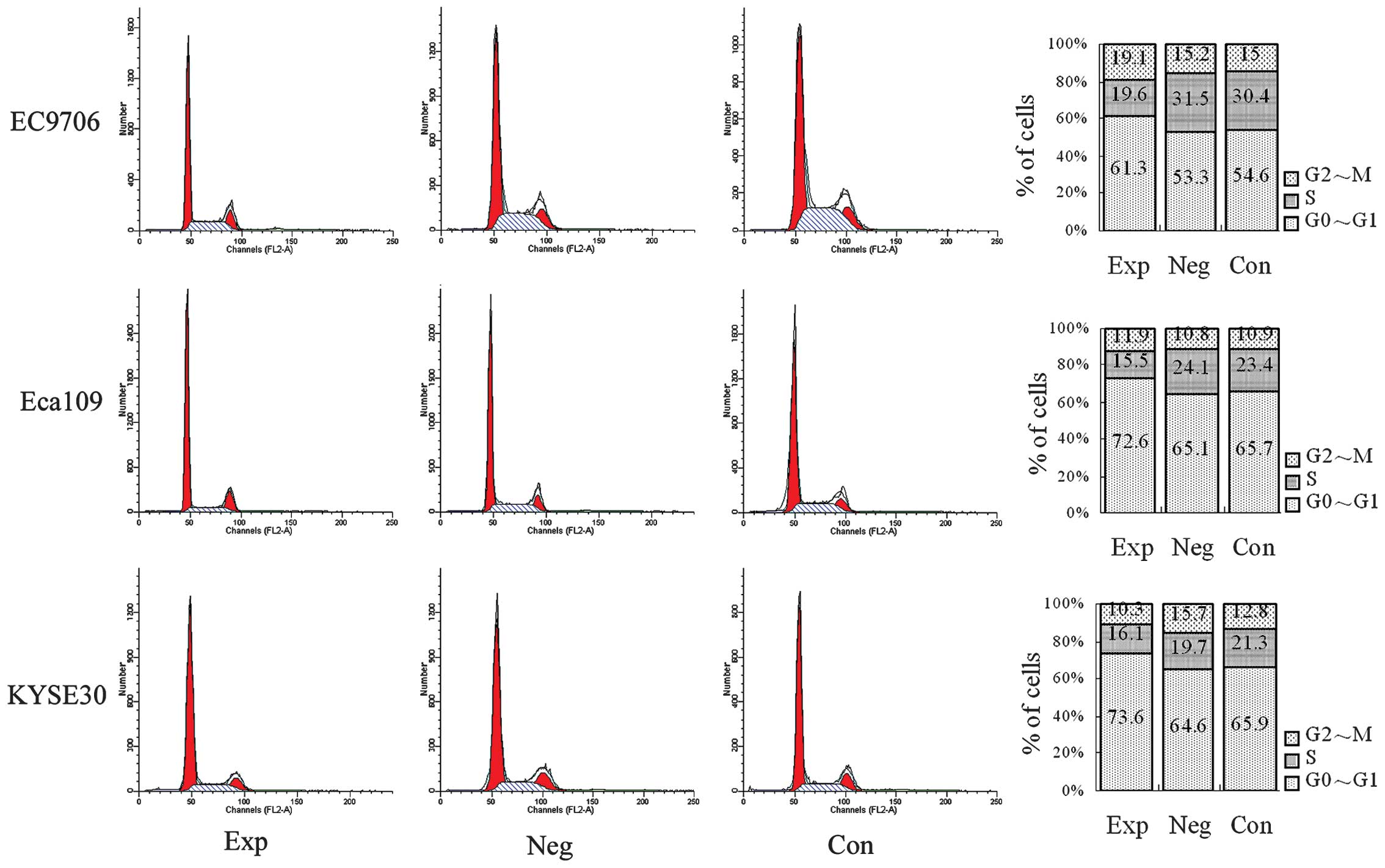
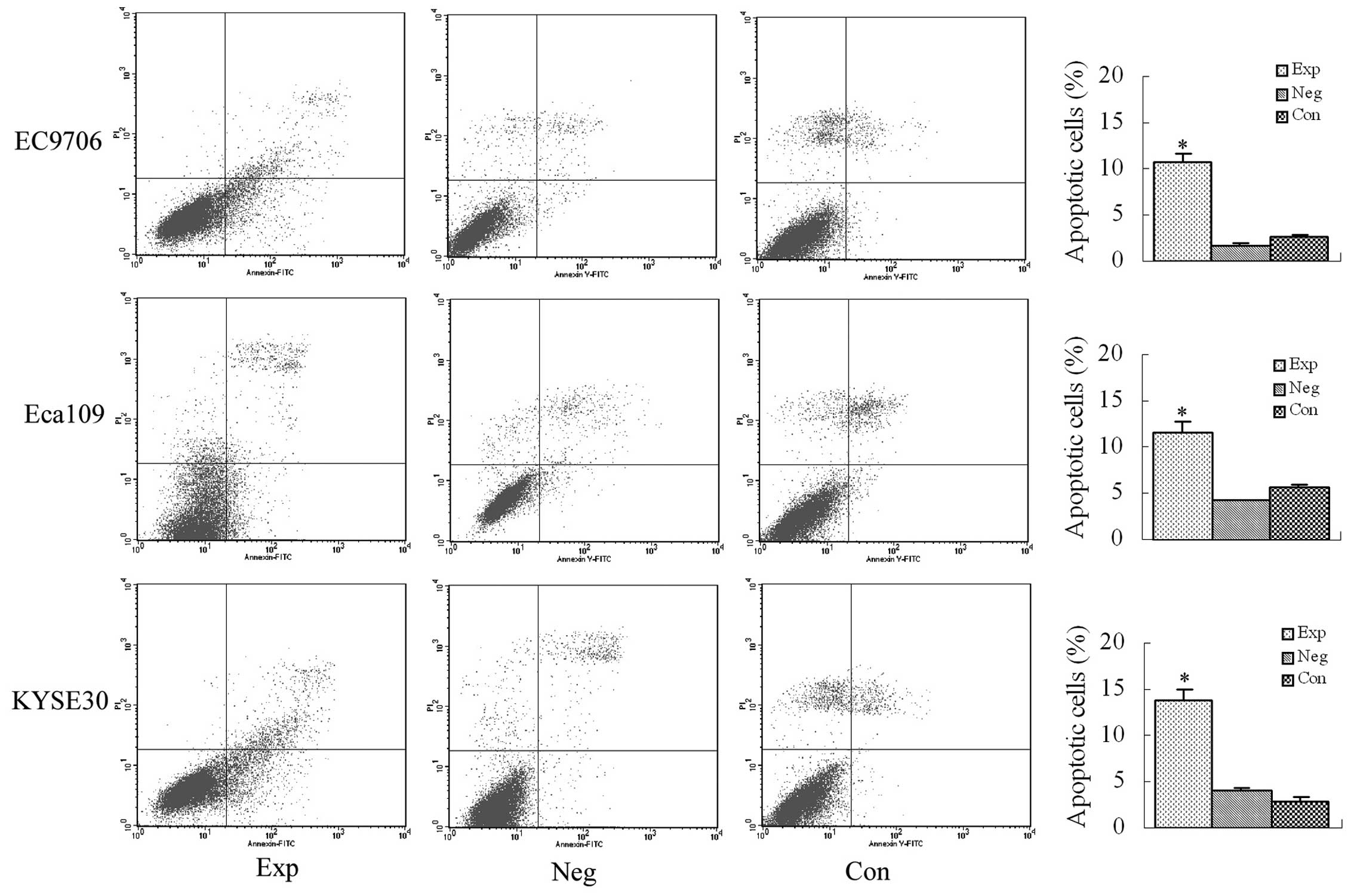
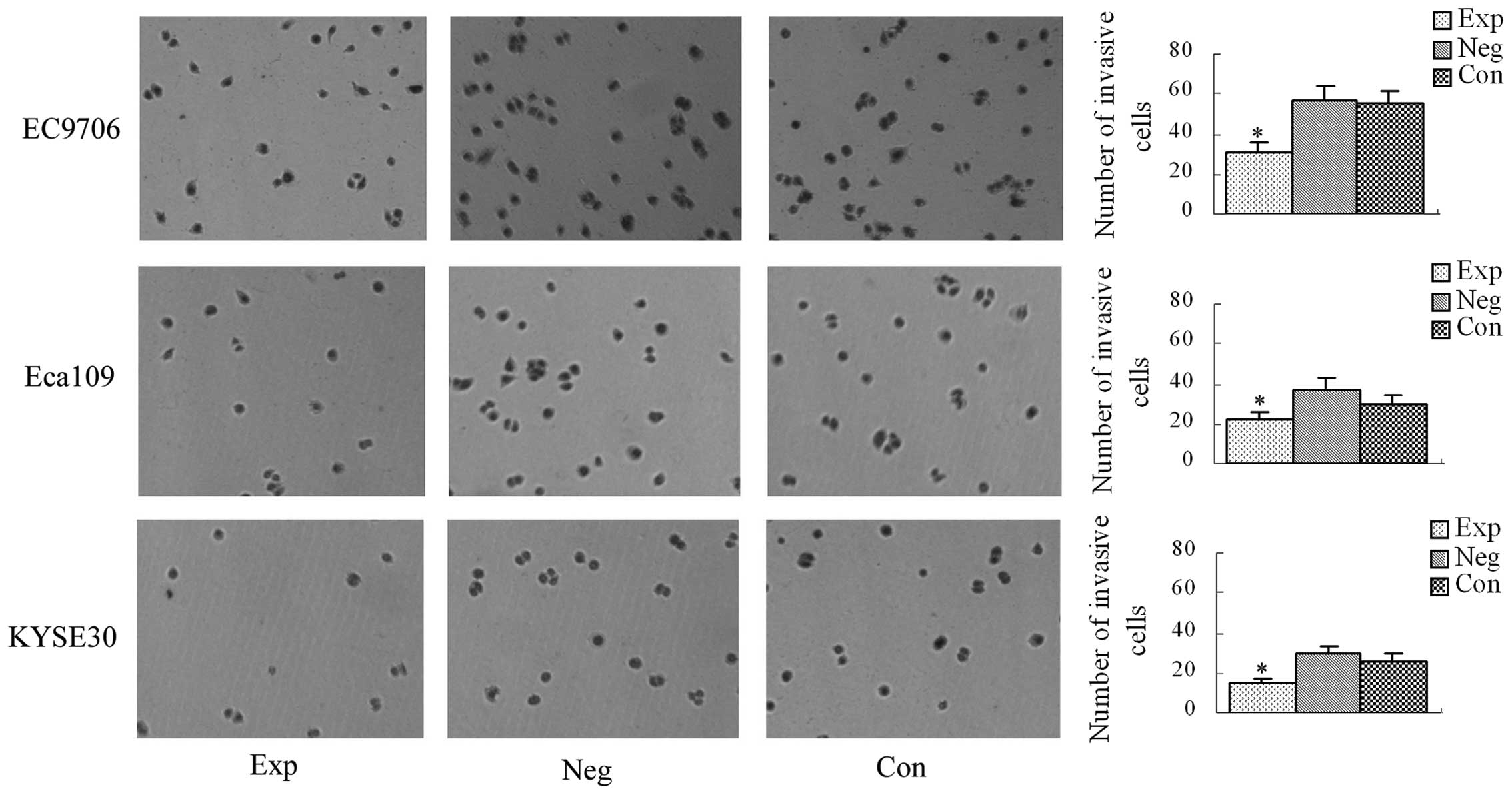
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Fujii S, Tominaga O, Nagawa H, Tsuno N,
Nita ME, Tsuruo T and Muto T: Quantitative analysis of the cyclin
expression in human esophageal cancer cell lines. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 7:491–496. 1998.
|
|
3
|
Meng X, Zhong J, Liu S, Murray M and
Gonzalez-Angulo AM: A new hypothesis for the cancer mechanism.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 31:247–268. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Meng X and Riordan NH: Cancer is a
functional repair tissue. Med Hypotheses. 66:486–490. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Erdman SE and Poutahidis T: Cancer
inflammation and regulatory T cells. Int J Cancer. 127:768–779.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Satyanarayana A and Kaldis P: Mammalian
cell-cycle regulation: several Cdks, numerous cyclins and diverse
compensatory mechanisms. Oncogene. 28:2925–2939. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sánchez I and Dynlacht BD: New insights
into cyclins, CDKs, and cell cycle control. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
16:311–321. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Stamatakos M, Palla V, Karaiskos I,
Xiromeritis K, Alexiou I, Pateras I and Kontzoglou K: Cell cyclins:
triggering elements of cancer or not? World J Surg Oncol.
8:1112010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Malumbres M and Barbacid M: To cycle or
not cycle: a critical decision in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
1:222–231. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Berretta M, Lleshi A, Fisichella R,
Berretta S, Basile F, Li Volti G, Bolognese A, Biondi A, De Paoli
P, Tirelli U and Cappellani A: The role of nutrition in the
development of esophageal cancer: what do we know? Front Biosci.
4:351–357. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen YK, Lee CH, Wu IC, Liu JS, Wu DC, Lee
JM, Goan YG, Chou SH, Huang CT, Lee CY, Hung HC, Yang JF and Wu MT:
Food intake and the occurrence of squamous cell carcinoma in
different sections of the esophagus in Taiwanese men. Nutrition.
25:753–761. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Islami F, Boffetta P, Ren JS, Pedoeim L,
Khatib D and Kamangar F: High-temperature beverages and foods and
esophageal cancer risk - a systematic review. Int J Cancer.
125:491–524. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Taghavi N, Biramijamal F, Sotoudeh M,
Khademi H, Malekzadeh R, Moaven O, Memar B, A’rabi A and
Abbaszadegan MR: p16INK4a hypermethylation and p53, p16 and MDM2
protein expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC
Cancer. 10:1382010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shimada H, Matsushita K and Tagawa M:
Recent advances in esophageal cancer gene therapy. Ann Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 14:3–8. 2008.
|
|
15
|
Shimada H, Matsubara H and Ochiai T: p53
gene therapy for esophageal cancer. J Gastroenterol. 37(Suppl 14):
87–91. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Xie F, Liu H, Zhu YH, Qin YR, Dai Y, Zeng
T, Chen L, Nie C, Tang H, Li Y, Fu L and Guan XY: Overexpression of
GPR39 contributes to malignant development of human esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 11:862011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tanaka T, Ishiguro H, Kuwabara Y, Kimura
M, Mitsui A, Katada T, Shiozaki M, Naganawa Y, Fujii Y and Takeyama
H: Vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) in esophageal
cancer correlates with lymph node metastasis and poor patient
prognosis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 29:832010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
He J, Sheng T, Stelter AA, Li C, Zhang X,
Sinha M, Luxon BA and Xie J: Suppressing Wnt signaling by the
hedgehog pathway through sFRP-1. J Biol Chem. 281:35598–35602.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Koff A, Cross F, Fisher A, Schumacher J,
Leguellec K, Philippe M and Roberts JM: Human cyclin E, a new
cyclin that interacts with two members of the CDC2 gene family.
Cell. 66:1217–1228. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sauer K and Lehner CF: The role of cyclin
E in the regulation of entry into S phase. Prog Cell Cycle Res.
1:125–139. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mazumder S, Plesca D and Almasan A: A
jekyll and hyde role of cyclin E in the genotoxic stress response:
switching from cell cycle control to apoptosis regulation. Cell
Cycle. 6:1437–1442. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schildkraut JM, Moorman PG, Bland AE,
Halabi S, Calingaert B, Whitaker R, Lee PS, Elkins-Williams T,
Bentley RC, Marks JR and Berchuck A: Cyclin E overexpression in
epithelial ovarian cancer characterizes an etiologic subgroup.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 17:585–593. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhou YJ, Xie YT, Gu J, Yan L, Guan GX and
Liu X: Overexpression of cyclin E isoforms correlates with poor
prognosis in rectal cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 37:1078–1084. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sharp PA: RNA interference: 2001. Genes
Dev. 15:485–490. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hannon GJ: RNA interference. Nature.
418:244–251. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Lendeckel W,
Yalcin A, Weber K and Tuschl T: Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs
mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature.
411:494–498. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
McCaffrey AP, Meuse L, Pham TT, Conklin
DS, Hannon GJ and Kay MA: RNA interference in adult mice. Nature.
418:38–39. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim DH and Rossi JJ: Strategies for
silencing human disease using RNA interference. Nat Rev Genet.
8:173–184. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jankovic R, Radulovic S and
Brankovic-Magic M: siRNA and miRNA for the treatment of cancer. J
BUON. 14(Suppl 1): S43–S49. 2009.
|
|
30
|
Gondi CS and Rao JS: Concepts in in vivo
siRNA delivery for cancer therapy. J Cell Physiol. 220:285–291.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liang Y, Gao H, Lin SY, Goss JA,
Brunicardi FC and Li K: siRNA-based targeting of cyclin E
overexpression inhibits breast cancer cell growth and suppresses
tumor development in breast cancer mouse model. PLoS One.
5:e128602010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|