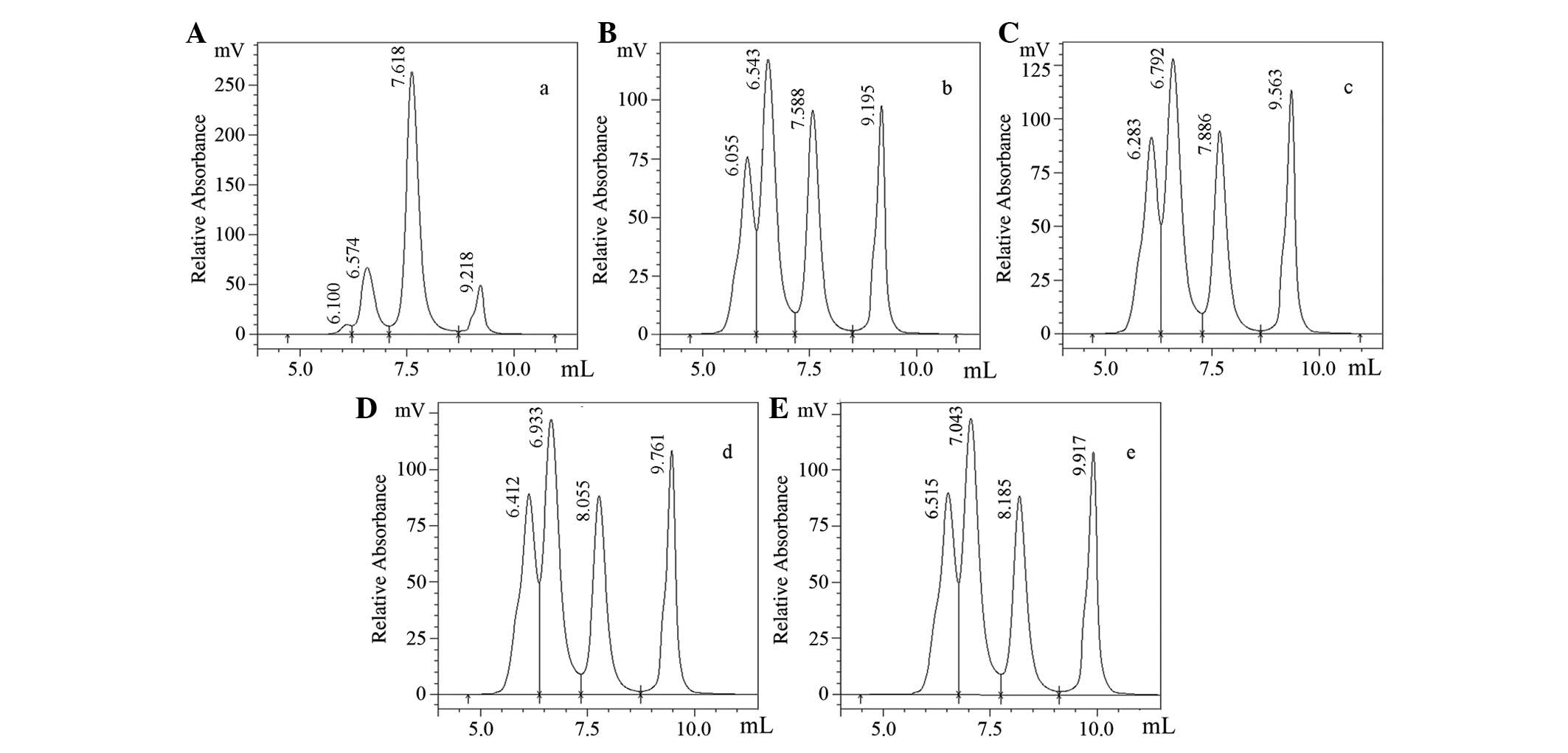
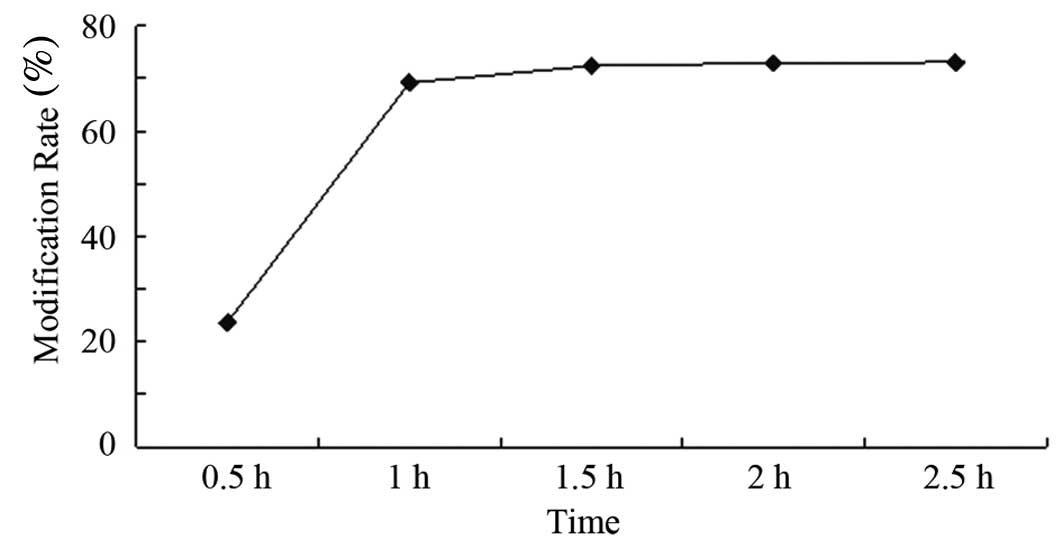
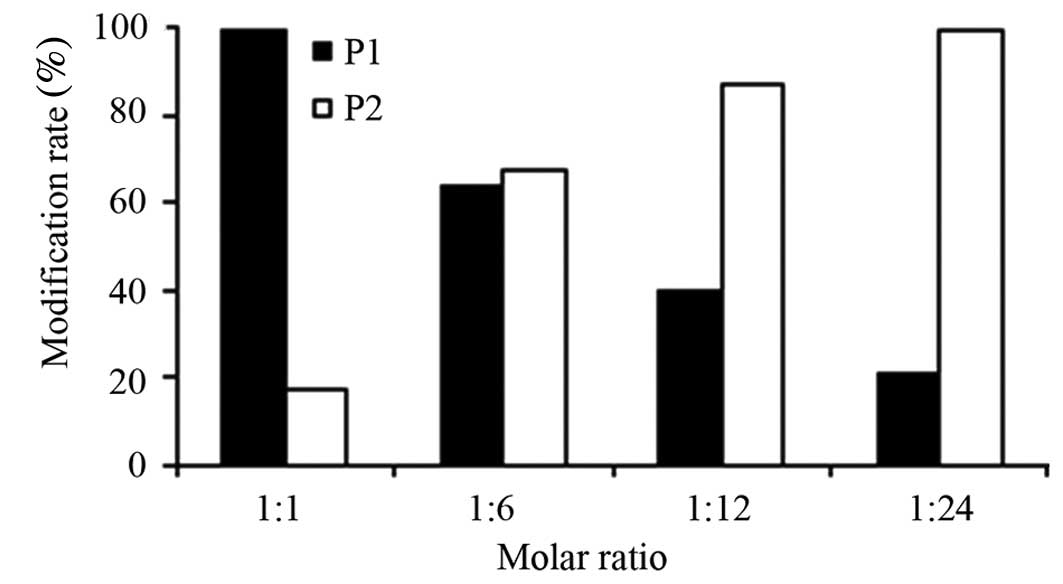
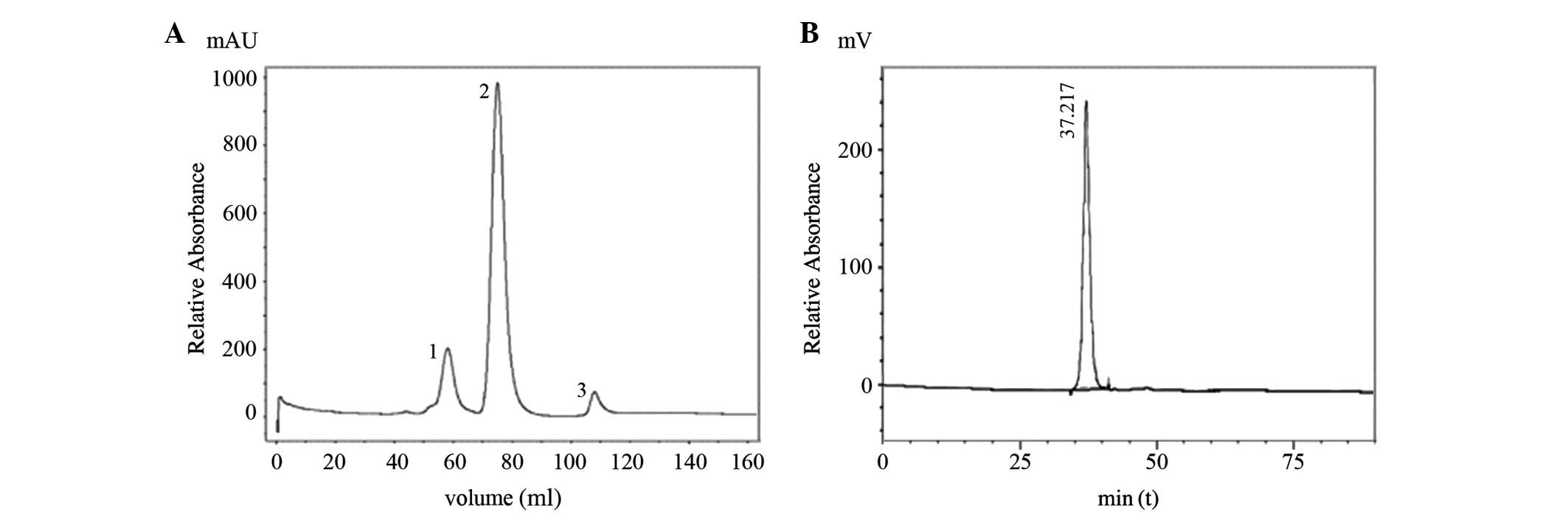
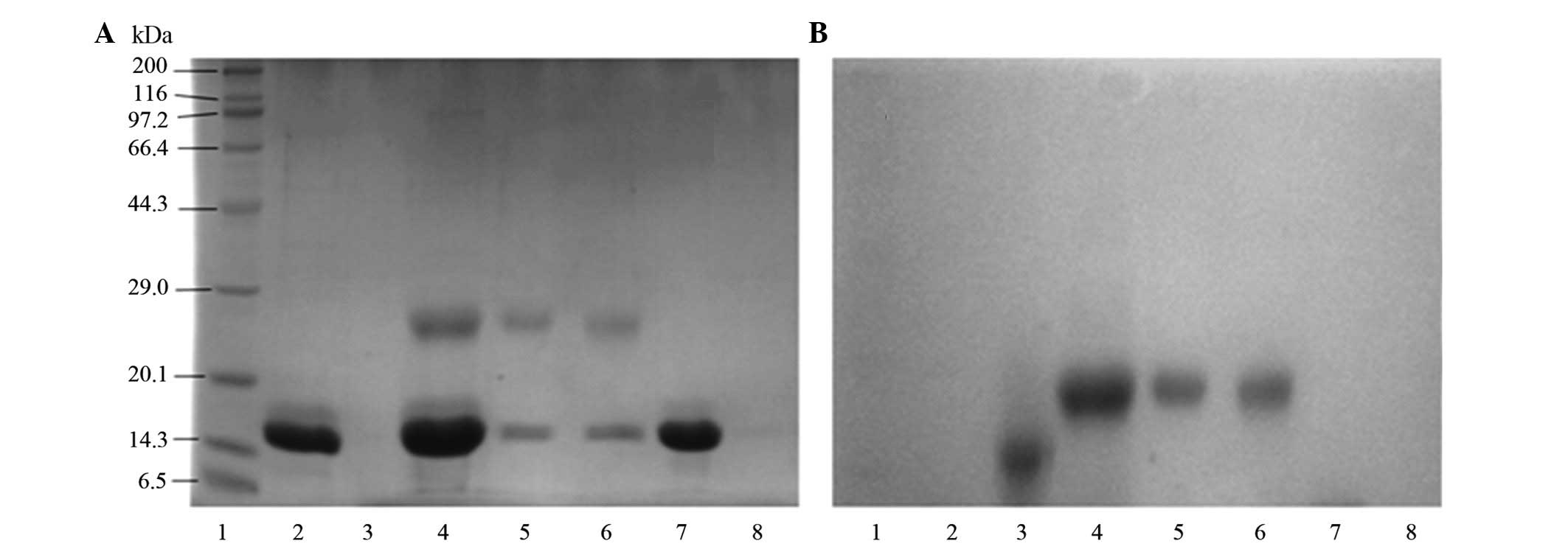
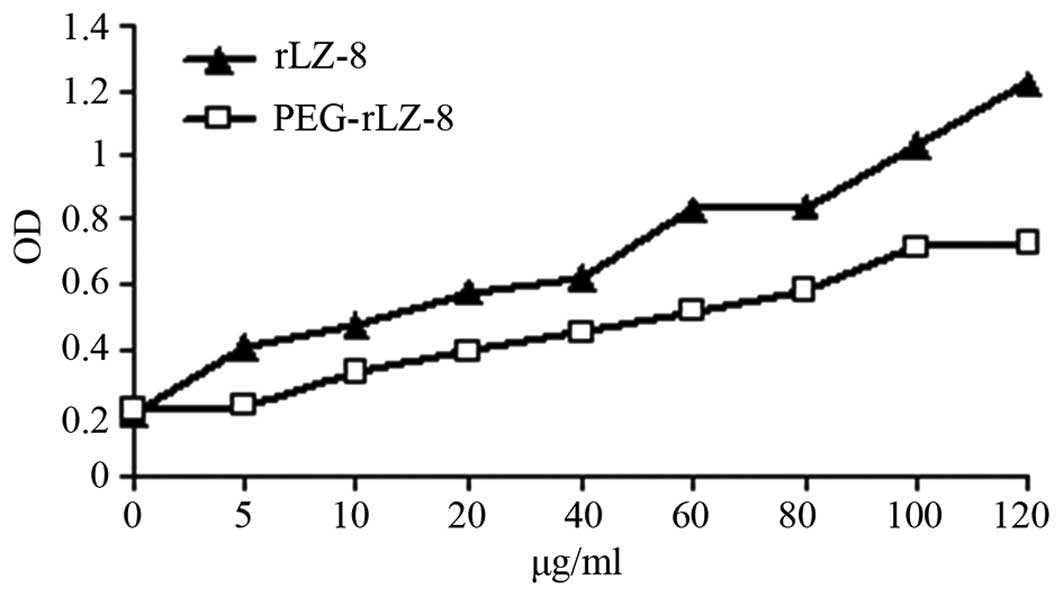
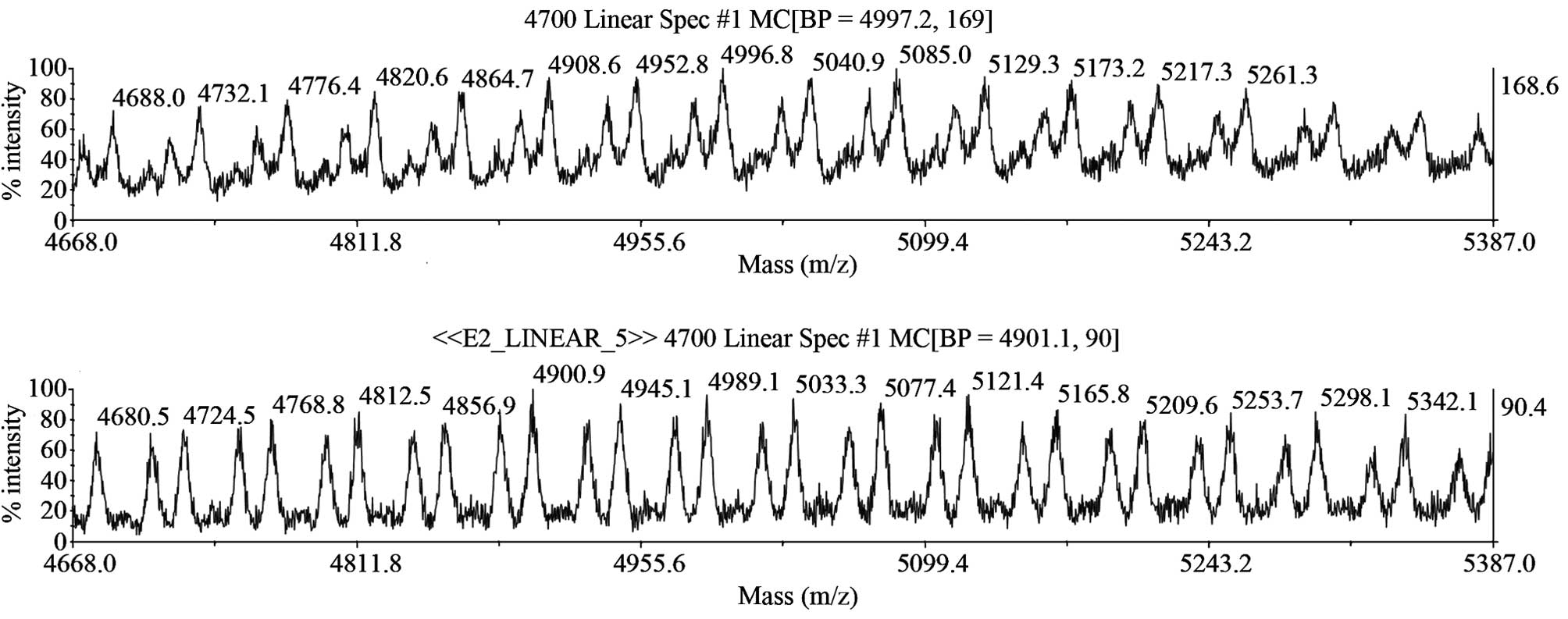
|
1
|
Liang C, Zhang S, Liu Z and Sun F:
Ganoderma lucidum immunomodulatory protein(Lz-8) expressed
in Pichia pastoris and the identification of
immunocompetence. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 25:441–447.
2009.
|
|
2
|
Lin JW, Hao LX, Xu GX, Sun F, Gao F, Zhang
R and Liu LX: Molecular cloning and recombinant expression of a
gene encoding a fungal immunomodulatory protein from Ganoderma
lucidum in Pichia pastoris. World J Microbiol
Biotechnol. 25:383–390. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Murasugi A, Tanaka S, Komiyama N, Iwata N,
Kino K, Tsunoo H and Sakuma S: Molecular cloning of a cDNA and a
gene encoding an immunomodulatory protein, Ling Zhi-8, from a
fungus, Ganoderma lucidum. J Biol Chem. 266:2486–2493.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang XL, Liang CY, Li HR, Li BZ and Sun F:
Recombinant Ganoderma lucidum immunoregulatory protein
(rLZ-8) induces nuclear-stress apoptosis in K562 cells. Zhongguo
Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 26:616–618. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
5
|
Guo Q, Sun H, Liang CY, Zhang SQ, Liu ZY
and Sun F: Inhibiting and apoptosis-inducing effects of recombinant
Ganoderma lucidum immunoregulatory protein on HL60 cells.
Zhongguo Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 26:520–522. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
6
|
Liang CY, Zhang SQ and Sun F: The dynamic
observation: cellular localization of fluorescein isothiocyanate
labeled recombinant Ganoderma lucidum immunoregulatory
protein (rLZ-8) in NB4 APL cell. Chemical Journal of Chinese
Universities: CJCU. 30:479–483. 2009.
|
|
7
|
Kino K, Mizumoto K, Sone T, Yamaji T,
Watanabe J, Yamashita A, Yamaoka K, Shimizu K, Ko K and Tsunoo H:
An immunomodulating protein, Ling Zhi-8 (LZ-8) prevents insulitis
in non-obese diabetic mice. Diabetologia. 33:713–718. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Haak-Frendscho M, Kino K, Sone T and
Jardieu P: Ling Zhi-8: a novel T cell mitogen induces cytokine
production and upregulation of ICAM-1 expression. Cell Immunol.
150:101–113. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hsieh KY, Hsu CI, Lin JY, Tsai CC and Lin
RH: Oral administration of an edible-mushroom-derived protein
inhibits the development of food-allergic reactions in mice. Clin
Exp Allergy. 33:1595–1602. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu YH, Kao MC, Lai YL and Tsai JJ:
Efficacy of local nasal immunotherapy for 10. Dp2-induced airway
inflammation in mice: using Dp2 peptide and fungal immunomodulatory
peptide. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 112:301–310. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ho JC, Sze SC, Shen WZ and Liu WK:
Mitogenic antivity of edible mushroom lectins. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1671:9–17. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wasser SP and Weis AL: Therapeutic effects
of substances occurring in higher Basidiomycetes mushrooms: a
modern perspective. Crit Rev Immunol. 19:65–96. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Llovet JM and Bruix J: Systematic review
of randomized trials for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma:
chemoembolization improves survival. Hepatology. 37:429–442. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Liang CY, Li H, Zhou H, Zhang SQ, Liu ZY,
Zhou Q and Sun F: Recombinant Lz-8 from Ganoderma lucidum
induces endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated autophagic cell death
in SGC-7901 human gastric cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 27:1079–1089.
2012.
|
|
15
|
van der Hem LG, van der Vliet JA, Bocken
CF, Kino K, Hoitsma AJ and Tax WJ: Ling Zhi-8: studies of a new
immunomodulating agent. Transplantation. 60:438–443.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhu JQ, Liang CY, Feng K, Gai XD, Sun X
and Sun F: Purification and properties of recombinant Ganoderma
lucidum immunoregulatory protein. Chem Res Chin Univ. 29:1–4.
2008.
|
|
17
|
Huang L, Sun F, Liang CY, He YX, Bao R,
Liu L and Zhou CZ: Crystal structure of LZ-8 from the medicinal
fungus Ganoderma lucidium. Proteins. 75:524–527. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lin WH, Hung CH, Hsu CI and Lin JY:
Dimerisation of the N-terminal amphipathic α-helix domain of the
fungal immunomodulatory protein from Ganoderma tsugae
(Fip-gts) defined by a yeast two-hybrid system and site-directed
mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 272:20044–20048. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tanaka S, Ko K, Kino K, Tsuchiya K,
Yamashita A, Murasugi A, Sakuma S and Tsunoo H: Complete amino acid
sequence of an immunomodulatory protein, ling zhi-8 (LZ-8). An
immunomodulator from a fungus, Ganoderma lucidium, having
similarity to immunoglobulin variable regions. J Biol Chem.
264:16372–16377. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Roberts MJ, Bentley MD and Harris JM:
Chemistry for peptide and protein PEGylation. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.
54:459–476. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fee CJ and Van Alstine JM: PEG-proteins:
Reaction engineering and separation issues. Chem Eng Sci.
61:924–939. 2005.
|
|
22
|
Kinstler O, Molineux G, Treuheit M, Ladd D
and Gegg C: Mono-N-terminal poly(ethylene glycol)-protein
conjugates. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 54:477–485. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Greenwald RB: PEG drugs: an overview. J
Control Release. 74:159–171. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Seyfried BK, Siekmann J, Belgacem O,
Wenzel RJ, Turecek PL and Allmaier G: MALDI linear TOF mass
spectrometry of PEGylated (glyco)proteins. J Mass Spectrom.
45:612–617. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ronda L, Pioselli B, Bruno S, Faggiano S
and Mozzarelli A: Electrophoretic analysis of PEGylated
hemoglobin-based blood substitutes. Anal Biochem. 408:118–123.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhai Y, Zhao Y, Lei J, Su Z and Ma G:
Enhanced circulation half-life of site-specific PEGylated rhG-CSF:
optimization of PEG molecular weight. J Biotechnol. 142:259–266.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Moosmann A, Christel J, Boettinger H and
Mueller E: Analytical and preparative separation of PEGylated
lysozyme for the characterization of chromatography media. J
Chromatogr A. 1217:209–215. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|