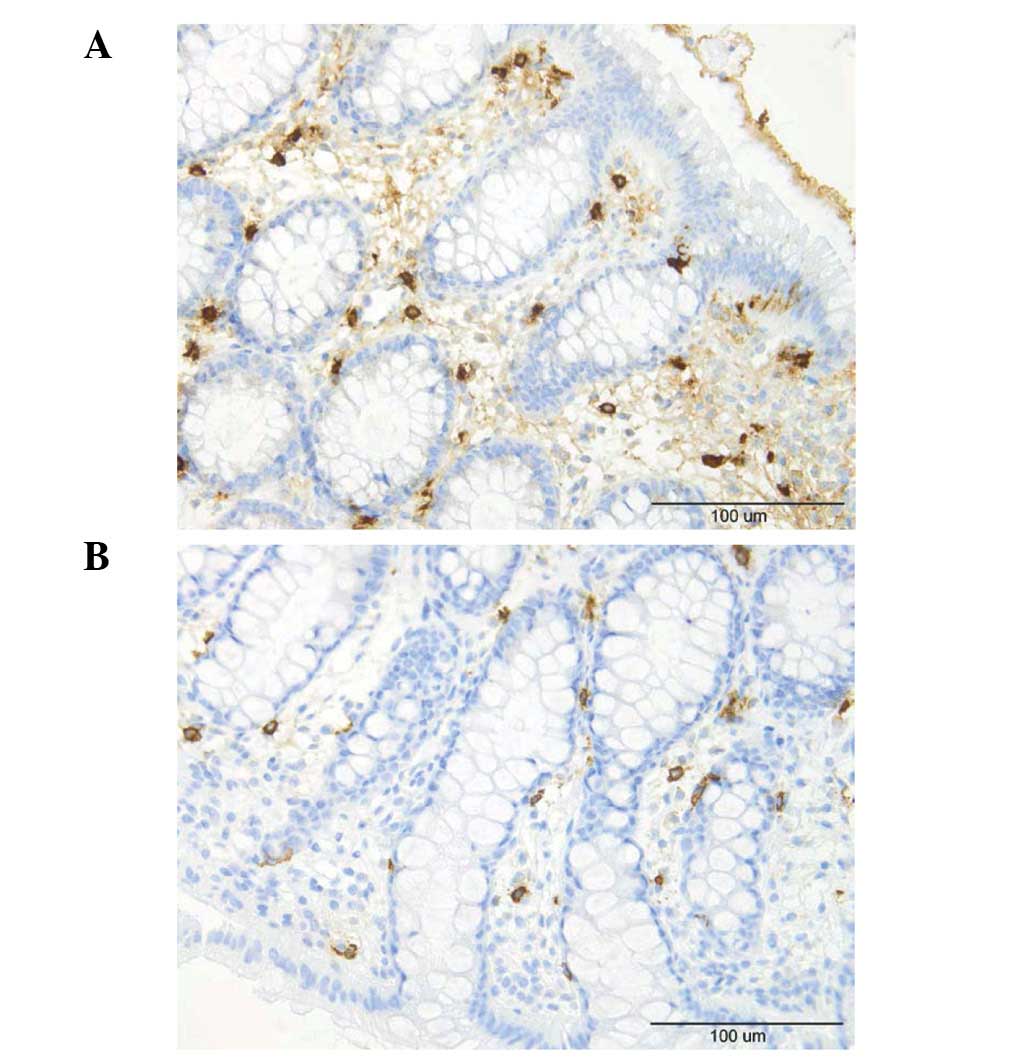
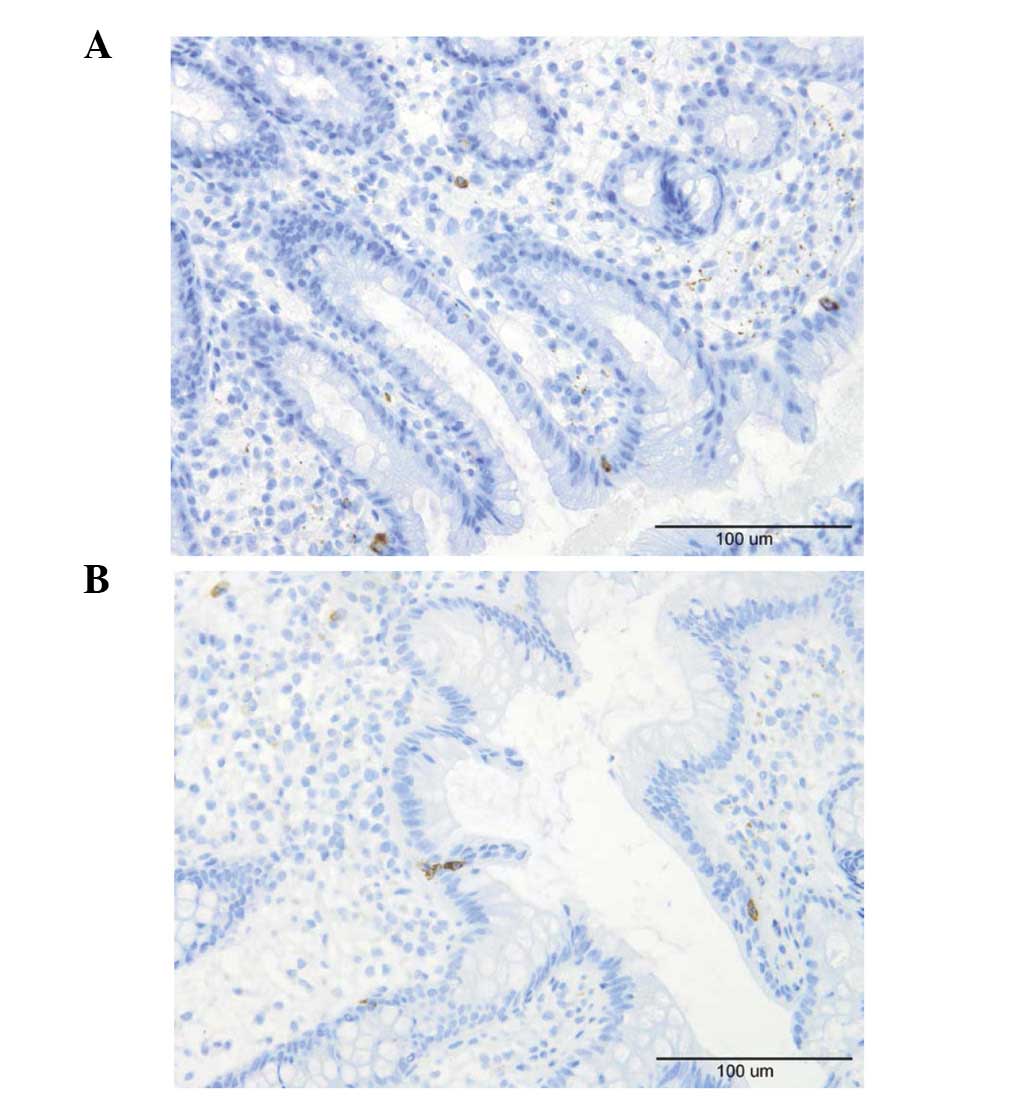
|
1
|
El-Salhy M, Gundersen D, Hatlebakk JG and
Hausken T: Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Nova Scientific Publishers;
New York, NY: 2012
|
|
2
|
Agréus L, Svärsudd K, Nygrén O and Tibblin
G: Irritable bowel syndrome and dyspepsia in the general
population: overlap and lack of stability over time.
Gastroenterology. 109:671–680. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Thompson WG and Heaton KW: Functional
bowel disorders in apparently healthy people. Gastorenterology.
79:283–288. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kennedy TM, Jones RH, Hungin AP,
O’Flanagan H and Kelly P: Irritable bowel syndrome,
gastro-oesophageal reflux, and bronchial hyper-responsiveness in
the general population. Gut. 43:770–774. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Drossman DA, Li Z, Andruzzi E, Temple RD,
Talley NJ, Thompson WG, Whitehead WE, Janssens J, Funch-Jensen P,
Corazziari E, et al: U.S. householder survey of functional
gastrointestinal disorders. Prevalence, sociodemography, and health
impact. Dig Dis Sci. 38:1569–1580. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Talley NJ, Gabriel SE, Harmsen WS,
Zinsmeister AR and Evans RW: Medical costs in community subjects
with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 109:1736–1741.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hungin AP, Whorwell PJ, Tack J and Mearin
F: The prevalence, patterns and impact of irritable bowel syndrome:
an international survey of 40,000 subjects. Aliment Pharmacol Ther.
17:643–650. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jones R and Lydeard S: Irritable bowel
syndrome in the general population. BMJ. 304:87–90. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bordie AK: Functional disorders of the
colon. J Indian Med Assoc. 58:451–456. 1972.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
O’Keefe EA, Talley NJ, Zinsmeister AR and
Jacobsen SJ: Bowel disorders impair functional status and quality
of life in the elderly: a population-based study. J Gerontol A Biol
Sci Med Sci. 50:M184–M189. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Everhart JE and Renault PF: Irritable
bowel syndrome in office-based practice in the United States.
Gastroenterology. 100:998–1005. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wilson S, Roberts L, Roalfe A, Bridge P
and Singh S: Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome: a community
survey. Br J Gen Pract. 54:495–502. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Harvey RF, Salih SY and Read AE: Organic
and functional disorders in 2000 gastroenterology outpatients.
Lancet. 1:632–634. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Spiegel BM: The burden of IBS: looking at
metrics. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 11:265–269. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Thompson WG: A world view of IBS.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Diagnosis and Treatment. Camilleri M and
Spiller R: Saunders Ltd; Philadelphia and London: pp. 17–26.
2002
|
|
16
|
Quigley EM, Locke GR, Mueller-Lissner S,
Paulo LG, Tytgat GN, Helfrich I and Schaefer E: Prevalence and
management of abdominal cramping and pain: a multinational survey.
Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 24:411–419. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Miller V, Whitaker K, Morris JA and
Whorwell PJ: Gender and irritable bowel syndrome: the male
connection. J Clin Gastroenterol. 38:558–560. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Whitehead WE, Burnett CK, Cook EW III and
Taub E: Impact of irritable bowel syndrome on quality of life. Dig
Dis Sci. 41:2248–2253. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gralnek IM, Hays RD, Kilbourne A, Naliboff
B and Mayer EA: The impact of irritable bowel syndrome on health
related quality of life. Gastroenterology. 119:654–660. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huerta I, Hinojosa C, Santa Maria A and
Schmulson M: Diferencias en la calidad de vida (CV) entre pacientes
con sindrome de Intestino irritable (SII) y la poblacon mexicana
evaluadas mediante el SF-36. Rev Mex Gastroenterol. 66(Suppl 2):
145–146. 2001.(In Spanish).
|
|
21
|
Schmulson M, Robles G, Kershenobich,
Lopez-Ridaura R, Hinojosa C and Durate A: Los pacientes con
trastornos funcionales digestivos (TFD) tienen major compromiso de
la calidad de vida (CV) evaluadas por el SF-36 comparados con
pacientes con hepatitis C y pancreatitis cronica. Rev Mex
Gastroenterol. 65(Suppl-Resumenes): 50–51. 2000.(In Spanish).
|
|
22
|
Weston AP, Biddle WL, Bhatia PS and Miner
PB Jr: Terminal ileal mucosal mast cells in irritable bowel
syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 38:1590–1595. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
O’Sullivan M, Clayton N, Breslin NP,
Herman I, Bountra C, McLaren A and O’Morain CA: Increased mast
cells in the irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil.
12:449–457. 2000.
|
|
24
|
Dunlop SP, Jenkins D, Neal KR and Spiller
RC: Relative importance of enterochromaffin cell hyperplasia,
anxiety and depression in post-infectious IBS. Gastroenterology.
125:1651–1659. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Barbara G, Stanghellini V, De Giorgio R,
Cremon C, Cottrell GS, Santini D, Pasquinelli G, Morselli-Labate
AM, Grady EF, Bunnett NW, Collins SM and Corinaldesi R: Activated
mast cells in proximity to colonic nerves correlate with abdominal
pain in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 126:693–702.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Spiller RC, Jenkins D, Thornley JP, Hebden
JM, Wright T, Skinner M and Neal KR: Increased rectal mucosal
enteroendocrine cells, T lymphocytes, and increased gut
permeability following acute Campylobacter enteritis and in
post-dysenteric irritable bowel syndrome. Gut. 47:804–811. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cremon C, Gargano L, Morselli-Labate AM,
Santini D, Cogliandro RF, De Giorgio R, Stanghellini V, Corinaldesi
R and Barbara G: Mucosal immune activation in irritable bowel
syndrome: gender-dependence and association with digestive
symptoms. Am J Gastroenterol. 104:392–400. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dizdar V, Hanevik K, Lærum OD, Gilja OH,
Langeland N and Hausken T: Duodenal mucosal lymphocytes in
Giardia-induced functional gastrointestinal disorder. In:
Presented at the 19th United European Gastroenterology Week (UEGW);
(abstract P0996). 2011
|
|
29
|
Longstreth GF, Thompson WG, Chey WD,
Houghton LA, Mearin F and Spiller RC: Functional bowel disorders.
Gastroenterology. 130:1480–1491. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ghoshal UC, Park H and Gwee KA: Bugs and
irritable bowel syndrome: The good, the bad and the ugly. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 25:244–251. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mckeown ES, Parry D, Stansfield R, Barton
JR and Welfare MR: Postinfectious irritable bowel syndrome may
occur after non-gastrointestinal and intestinal infection.
Neurogastroenterol Motil. 18:839–843. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Longstreth CF, Hawkey CJ, Mayer EA, Jones
RH, Naesdal J, Wilson IK, Peacock RA and Wiklund IK:
Characteristics of patients with irritable bowel syndrome recruited
from three sources: implications for clinical trials. Aliment
Pharmacol Ther. 15:959–964. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Spiller R and Garsed K: Infection,
inflammation and the irritable bowel syndrome. Dig Liver Dis.
41:844–849. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wheatcroft J, Wakelin D, Smith A, Mahoney
CR, Mawe G and Spiller R: Enterochromaffin cell hyperplasia and
decreased serotonin transporter in a mouse model of postinfectious
bowel dysfunction. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 17:863–870. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang LH, Fang XC and Pan GZ: Bacillary
dysentery as a causative factor for irritable bowel syndrome and
its pathogenesis. Gut. 53:1096–1101. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lee KJ, Kim YB, Kim JH, Kwon HC, Kim DK
and Cho SW: The alteration of enterochromaffin cell, mast cell, and
lamina propria T lymphocyte numbers in irritable bowel syndrome and
its relationship with psychological factors. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 23:1689–1694. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|