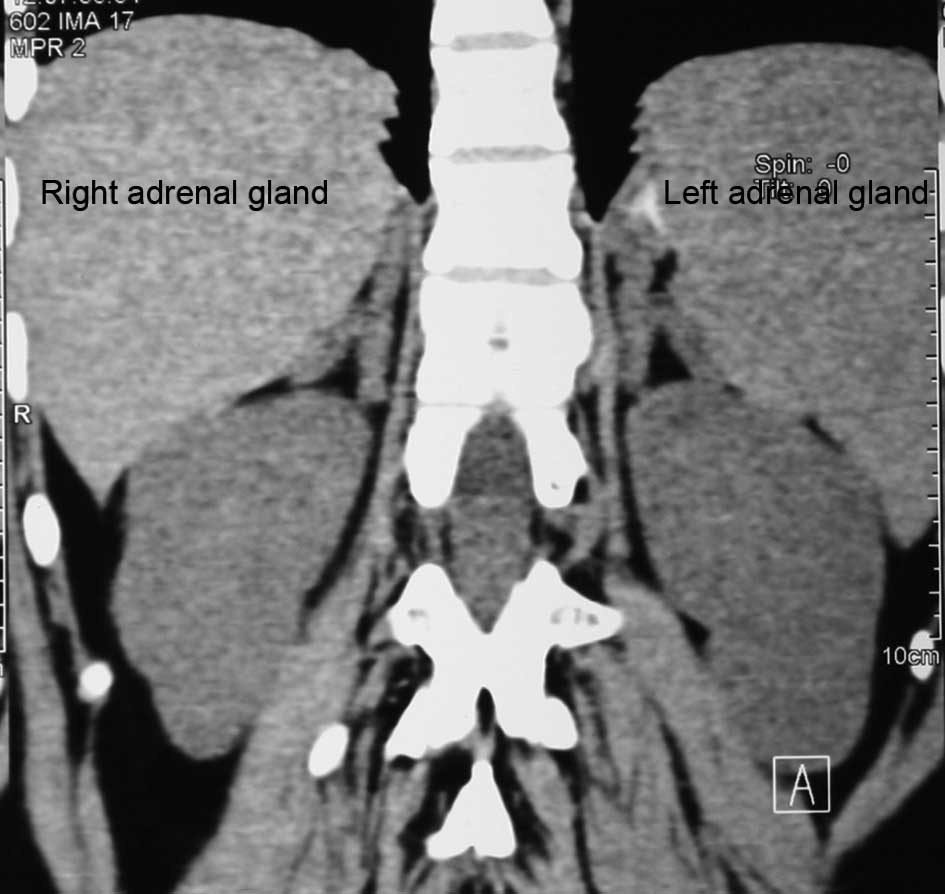
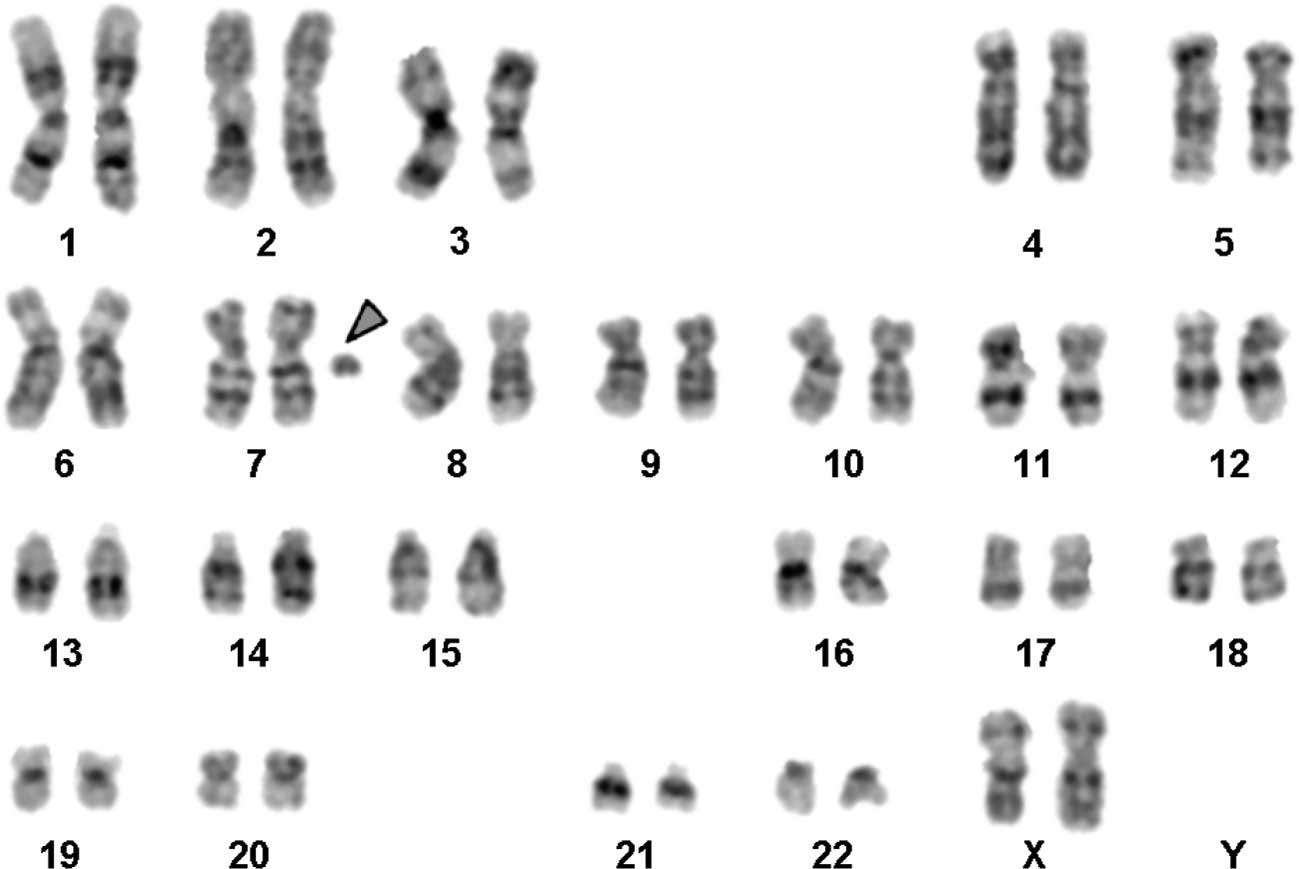
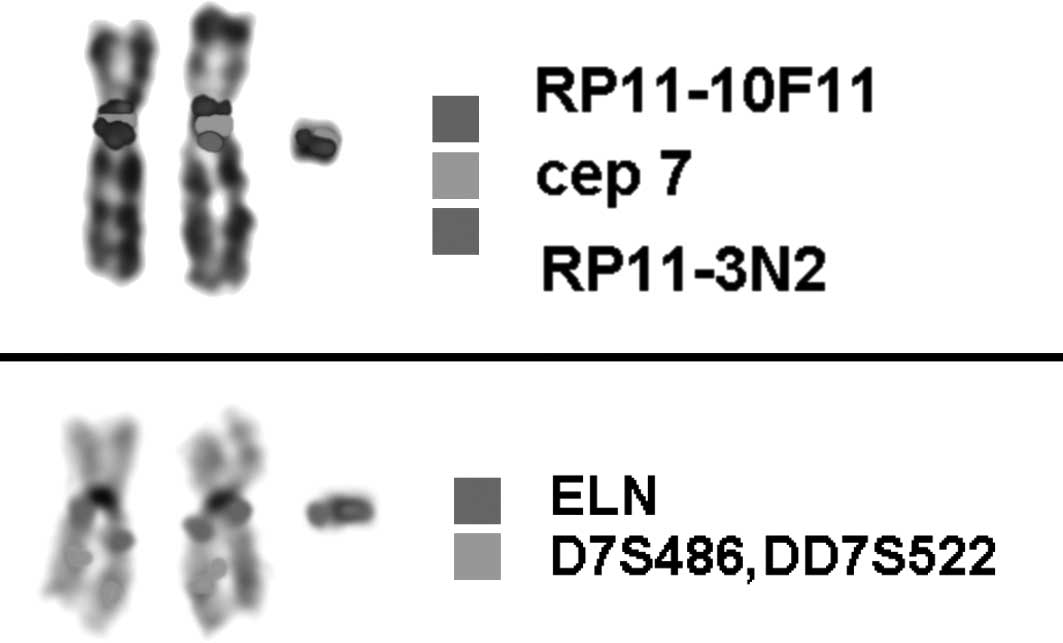
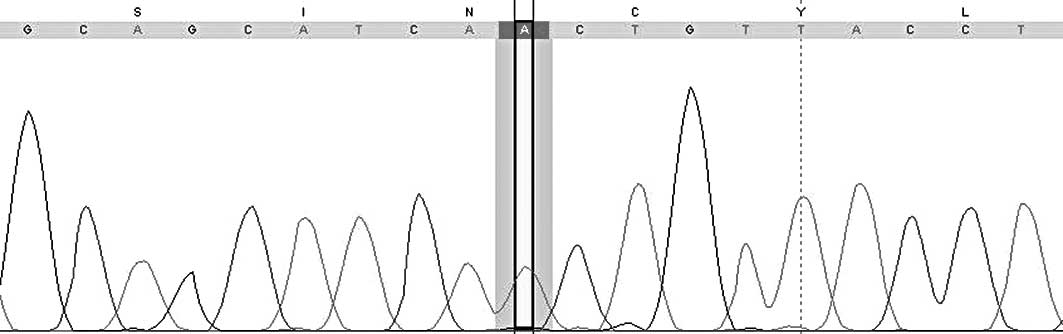
|
1
|
Liehr T, Claussen U and Starke H: Small
supernumerary marker chromosomes (sSMC) in humans. Cytogenet Genome
Res. 107:55–67. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liehr T and Weise A: Frequency of small
supernumerary marker chromosomes in prenatal, newborn,
developmentally retarded and infertility diagnostics. Int J Mol
Med. 19:719–731. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liehr T: Small supernumerary marker
chromosomes (sSMCs): a spotlight on some nomenclature problems. J
Histochem Cytochem. 57:991–993. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Miyoshi O, Kondoh T, Taneda H, Otsuka K,
Matsumoto T and Niikawa N: 47,XX,UPD(7)mat,r(7)pat/46,XX,UPD(7)mat
mosaicism in a girl with Silver-Russell syndrome (SRS): possible
exclusion of the putative SRS gene from a 7p13-q11 region. J Med
Genet. 36:326–329. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liehr T: Cytogenetic contribution to
uniparental disomy (UPD). Mol Cytogenet. 3:82010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
White PC, Tusie-Luna MT, New MI and
Speiser PW: Mutations in steroid 21-hydroxylase (CYP21). Hum Mutat.
3:373–378. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Speiser PW and White PC: Congenital
adrenal hyperplasia. N Engl J Med. 349:776–788. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kawaguchi H, O’hUigin C and Klein J:
Evolutionary origin of mutations in the primate cytochrome P450c21
gene. Am J Hum Genet. 50:766–780. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Levine LS, Zachmann M, New MI, Prader A,
Pollack MS, O’Neill GJ, Yang SY, Oberfield SE and Dupont B: Genetic
mapping of the 21-hydroxylase-deficiency gene within the HLA
linkage group. N Engl J Med. 299:911–915. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tajima T, Fujieda K and Fujii-Kuriyama Y:
De novo mutation causes steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency in one
family of HLA-identical affected and unaffected siblings. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 77:86–89. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
White PC and Speiser PW: Congenital
adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Endocr Rev.
21:245–291. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jaaskelainen J, Levo A, Voutilainen R and
Partanen J: Population-wide evaluation of disease manifestation in
relation to molecular genotype in steroid 21-hydroxylase (CYP21)
deficiency: good correlation in a well defined population. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 82:3293–3297. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Krone N, Braun A, Roscher AA, Knorr D and
Schwarz HP: Predicting phenotype in steroid 21-hydroxylase
deficiency? Comprehensive genotyping in 155 unrelated, well defined
patients from southern Germany. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
85:1059–1065. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Claussen U, Michel S, Mühlig P, Westermann
M, Grummt UW, Kromeyer-Hauschild K and Liehr T: Demystifying
chromosome preparation and the implications for the concept of
chromosome condensation during mitosis. Cytogenet Genome Res.
98:136–146. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shaffer L, Slovak M and Cambell L: ISCN
(2009): An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature.
S. Karger; Basel: 2009
|
|
16
|
Nietzel A, Rocchi M, Starke H, Heller A,
Fiedler W, Wlodarska I, Loncarevic IF, Beensen V, Claussen U and
Liehr T: A new multicolor-FISH approach for the characterization of
marker chromosomes: centromerespecific multicolor-FISH (cenM-FISH).
Hum Genet. 108:199–204. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Oliver-Bonet M, Liehr T, Nietzel A, Heller
A, Starke H, Claussen U, Codina-Pascual M, Pujol A, Abad C, Egozcue
J, Navarro J and Benet J: Karyotyping of human synaptonemal
complexes by cenM-FISH. Eur J Hum Genet. 11:879–883. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Starke H, Nietzel A, Weise A, Heller A,
Mrasek K, Belitz B, Kelbova C, Volleth M, Albrecht B, Mitulla B,
Trappe R, et al: Small supernumerary marker chromosomes (SMC):
genotype-phenotype correlation and classification. Hum Genet.
114:51–67. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Berg JS, Brunetti-Pierri N, Peters SU,
Kang SH, Fong CT, Salamone J, Freedenberg D, Hannig VL, Prock LA,
Miller DT, Raffalli P, et al: Speech delay and autism spectrum
behaviors are frequently associated with duplication of the 7q11.23
Williams-Beuren syndrome region. Genet Med. 9:427–441. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lichtenbelt KD, Hochstenbach R, van Dam
WM, Eleveld MJ, Poot M and Beemer FA: Supernumerary ring chromosome
mosaicism: case report, investigation of the gene content, and
delineation of the phenotype. Am J Med Genet Part A. 132:93–100.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bertini V, Valetto A, Uccelli A,
Bonuccelli A, Tarantino E, Taddeucci G and Simi P: Molecular
cytogenetic characterization of a de novo mosaic supernumerary ring
chromosome 7: report of a new patient. Am J Med Genet part A.
146A:2955–2959. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dubey S, Idicula-Thomas S, Anwaruddin M,
Saravanan C, Varma RR and Maitra A: A novel 9-bp insertion detected
in steroid 21-hydroxylase gene (CYP21A2): prediction of its
structural and functional implications by computational methods. J
Biomed Sci. 16:32009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Higashi Y, Tanae A, Inoue H and
Fujii-Kuriyama Y: Evidence for frequent gene conversion in the
steroid 21-hydroxylase (P450c21) gene: implications for steroid
21-hydroxylase deficiency. Am J Hum Genet. 42:17–25.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wedell A, Thilén A, Ritzén EM, Stengler B
and Luthman H: Mutational spectrum of the steroid 21-hydroxylase
gene in Sweden: implications for genetic diagnosis and association
with disease manifestation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 78:1145–1152.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Billerbeck AE, Bachega TA, Frazatto ET,
Nishi MY, Goldberg AC, Marin ML, Madureira G, Monte O, Arnhold IJ
and Mendonca BB: A novel missense mutation, G424S, in Brazilian
patients with 21-hydroxylase deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
84:2870–2872. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Barbaro M, Lajic S, Baldazzi L, Balsamo A,
Pirazzoli P, Cicognani A, Wedell A and Cacciari E: Functional
analysis of two recurrent aminoacid substitution in the CYP21 gene
from Italian patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 89:2402–2407. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Database of CYP21A2 by human Cytochrome
P450 (CYP) Allele Nomenclature Committee. [http://www.imm.ki.se/CYPalleles/cyp21.htm].
|
|
28
|
Robins T, Bellanne-Chantelot C, Barbaro M,
Cabrol S, Wedell A and Lajic S: Characterization of novel missense
mutations in CYP21 causing congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Mol
Med. 85:247–255. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Menassa R, Tardy V, Despert F,
Bouvattier-Morel C, Brossier JP, Cartigny M and Morel Y: p.H62L, a
rare mutation of the CYP21 gene identified in two forms of
21-hydroxylase deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 93:1901–1908.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Soardi FC, Barbaro M, Lau IF, Lemos-Marini
SHV, Baptista MTM, Guerra-Junior G, Wedell A, Lajic S and de Mello
MP: Inhibition of CYP21A2 enzyme activity caused by novel missense
mutations identified in Brazilian and Scandinavian patients. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 93:2416–2420. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Riepe FG, Hiort O, Grtzinger J, Sippell
WG, Krone N and Holterhus PM: Functional and structural
consequences of a novel point mutation in the CYP21A2 gene causing
congenital adrenal hyperplasia: potential relevance of helix C for
P450 oxidoreductase-21-hydroxylase interaction. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 93:2891–2895. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|