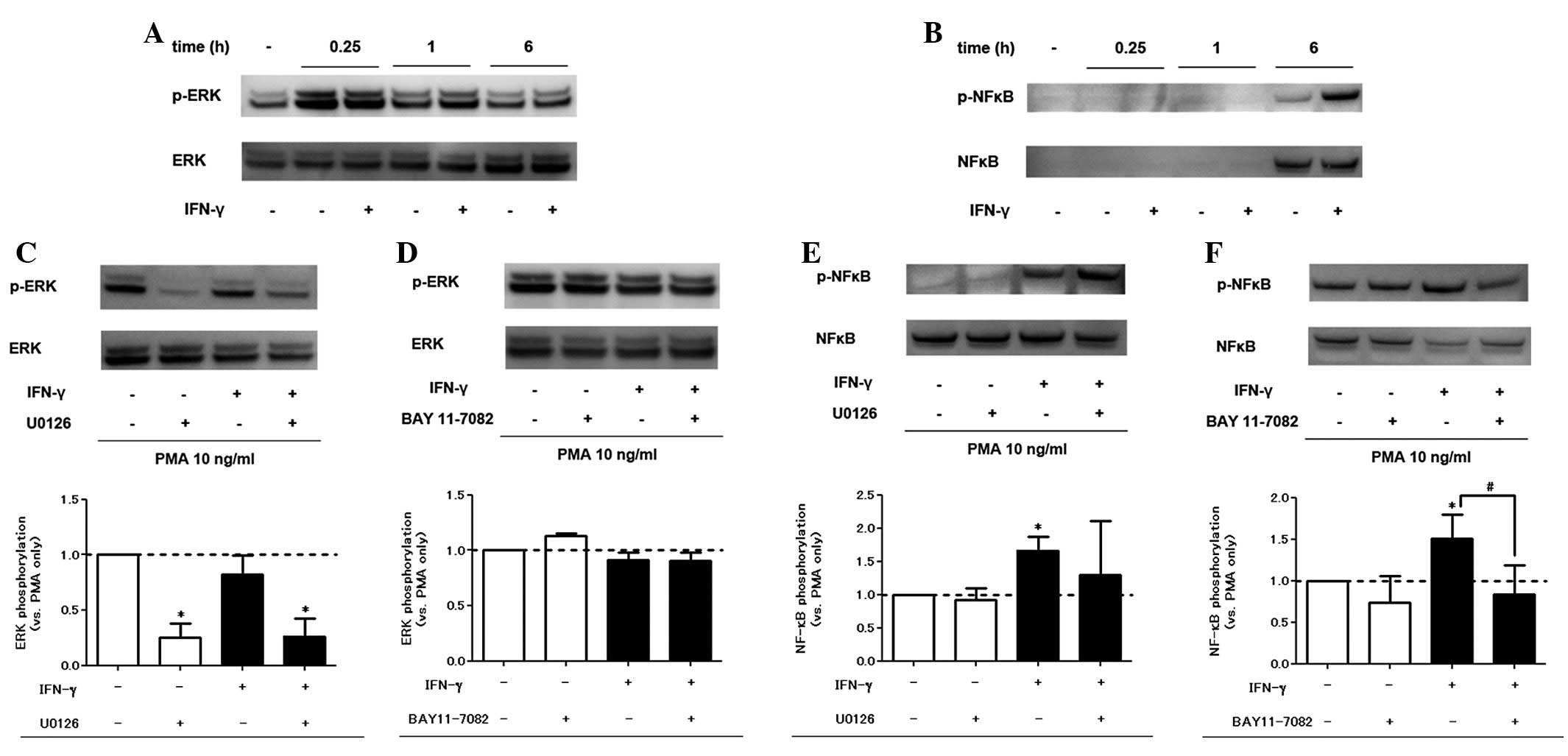
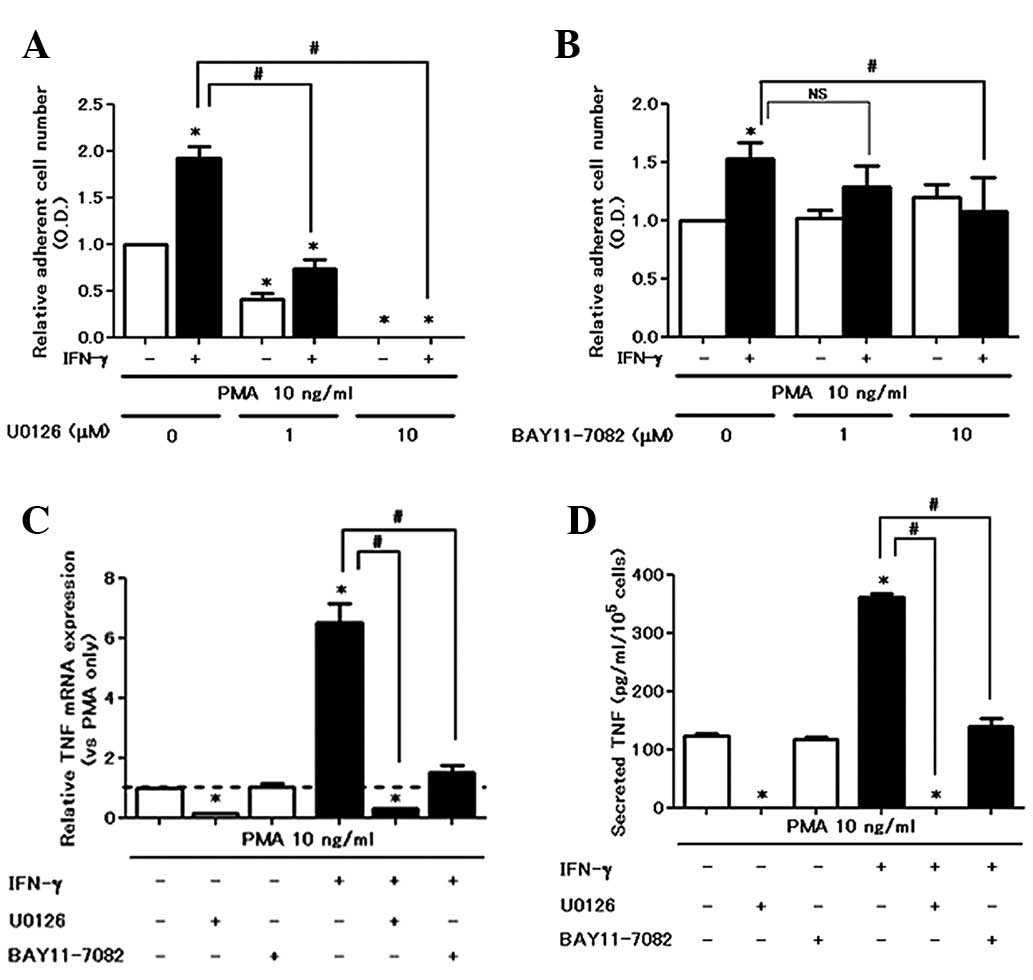
|
1
|
Takeda K, Ichiki T, Narabayashi E, et al:
Inhibition of prolyl hydroxylase domain-containing protein
suppressed lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-α expression.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29:2132–2137. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Allison AC, Ferluga H and Schorlemmer HU:
The role of macrophage activation in chronic inflammation. Agents
Actions. 8:27–35. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sorg C: Macrophages in acute and chronic
inflammation. Chest. 100:173S–175S. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Todd RF III, Alvarez PA, Brott DA and Liu
DY: Bacterial lipopolysaccharide, phorbol myristate acetate, and
muramyl dipeptide stimulate the expression of a human monocyte
surface antigen, Mo3e. J Immunol. 135:3869–3877. 1985.
|
|
5
|
Schroder K, Hertzog PJ, Ravasi T and Hume
DA: Interferon-γ: an overview of signals, mechanisms and functions.
J Leukoc Biol. 75:163–189. 2004.
|
|
6
|
Scheibenbogen C and Andreesen R:
Development regulation of the cytokine repertoire in human
macrophages: IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, and M-CSF. J Leukoc Biol. 50:35–42.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cassatella MA, Bazzoni F, Flynn RM, Dusi
S, Trinchieri G and Rossi F: Molecular basis of interferon-γ and
lipopolysaccharide enhancement of phagocyte respiratory burst
capability. Studies on the gene expression of several NADPH oxidase
components. J Biol Chem. 265:20241–20246. 1990.
|
|
8
|
Moller DR: Cells and cytokines involved in
the pathogenesis of sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis.
16:24–31. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sasaki M, Namioka Y, Ito T, et al: Role of
ICAM-1 in the aggregation and adhesion of human alveolar
macrophages in response to TNF-α and IFN-γ. Mediators Inflamm.
10:309–313. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chanput W, Mes J, Vreeburg RA, Savelkoul
HF and Wichers HJ: Trascription profiles of LPS-stimulated THP-1
monocytes and macrophages: a tool to study inflammation modulating
effects of food-derived compounds. Food Funct. 1:254–261. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kurihara Y, Nakahara T and Furue M:
αVβ3-integrin expression through ERK
activation mediates cell attachment and is necessary for production
of tumor necrosis factor alpha in monocytic THP-1 cells stimulated
by phorbol myristate acetate. Cell Immunol. 270:25–31. 2011.
|
|
12
|
Kimball ES, Kovacs E, Clark MC and
Schneider CR: Activation of cytokine production and adhesion
molecule on THP-1 myelomonocytic cells by macrophage
colony-stimulating factor in combination with interferon-γ. J
Leukoc Biol. 58:585–594. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hayes MP, Freeman SL and Donnelly RP:
IFN-γ priming of monocytes enhances LPS-induced TNF production by
augmenting both transcription and mRNA stability. Cytokine.
7:427–435. 1995.
|
|
14
|
Klinge U, Theuer S, Krott E and Fiebeler
A: Absence of circulating aldosterone attenuates foreign body
reaction around surgical sutures. Lagenbecks Arch Surg.
395:429–435. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Anderson JM, Rodriguez A and Chang DT:
Foreign body reaction to biomaterials. Semin Immunol. 20:86–100.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Khouw IM, van Wachem PB, van der Worp RJ,
van den Berg TK, de Leij LF and van Luyn MJ: Systemic anti-IFN-γ
treatment and role of macrophage subsets in the foreign body
reaction to dermal sheep collagen in rats. J Biomed Mater Res.
49:297–304. 2000.
|
|
17
|
Juliana C, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Wu J, et
al: Anti-inflammatory compounds parthenolide and Bay 11-7082 are
direct inhibitors of the inflammasome. J Biol Chem. 285:9792–9802.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhu B, Liu Z, Wang P, Wu C and Xu H: A
nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitor BAY11-7082 inhibits interaction
between human endothelial cells, T cells and monocytes. Transplant
Proc. 40:2724–2728. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|