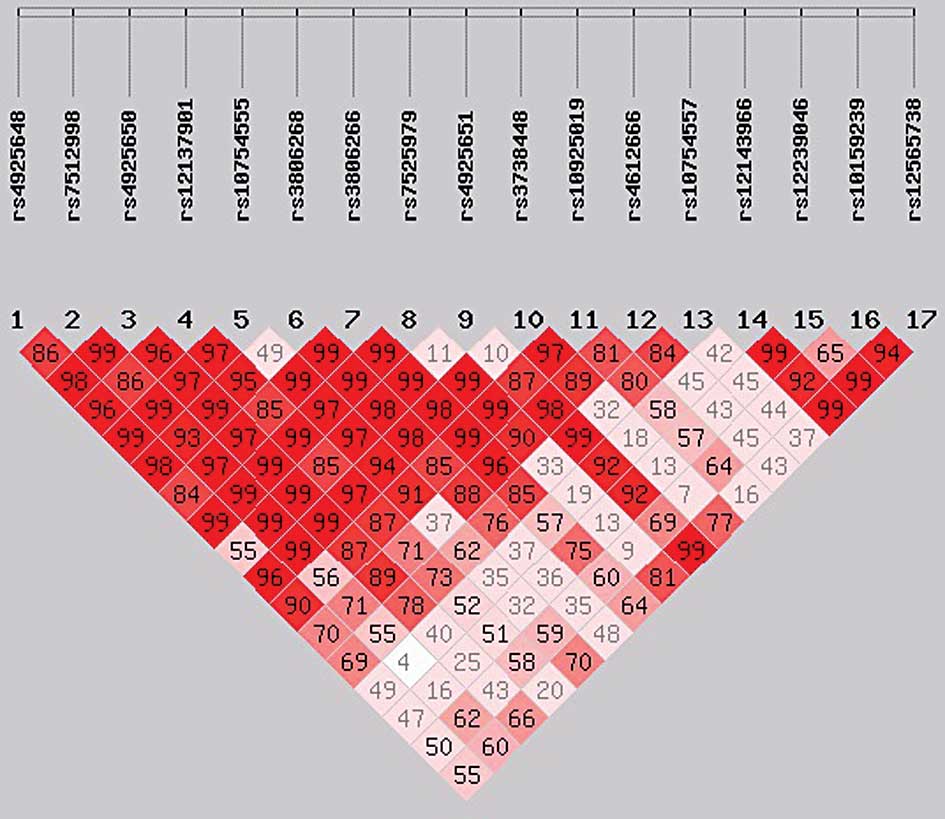
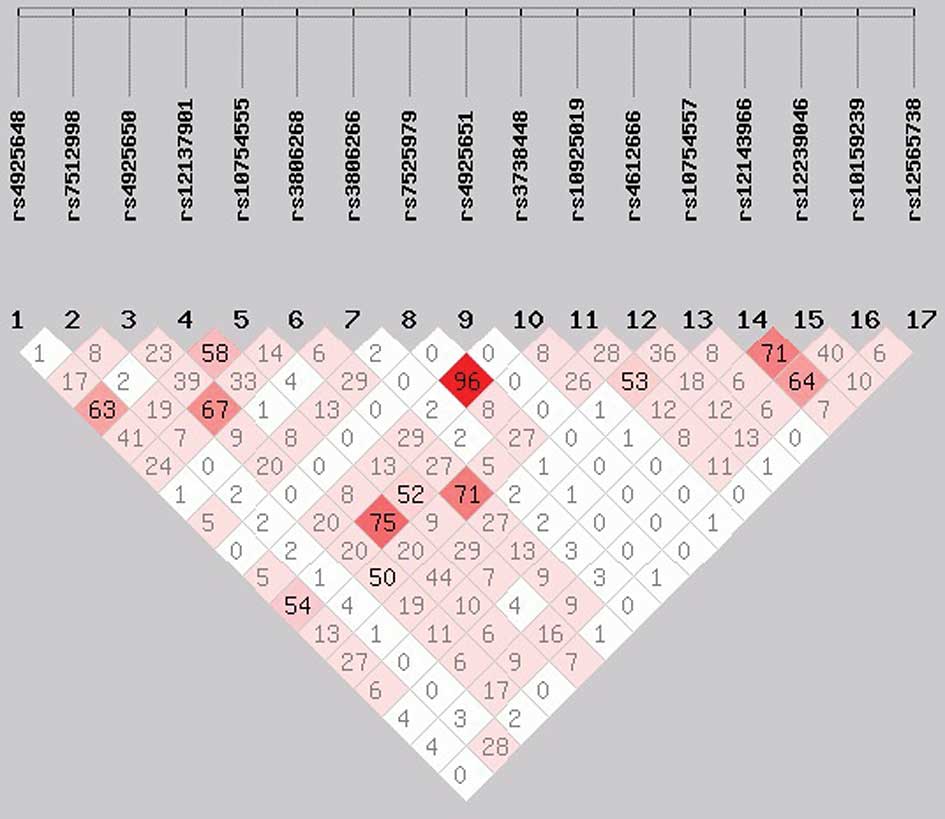
|
1
|
Roddy E, Zhang W and Doherty M: The
changing epidemiology of gout. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 3:443–449.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Terkeltaub R: Gout in 2006: the perfect
storm. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 64:82–86. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Falasca GF: Metabolic diseases: gout. Clin
Dermatol. 24:498–508. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zaka R and Williams CJ: New developments
in the epidemiology and genetics of gout. Curr Rheumatol Rep.
8:215–223. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Becker MA and Jolly M: Hyperuricemia and
associated diseases. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 32:275–293. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mikuls TR and Saag KG: New insights into
gout epidemiology. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 18:199–203. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Masseoud D, Rott K, Liu-Bryan R and
Agudelo C: Overview of hyperuricaemia and gout. Curr Pharm Des.
11:4117–4124. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Choi HK, Ford ES, Li C and Curhan G:
Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in patients with gout: the
Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Arthritis
Rheum. 57:109–115. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Choi HK, De Vera MA and Krishnan E: Gout
and the risk of type 2 diabetes among men with a high
cardiovascular risk profile. Rheumatology (Oxford). 47:1567–1570.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Taniguchi A and Kamatani N: Control of
renal uric acid excretion and gout. Curr Opin Rheumatol.
20:192–197. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shima Y, Teruya K and Ohta H: Association
between intronic SNP in urate-anion exchanger gene, SLC22A12, and
serum uric acid levels in Japanese. Life Sci. 79:2234–2237. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vázquez-Mellado J, Jiménez-Vaca AL,
Cuevas-Covarrubias S, Alvarado-Romano V, Pozo-Molina G and
Burgos-Vargas R: Molecular analysis of the SLC22A12 (URAT1) gene in
patients with primary gout. Rheumatology (Oxford). 46:215–219.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Miao ZM, Zhao SH, Yan SL, Li CG, Wang YG,
Meng DM, Zhou L and Mi QS: NALP3 inflammasome functional
polymorphisms and gout susceptibility. Cell Cycle. 8:27–30. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Miao ZM, Zhao SH, Wang YG, Li CG, Wang ZC,
Chen Y, Chen XY and Yan SL: Epidemiological survey of hyperuricemia
and gout in coastal areas of Shandong Province. Chin J Endocrinol
Metab. 22:421–425. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Jin C and Flavell RA: Molecular mechanism
of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J Clin Immunol. 30:628–631. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Agostini L, Martinon F, Burns K, McDermott
MF, Hawkins PN and Tschopp J: NALP3 forms an IL-1beta-processing
inflammasome with increased activity in Muckle-Wells
autoinflammatory disorder. Immunity. 20:319–325. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Martinon F and Tschopp J: Inflammatory
caspases: linking an intracellular innate immune system to
autoinflammatory diseases. Cell. 117:561–574. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Miao Z, Li C, Chen Y, Zhao S, Wang Y, Wang
Z, Chen X, Xu F, Wang F, Sun R, Hu J, Song W, Yan S and Wang CY:
Dietary and lifestyle changes associated with high prevalence of
hyperuricemia and gout in the Shandong coastal cities of Eastern
China. J Rheumatol. 35:1859–1864. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Martinon F: Mechanisms of uric acid
crystal-mediated autoinflammation. Immunol Rev. 233:218–232. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hoffman HM, Mueller JL, Broide DH,
Wanderer AA and Kolodner RD: Mutation of a new gene encoding a
putative pyrin-like protein causes familial cold autoinflammatory
syndrome and Muckle-Wells syndrome. Nat Genet. 29:301–305. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Church LD, Cook GP and McDermott MF:
Primer: inflammasomes and interleukin 1beta in inflammatory
disorders. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 4:34–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pétrilli V and Martinon F: The
inflammasome, autoinflammatory diseases, and gout. Joint Bone
Spine. 74:571–576. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Masters SL, Lobito AA, Chae J and Kastner
DL: Recent advances in the molecular pathogenesis of hereditary
recurrent fevers. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 6:428–433. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Stojanov S and Kastner DL: Familial
autoinflammatory diseases: genetics, pathogenesis and treatment.
Curr Opin Rheumatol. 17:586–599. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kastner DL: Hereditary periodic fever
syndromes. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 74–81. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wallace SL, Robinson H, Masi AT, Decker
JL, McCarty DJ and Yü TF: Preliminary criteria for the
classification of the acute arthritis of primary gout. Arthritis
Rheum. 20:895–900. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J and Daly MJ:
Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps.
Bioinformatics. 21:263–265. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nakamura Y, Kambe N, Saito M, Nishikomori
R, Kim YG, Murakami M, Núñez G and Matsue H: Mast cells mediate
neutrophil recruitment and vascular leakage through the NLRP3
inflammasome in histamine-independent urticaria. J Exp Med.
206:1037–1046. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mason DR, Beck PL and Muruve DA:
Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors and
inflammasomes in the pathogenesis of non-microbial inflammation and
diseases. J Innate Immun. 4:16–30. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang CS, Shin DM and Jo EK: The Role of
NLR-related Protein 3 Inflammasome in Host Defense and Inflammatory
Diseases. Int Neurourol J. 16:2–12. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Villani AC, Lemire M, Fortin G, Louis E,
Silverberg MS, et al: Common variants in the NLRP3 region
contribute to Crohn’s disease susceptibility. Nat Genet. 41:71–76.
2009.
|
|
32
|
Vandanmagsar B, Youm YH, Ravussin A,
Galgani JE, Stadler K, et al: The NLRP3 inflammasome instigates
obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Nat Med.
17:179–188. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Serlin DM, Kuang PP, Subramanian M,
O’Regan A, Li X, Berman JS and Goldstein RH: Interleukin-1beta
induces osteopontin expression in pulmonary fibroblasts. J Cell
Biochem. 97:519–529. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Qu Y, Ramachandra L, Mohr S, Franchi L,
Harding CV, Nunez G and Dubyak GR: P2X7 receptor-stimulated
secretion of MHC class II-containing exosomes requires the
ASC/NLRP3 inflammasome but is independent of caspase-1. J Immunol.
182:5052–5062. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Eisenbarth SC, Colegio OR, O’Connor W,
Sutterwala FS and Flavell RA: Crucial role for the Nalp3
inflammasome in the immunostimulatory properties of aluminium
adjuvants. Nature. 453:1122–1126. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wynn TA: Fibrotic disease and the
T(H)1/T(H)2 paradigm. Nat Rev Immunol. 4:583–594. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|