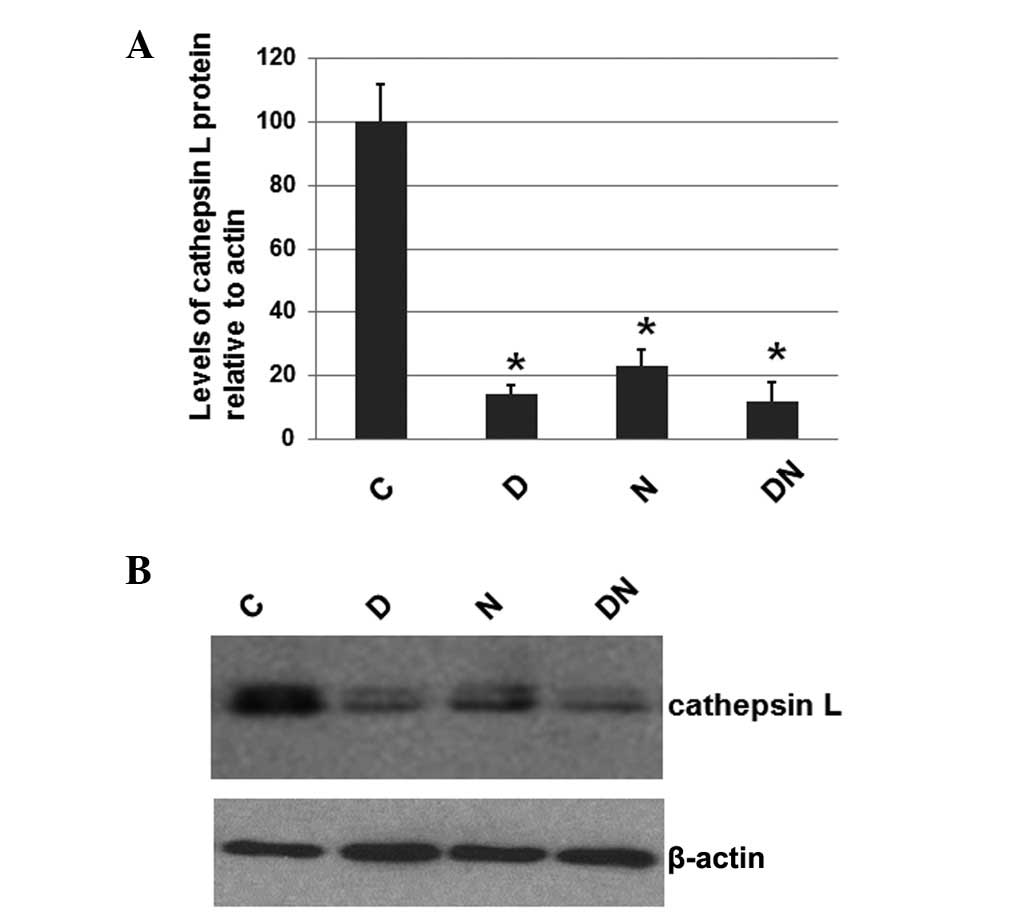
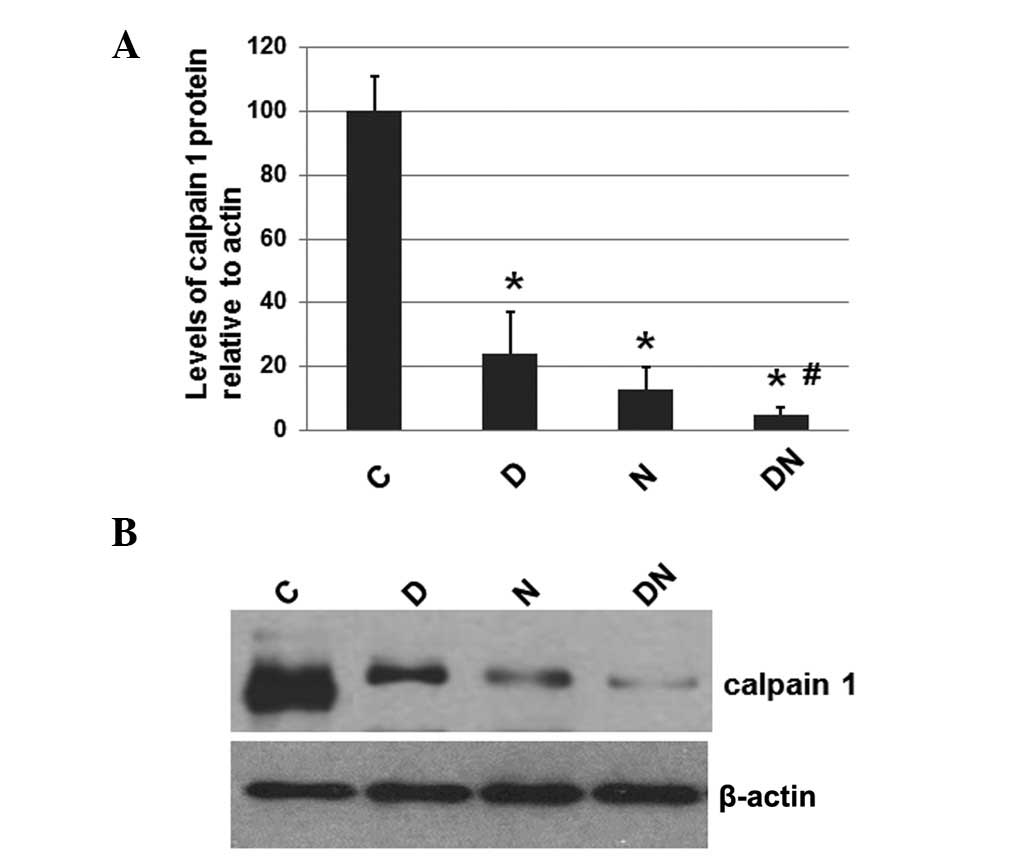
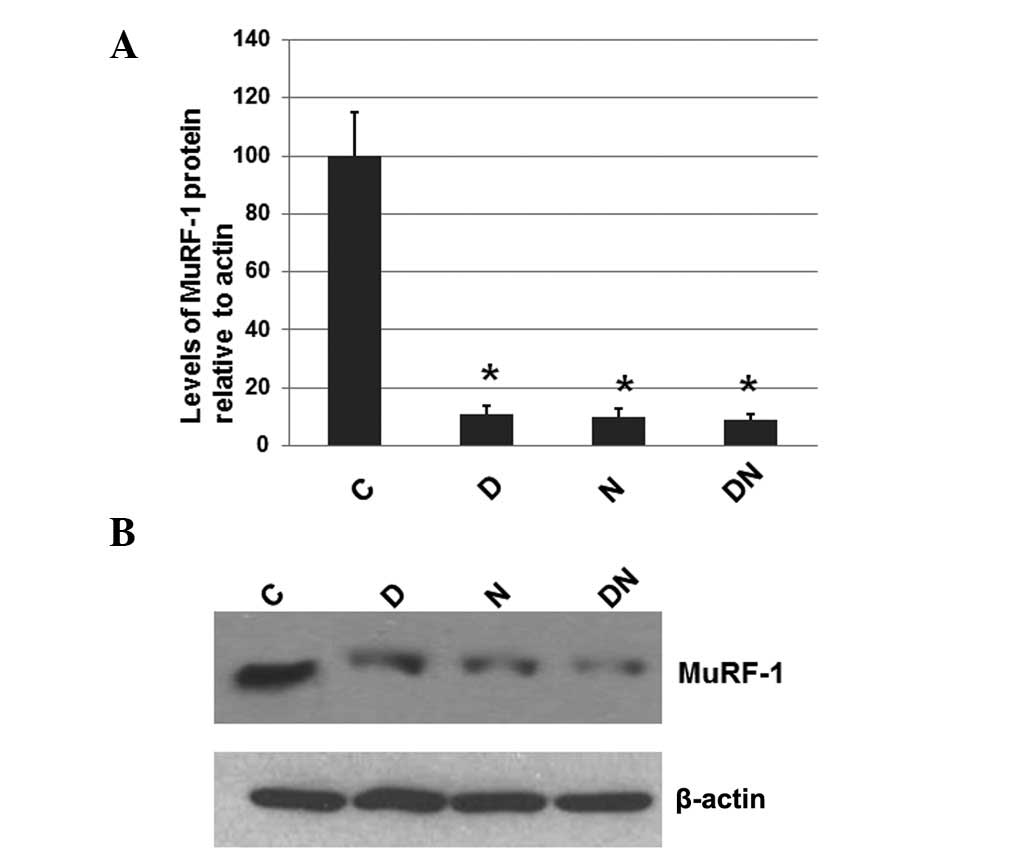
|
1
|
Dow DE, Cederna PS, Hassett CA,
Kostrominova TY, Faulkner JA and Dennis RG: Number of contractions
to maintain mass and force of a denervated rat muscle. Muscle
Nerve. 30:77–86. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Russo TL, Peviani SM, Freria CM,
Gigo-Benato D, Geuna S and Salvini TF: Electrical stimulation based
on chronaxie reduces atrogin-1 and myoD gene expressions in
denervated rat muscle. Muscle Nerve. 35:87–97. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fujita N, Fujimoto T, Tasaki H, Arakawa T,
Matsubara T and Miki A: Influence of muscle length on muscle
atrophy in the mouse tibialis anterior and soleus muscles. Biomed
Res. 30:39–45. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fujita N, Arakawa T, Matsubara T, Ando H
and Miki A: Influence of fixed muscle length and contractile
properties on atrophy and subsequent recovery in the rat soleus and
plantaris muscles. Arch Histol Cytol. 72:151–163. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fujino H, Ishihara A, Murakami S, et al:
Protective effects of exercise preconditioning on hindlimb
unloading-induced atrophy of rat soleus muscle. Acta Physiol (Oxf).
197:65–74. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Takeda I, Fujino H, Murakami S, Kondo H,
Nagatomo F and Ishihara A: Thermal preconditioning prevents fiber
type transformation of the unloading induced-atrophied muscle in
rats. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 30:145–152. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Roy RR, Zhong H, Hodgson JA, Grossman EJ,
Siengthai B, Talmadge RJ and Edgerton VR: Influences of
electromechanical events in defining skeletal muscle properties.
Muscle Nerve. 26:238–251. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim SJ, Roy RR, Zhong H, Suzuki H, et al:
Electromechanical stimulation ameliorates inactivity-induced
adaptations in the medial gastrocnemius of adult rats. J Appl
Physiol. 103:195–205. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim SJ, Roy RR, Kim JA, Zhong H, Haddad F,
Baldwin KM and Edgerton VR: Gene expression during
inactivity-induced muscle atrophy: effects of brief bouts of a
forceful contraction countermeasure. J Appl Physiol. 105:1246–1254.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fitts RH: Effects of regular exercise
training on skeletal muscle contractile function. Am J Phys Med
Rehabil. 82:320–331. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hurst JE and Fitts RH: Hindlimb
unloading-induced muscle atrophy and loss of function: protective
effect of isometric exercise. J Appl Physiol. 95:1405–1417. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Misawa A, Shimada Y, Matsunaga T and Sato
K: The effects of therapeutic electric stimulation on acute muscle
atrophy in rats after spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil.
82:1596–1603. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Boonyarom O, Kozuka N, Matsuyama K and
Murakami S: Effect of electrical stimulation to prevent muscle
atrophy on morphologic and histologic properties of hindlimb
suspended rat hindlimb muscles. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 88:719–726.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dennis RG, Dow DE and Faulkner JA: An
implantable device for stimulation of denervated muscles in rats.
Med Eng Phys. 25:239–253. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fujita N, Murakami S, Arakawa T, Miki A
and Fujino H: The combined effect of electrical stimulation and
resistance isometric contraction on muscle atrophy in rat tibialis
anterior muscle. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 11:74–79. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jackman RW and Kandarian SC: The molecular
basis of skeletal muscle atrophy. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
287:C834–C843. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Glickman MH and Ciechanover A: The
ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway: destruction for the sake
of construction. Physiol Rev. 82:373–428. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Taillandier D, Aurousseau E, Meynial-Denis
D, et al: Coordinate activation of lysosomal,
Ca2+-activated and ATP-ubiquitin-dependent proteinases
in the unweighted rat soleus muscle. Biochem J. 316:65–72.
1996.
|
|
19
|
Fortuna R, Horisberger M, Vaz MA, Van der
Marel R and Herzog W: The effects of electrical stimulation
exercise on muscles injected with botulinum toxin type-A (botox). J
Biomech. 46:36–42. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Clair-Auger JM, Lagerquist O and Collins
DF: Depression and recovery of reflex amplitude during electrical
stimulation after spinal cord injury. Clin Neurophysiol.
124:723–731. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lagerquist O, Mang CS and Collins DF:
Changes in spinal but not cortical excitability following combined
electrical stimulation of the tibial nerve and voluntary
plantar-flexion. Exp Brain Res. 222:41–53. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wall BT, Dirks ML, Verdijk LB, et al:
Neuromuscular electrical stimulation increases muscle protein
synthesis in elderly type 2 diabetic men. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 303:E614–E623. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang J, Lu L, Zhang J, et al: Electrical
stimulation to conductive scaffold promotes axonal regeneration and
remyelination in a rat model of large nerve defect. PLoS One.
7:e395262012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Santoro GA, Infantino A, Cancian L,
Battistella G and Di Falco G: Sacral nerve stimulation for fecal
incontinence related to external sphincter atrophy. Dis Colon
Rectum. 55:797–805. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|