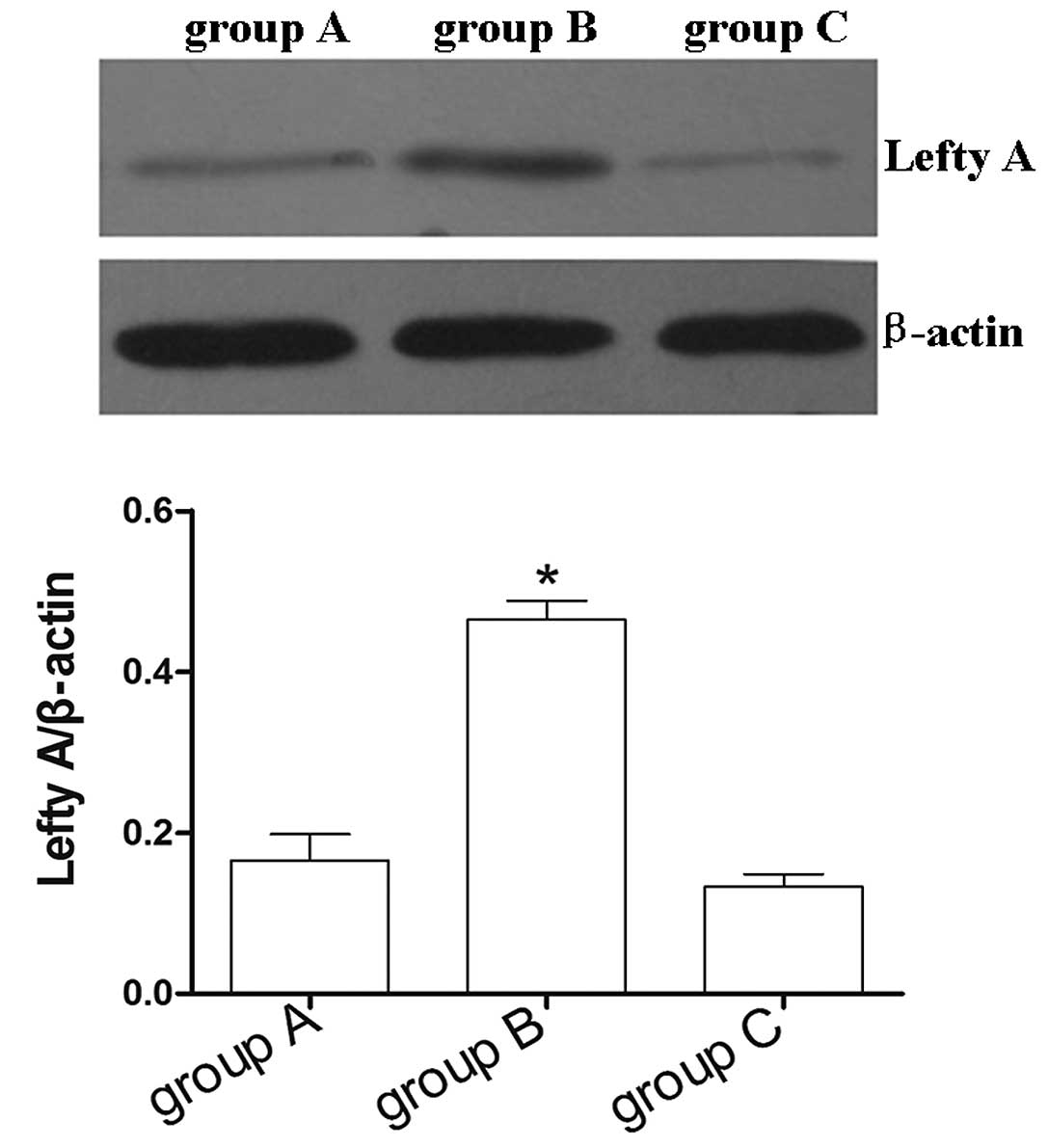
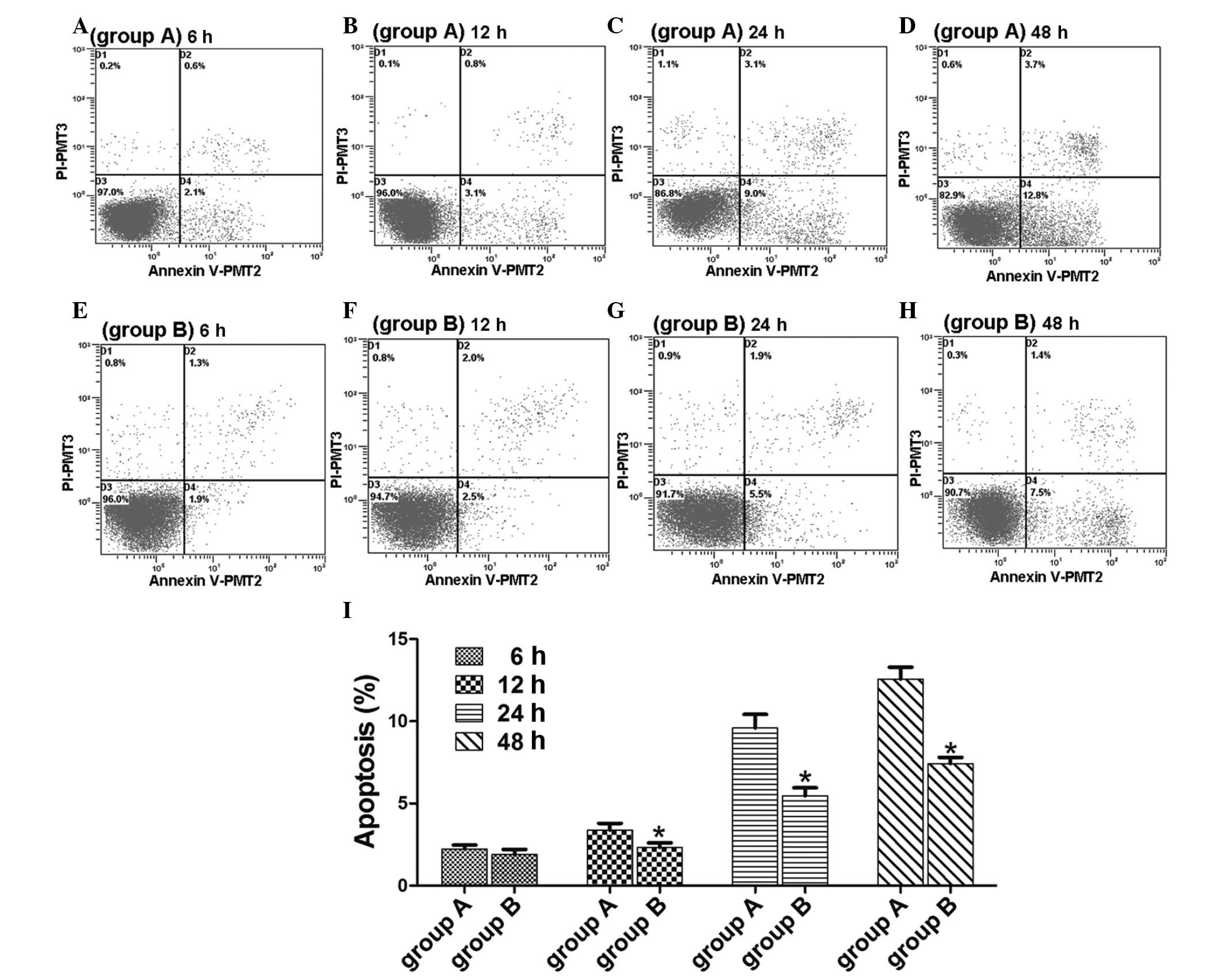
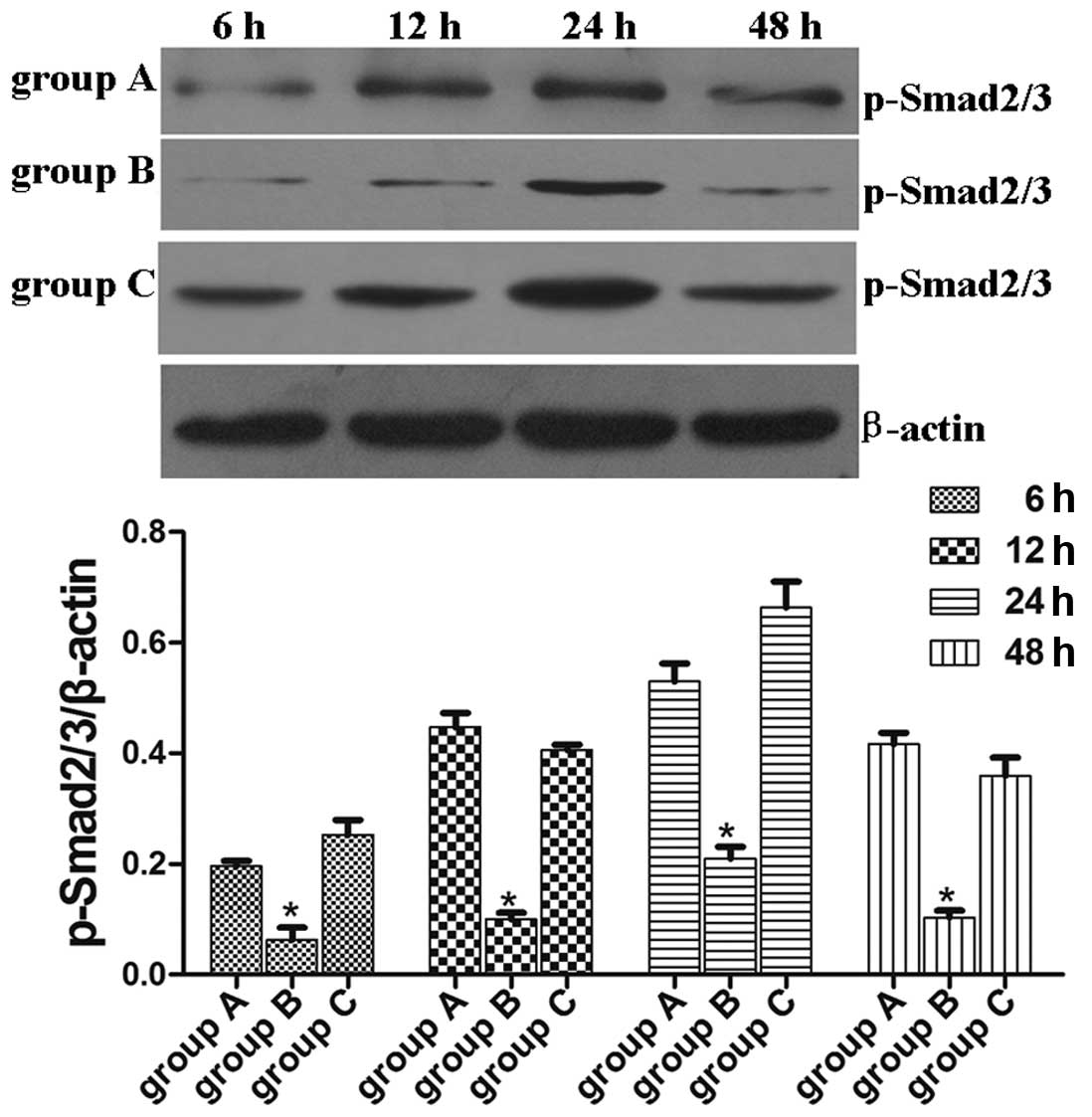
|
1
|
Padanilam BJ: Cell death induced by acute
renal injury: a perspective on the contributions of apoptosis and
necrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 284:F608–F627. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Carson DA and Ribeiro JM: Apoptosis and
disease. Lancet. 341:1251–1254. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sánchez-Capelo A: Dual role for TGF-beta1
in apoptosis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16:15–34. 2005.
|
|
4
|
Rana A, Sathyanarayana P and Lieberthal W:
Role of apoptosis of renal tubular cells in acute renal failure:
therapeutic implications. Apoptosis. 6:83–102. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Havasi A and Borkan SC: Apoptosis and
acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 80:29–40. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Razzaque MS, Ahsan N and Taguchi T: Role
of apoptosis in fibrogenesis. Nephron. 90:365–372. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zeisberg M, Strutz F and Müller GA: Renal
fibrosis: an update. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 10:315–320. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Böttinger EP and Bitzer M: TGF-beta
signaling in renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 13:2600–2610.
2002.
|
|
9
|
Kopp JB: TGF-beta signaling and the renal
tubular epithelial cell: too much, too little, and just right. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 21:1241–1243. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Meno C, Ito Y, Saijoh Y, et al: Two
closely-related left-right asymmetrically expressed genes, lefty-1
and lefty-2: their distinct expression domains, chromosomal linkage
and direct neuralizing activity in Xenopus embryos. Genes
Cells. 2:513–524. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Meno C, Saijoh Y, Fujii H, et al:
Left-right asymmetric expression of the TGF beta-family member
lefty in mouse embryos. Nature. 381:151–155. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kothapalli R, Buyuksal I, Wu SQ, Chegini N
and Tabibzadeh S: Detection of ebaf, a novel human gene of the
transforming growth factor beta superfamily association of gene
expression with endometrial bleeding. J Clin Invest. 99:2342–2350.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kosaki K, Bassi MT, Kosaki R, et al:
Characterization and mutation analysis of human LEFTY A and LEFTY
B, homologues of murine genes implicated in left-right axis
development. Am J Hum Genet. 64:712–721. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hamada H, Meno C, Watanabe D and Saijoh Y:
Establishment of vertebrate left-right asymmetry. Nat Rev Genet.
3:103–113. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dvash T, Mayshar Y, Darr H, et al:
Temporal gene expression during differentiation of human embryonic
stem cells and embryoid bodies. Hum Reprod. 19:2875–2883. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Marjoram L and Wright C: Rapid
differential transport of Nodal and Lefty on sulfated
proteoglycan-rich extracellular matrix regulates left-right
asymmetry in Xenopus. Development. 138:475–485. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ulloa L and Tabibzadeh S: Lefty inhibits
receptor-regulated Smad phosphorylation induced by the activated
transforming growth factor-beta receptor. J Biol Chem.
276:21397–21404. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mason JM, Xu HP, Rao SK, et al: Lefty
contributes to the remodeling of extracellular matrix by inhibition
of connective tissue growth factor and collagen mRNA expression and
increased proteolytic activity in a fibrosarcoma model. J Biol
Chem. 277:407–415. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Miyajima A, Chen J, Lawrence C, et al:
Antibody to transforming growth factor-beta ameliorates tubular
apoptosis in unilateral ureteral obstruction. Kidney Int.
58:2301–2313. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dai C, Yang J and Liu Y: Transforming
growth factor-beta1 potentiates renal tubular epithelial cell death
by a mechanism independent of Smad signaling. J Biol Chem.
278:12537–12545. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li Y, Ge Y, Liu FY, et al: Norcantharidin,
a protective therapeutic agent in renal tubulointerstitial
fibrosis. Mol Cell Biochem. 361:79–83. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang X, Sun W, Zhang C, et al: TGF-beta1
inhibits the growth and metastasis of tongue squamous carcinoma
cells through Smad4. Gene. 485:160–166. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li J, Deane JA, Campanale NV, Bertram JF
and Ricardo SD: Blockade of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
and TGF-beta1/Smad signaling pathways rescues bone marrow-derived
peritubular capillary endothelial cells in adriamycin-induced
nephrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 17:2799–2811. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Inazaki K, Kanamaru Y, Kojima Y, et al:
Smad3 deficiency attenuates renal fibrosis, inflammation, and
apoptosis after unilateral ureteral obstruction. Kidney Int.
66:597–604. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang YJ, Mei YM, Wang YQ, et al:
Transfection and expression of Smad7 inhibits transforming growth
factor-β1 effects on renal tubular cells (Chinese). J Third
Military Medical University. 25:1049–1052. 2003.
|