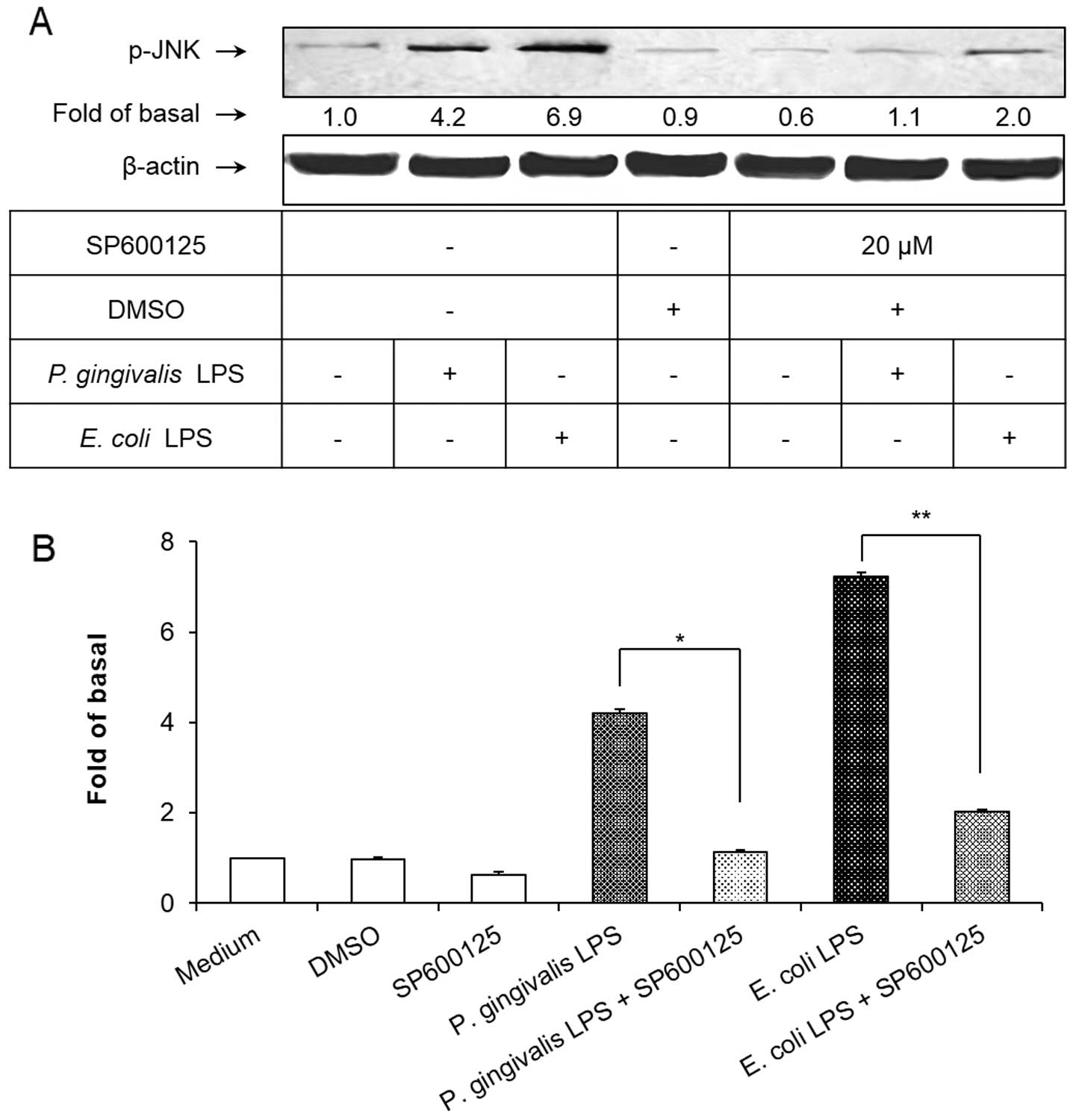
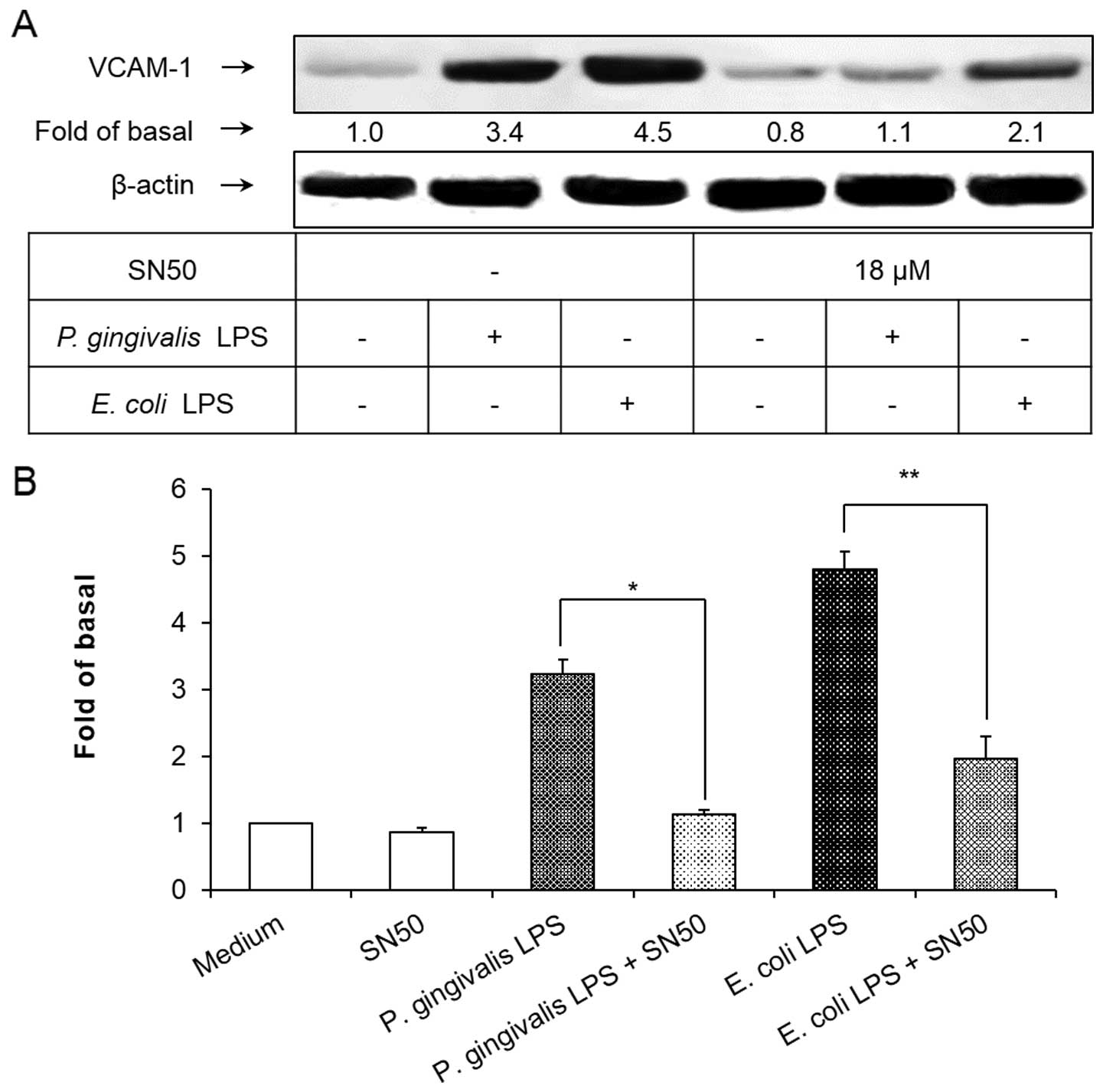
|
1
|
Lalla E, Lamster IB, Hofmann MA, et al:
Oral infection with a periodontal pathogen accelerates early
atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-null mice. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 23:1405–1411. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cavrini F, Sambri V, Moter A, et al:
Molecular detection of Treponema denticola and
Porphyromonas gingivalis in carotid and aortic atheromatous
plaques by FISH: report of two cases. J Med Microbiol. 54:93–96.
2005.
|
|
3
|
Zhang MZ, Li CL, Jiang YT, et al:
Porphyromonas gingivalis infection accelerates intimal
thickening in iliac arteries in a balloon-injured rabbit model. J
Periodontol. 79:1192–1199. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Liu B, Cheng L, Liu D, et al: Role of p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in Porphyromonas
gingivalis lipopolysaccharide-induced VCAM-1 expression in
human aortic endothelial cells. J Periodontol. 83:955–962. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Raetz CR: Biochemistry of endotoxins. Annu
Rev Biochem. 59:129–170. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rice JB, Stoll LL, Li WG, et al: Low-level
endotoxin induces potent inflammatory activation of human blood
vessels: inhibition by statins. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
23:1576–1582. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stoll LL, Denning GM and Weintraub NL:
Potential role of endotoxin as a proinflammatory mediator of
atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 24:2227–2236. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Holt SC, Kesavalu L, Walker S and Genco
CA: Virulence factors of Porphyromonas gingivalis.
Periodontol 2000. 20:168–238. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Geerts SO, Nys M, De MP, et al: Systemic
release of endotoxins induced by gentle mastication: association
with periodontitis severity. J Periodontol. 73:73–78. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ide M, Jagdev D, Coward PY, Crook M,
Barclay GR and Wilson RF: The short-term effects of treatment of
chronic periodontitis on circulating levels of endotoxin,
C-reactive protein, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and interleukin-6.
J Periodontol. 75:420–428. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pussinen PJ, Vilkuna-Rautiainen T, Alfthan
G, et al: Severe periodontitis enhances macrophage activation via
increased serum lipopolysaccharide. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
24:2174–2180. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lafaurie GI, Mayorga-Fayad I, Torres MF,
et al: Periodontopathic microorganisms in peripheric blood after
scaling and root planing. J Clin Periodontol. 34:873–879. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Erridge C, Spickett CM and Webb DJ:
Non-enterobacterial endotoxins stimulate human coronary artery but
not venous endothelial cell activation via Toll-like receptor 2.
Cardiovasc Res. 73:181–189. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nakamura N, Yoshida M, Umeda M, et al:
Extended exposure of lipopolysaccharide fraction from
Porphyromonas gingivalis facilitates mononuclear cell
adhesion to vascular endothelium via Toll-like receptor-2 dependent
mechanism. Atherosclerosis. 196:59–67. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fries JW, Williams AJ, Atkins RC, Newman
W, Lipscomb MF and Collins T: Expression of VCAM-1 and E-selectin
in an in vivo model of endothelial activation. Am J Pathol.
143:725–737. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cybulsky MI, Iiyama K, Li H, et al: A
major role for VCAM-1, but not ICAM-1, in early atherosclerosis. J
Clin Invest. 107:1255–1262. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ley K and Huo Y: VCAM-1 is critical in
atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest. 107:1209–1210. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang CC, Lin WN, Lee CW, et al:
Involvement of p42/p44 MAPK, p38 MAPK, JNK, and NF-kappaB in
IL-1beta-induced VCAM-1 expression in human tracheal smooth muscle
cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 288:L227–L237. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee CW, Lin WN, Lin CC, et al:
Transcriptional regulation of VCAM-1 expression by tumor necrosis
factor-alpha in human tracheal smooth muscle cells: involvement of
MAPKs, NF-kappaB, p300, and histone acetylation. J Cell Physiol.
207:174–186. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Binion DG, Heidemann J, Li MS, Nelson VM,
Otterson MF and Rafiee P: Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1
expression in human intestinal microvascular endothelial cells is
regulated by PI 3-kinase/Akt/MAPK/NF-kappaB: inhibitory role of
curcumin. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 297:G259–G268.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shan Y, Lin N, Yang X, et al:
Sulphoraphane inhibited the expressions of intercellular adhesion
molecule-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 through
MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor-4 pathway in cultured
endothelial cells. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 22:215–222. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Han J, Lee JD, Bibbs L and Ulevitch RJ: A
MAP kinase targeted by endotoxin and hyperosmolarity in mammalian
cells. Science. 265:808–811. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang Y, Chen C, Li Z, et al:
Characterization of the structure and function of a new
mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38beta). J Biol Chem.
271:17920–17926. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang Y, Gram H, Zhao M, et al:
Characterization of the structure and function of the fourth member
of p38 group mitogen-activated protein kinases, p38delta. J Biol
Chem. 272:30122–30128. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Schaeffer HJ and Weber MJ:
Mitogen-activated protein kinases: specific messages from
ubiquitous messengers. Mol Cell Biol. 19:2435–2444. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lin WN, Luo SF, Lee CW, Wang CC, Wang JS
and Yang CM: Involvement of MAPKs and NF-kappaB in LPS-induced
VCAM-1 expression in human tracheal smooth muscle cells. Cell
Signal. 19:1258–1267. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Watanabe K, Yilmaz O, Nakhjiri SF, Belton
CM and Lamont RJ: Association of mitogen-activated protein kinase
pathways with gingival epithelial cell responses to
Porphyromonas gingivalis infection. Infect Immun.
69:6731–6737. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Choi EK, Park SA, Oh WM, et al: Mechanisms
of Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced monocyte chemoattractant
protein-1 expression in endothelial cells. FEMS Immunol Med
Microbiol. 44:51–58. 2005.
|
|
29
|
Lee SD, Wu CC, Kuo WW, et al:
Porphyromonas gingivalis-related cardiac cell apoptosis was
majorly co-activated by p38 and extracellular signal-regulated
kinase pathways. J Periodontal Res. 41:39–46. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lazaar AL, Albelda SM, Pilewski JM,
Brennan B, Pure E and Panettieri RA Jr: T lymphocytes adhere to
airway smooth muscle cells via integrins and CD44 and induce smooth
muscle cell DNA synthesis. J Exp Med. 180:807–816. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hamada S, Koga T, Nishihara T, Fujiwara T
and Okahashi N: Characterization and immunobiologic activities of
lipopolysaccharides from periodontal bacteria. Adv Dent Res.
2:284–291. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ogawa T and Yagi T: Bioactive mechanism of
Porphyromonas gingivalis lipid A. Periodontol 2000.
54:71–77. 2010.
|
|
33
|
Bennett BL, Sasaki DT, Murray BW, et al:
SP600125, an anthrapyrazolone inhibitor of Jun N-terminal kinase.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:13681–13686. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lin YZ, Yao SY, Veach RA, Torgerson TR and
Hawiger J: Inhibition of nuclear translocation of transcription
factor NF-kappa B by a synthetic peptide containing a cell
membrane-permeable motif and nuclear localization sequence. J Biol
Chem. 270:14255–14258. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Muller WA: Mechanisms of leukocyte
transendothelial migration. Annu Rev Pathol. 6:323–344. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Eder J: Tumour necrosis factor alpha and
interleukin 1 signalling: do MAPKK kinases connect it all? Trends
Pharmacol Sci. 18:319–322. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Robinson MJ and Cobb MH: Mitogen-activated
protein kinase pathways. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 9:180–186. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang CM, Luo SF, Wang CC, et al: Tumour
necrosis factor-alpha- and interleukin-1beta-stimulated cell
proliferation through activation of mitogen-activated protein
kinase in canine tracheal smooth muscle cells. Br J Pharmacol.
130:891–899. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Diya Z, Lili C, Shenglai L, Zhiyuan G and
Jie Y: Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) of Porphyromonas gingivalis
induces IL-1beta, TNF-alpha and IL-6 production by THP-1 cells in a
way different from that of Escherichia coli LPS. Innate
Immun. 14:99–107. 2008.
|
|
40
|
Swift MR and Weinstein BM: Arterial-venous
specification during development. Circ Res. 104:576–588. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wu X, Zou Y, Liang Y, et al: COUP-TFII
switches responses of venous endothelium to atherosclerotic factors
through controlling the profile of various inherent genes
expression. J Cell Biochem. 112:256–264. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Zhang D, Zheng H, Zhao J, et al:
Porphorymonas gingivalis induces intracellular adhesion
molecule-1 expression in endothelial cells through the nuclear
factor-kappaB pathway, but not through the p38 MAPK pathway. J
Periodontal Res. 46:31–38. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Brown J, Reading SJ, Jones S, et al:
Critical evaluation of ECV304 as a human endothelial cell model
defined by genetic analysis and functional responses: a comparison
with the human bladder cancer derived epithelial cell line T24/83.
Lab Invest. 80:37–45. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Ju JW, Kim SJ, Jun CD and Chun JS: p38
kinase and c-Jun N-terminal kinase oppositely regulates tumor
necrosis factor alpha-induced vascular cell adhesion molecule-1
expression and cell adhesion in chondrosarcoma cells. IUBMB Life.
54:293–299. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Hosokawa Y, Hosokawa I, Ozaki K, Nakae H
and Matsuo T: Cytokines differentially regulate ICAM-1 and VCAM-1
expression on human gingival fibroblasts. Clin Exp Immunol.
144:494–502. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ho AW, Wong CK and Lam CW: Tumor necrosis
factor-alpha up-regulates the expression of CCL2 and adhesion
molecules of human proximal tubular epithelial cells through MAPK
signaling pathways. Immunobiology. 213:533–544. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Newton R, Kuitert LM, Bergmann M, Adcock
IM and Barnes PJ: Evidence for involvement of NF-kappaB in the
transcriptional control of COX-2 gene expression by IL-1beta.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 237:28–32. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen CC, Chen JJ and Chou CY: Protein
kinase calpha but not p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinase, p38,
or c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase is required for intercellular
adhesion molecule-1 expression mediated by interleukin-1beta:
involvement of sequential activation of tyrosine kinase, nuclear
factor-kappaB-inducing kinase, and IkappaB kinase 2. Mol Pharmacol.
58:1479–1489. 2000.
|
|
49
|
Guha M and Mackman N: LPS induction of
gene expression in human monocytes. Cell Signal. 13:85–94. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bian ZM, Elner SG, Yoshida A, Kunkel SL,
Su J and Elner VM: Activation of p38, ERK1/2 and NIK pathways is
required for IL-1beta and TNF-alpha-induced chemokine expression in
human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Exp Eye Res. 73:111–121.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|