Spandidos Publications style
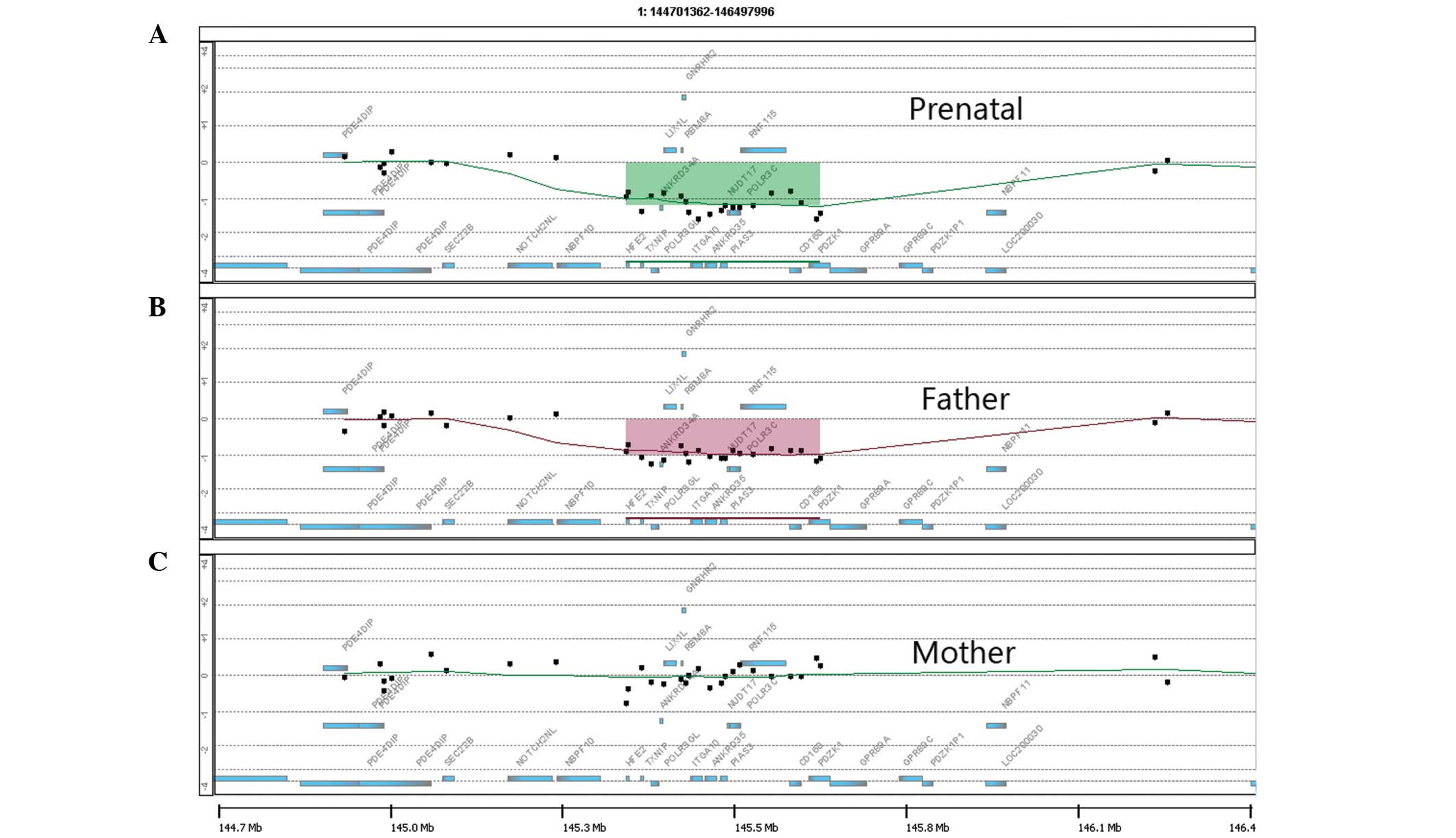
Papoulidis I, Oikonomidou E, Orru S, Siomou E, Kontodiou M, Eleftheriades M, Bacoulas V, Cigudosa JC, Suela J, Thomaidis L, Thomaidis L, et al: Prenatal detection of TAR syndrome in a fetus with compound inheritance of an RBM8A SNP and a 334‑kb deletion: A case report. Mol Med Rep 9: 163-165, 2014.
APA
Papoulidis, I., Oikonomidou, E., Orru, S., Siomou, E., Kontodiou, M., Eleftheriades, M. ... Manolakos, E. (2014). Prenatal detection of TAR syndrome in a fetus with compound inheritance of an RBM8A SNP and a 334‑kb deletion: A case report. Molecular Medicine Reports, 9, 163-165. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2013.1788
MLA
Papoulidis, I., Oikonomidou, E., Orru, S., Siomou, E., Kontodiou, M., Eleftheriades, M., Bacoulas, V., Cigudosa, J. C., Suela, J., Thomaidis, L., Manolakos, E."Prenatal detection of TAR syndrome in a fetus with compound inheritance of an RBM8A SNP and a 334‑kb deletion: A case report". Molecular Medicine Reports 9.1 (2014): 163-165.
Chicago
Papoulidis, I., Oikonomidou, E., Orru, S., Siomou, E., Kontodiou, M., Eleftheriades, M., Bacoulas, V., Cigudosa, J. C., Suela, J., Thomaidis, L., Manolakos, E."Prenatal detection of TAR syndrome in a fetus with compound inheritance of an RBM8A SNP and a 334‑kb deletion: A case report". Molecular Medicine Reports 9, no. 1 (2014): 163-165. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2013.1788