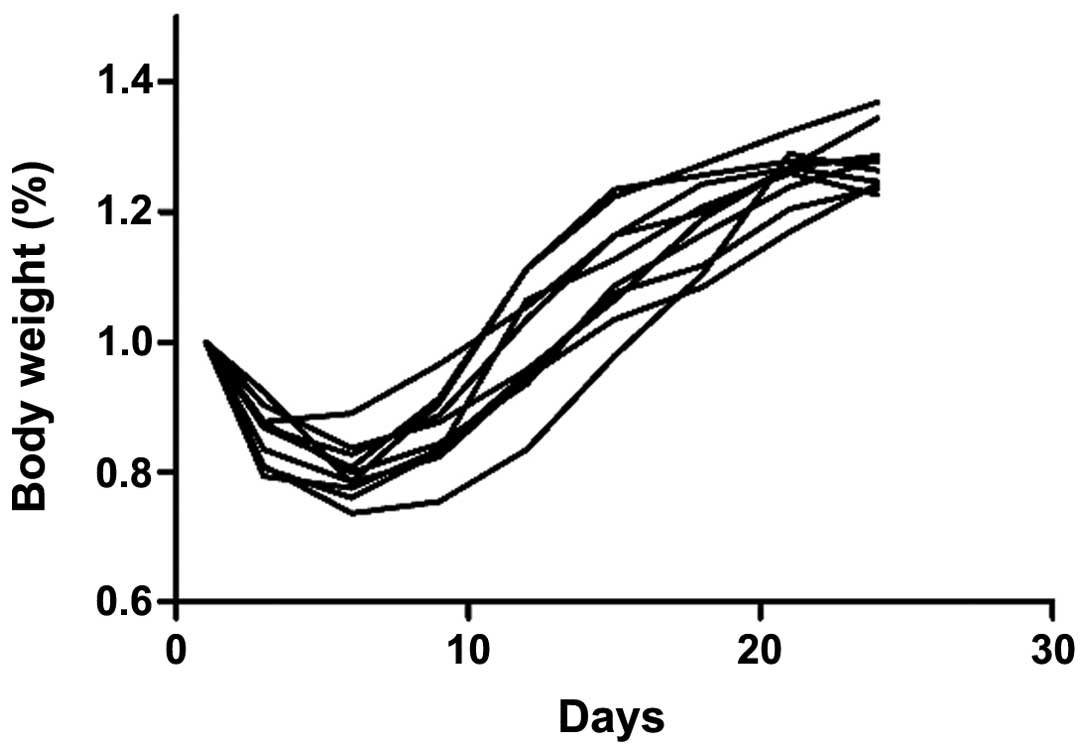
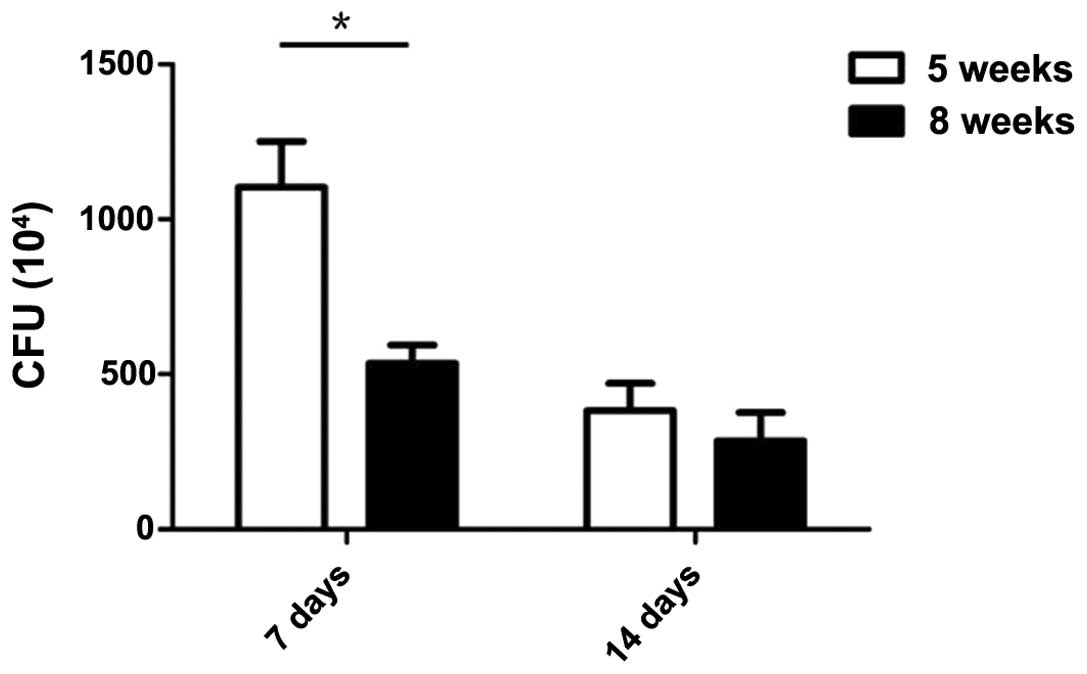
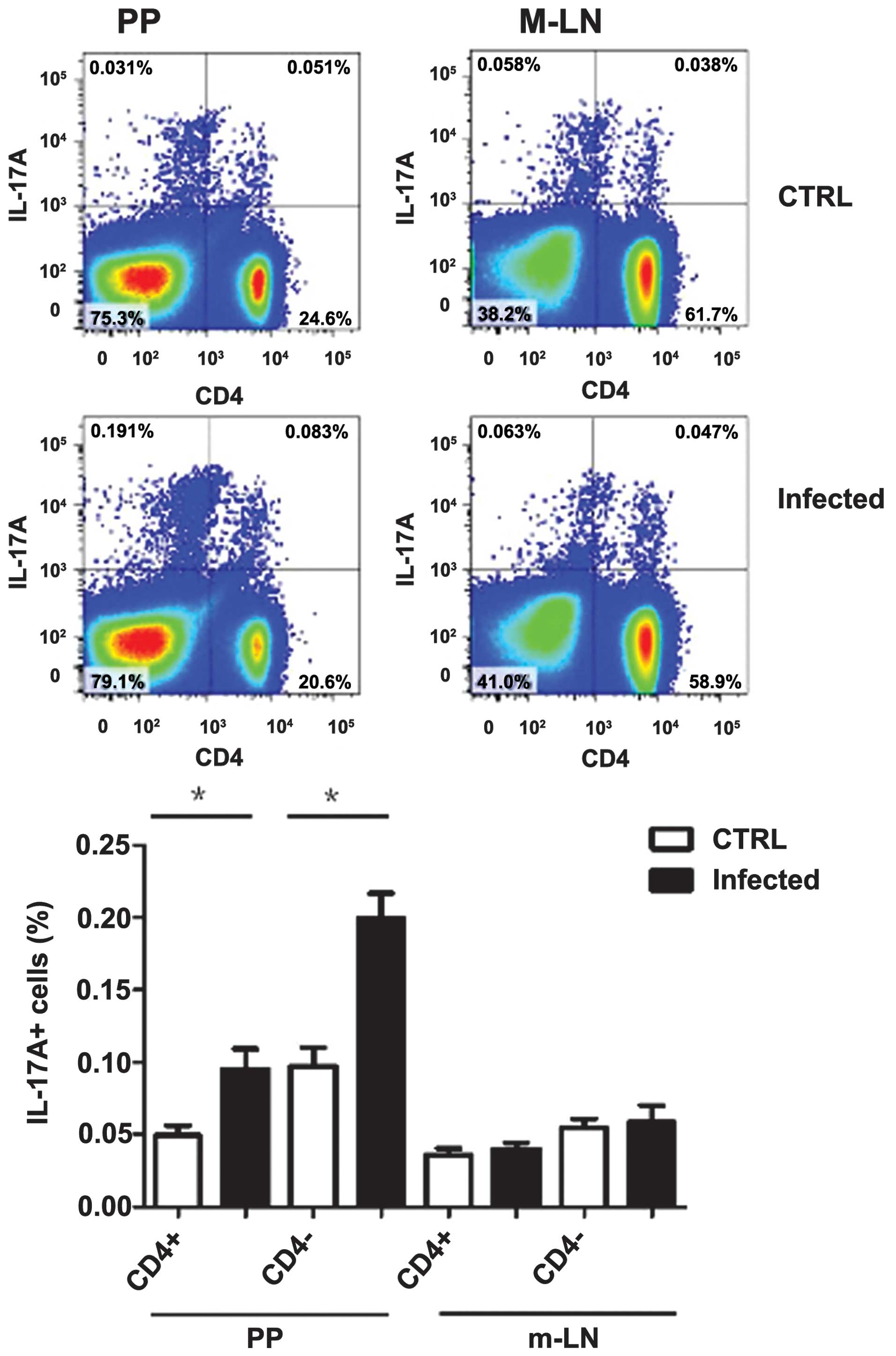
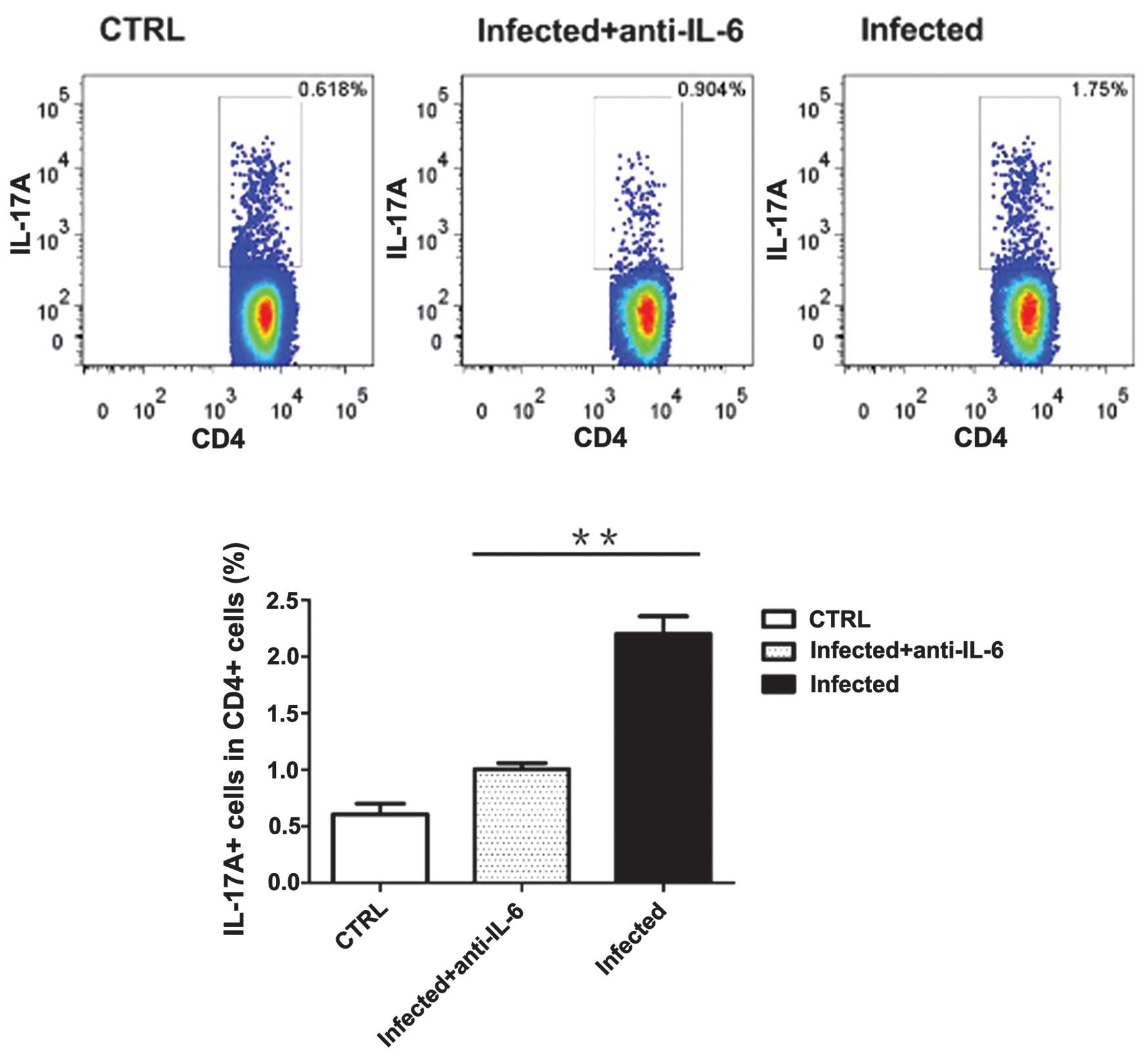
Spandidos Publications style
Li L, Shi QG, Lin F, Liang YG, Sun LJ, Mu JS, Wang YG, Su HB, Xu B, Ji CC, Ji CC, et al: Cytokine IL‑6 is required in Citrobacter rodentium infection‑induced intestinal Th17 responses and promotes IL‑22 expression in inflammatory bowel disease. Mol Med Rep 9: 831-836, 2014.
APA
Li, L., Shi, Q., Lin, F., Liang, Y., Sun, L., Mu, J. ... Wang, H. (2014). Cytokine IL‑6 is required in Citrobacter rodentium infection‑induced intestinal Th17 responses and promotes IL‑22 expression in inflammatory bowel disease. Molecular Medicine Reports, 9, 831-836. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2014.1898
MLA
Li, L., Shi, Q., Lin, F., Liang, Y., Sun, L., Mu, J., Wang, Y., Su, H., Xu, B., Ji, C., Huang, H., Li, K., Wang, H."Cytokine IL‑6 is required in Citrobacter rodentium infection‑induced intestinal Th17 responses and promotes IL‑22 expression in inflammatory bowel disease". Molecular Medicine Reports 9.3 (2014): 831-836.
Chicago
Li, L., Shi, Q., Lin, F., Liang, Y., Sun, L., Mu, J., Wang, Y., Su, H., Xu, B., Ji, C., Huang, H., Li, K., Wang, H."Cytokine IL‑6 is required in Citrobacter rodentium infection‑induced intestinal Th17 responses and promotes IL‑22 expression in inflammatory bowel disease". Molecular Medicine Reports 9, no. 3 (2014): 831-836. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2014.1898