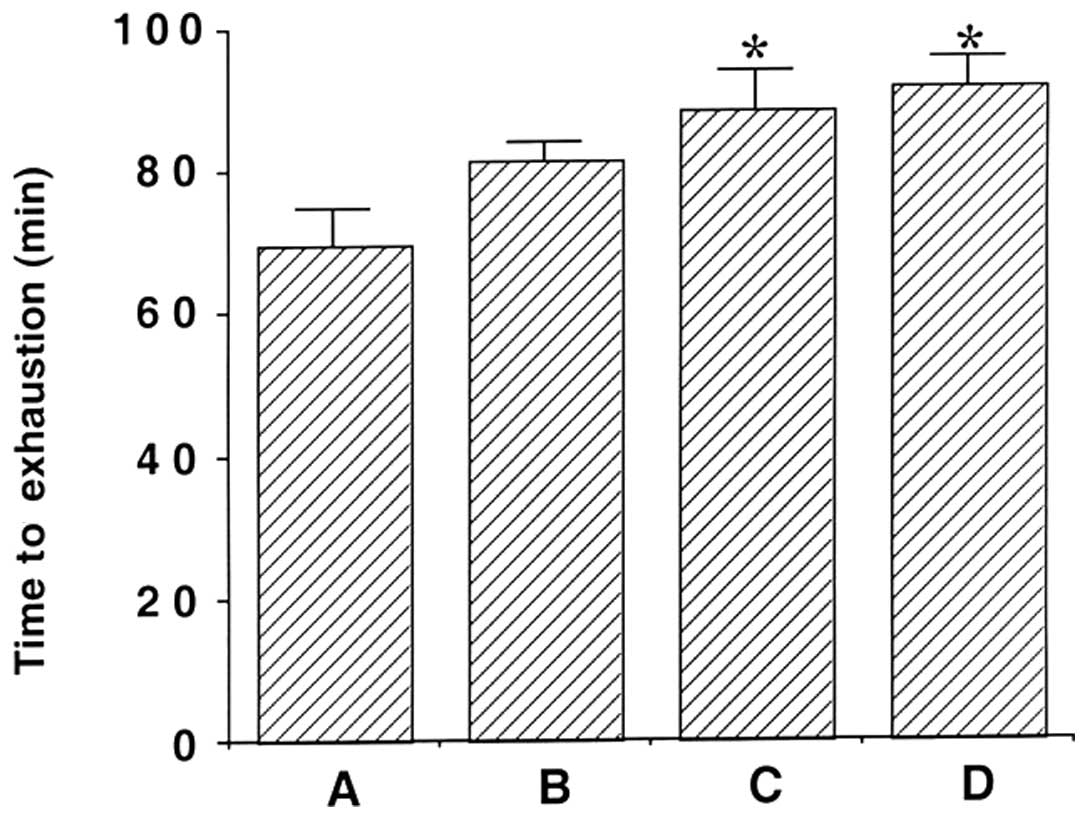
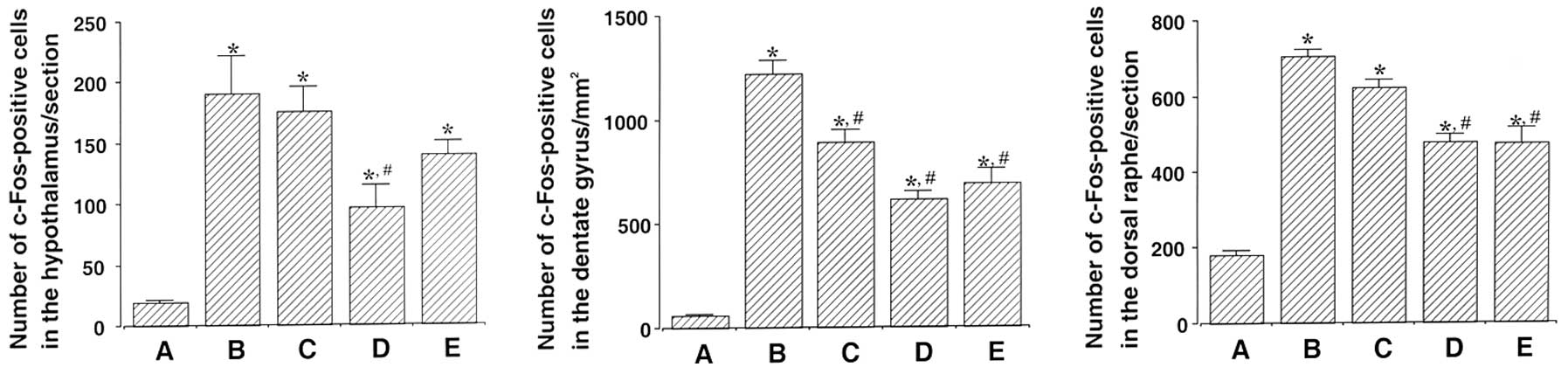
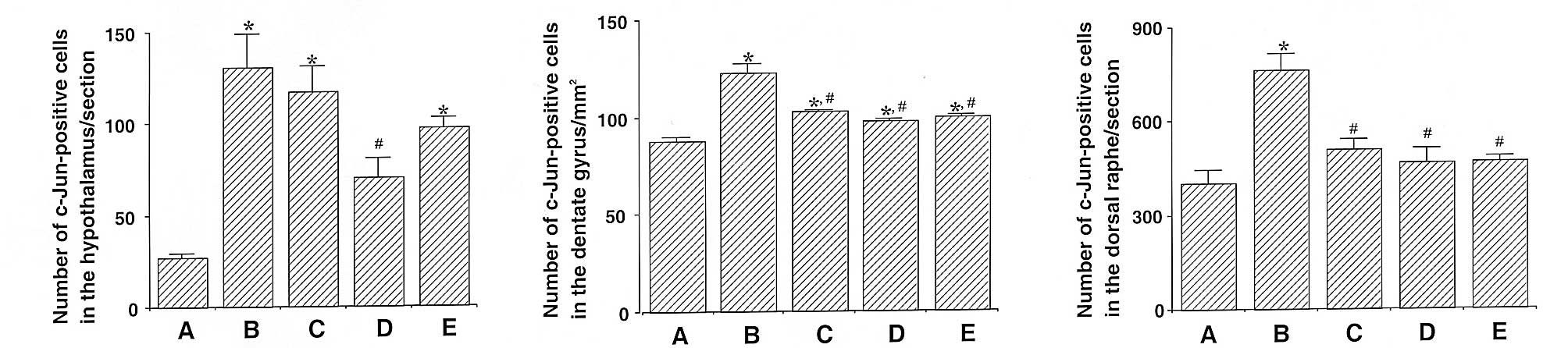
|
1
|
Schreiber SS, Tocco G, Shors TJ and
Thompson RF: Activation of immediate early genes after acute
stress. Neuroreport. 2:17–20. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Honkaniemi J, Kainu T, Ceccatelli S,
Rechardt L, Hökfelt T and Pelto-Huikko M: Fos and jun in rat
central amygdaloid nucleus and paraventricular nucleus after
stress. Neuroreport. 3:849–852. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zamora-González EO, Santerre A,
Palomera-Avalos V and Morales-Villagrán A: A chronic combinatory
stress model that activates the HPA axis and avoids habituation in
BALB/C mice. J Neurosci Methods. 213:70–75. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Imaki T, Shibasaki T, Chikada N, Harada S,
Naruse M and Demura H: Different expression of immediate-early
genes in the rat paraventricular nucleus induced by stress:
relation to corticotropin-releasing factor gene transcription.
Endocr J. 43:629–638. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Singewald N, Salchner P and Sharp T:
Induction of c-Fos expression in specific areas of the fear
circuitry in rat forebrain by anxiogenic drugs. Biol Psychiatry.
53:275–283. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Soya H, Mukai A, Deocaris CC, Ohiwa N,
Chang H, Nishijima T, Fujikawa T, Togashi K and Saito T:
Threshold-like pattern of neuronal activation in the hypothalamus
during treadmill running: establishment of a minimum running stress
(MRS) rat model. Neurosci Res. 58:341–348. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kovary K and Bravo R: Expression of
different Jun and Fos proteins during the G0-to-G1 transition in
mouse fibroblasts: in vitro and in vivo associations. Mol Cell
Biol. 11:2451–2459. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kovary K and Bravo R: The jun and fos
protein families are both required for cell cycle progression in
fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 11:4466–4472. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Caubet JF: c-fos proto-oncogene expression
in the nervous system during mouse development. Mol Cell Biol.
9:2269–2272. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wilkinson DG, Bhatt S, Ryseck RP and Bravo
R: Tissue-specific expression of c-jun and junB during
organogenesis in the mouse. Development. 106:465–471.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Akins PT, Liu PK and Hsu CY: Immediate
early gene expression in response to cerebral ischemia. Friend or
foe? Stroke. 27:1682–1687. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sheng M and Greenberg ME: The regulation
and function of c-fos and other immediate early genes in the
nervous system. Neuron. 4:477–485. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Jung JA, Yoo KS and Hwang KK: Changes of
c-Fos immunoreactivity in midbrain by deep pain and effects of
aspirin. Korean J Pediatr. 46:695–701. 2003.
|
|
14
|
Seo JH, Kim TW, Kim CJ, Sung YH and Lee
SJ: Treadmill exercise during pregnancy ameliorates post-traumatic
stress disorder-induced anxiety-like responses in maternal rats.
Mol Med Rep. 7:389–395. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kohut ML, Boehm GW and Moynihan JA:
Prolonged exercise suppresses antigen-specific cytokine response to
upper respiratory infection. J Appl Physiol (1985). 90:678–684.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pedersen BK and Hoffman-Goetz L: Exercise
and the immune system: regulation, integration, and adaptation.
Physiol Rev. 80:1055–1081. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hong JA, Chung SH, Lee JS, Kim SS, Shin
HD, Kim H, Jang MH, Lee TH, Lim BV, Kim YP and Kim CJ: Effects of
Paeonia radix on 5-hydroxytryptamine synthesis and tryptophan
hydroxylase expression in the dorsal raphe of exercised rats. Biol
Pharm Bull. 26:166–169. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lim BV, Jang MH, Shin MC, Kim HB, Kim YJ,
Kim YP, Chung JH, Kim H, Shin MS, Kim SS, et al: Caffeine inhibits
exercise-induced increase in tryptophan hydroxylase expression in
dorsal and median raphe of Sprague-Dawley rats. Neurosci Lett.
308:25–28. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Seo JH, Sung YH, Kim KJ, Shin MS, Lee EK
and Kim CJ: Effects of Phellinus linteus administration on
serotonin synthesis in the brain and expression of monocarboxylate
transporters in the muscle during exhaustive exercise in rats. J
Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 57:95–103. 2011.
|
|
20
|
Lee MK, Lim HH, Song YK, Ko IG, Kim H,
Shin MS, Lee TH, Kim CJ, Joo KJ, Park JK and Choi HH: Effects of
the mixture of red ginseng and Paeonia radix on the treadmill
running and swimming exercise in rats. J Exerc Nutr Biochem.
10:255–263. 2006.(In Korean).
|
|
21
|
Mantovani MS, Bellini MF, Angeli JP,
Oliveira RJ, Silva AF and Ribeiro LR: beta-Glucans in promoting
health: prevention against mutation and cancer. Mutat Res.
658:154–161. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rice PJ, Adams EL, Ozment-Skelton T,
Gonzalez AJ, Goldman MP, Lockhart BE, Barker LA, Breuel KF, Deponti
WK, Kalbfleisch JH, et al: Oral delivery and gastrointestinal
absorption of soluble glucans stimulate increased resistance to
infectious challenge. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 314:1079–1086. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hong F, Yan J, Baran JT, Allendorf DJ,
Hansen RD, Ostroff GR, Xing PX, Cheung NK and Ross GD: Mechanism by
which orally administered beta-1,3-glucans enhance the tumoricidal
activity of antitumor monoclonal antibodies in murine tumor models.
J Immunol. 173:797–806. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Neumann-Haefelin T, Wiessner C, Vogel P,
Back T and Hossmann KA: Differential expression of the immediate
early genes c-fos, c-jun, junB, and NGFI-B in the rat brain
following transient forebrain ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
14:206–216. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hiroi N, Brown JR, Haile CN, Ye H,
Greenberg ME and Nestler EJ: FosB mutant mice: loss of chronic
cocaine induction of Fos-related proteins and heightened
sensitivity to cocaine’s psychomotor and rewarding effects. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:10397–10402. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dragunow M and Faull R: The use of c-Fos
as a metabolic marker in neuronal pathway tracing. J Neurosci
Methods. 29:261–265. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ko IG, Kim SE, Kim CJ, Jung JH, Lee SJ,
Kim DH, Lee KY and Kim KH: Effect of treadmill exercise on
leak-point pressure and neuronal activation in brain of rats with
stress urinary incontinence. Int Neurourol J. 14:141–148. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hoene M, Franken H, Fritsche L, Lehmann R,
Pohl AK, Häring HU, Zell A, Schleicher ED and Weigert C: Activation
of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signalling pathway
in the liver of mice is related to plasma glucose levels after
acute exercise. Diabetologia. 53:1131–1141. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Han SB, Lee CW, Jeon YJ, Hong ND, Yoo ID,
Yang KH and Kim HM: The inhibitory effect of polysaccharides
isolated from Phellinus linteus on tumor growth and
metastasis. Immunopharmacology. 41:157–164. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Song YS, Kim SH, Sa JH, Jin C, Lim CJ and
Park EH: Anti-angiogenic, antioxidant and xanthine oxidase
inhibition activities of the mushroom Phellinus linteus. J
Ethnopharmacol. 88:113–116. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim SH, Song YS, Kim SK, Kim BC, Lim CJ
and Park EH: Anti-inflammatory and related pharmacological
activities of the n-BuOH subfraction of mushroom Phellinus
linteus. J Ethnopharmacol. 93:141–146. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zaidman BZ, Yassin M, Mahajna J and Wasser
SP: Medicinal mushroom modulators of molecular targets as cancer
therapeutics. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 67:453–468. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Majtan J: Pleuran (β-glucan from
Pleurotus ostreatus): an effective nutritional supplement
against upper respiratory tract infections? Med Sport Sci.
59:57–61. 2012.
|
|
34
|
Carpenter KC, Breslin WL, Davidson T,
Adams A and McFarlin BK: Baker’s yeast β-glucan supplementation
increases monocytes and cytokines post-exercise: implications for
infection risk? Br J Nutr. 109:478–486. 2013.
|
|
35
|
Xu C, Lv J, Lo YM, Cui SW, Hu X and Fan M:
Effects of oat β-glucan on endurance exercise and its anti-fatigue
properties in trained rats. Carbohydr Polym. 92:1159–1165.
2013.
|