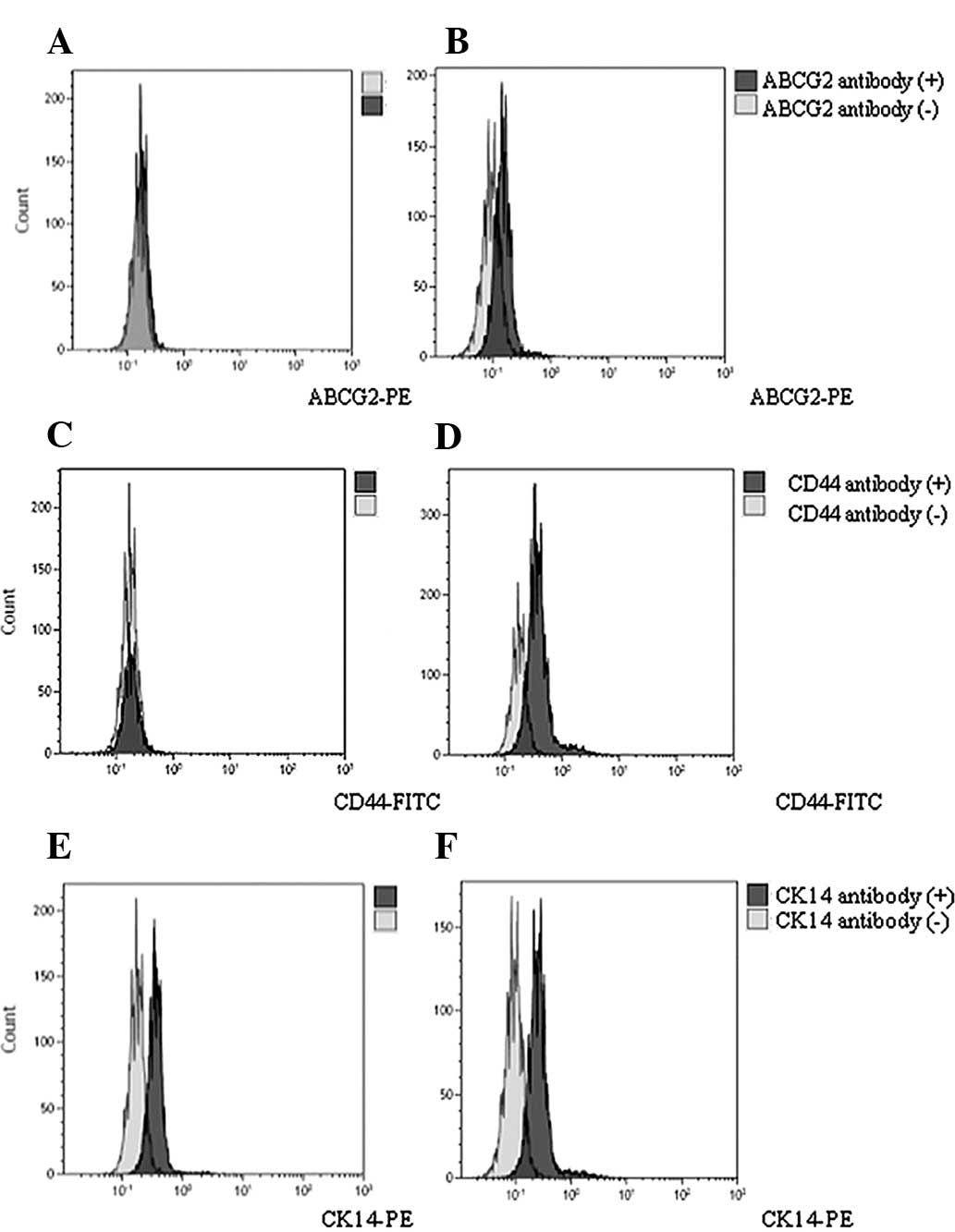
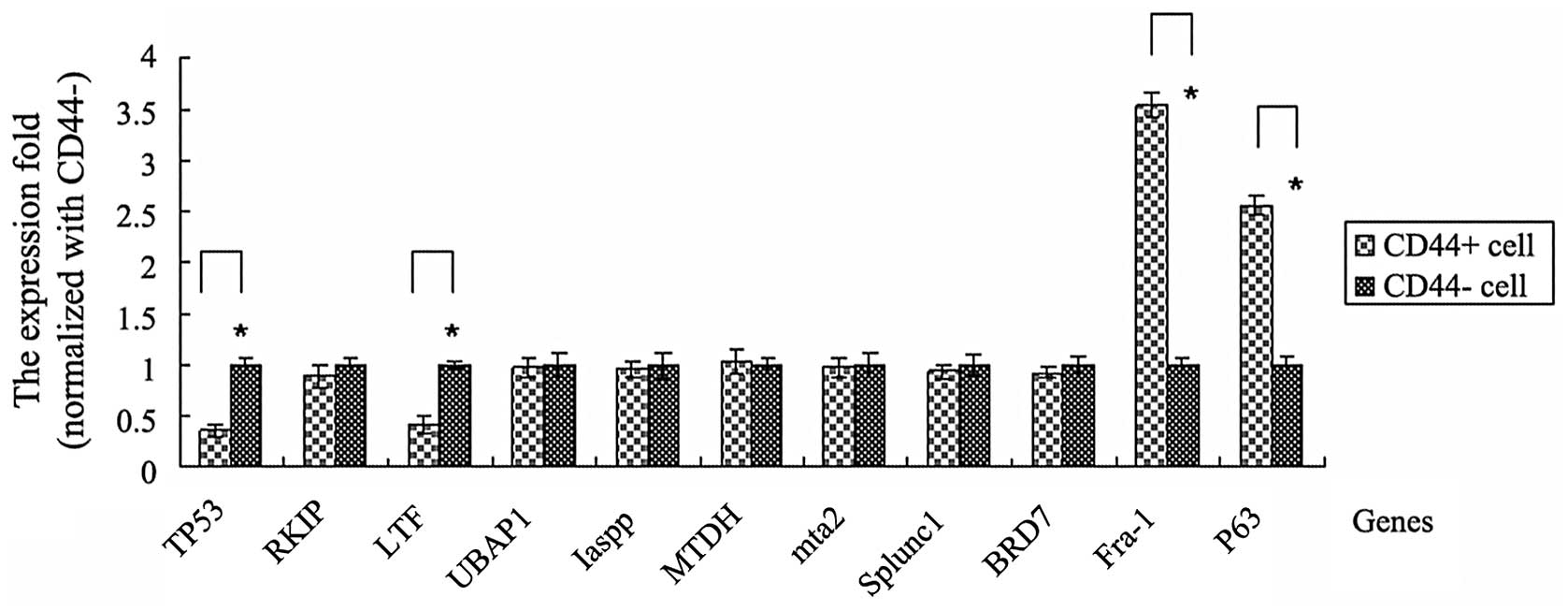
|
1
|
Parish SL, Swaine JG, Son E and Luken K:
Determinants of cervical cancer screening among women with
intellectual disabilities: evidence from medical records. Public
Health Rep. 128:519–526. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wobus M, Kuns R, Wolf C, Horn LC, Köhler
U, Sheyn I, Werness BA and Sherman LS: CD44 mediates constitutive
type I receptor signaling in cervical carcinoma cells. Gynecol
Oncol. 83:227–234. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wu JH, Liang XA, Wu YM, Li FS and Dai YM:
Identification of DNA methylation of SOX9 in cervical cancer using
methylated-CpG island recovery assay. Oncol Rep. 29:125–132.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dobo C, Stavale JN, de Lima FO, Ribeiro
DA, Arias V, Gomes TS and Oshima CT: HSP27 is commonly expressed in
cervical intraepithelial lesions of brazilian women. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 14:5007–5010. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Saavedra KP, Brebi PM and Roa JC:
Epigenetic alterations in preneoplastic and neoplastic lesions of
the cervix. Clin Epigenetics. 4:132012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang J, Wang Q, Liu H, Shao N, Tan B,
Zhang G, Wang K, Jia Y, Ma W, Wang N and Cheng Y: The association
of miR-146a rs2910164 and miR-196a2 rs11614913 polymorphisms with
cancer risk: a meta-analysis of 32 studies. Mutagenesis.
27:779–788. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Makrydimas G, Zagorianakou N, Zagorianakou
P and Agnantis NJ: CD44 family and gynaecological cancer. In Vivo.
17:633–640. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ibrahim EM, Stewart RL, Corke K, Blackett
AD, Tidy JA and Wells M: Upregulation of CD44 expression by
interleukins 1, 4, and 13, transforming growth factor-beta1,
estrogen, and progestogen in human cervical adenocarcinoma cell
lines. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 16:1631–1642. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Speiser P, Wanner C, Tempfer C, Mittelböck
M, Hanzal E, Bancher-Todesca D, Gitsch G, Reinthaller A and Kainz
C: CD44 is an independent prognostic factor in early-stage cervical
cancer. Int J Cancer. 74:185–188. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mostaan LV, Khorsandi MT, Sharifian SM,
Shandiz FH, Mirashrafi F, Sabzari H, Badiee R, Borghei H and
Yazdani N: Correlation between E-cadherin and CD44 adhesion
molecules expression and cervical lymph node metastasis in oral
tongue SCC: Predictive significance or not. Pathol Res Pract.
207:448–451. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Oberprieler NG and Taskén K: Analysing
phosphorylation-based signalling networks by phospho flow
cytometry. Cell Signal. 23:14–18. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhou Y, Zeng Z, Zhang W, Xiong W, Wu M,
Tan Y, Yi W, Xiao L, Li X, Huang C, et al: Lactotransferrin: a
candidate tumor suppressor-deficient expression in human
nasopharyngeal carcinoma and inhibition of NPC cell proliferation
by modulating the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Int J
Cancer. 123:2065–2072. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Krutzik PO, Irish JM, Nolan GP and Perez
OD: Analysis of protein phosphorylation and cellular signaling
events by flow cytometry: techniques and clinical applications.
Clin Immunol. 110:206–221. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang L, Tang A, Zhou Y, Tang J, Luo Z,
Jiang C, Li X, Xiang J and Li G: Tumor-conditioned mesenchymal stem
cells display hematopoietic differentiation and diminished influx
of Ca2+. Stem Cells Dev. 21:1418–1428. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou Y, Wang W, Zheng D, Peng S, Xiong W,
Ma J, Zeng Z, Wu M, Zhou M, Xiang J, et al: Risk of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma associated with polymorphic lactotransferrin haplotypes.
Med Oncol. 29:1456–1462. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Salehi M, Taheri T, Mohit E, Zahedifard F,
Seyed N, Taslimi Y, Sattari M, Bolhassani A and Rafati S:
Recombinant Leishmania tarentolae encoding the HPV type 16
E7 gene in tumor mice model. Immunotherapy. 4:1107–1120. 2012.
|
|
18
|
Sahiner F, Gümral R, Sener K, Yiğit N,
Dede M, Yapar M and Kubar A: Investigation of HPV-DNA in cervical
smear samples by two different methods: MY09/11 consensus PCR and
type-specific real-time PCR. Mikrobiyol Bul. 46:624–636. 2012.(In
Turkish).
|
|
19
|
Balbi G, Napolitano A, Giordano F, Capuano
S, Manganaro MA, Di Martino L, Fusco D, Grauso F and Seguino E:
Role of the association of high-risk HPV identified by real-time
PCR in cervical preneoplastic lesions. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol.
33:467–471. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Raychaudhuri S and Mandal S: Current
status of knowledge, attitude and practice (KAP) and screening for
cervical cancer in countries at different levels of development.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:4221–4227. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gadducci A, Guerrieri ME and Greco C:
Tissue biomarkers as prognostic variables of cervical cancer. Crit
Rev Oncol Hematol. 86:104–129. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mocarska A, Starosławska E,
Zelazowska-Cieślińska I, Łosicki M, Stasiewicz D, Kieszko D and
Burdan F: Epidemiology and risk factors of the cervical squamous
cell carcinoma. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 33:101–106. 2012.(In
Polish).
|
|
23
|
Bourguignon LY, Wong G, Earle C and Chen
L: Hyaluronan-CD44v3 interaction with Oct4-Sox2-Nanog promotes
miR-302 expression leading to self-renewal, clonal formation, and
cisplatin resistance in cancer stem cells from head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. J Biol Chem. 287:32800–32824. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dhingra S, Feng W, Brown RE, Zhou Z,
Khoury T, Zhang R and Tan D: Clinicopathologic significance of
putative stem cell markers, CD44 and nestin, in gastric
adenocarcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 4:733–741. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mascolo M, Ilardi G, Romano MF, Celetti A,
Siano M, Romano S, Luise C, Merolla F, Rocco A, Vecchione ML, De
Rosa G and Staibano S: Overexpression of chromatin assembly
factor-1 p60, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 and nestin predicts
metastasizing behaviour of oral cancer. Histopathology.
61:1089–1105. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Godar S, Ince TA, Bell GW, Feldser D,
Donaher JL, Bergh J, Liu A, Miu K, Watnick RS, Reinhardt F, et al:
Growth-inhibitory and tumor-suppressive functions of p53 depend on
its repression of CD44 expression. Cell. 134:62–73. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bidaud P, Chasle J, Sichel F, Rousseau S,
Petit P, Pottier D, Picquenot JM, Louis MY and Lechevrel M:
Expression of p53 family members and CD44 in oral squamous cell
carcinoma (OSCC) in relation to tumorigenesis. Histol Histopathol.
25:331–339. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ramos-Nino ME, Blumen SR, Pass H and
Mossman BT: Fra-1 governs cell migration via modulation of CD44
expression in human mesotheliomas. Mol Cancer. 6:812007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kajanne R, Miettinen P, Tenhunen M and
Leppä S: Transcription factor AP-1 promotes growth and
radioresistance in prostate cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
35:1175–1182. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|