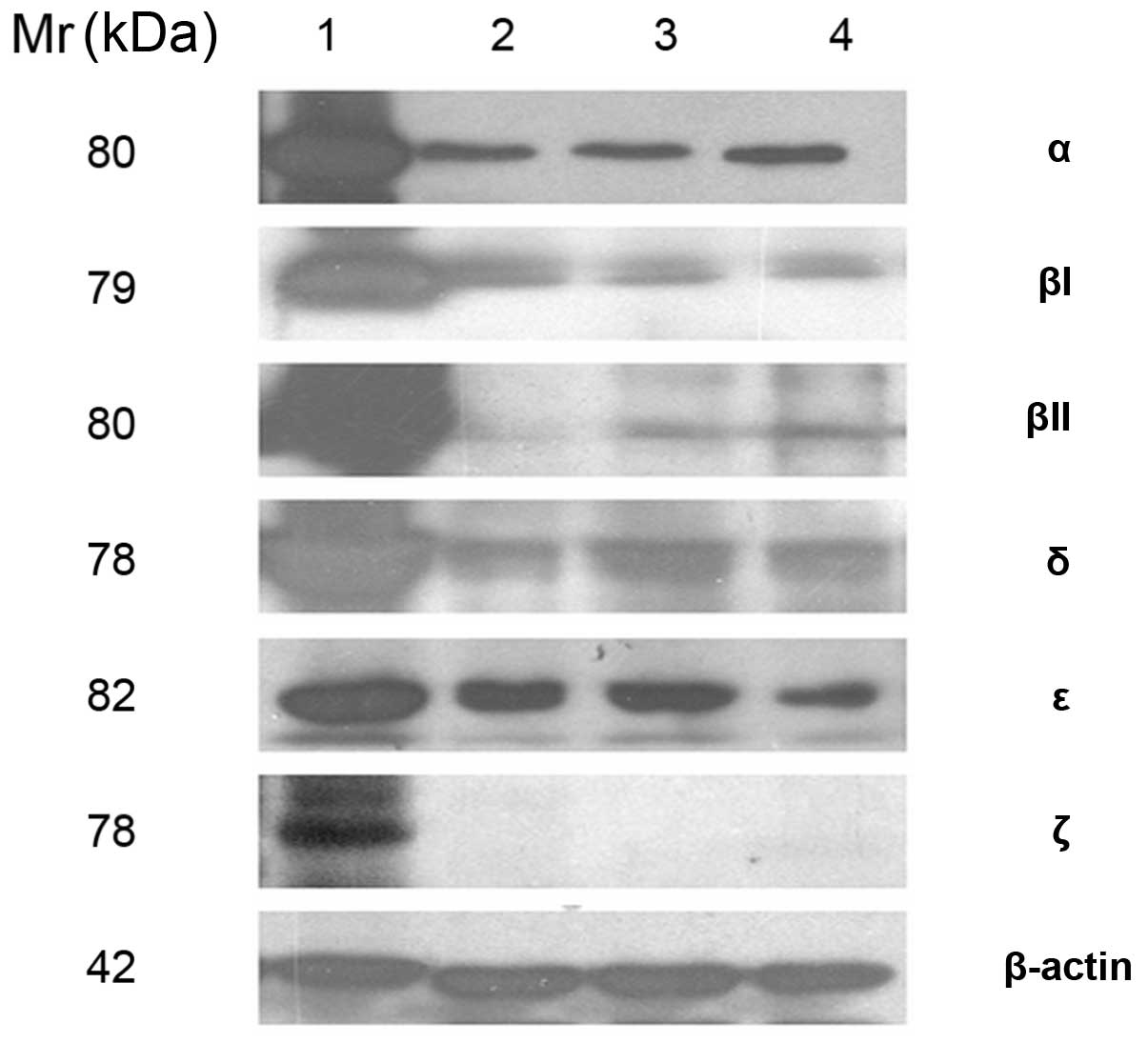
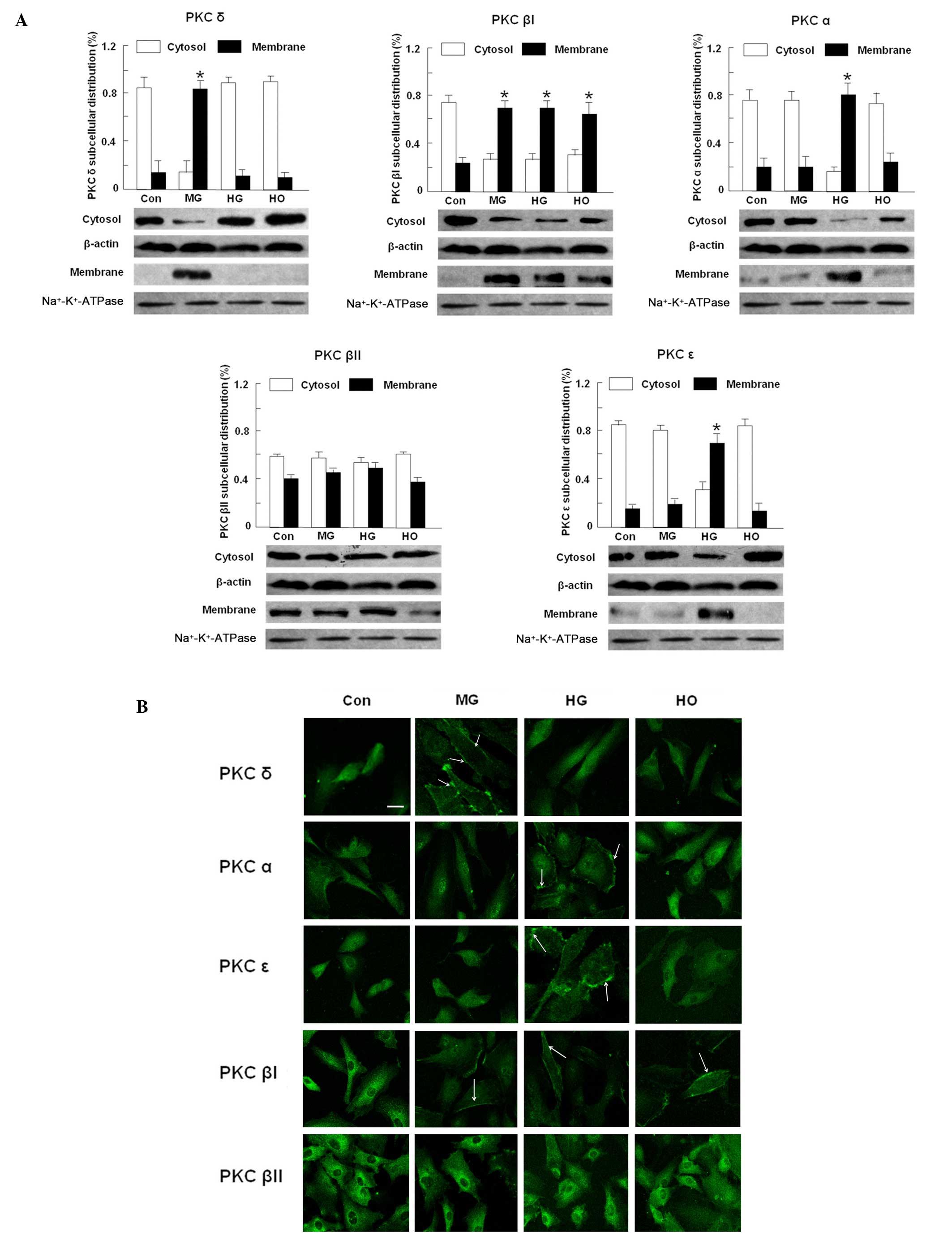
|
1
|
Lu M, Kuroki M, Amano S, et al: Advanced
glycation end products increase retinal vascular endothelial growth
factor expression. J Clin Invest. 101:1219–1224. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kern TS and Engerman RL: Capillary lesions
develop in retina rather than cerebral cortex in diabetes and
experimental galactosemia. Arch Ophthalmol. 114:306–310. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Agardh CD, Agardh E, Zhang H and Ostenson
CG: Altered endothelial/pericyte ratio in Goto-Kakizaki rat retina.
J Diabetes Complications. 11:158–162. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Crawford TN, Alfaro DV 3rd, Kerrison JB
and Jablon EP: Diabetic retinopathy and angiogenesis. Curr Diabetes
Rev. 5:8–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Das Evcimen N and King GL: The role of
protein kinase C activation and the vascular complications of
diabetes. Pharmacol Res. 55:498–510. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Steinberg SF: Structural basis of protein
kinase C isoform function. Physiol Rev. 88:1341–1378. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pedro G and George LK: Activation of
protein kinase C isoforms and its impact on diabetic complications.
Circ Res. 106:1319–1331. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Park JY, Takahara N, Gabriele A, et al:
Induction of endothelin-1 expression by glucose: an effect of
protein kinase C activation. Diabetes. 49:1239–1248. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gao R, Zhu BH, Tang SB, et al:
Scutellarein inhibits hypoxia- and moderately-high glucose-induced
proliferation and VEGF expression in human retinal endothelial
cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 29:707–712. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lai P, Li T, Yang J, et al: Upregulation
of stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1) expression in
microvasculature endothelial cells in retinal ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 246:1707–1713. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li X, Hahn CN, Parsons M, et al: Role of
protein kinase C zeta in thrombin-induced endothelial permeability
changes: inhibition by angiopoietin-1. Blood. 104:1716–1724. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sakai H, Yamamoto M, Chiba Y, et al: Some
different effect of PKC inhibitors on the acetylcholine, and
endothelin-1-induced contractions of rat bronchial smooth muscle.
Eur J Pharmacol. 618:58–62. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wong C and Jin ZG: Protein kinase
C-dependent protein kinase D activation modulates ERK signal
pathway and endothelial cell proliferation by vascular endothelial
growth factor. J Biol Chem. 280:33262–33269. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Griger Z, Páyer E, Kovács I, et al:
Protein kinase C-β and -δ isoenzymes promote arachidonic acid
production and proliferation of MonoMac-6 cells. J Mol Med.
85:1031–1042. 2007.
|
|
15
|
Kim JH, Kim JH, Jun HO, et al: Inhibition
of protein kinase C attenuates blood-retinal barrier breakdown in
diabetic retinopathy. Am J Pathol. 176:1517–1524. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wilkinson SE, Parker PJ and Nixon JS:
Isoenzyme specificity of bisindolylmaleimides, selective inhibitors
of protein kinase C. Biochem J. 294:335–337. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ding M, Huang C, Lu Y, et al: Involvement
of protein kinase C in crystalline silica-induced activation of the
MAP kinase and AP-1 pathway. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
290:L291–L297. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Eitel I, Hintze S, de Waha S, et al:
Prognostic impact of hyperglycemia in nondiabetic and diabetic
patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction insights from
contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Circulation:
Cardiovascular Imaging. 5:708–718. 2012.
|
|
19
|
Premanand C, Rema M, Sameer MZ, et al:
Effect of curcumin on proliferation of human retinal endothelial
cells under in vitro conditions. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
47:2179–2184. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rojas S, Rojas R, Lamperti L, et al:
Hyperglycaemia inhibits thymidine incorporation and cell growth via
protein kinase C, mitogen-activated protein kinases and nitric
oxide in human umbilical vein endothelium. Exp Physiol. 88:209–219.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kishimoto A, Takai Y and Nishizuka Y:
Activation of glycogen phosphorylase kinase by a calcium-activated,
cyclic nucleotide-independent protein kinase system. J Biochem.
82:1167–1172. 1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Osborne NN, Barnett NL, Morris NJ, et al:
The occurrence of three isoenzymes of protein kinase C (alpha, beta
and gamma) in retinas of different species. Brain Res. 570:161–166.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu KM, Ma P, Ge J, et al: Expression of
protein kinase C isoforms in cultured human retinal pigment
epithelial cells. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 245:993–999.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Keshamouni VG, Mattingly RR and Reddy KB:
Mechanism of 17-β-estradiol-induced Erk1/2 activation in breast
cancer cells. A role for HER2 and PKCδ. J Biol Chem.
277:22558–22565. 2002.
|
|
25
|
Abbas T, White D, Hui L, et al: Inhibition
of human p53 basal transcription by down-regulation of protein
kinase Cδ. J Biol Chem. 279:9970–9977. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Steinberg SF: Distinctive activation
mechanisms and functions for protein kinase C delta. Biochem J.
384:449–459. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Inoguchi T, Battan R, Handler E, et al:
Preferential elevation of protein kinase C isoform beta II and
diacylglycerol levels in the aorta and heart of diabetic rats:
differential reversibility to glycemic control by islet cell
transplantation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:11059–11063. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Idris I, Gray S and Donnelly R: Protein
kinase C activation: isozyme-specific effects on metabolism and
cardiovascular complications in diabetes. Diabetologia. 44:659–673.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gao Q, Tan J, Ma P, et al: PKC alpha
affects cell cycle progression and proliferation in human RPE cells
through the downregulation of p27kip1. Mol Vis. 15:2683–2695.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Murakami M, Horowitz A, Tang S, et al:
Protein kinase C (PKC) delta regulates PKC alpha activity in a
Syndecan-4-dependent manner. J Biol Chem. 277:20367–20371. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wellner M, Maasch C, Kupprion C, et al:
The proliferative effect of vascular endothelial growth factor
requires protein kinase C-alpha and protein kinase C-zeta.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 19:178–185. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bright R and Mochly-Rosen D: The role of
protein kinase C in cerebral ischemic and reperfusion injury.
Stroke. 36:2781–2790. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Murriel CL and Mochly-Rosen D: Opposing
roles of delta and epsilon PKC in cardiac ischemia and reperfusion:
targeting the apoptotic machinery. Arch Biochem Biophys.
420:246–254. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Aiello LP, Northrup JM, Keyt BA, et al:
Hypoxic regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in retinal
cells. Arch Ophthalmol. 113:1538–1544. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Short MD, Fox SM, Lam CF, et al: Protein
kinase Cζ attenuates hypoxia-induced proliferation of fibroblasts
by regulating MAP kinase phosphatase-1 expression. Mol Biol Cell.
17:1995–2008. 2006.
|