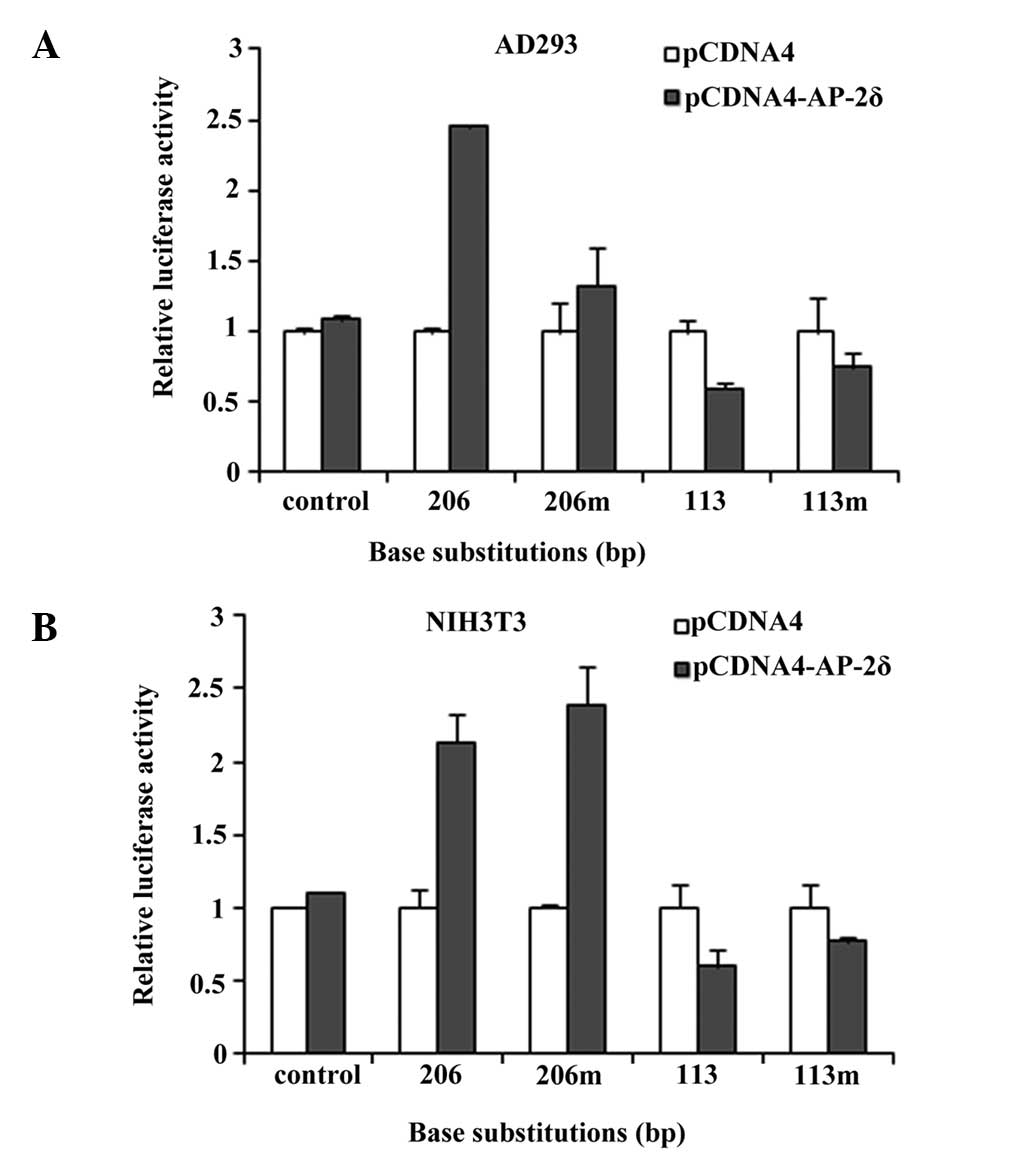
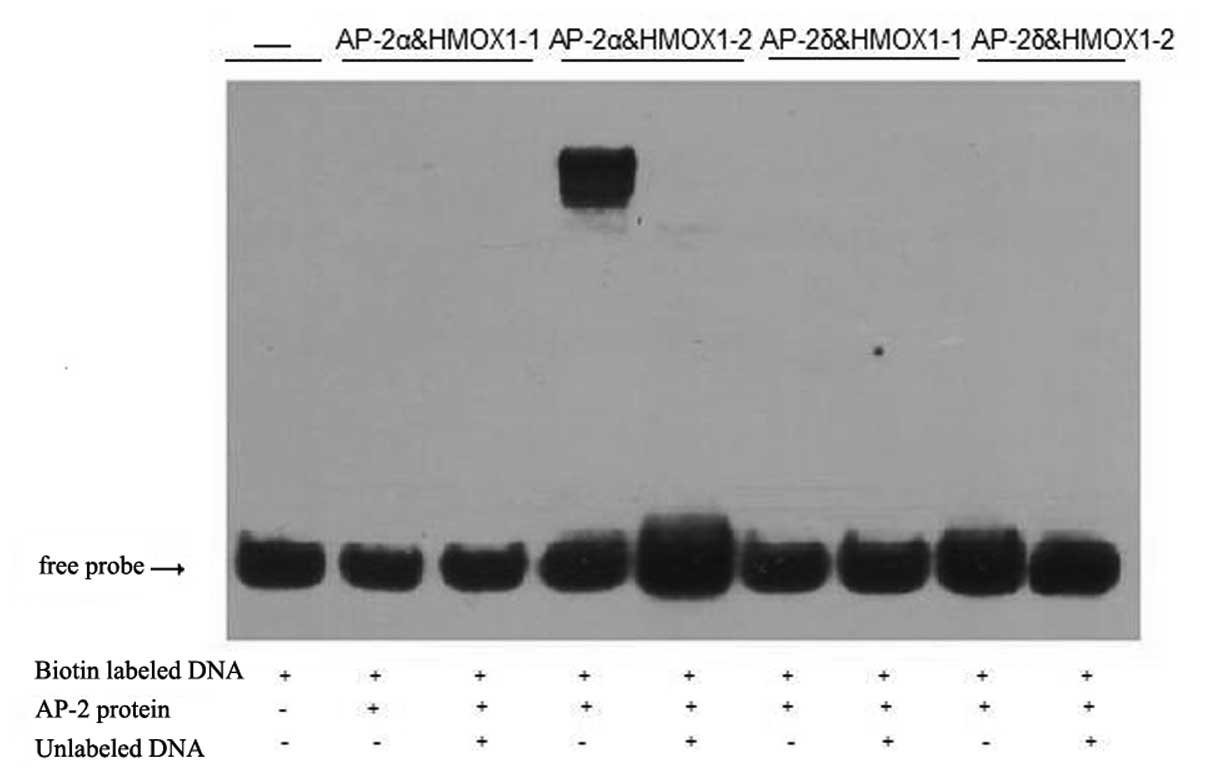
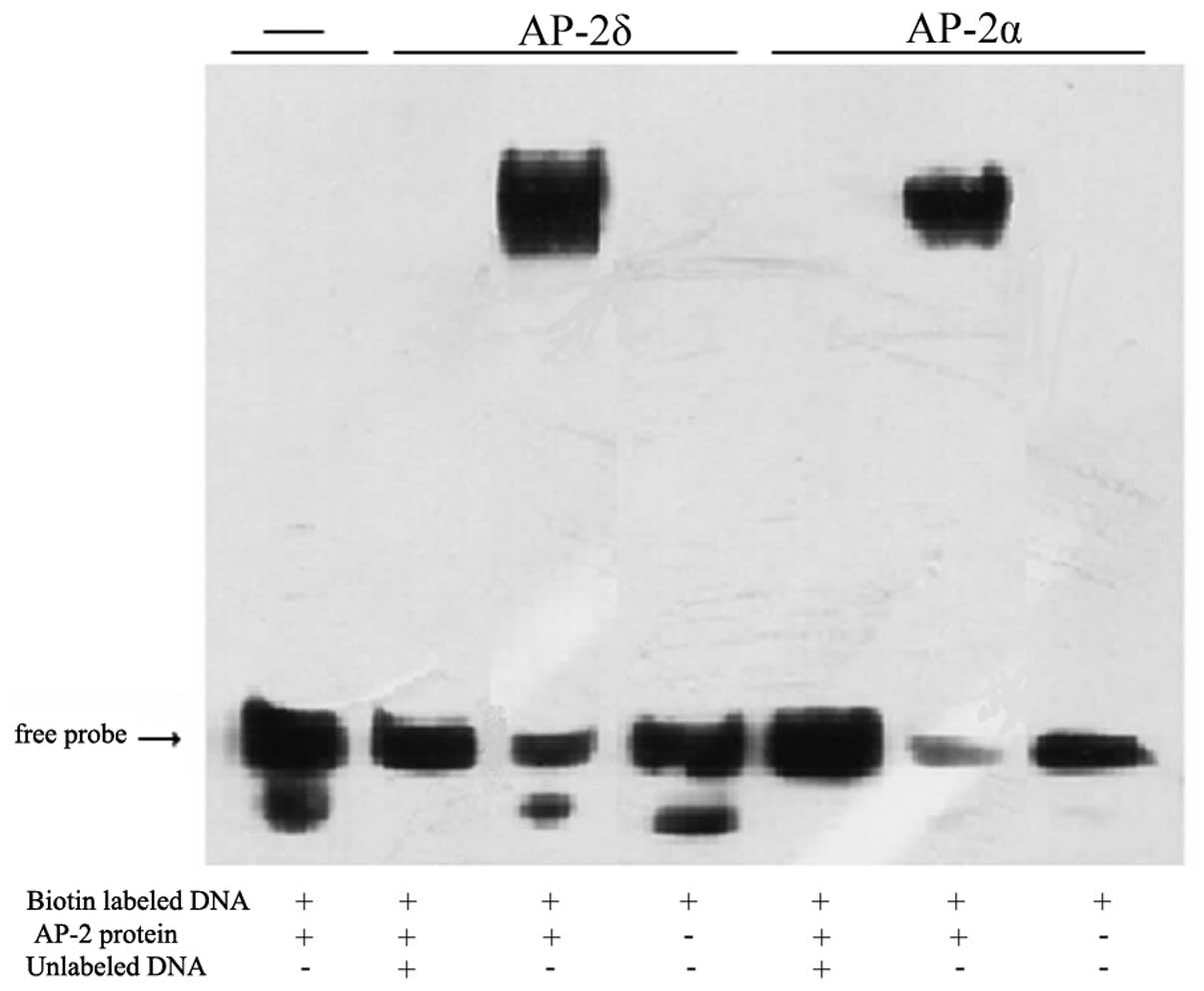
|
1
|
Wenke AK and Bosserhoff AK: Roles of AP-2
transcription factors in the regulation of cartilage and skeletal
development. FEBS J. 277:894–902. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dietz KJ, Vogel MO and Viehhauser A:
AP2/EREBP transcription factors are part of gene regulatory
networks and integrate metabolic, hormonal and environmental
signals in stress acclimation and retrograde signalling.
Protoplasma. 245:3–14. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bisgrove DA, Monckton EA and Godbout R:
Involvement of AP-2 in regulation of the R-FABP gene in the
developing chick retina. Mol Cell Biol. 17:5935–5945.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ebert SN, Ficklin MB, Her S, et al:
Glucocorticoid-dependent action of neural crest factor AP-2:
stimulation of phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase gene
expression. J Neurochem. 70:2286–2295. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Maconochie M, Krishnamurthy R, Nonchev S,
et al: Regulation of Hoxa2 in cranial neural crest cells involves
members of the AP-2 family. Development. 126:1483–1494.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Batsché E, Muchardt C, Behrens J, Hurst HC
and Crémisi C: RB and c-Myc activate expression of the E-cadherin
gene in epithelial cells through interaction with transcription
factor AP-2. Mol Cell Biol. 18:3647–3658. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lin HH, Chen YH, Chiang MT, Huang PL and
Chau LY: Activator protein-2α mediates carbon monoxide-induced
stromal cell-derived factor-1α expression and vascularization in
ischemic heart. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 33:785–794.
2013.
|
|
8
|
Debiève F, Depoix Ch and Hubinont C:
Transcription factor AP2 regulates human inhibin α subunit gene
expression during in vitro trophoblast differentiation. Mol Hum
Reprod. 17:702–709. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Maconochie M, Krishnamurthy R, Nonchev S,
et al: Regulation of Hoxa2 in cranial neural crest cells involves
members of the AP-2 family. Development. 126:1483–1494.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schorle H, Meier P, Buchert M, Jaenisch R
and Mitchell PJ: Transcription factor AP-2 essential for cranial
closure and craniofacial development. Nature. 381:235–238. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang J, Hagopian-Donaldson S, Serbedzija
G, et al: Neural tube, skeletal and body wall defects in mice
lacking transcription factor AP-2. Nature. 381:238–241. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Grochot-Przeczek A, Dulak J and Jozkowicz
A: Haem oxygenase-1: non-canonical roles in physiology and
pathology. Clin Sci (Lond). 122:93–103. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu X, Fan WG, Li DP, Kung H and Lin MC:
Heme oxygenase-1 system and gastrointestinal inflammation: a short
review. World J Gastroenterol. 17:4283–4288. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu ML, Layne MD and Yet SF: Heme
oxygenase-1 in environmental toxin-induced lung disease. Toxicol
Mech Methods. 22:323–329. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hou WH, Rossi L, Shan Y, Zheng JY,
Lambrecht RW and Bonkovsky HL: Iron increases HMOX1 and decreases
hepatitis C viral expression in HCV-expressing cells. World J
Gastroenterol. 15:4499–4510. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xiang Y, Liu G, Yang L and Zhong JL:
UVA-induced protection of skin through the induction of heme
oxygenase-1. Biosci Trends. 5:239–244. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hirota A, Kawachi Y, Itoh K, Nakamura Y,
et al: Ultraviolet A irradiation induces NF-E2-related factor 2
activation in dermal fibroblasts: protective role in UVA-induced
apoptosis. J Invest Dermatol. 124:825–832. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sun J, Hoshino H, Takaku K, et al:
Hemoprotein Bach1 regulates enhancer availability of heme
oxygenase-1 gene. EMBO J. 21:5216–5224. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mohibullah N, Donner A, Ippolito JA and
Williams T: SELEX and missing phosphate contact analyses reveal
flexibility within the AP-2(alpha) protein: DNA binding complex.
Nucleic Acids Res. 27:2760–2769. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Williams T and Tjian R: Analysis of the
DNA-binding and activation properties of the human transcription
factor AP-2. Genes Dev. 5:670–682. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wankhade S, Yu Y, Weinberg J, Tainsky MA
and Kannan P: Characterization of the activation domains of AP-2
family transcription factors. J Biol Chem. 275:29701–29708. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
McPherson LA and Weigel RJ: AP2alpha and
AP2gamma: a comparison of binding site specificity and
trans-activation of the estrogen receptor promoter and single site
promoter constructs. Nucleic Acids Res. 27:4040–4049. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Williams T and Tjian R: Characterization
of a dimerization motif in AP-2 and its function in heterologous
DNA-binding proteins. Science. 251:1067–1071. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schmidt M, Huber L, Majdazari A, Schütz G,
Williams T and Rohrer H: The transcription factors AP-2β and AP-2α
are required for survival of sympathetic progenitors and
differentiated sympathetic neurons. Dev Biol. 355:89–100. 2011.
|
|
25
|
Li X, Glubrecht DD and Godbout R: AP2
transcription factor induces apoptosis in retinoblastoma cells.
Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 49:819–830. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Moser M, Rüschoff J and Buettner R:
Comparative analysis of AP-2 alpha and AP-2 beta gene expression
during murine embryogenesis. Dev Dynam. 208:115–124. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chazaud C, Oulad-Abdelghani M, Bouillet P,
et al: AP-2.2, a novel gene related to AP-2, is expressed in the
forebrain, limbs and face during mouse embryogenesis. Mech Dev.
54:83–94. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sun L, Huang S, Wu Q, et al:
Identification of genes differentially regulated by transcription
factor, AP-2delta. Front Biosci. 12:1699–1706. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu XM, Peyton KJ and Durante W:
Physiological cyclic strain promotes endothelial cell survival via
the induction of heme oxygenase-1. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
304:H1634–H1643. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jozkowicz A, Was H and Dulak J: Heme
oxygenase-1 in tumors: is it a false friend? Antioxid Redox Signal.
9:2099–2117. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|