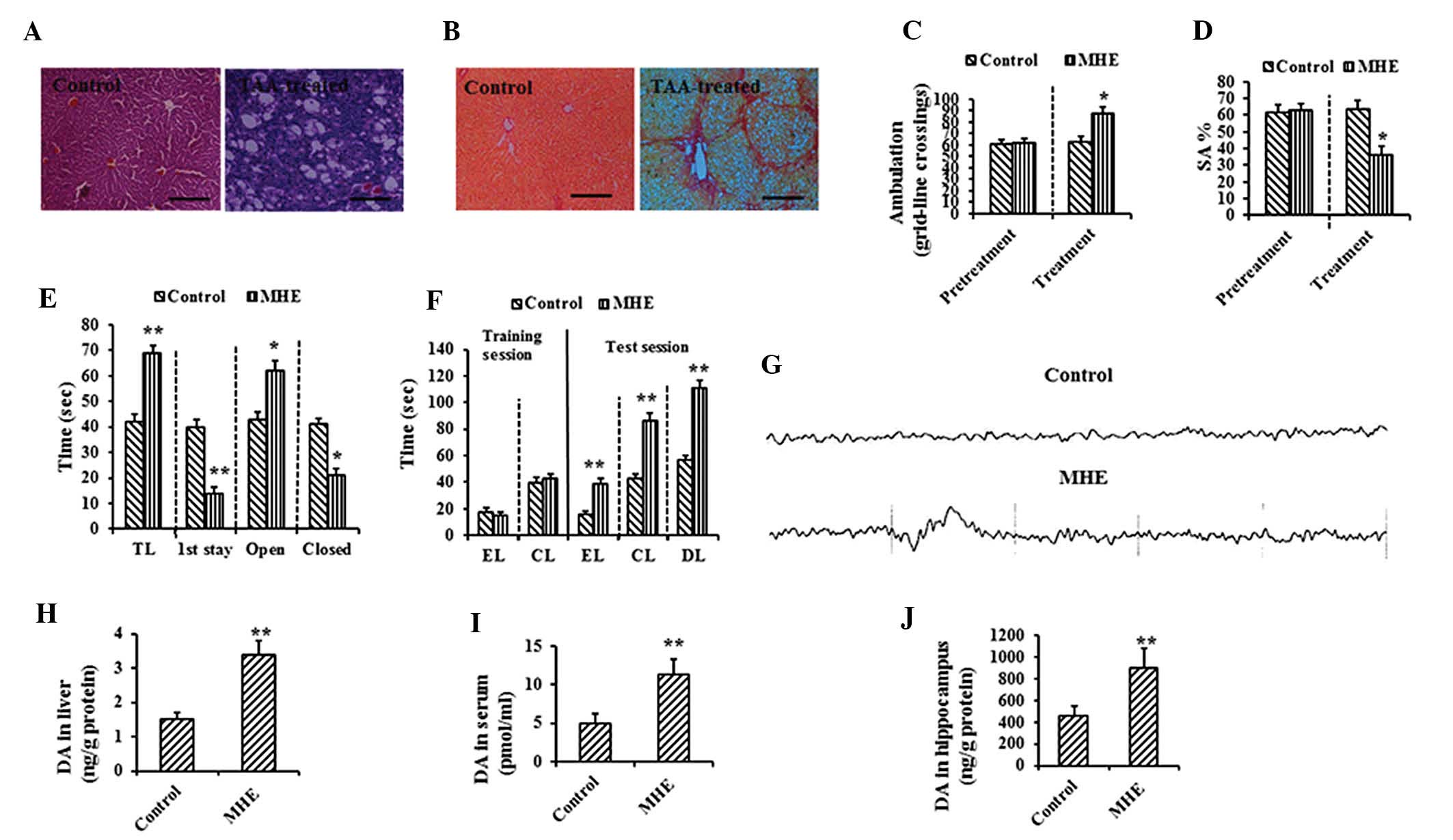
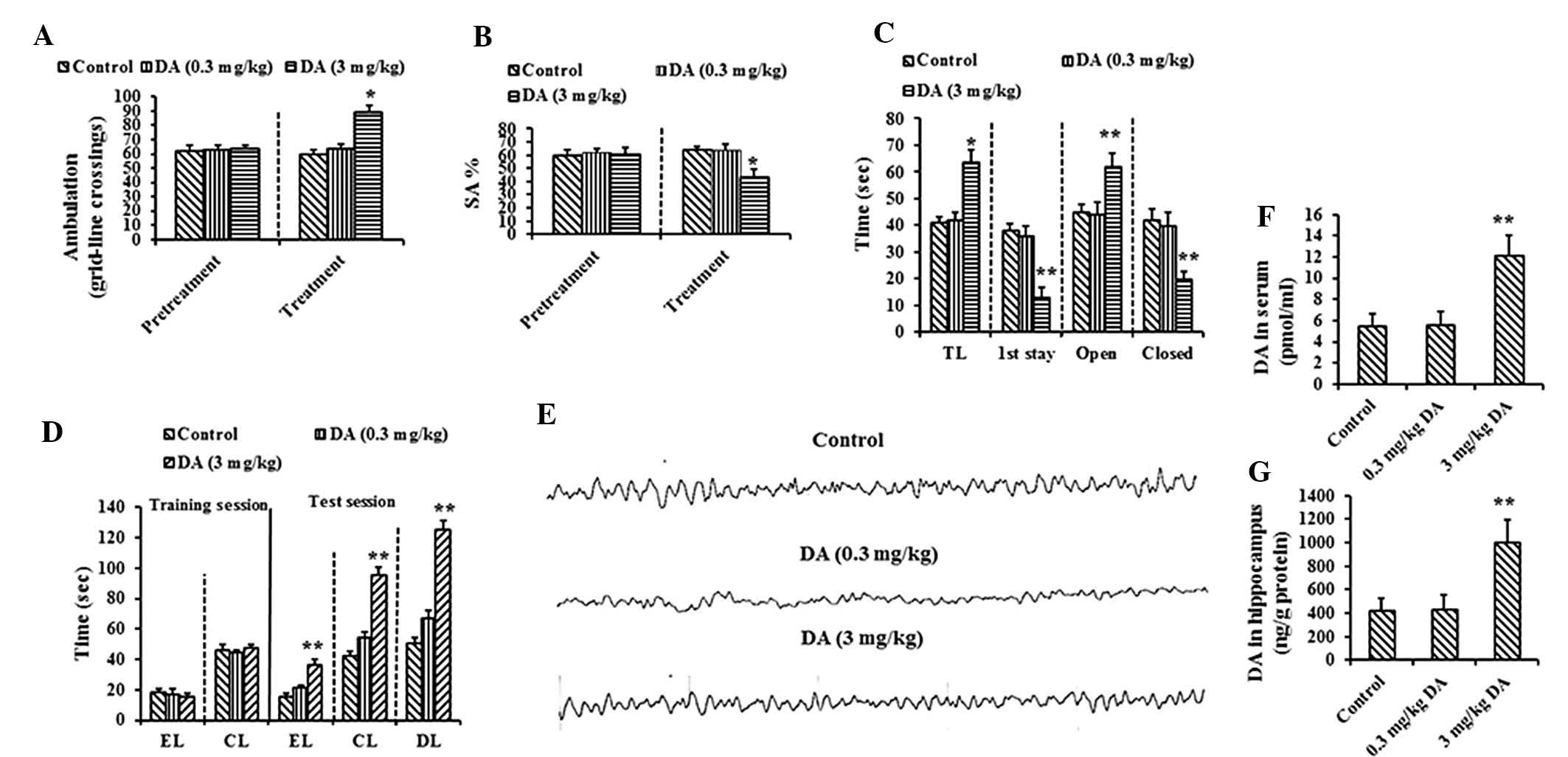
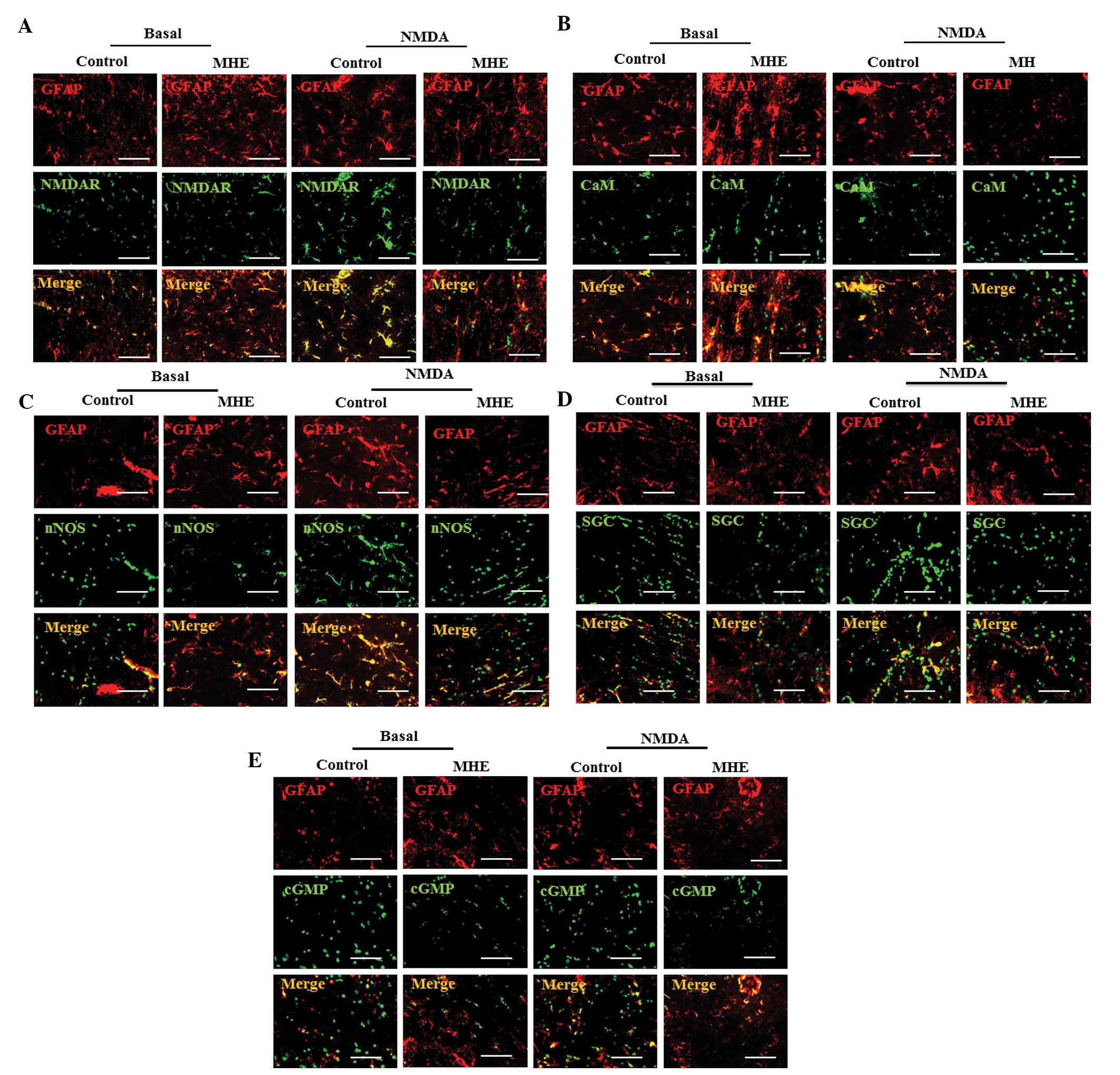
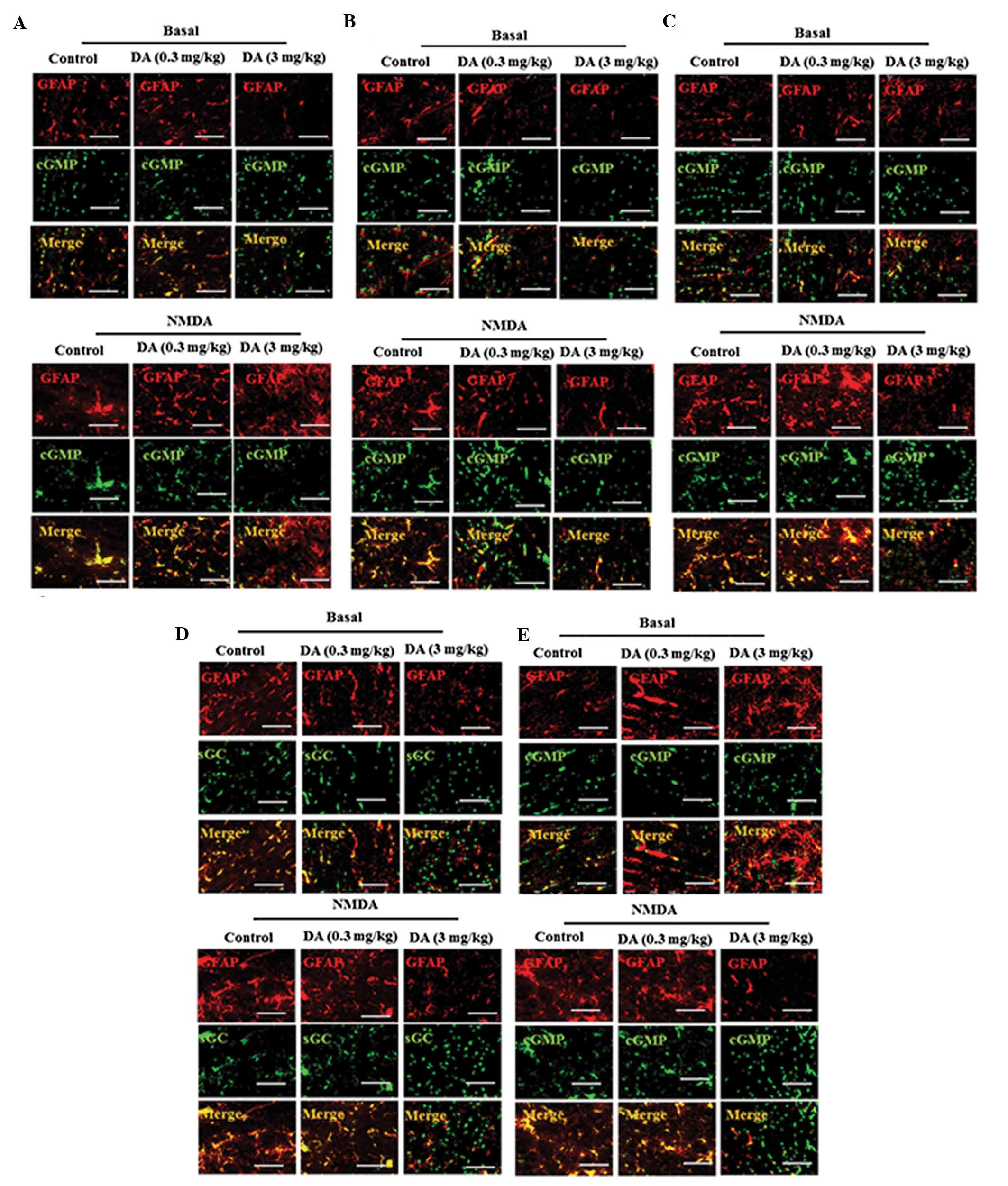
|
1
|
Tan HH, Lee GH, Thia KT, Ng HS, Chow WC
and Lui HF: Minimal hepatic encephalopathy runs a fluctuating
course: results from a three-year prospective cohort follow-up
study. Singapore Med J. 50:255–260. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yamada K, Hiramatsu M, Noda Y, et al: Role
of nitric oxide and cyclic GMP in the dizocilpine-induced
impairment of spontaneous alternation behavior in mice.
Neuroscience. 74:365–374. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Erceg S, Monfort P, Hernandez-Viadel M,
Rodrigo R, Montoliu C and Felipo V: Oral administration of
sildenafil restores learning ability in rats with hyperammonemia
and with portacaval shunts. Hepatology. 41:299–306. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ding S, Liu L, Jing H, et al: Dopamine
from cirrhotic liver contributes to the impaired learning and
memory ability of hippocampus in minimal hepatic encephalopathy.
Hepatol Int. 7:923–936. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Manzoni O, Prezeau L, Sladeczek F and
Bockaert J: Trans-ACPD inhibits cAMP formation via a pertussis
toxin-sensitive G-protein. Eur J Pharmacol. 225:357–358. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schoepp DD, Johnson BG and Monn JA:
Inhibition of cyclic AMP formation by a selective metabotropic
glutamate receptor agonist. J Neurochem. 58:1184–1186. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wroblewska B, Wroblewski JT, Saab OH and
Neale JH: N-acetylaspartylglutamate inhibits forskolin-stimulated
cyclic AMP levels via a metabotropic glutamate receptor in cultured
cerebellar granule cells. J Neurochem. 61:943–948. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wroblewska B, Santi MR and Neale JH:
N-acetylaspartylglutamate activates cyclic AMP-coupled metabotropic
glutamate receptors in cerebellar astrocytes. Glia. 24:172–179.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bredt DS and Snyder SH: Nitric oxide: a
physiologic messenger molecule. Annu Rev Biochem. 63:175–195. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bellamy TC and Garthwaite J: The
receptor-like properties of nitric oxide-activated soluble guanylyl
cyclase in intact cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 230:165–176. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Newman EA: Propagation of intercellular
calcium waves in retinal astrocytes and Müller cells. J Neurosci.
21:2215–2223. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jia L and Zhang MH: Comparison of
probiotics and lactulose in the treatment of minimal hepatic
encephalopathy in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 11:908–911. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kawasumi M, Chiba T, Yamada M, et al:
Targeted introduction of V642I mutation in amyloid precursor
protein gene causes functional abnormality resembling early stage
of Alzheimer’s disease in aged mice. Eur J Neurosci. 19:2826–2838.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yamada M, Chiba T, Sasabe J, et al:
Implanted cannula-mediated repetitive administration of Abeta25–35
into the mouse cerebral ventricle effectively impairs spatial
working memory. Behav Brain Res. 164:139–146. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Itoh J, Nabeshima T and Kameyama T:
Utility of an elevated plus-maze for the evaluation of memory in
mice: effects of nootropics, scopolamine and electroconvulsive
shock. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 101:27–33. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ichihara K, Nabeshima T and Kameyama T:
Differential effects of pimozide and SCH 23390 on acquisition of
learning in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 164:189–195. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mamiya T, Noda Y, Nishi M, Takeshima H and
Nabeshima T: Enhancement of spatial attention in
nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor-knockout mice. Brain Res.
783:236–240. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Colado MI, Ormazabal MJ, Alfaro MJ and
Martin MI: Effect of Bay K 8644 on the synthesis and metabolism of
dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine in various brain areas of the rat.
J Pharm Pharmacol. 45:220–222. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bernabeu R, Schmitz P, Faillace MP,
Izquierdo I and Medina JH: Hippocampal cGMP and cAMP are
differentially involved in memory processing of inhibitory
avoidance learning. Neuroreport. 7:585–588. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Marcaida G, Miñana MD, Burgal M, Grisolía
S and Felipo V: Ammonia prevents activation of NMDA receptors by
glutamate in rat cerebellar neuronal cultures. Eur J Neurosci.
7:2389–2396. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Verdon CP, Burton BA and Prior RL: Sample
pretreatment with nitrate reductase and glucose-6-phosphate
dehydrogenase quantitatively reduces nitrate while avoiding
interference by NADP+ when the Griess reaction is used to assay for
nitrite. Anal Biochem. 224:502–508. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yi Z, Petralia RS, Fu Z, et al: The role
of the PDZ protein GIPC in regulating NMDA receptor trafficking. J
Neurosci. 27:11663–11675. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Castro NG, de Mello MC, de Mello FG and
Aracava Y: Direct inhibition of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor
channel by dopamine and (+)-SKF38393. Br J Pharmacol.
126:1847–1855. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zheng P, Zhang XX, Bunney BS and Shi WX:
Opposite modulation of cortical N-methyl-D-aspartate
receptor-mediated responses by low and high concentrations of
dopamine. Neuroscience. 91:527–535. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Seamans JK and Yang CR: The principal
features and mechanisms of dopamine modulation in the prefrontal
cortex. Prog Neurobiol. 74:1–58. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cui C, Xu M and Atzori M:
Voltage-dependent block of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors by
dopamine D1 receptor ligands. Mol Pharmacol. 70:1761–1770. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Altar CA, Boyar WC and Kim HS:
Discriminatory roles for D1 and D2 dopamine receptor subtypes in
the in vivo control of neostriatal cyclic GMP. Eur J Pharmacol.
181:17–21. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Di Stefano A, Sozio P, Cacciatore I, et
al: Preparation and pharmacological characterization of
trans-2-amino-5(6)-fluoro-6(5)-hydroxy-1-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indenes
as D2-like dopamine receptor agonists. J Med Chem. 48:2646–2654.
2005.
|
|
29
|
Hoque KE, Indorkar RP, Sammut S and West
AR: Impact of dopamine-glutamate interactions on striatal neuronal
nitric oxide synthase activity. Psychopharmacology (Berl).
207:571–581. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Morris RG, Hagan JJ and Rawlins JN:
Allocentric spatial learning by hippocampectomised rats: a further
test of the ‘spatial mapping’ and ‘working memory’ theories of
hippocampal function. Q J Exp Psychol B. 38:365–395.
1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Park DJ and West AR: Regulation of
striatal nitric oxide synthesis by local dopamine and glutamate
interactions. J Neurochem. 111:1457–1465. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sammut S, Dec A, Mitchell D, Linardakis J,
Ortiguela M and West AR: Phasic dopaminergic transmission increases
NO efflux in the rat dorsal striatum via a neuronal NOS and a
dopamine D(1/5) receptor-dependent mechanism.
Neuropsychopharmacology. 31:493–505. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Siuciak JA, McCarthy SA, Chapin DS, et al:
Genetic deletion of the striatum-enriched phosphodiesterase PDE10A:
evidence for altered striatal function. Neuropharmacology.
51:374–385. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Calabresi P, Centonze D, Gubellini P,
Marfia GA, Pisani A, Sancesario G and Bernardi G: Synaptic
transmission in the striatum: from plasticity to neurodegeneration.
Prog Neurobiol. 61:231–265. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Centonze D, Gubellini P, Pisani A,
Bernardi G and Calabresi P: Dopamine, acetylcholine and nitric
oxide systems interact to induce corticostriatal synaptic
plasticity. Rev Neurosci. 14:207–216. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kawaguchi Y: Neostriatal cell subtypes and
their functional roles. Neurosci Res. 27:1–8. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
West AR and Grace AA: Opposite influences
of endogenous dopamine D1 and D2 receptor activation on activity
states and electrophysiological properties of striatal neurons:
studies combining in vivo intracellular recordings and reverse
microdialysis. J Neurosci. 22:294–304. 2002.
|
|
38
|
Galati S, D’angelo V, Scarnati E, et al:
In vivo electrophysiology of dopamine-denervated striatum: focus on
the nitric oxide/cGMP signaling pathway. Synapse. 62:409–420. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|