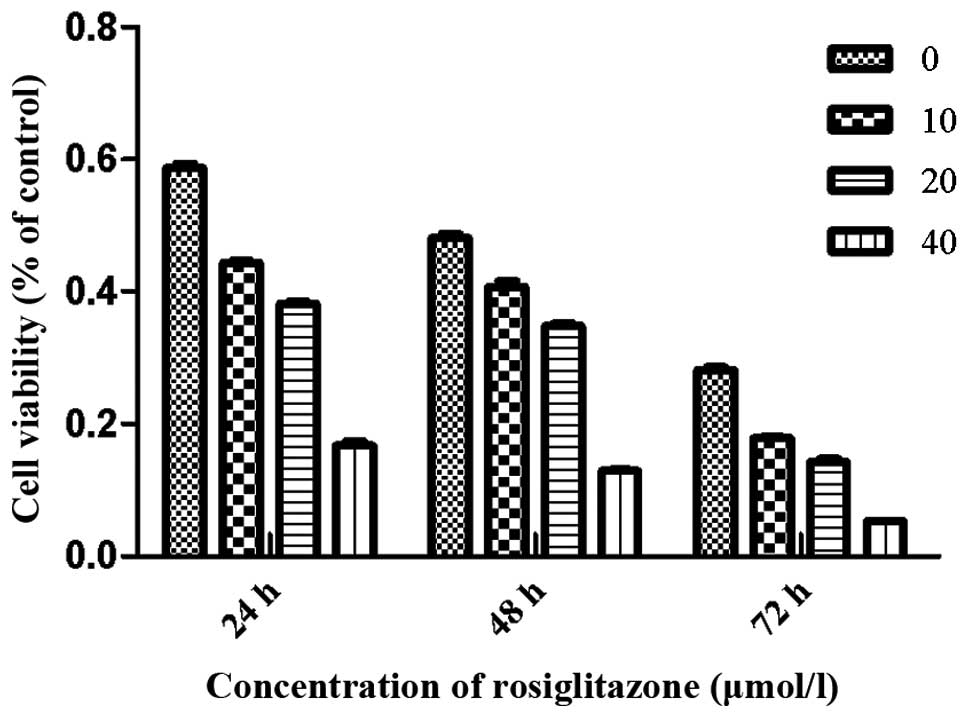
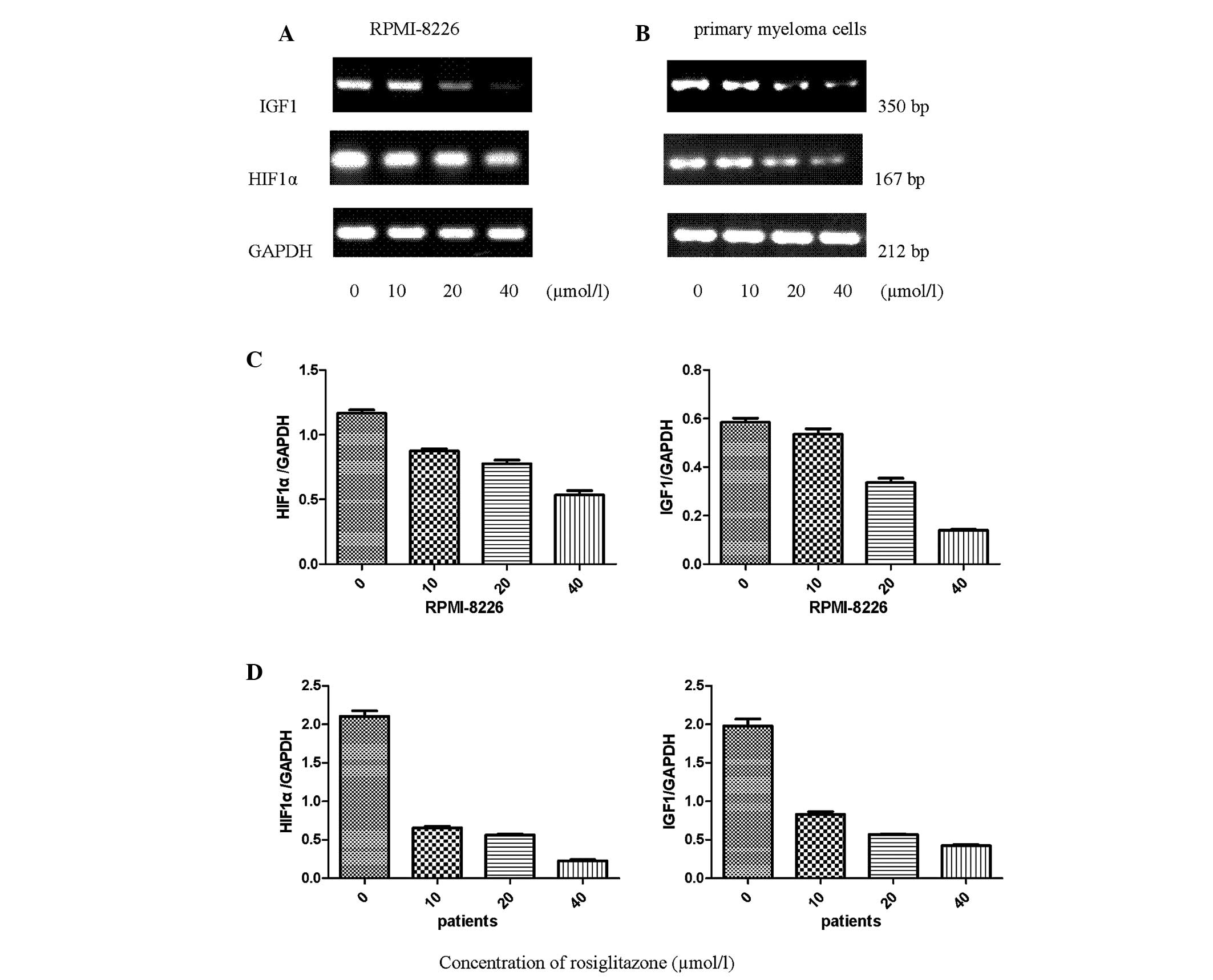
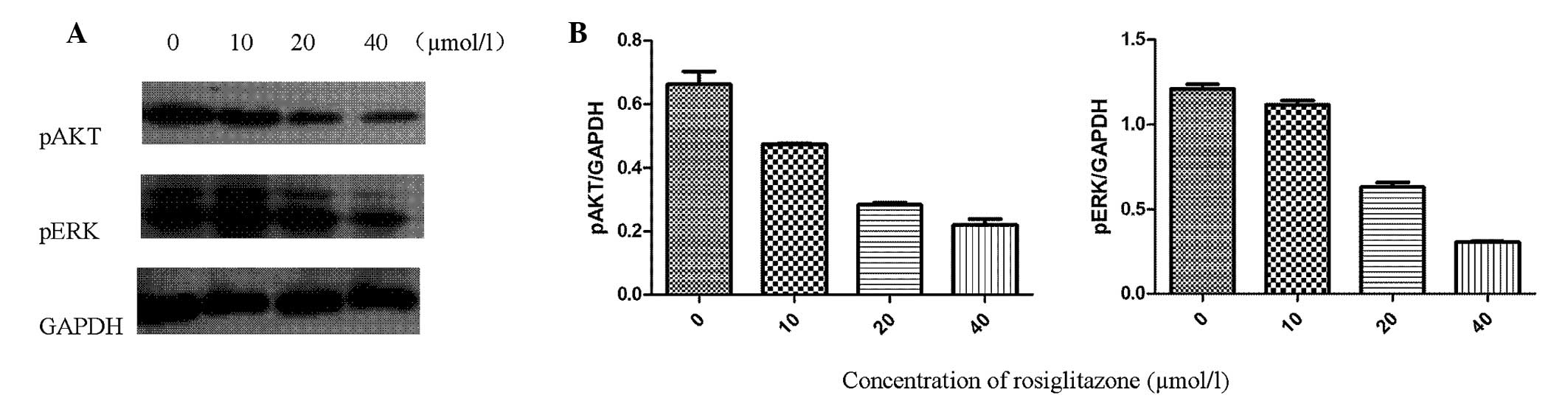
|
1
|
Rajkumar SV: Treatment of multiple
myeloma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 8:479–491. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ribatti D, Vacca A, Dammacco F and English
D: Angiogenesis and anti-angiogenesis in hematological
malignancies. J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 12:11–22. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ribatti D, Nico B and Vacca A: Importance
of the bone marrow microenvironment in inducing the angiogenic
response in multiple myeloma. Oncogene. 25:4257–4266. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Giatromanolaki A, Bai M, Margaritis D, et
al: Hypoxia and activated VEGF/receptor pathway in multiple
myeloma. Anticancer Res. 30:2831–2836. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Martin SK, Diamond P, Williams SA, et al:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-2 is a novel regulator of aberrant CXCL12
expression in multiple myeloma plasma cells. Haematologica.
95:776–784. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Colla S, Storti P, Donofrio G, et al: Low
bone marrow oxygen tension and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
overexpression characterize patients with multiple myeloma: role on
the transcriptional and proangiogenic profiles of CD138(+) cells.
Leukemia. 24:1967–1970. 2010.
|
|
7
|
Zhang J, Sattler M, Tonon G, et al:
Targeting angiogenesis via a c-Myc/hypoxia-inducible
factor-1alpha-dependent pathway in multiple myeloma. Cancer Res.
69:5082–5090. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Menu E, Jernberg-Wiklund H, De Raeve H, et
al: Targeting the IGF-1R using picropodophyllin in the
therapeutical 5T2MM mouse model of multiple myeloma: beneficial
effects on tumor growth, angiogenesis, bone disease and survival.
Int J Cancer. 121:1857–1861. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Menu E, van Valckenborgh E, van Camp B and
Vanderkerken K: The role of the insulin-like growth factor 1
receptor axis in multiple myeloma. Arch Physiol Biochem. 115:49–57.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pappa CA, Tsirakis G, Psarakis FE, Kolovou
A, Tsigaridaki M, Stafylaki D, Sfiridaki K and Alexandrakis MG:
Lack of correlation between angiogenic cytokines and serum
insulin-like growth factor-1 in patients with multiple myeloma. Med
Oncol. Mar;30:3632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Stoeltzing O, Liu W, Reinmuth N, et al:
Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, vascular endothelial
growth factor, and angiogenesis by an insulin-like growth factor-I
receptor autocrine loop in human pancreatic cancer. Am J Pathol.
163:1001–1011. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Fukuda R, Hirota K, Fan F, et al:
Insulin-like growth factor 1 induces hypoxia-inducible
factor1-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor expression,
which is dependent on MAP kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
signaling in colon cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 277:38205–38211.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Treins C, Giorgetti-Peraldi S, Murdaca J,
et al: Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 activity and
expression of HIF hydroxylases in response to insulin-like growth
factor I. Mol Endocrinol. 19:1304–1317. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Menu E, Kooijman R, Van Valckenborgh E, et
al: Specific roles for the PI3K and the MEK-ERK pathway in
IGF-1-stimulated chemotaxis, VEGF secretion and proliferation of
multiple myeloma cells: study in the 5T33MM model. Br J Cancer.
90:1076–1083. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Poulaki V, Mitsiades CS, McMullan C, et
al: Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression by
insulin-like growth factor I in thyroid carcinomas. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 88:5392–5398. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sang N, Stiehl DP, Bohensky J, Leshchinsky
I, Srinivas V and Caro J: MAPK signaling up-regulates the activity
of hypoxia-inducible factors by its effects on p300. J Biol Chem.
278:14013–14019. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Minet E, Arnould T, Michel G, Roland I,
Mottet D, Raes M, Remacle J and Michiels C: ERK activation upon
hypoxia: involvement in HIF-1 activation. FEBS Lett. 468:53–58.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shi YH, Wang YX, Bingle L, Gong LH, Heng
WJ, Li Y and Fang WG: In vitro study of HIF-1 activation and VEGF
release by bFGF in the T47D breast cancer cell line under normoxic
conditions: involvement of PI-3K/Akt and MEK1/ERK pathways. J
Pathol. 205:530–536. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang H, Wu D, Fu J, Chen G, Chang W, Chow
HC, Leung AY and Liang R: All-trans retinoic acid can intensify the
growth inhibition and differentiation induction effect of
rosiglitazone on multiple myeloma cells. Eur J Haematol.
83:191–202. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lecka-Czernik B, Ackert-Bicknell C, Adamo
ML, et al: Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
gamma (PPARgamma) by rosiglitazone suppresses components of the
insulin-like growth factor regulatory system in vitro and in vivo.
Endocrinology. 148:903–911. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kang BY, Kleinhenz JM, Murphy TC and Hart
CM: The PPARγ ligand rosiglitazone attenuates hypoxia-induced
endothelin signaling in vitro and in vivo. Am J Physiol Lung Cell
Mol Physiol. 301:L881–L891. 2011.
|
|
22
|
Nickkho-Amiry M, McVey R and Holland C:
Peroxisome proliferator activated receptors modulate proliferation
and angiogenesis in human endometrial carcinoma. Mol Cancer Res.
10:441–453. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yokoyama Y, Xin B, Shigeto T and Mizunuma
H: Combination of ciglitazone, a peroxisome proliferator activated
receptor gamma ligand, and cisplatin enhances the inhibition of
growth of human ovarian cancers. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
137:1219–1228. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Reka AK, Goswami MT, Krishnapuram R,
Standiford TJ and Keshamouni VG: Molecular cross-regulation between
PPAR-γ and other signaling pathways: implications for lung cancer
therapy. Lung Cancer. 72:154–159. 2011.
|
|
25
|
Dong YW, Wang XP and Wu K: Suppression of
pancreatic carcinoma growth by activating peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma involves angiogenesis
inhibition. World J Gastroenterol. 15:441–448. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kim KY, Ahn JH and Cheon HG:
Anti-angiogenic action of PPARγ ligand in human umbilical vein
endothelial cells is mediated by PTEN upregulation and VEGFR-2
downregulation. Mol Cell Biochem. 358:375–385. 2011.
|
|
27
|
Weidner N, Folkman J, Pozza F, Bevilacqua
P, Allred EN, Moore DH, Meli S and Gasparini G: Tumor angiogenesis:
a new significant and independent prognostic indicator in
early-stage breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 84:1875–1887.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bertolini F, Mancuso P, Gobbi A and
Pruneri G: The thin red line: angiogenesis in normal and malignant
hematopoiesis. Exp Hematol. 28:993–1000. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bhaskar A, Gupta R, Vishnubhatla S, Kumar
L, Sharma A, Sharma MC, Das P and Thakur SC: Angiopoietins as
biomarker of disease activity and response to therapy in multiple
myeloma. Leuk Lymphoma. 54:1473–1478. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ribatti D, Nico B, Crivellato E, Roccaro
AM and Vacca A: The history of the angiogenic switch concept.
Leukemia. 21:44–52. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen MC, Lee CF, Huang WH and Chou TC:
Magnolol suppresses hypoxia-induced angiogenesis via inhibition of
HIF-1α/VEGF signaling pathway in human bladder cancer cells.
Biochem Pharmacol. 85:1278–1287. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen C, Cai S, Wang G, Cao X, Yang X, Luo
X, Feng Y and Hu J: c-Myc enhances colon cancer cell-mediated
angiogenesis through the regulation of HIF-1α. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 430:505–511. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhou H, Fei W, Bai Y, Zhu S, Luo E, Chen K
and Hu J: RNA interference-mediated downregulation of
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α inhibits angiogenesis and survival of
oral squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Cancer
Prev. 21:289–299. 2012.
|
|
34
|
Jeong JH, Jeong YJ, Cho HJ, et al:
Ascochlorin inhibits growth factor-induced HIF-1α activation and
tumor-angiogenesis through the suppression of EGFR/ERK/p70S6K
signaling pathway in human cervical carcinoma cells. J Cell
Biochem. 113:1302–1313. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen Y, Gou X, Ke X, Cui H and Chen Z:
Human tumor cells induce angiogenesis through positive feedback
between CD147 and insulin-like growth factor-I. PLoS One.
7:e409652012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Tsai AC, Pan SL, Lai CY, et al: The
inhibition of angiogenesis and tumor growth by denbinobin is
associated with the blocking of insulin-like growth factor-1
receptor signaling. J Nutr Biochem. 22:625–633. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nakamura K, Sasajima J, Mizukami Y, et al:
Hedgehog promotes neovascularization in pancreatic cancers by
regulating Ang-1 and IGF-1 expression in bone-marrow derived
pro-angiogenic cells. PLoS One. 5:e88242010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Tang X, Zhang Q, Shi S, Yen Y, Li X, Zhang
Y, Zhou K and Le AD: Bisphosphonates suppress insulin-like growth
factor 1-induced angiogenesis via the HIF-1alpha/VEGF signaling
pathways in human breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 126:90–103.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shushanov SS, Mar’ina LG, Kravtsova TA,
Chernykh YB and Kakpakova ES: Coexpression of two mRNA isoforms of
insulin-like growth factor-1 gene and mRNA of YB-1 gene in patients
with multiple myeloma. Bull Exp Biol Med. 154:654–657. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Baek YY, Cho DH, Choe J, et al:
Extracellular taurine induces angiogenesis by activating ERK-,
Akt-, and FAK-dependent signal pathways. Eur J Pharmacol.
674:188–199. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chung BH, Cho YL, Kim JD, et al: Promotion
of direct angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo by Puerariae
flos extract via activation of MEK/ERK-, PI3K/Akt/eNOS-, and
Src/FAK-dependent pathways. Phytother Res. 24:934–940.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shen K, Ji L, Gong C, Ma Y, Yang L, Fan Y,
Hou M and Wang Z: Notoginsenoside Ft1 promotes angiogenesis via
HIF-1α mediated VEGF secretion and the regulation ofPI3K/AKT and
Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathways. Biochem Pharmacol. 84:784–792.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhu C, Qi X, Chen Y, Sun B, Dai Y and Gu
Y: PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK1/2 signaling pathways are involved in
IGF-1-induced VEGF-C upregulation in breast cancer. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 137:1587–1594. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yang XM, Wang YS, Zhang J, et al: Role of
PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK in mediating hypoxia-induced expression of
HIF-1alpha and VEGF in laser-induced rat choroidal
neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 50:1873–1879. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Choi IJ, Kim SY, Kwon CH and Kim YK:
Rosiglitazone inhibits proliferation of renal proximal tubular
cells via down-regulation of ERK and Akt. Ren Fail. 32:103–111.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cantini G, Lombardi A, Piscitelli E, et
al: Rosiglitazone inhibits adrenocortical cancer cell proliferation
by interfering with the IGF-IR intracellular signaling. PPAR Res.
2008:9040412008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|