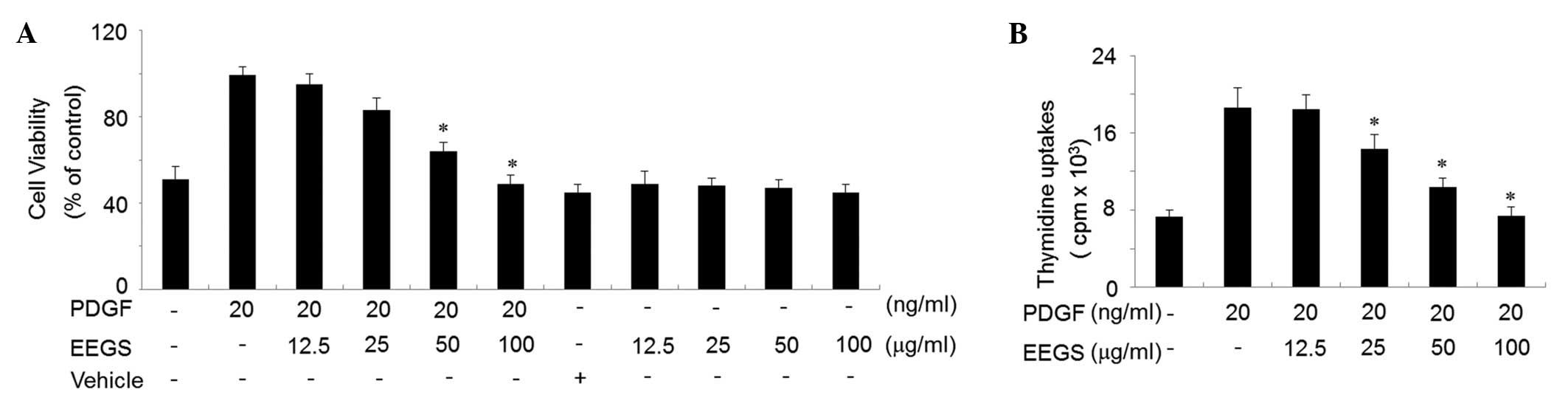
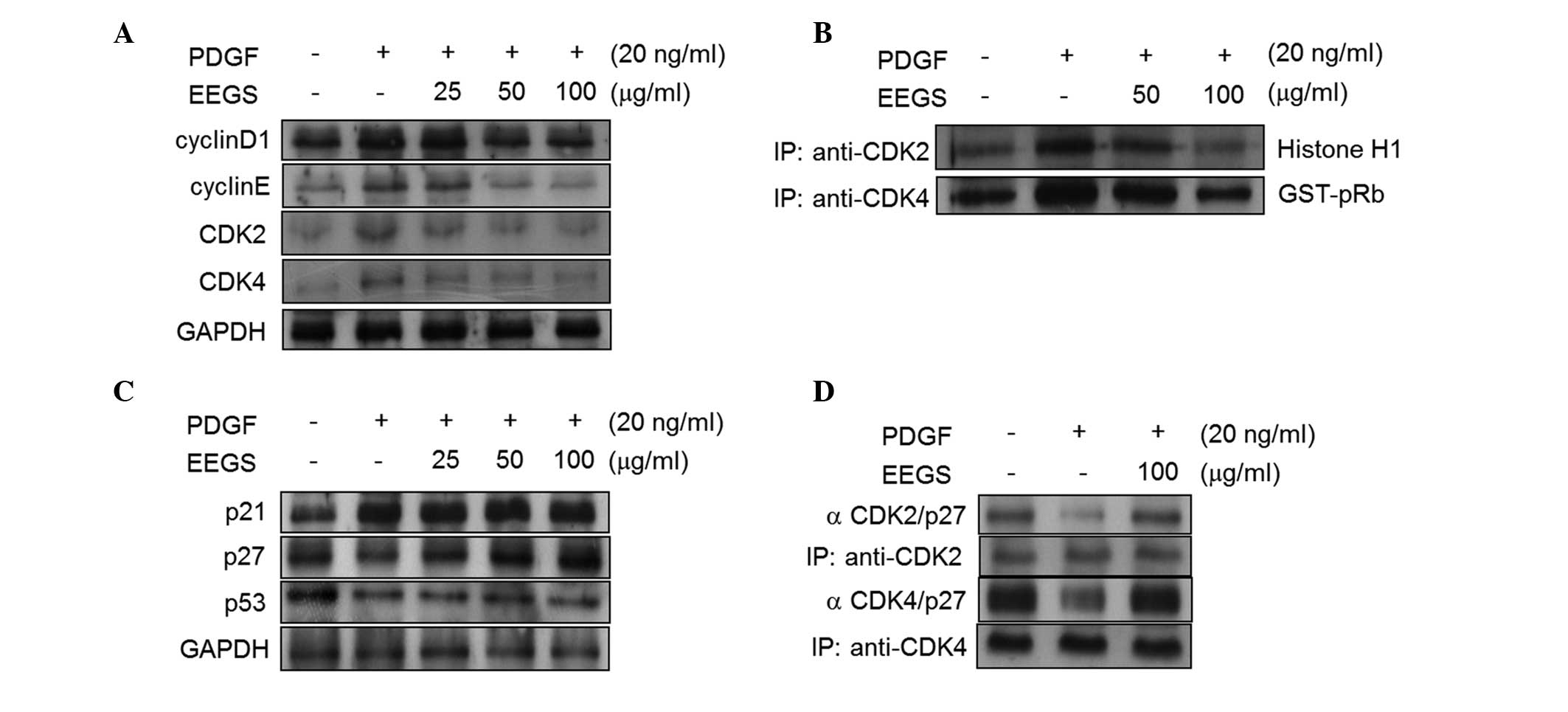
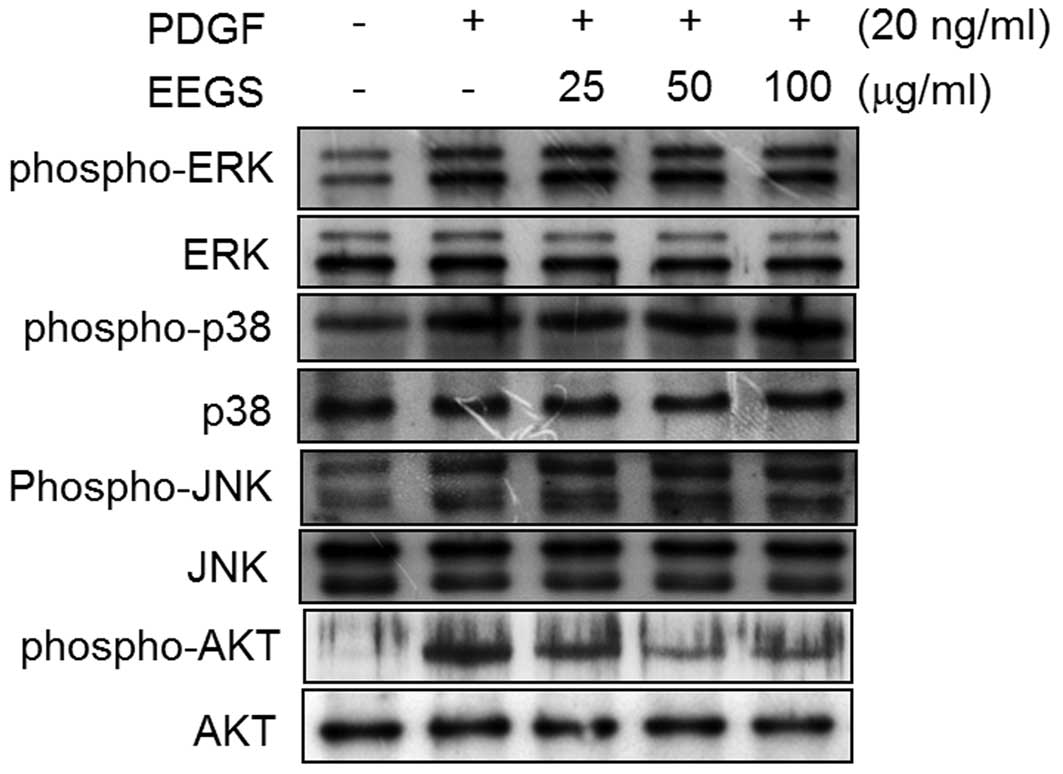
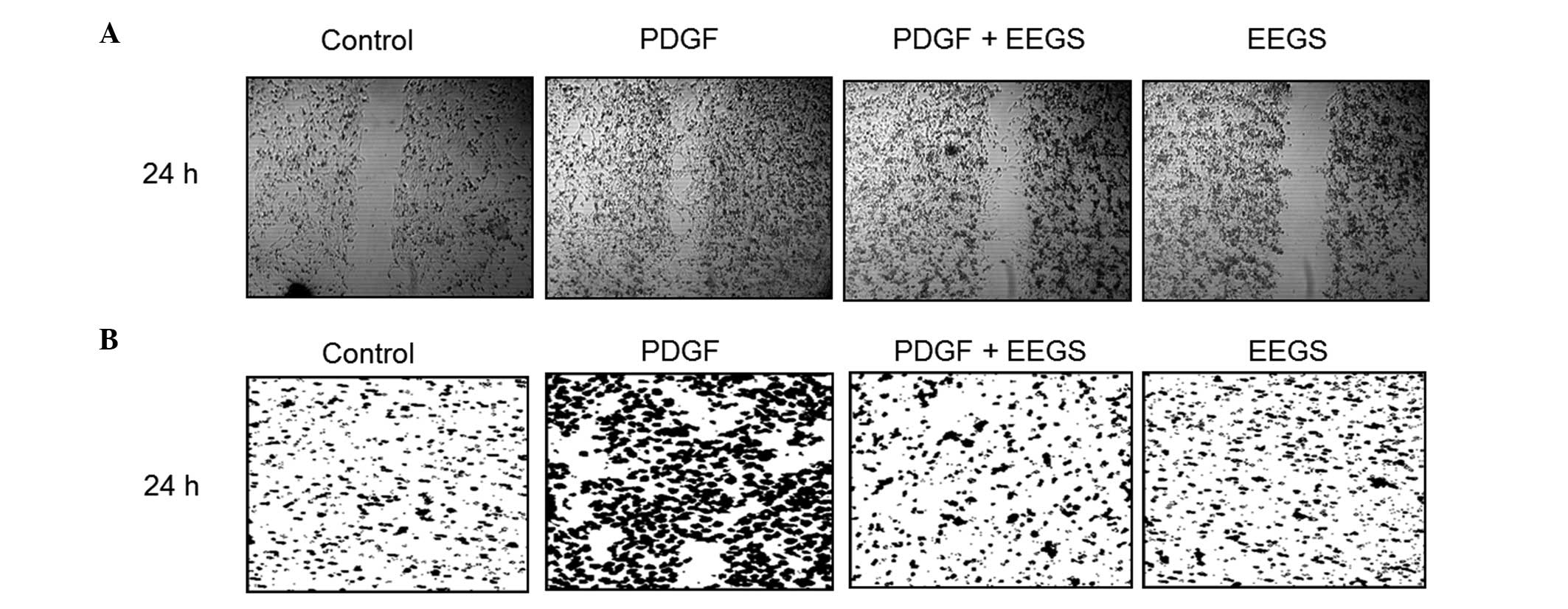
|
1
|
Ross R: Cell biology of atherosclerosis.
Annu Rev Physiol. 57:791–804. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Dzau VJ, Braun-Dullaeus RC and Sedding DG:
Vascular proliferation and atherosclerosis: new perspectives and
therapeutic strategies. Nat Med. 8:1249–1256. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Doran AC, Meller N and McNamara CA: Role
of smooth muscle cells in the initiation and early progression of
atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 28:812–819. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Heldin CH and Westermark B: Mechanism of
action and in vivo role of platelet-derived growth factor. Physiol
Rev. 79:1283–1316. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhan Y, Kim S, Izumi Y, Izumiya Y, Nakao
T, Miyazaki H and Iwao H: Role of JNK, p38, and ERK in
platelet-derived growth factor-induced vascular proliferation,
migration, and gene expression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
23:795–801. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sherr CJ: G1 phase progression: cycling on
cue. Cell. 79:551–555. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xiong Y, Hannon GJ, Zhang H, Casso D,
Kobayashi R and Beach D: p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin
kinases. Nature. 366:701–704. 1993. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Toyoshima H and Hunter T: p27, a novel
inhibitor of G1 cyclin-cdk protein kinase activity, is related to
p21. Cell. 78:67–74. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Newby AC and Zaltsman AB: Molecular
mechanisms in intimal hyperplasia. J Pathol. 190:300–309. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cho A and Reidy MA: Matrix
metalloproteinase-9 is necessary for the regulation of smooth
muscle cell replication and migration after arterial injury. Circ
Res. 91:845–851. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Galis ZS, Johnson C, Godin D, Magid R,
Shipley JM, Senior RM and Ivan E: Targeted disruption of the matrix
metalloproteinase-9 gene impairs smooth muscle cell migration and
geometrical arterial remodeling. Circ Res. 91:852–859. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cho A, Graves J and Reidy MA:
Mitogen-activated protein kinases mediate matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 20:2527–2532. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Moon SK, Cha BY and Kim CH: ERK1/2
mediates TNF-alpha-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in
human vascular smooth muscle cells via the regulation of NF-kappaB
and AP-1: Involvement of the ras dependent pathway. J Cell Physiol.
198:417–427. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Dollery CM, McEwan JR and Henney AM:
Matrix metalloproteinases and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res.
77:863–868. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hansson GK and Robertson AK: TGF-beta in
atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 24:E1372004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lim JC, Park JH, Budesinsky M, Kasal A,
Han YH, Koo BS, Lee SI and Lee DU: Antimutagenic constituents from
the thorns of Gleditsia sinensis. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo).
53:561–564. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou L, Li D, Wang J, Liu Y and Wu J:
Antibacterial phenolic compounds from the spines of Gleditsia
sinensis Lam. Nat Prod Res. 21:283–291. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li WH, Zhang XM, Tian RR, Zheng YT, Zhao
WM and Qiu MH: A new anti-HIV lupane acid from Gleditsia
sinensis Lam. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 9:551–555. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shin TY and Kim DK: Inhibitory effect of
mast cell-dependent anaphylaxis by Gleditsia sinensis. Arch
Pharm Res. 23:401–406. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Park E and Shin MJ: Anti-inflammatory
activity of aqueous extract from Gleditsiae Spina. J
Pharmaceut Soc Korea. 37:124–128. 1993.
|
|
21
|
Lee SJ, Cho YH, Kim H, Park K, Park SK, Ha
SD, Kim WJ and Moon SK: Inhibitory effects of the ethanol extract
of Gleditsia sinensis thorns on human colon cancer HCT116
cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Rep. 22:1505–1512.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou L, Li D, Jiang W, Qin Z, Zhao S, Qiu
M and Wu J: Two ellagic acid glycosides from Gleditsia
sinensis Lam. with antifungal activity on Magnaporthe
grisea. Nat Prod Res. 21:303–309. 2007.
|
|
23
|
Lee SJ, Park SS, Kim WJ and Moon SK:
Gleditsia sinensis thorn extract inhibits proliferation and
TNF-α-induced MMP-9 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am
J Chin Med. 40:373–386. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Tanner FC, Yang ZY, Duckers E, Gordon D,
Nabel GJ and Nabel EG: Expression of cyclin-dependent kinase
inhibitors in vascular disease. Circ Res. 82:396–403. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen D, Krasinski K, Sylvester A, Chen J,
Nisen PD and Andrés V: Downregulation of cyclin-dependent kinase 2
activity and cyclin A promoter activity in vascular smooth muscle
cells by p27(KIP1), an inhibitor of neointima formation in the rat
carotid artery. J Clin Invest. 99:2334–2341. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Moon SK, Kim HM, Lee YC and Kim CH:
Disialoganglioside (GD3) synthase gene expression suppresses
vascular smooth muscle cell responses via the inhibition of ERK1/2
phosphorylation, cell cycle progression, and matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression. J Biol Chem. 279:33063–33070. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shankland SJ and Wolf G: Cell cycle
regulatory proteins in renal disease: role in hypertrophy,
proliferation, and apoptosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
278:F515–F529. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Uchida K, Sasahara M, Morigami N, Hazama F
and Kinoshita M: Expression of platelet-derived growth factor
B-chain in neointimal smooth muscle cells of balloon injured rabbit
femoral arteries. Atherosclerosis. 124:9–23. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|