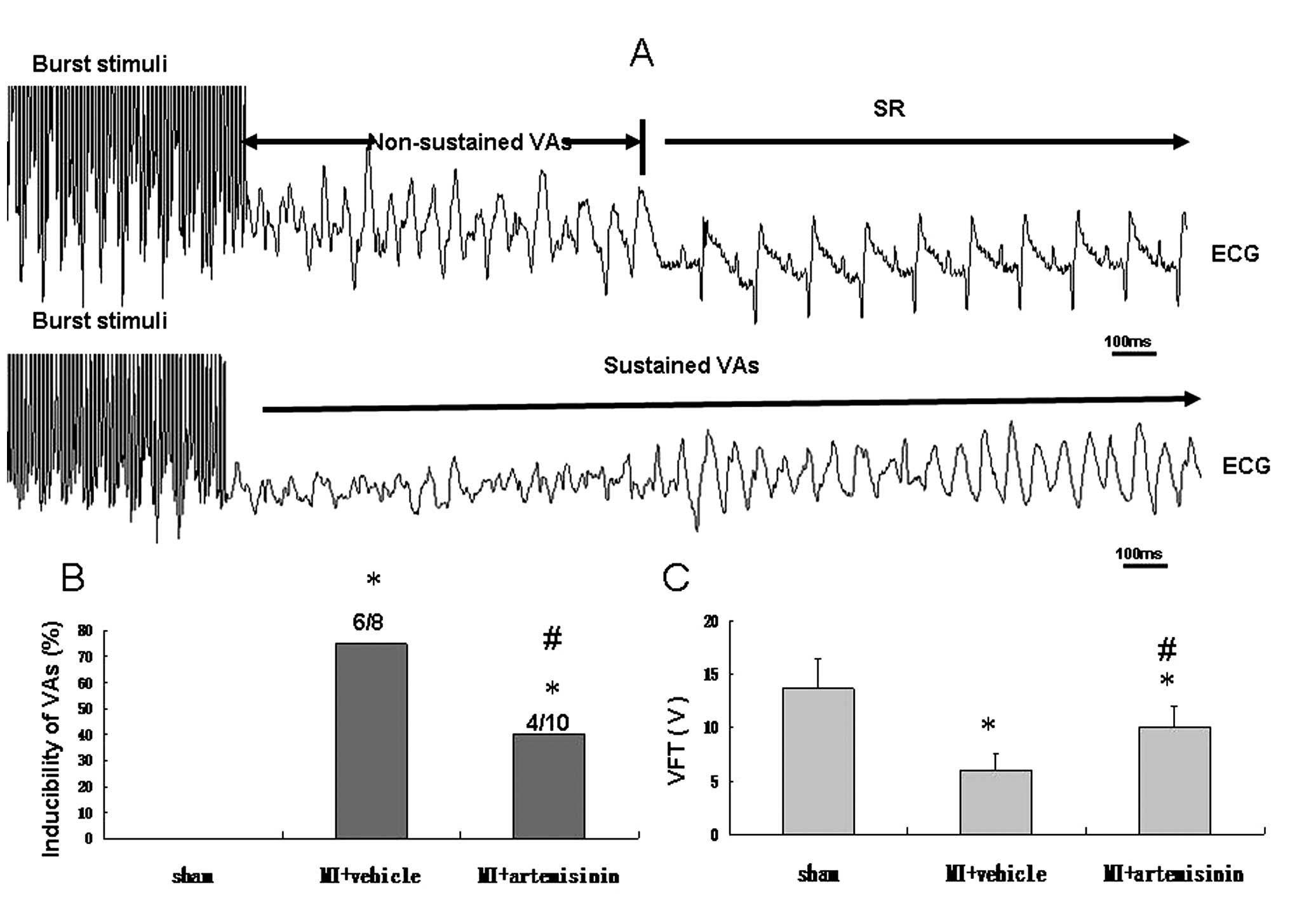
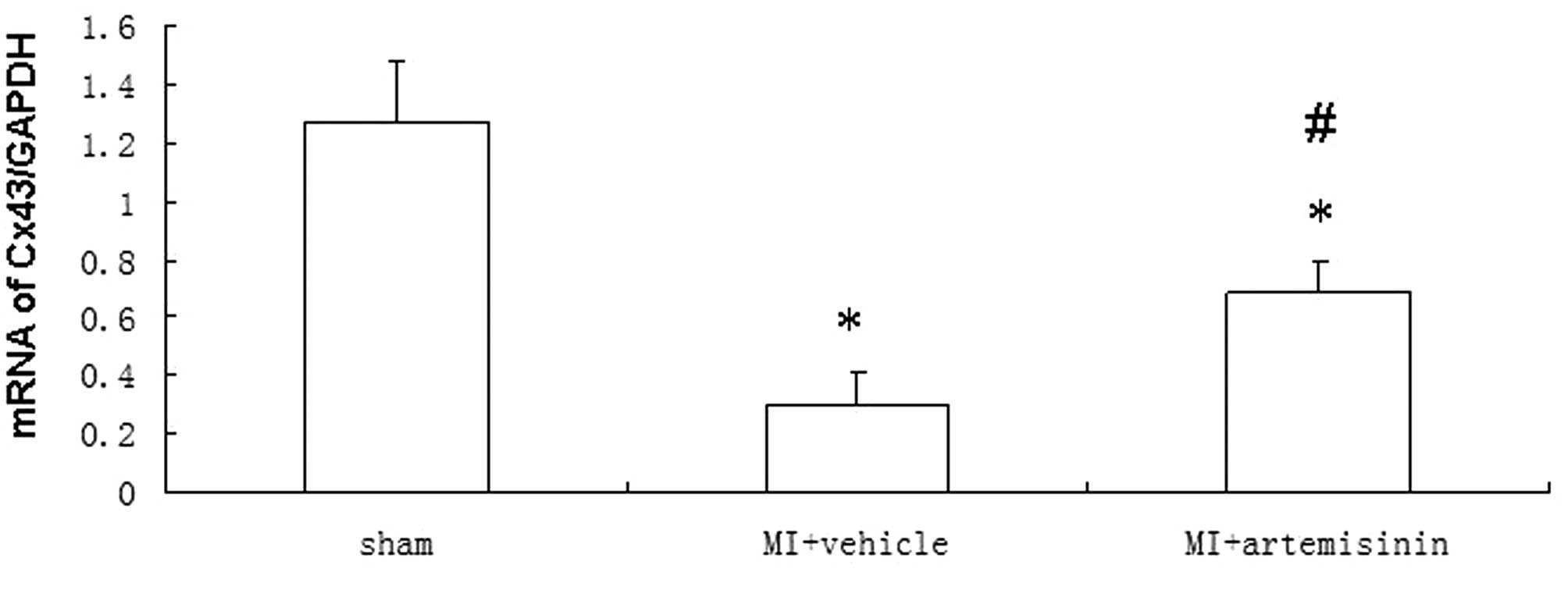
|
1
|
Haynes RK: Artemisinin and derivatives:
the future for malaria treatment? Curr Opin Infect Dis. 14:719–726.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gu Y, Wang X, Wang X, Yuan M, Wu G, Hu J,
Tang Y and Huang C: Artemisinin attenuates post-infarct myocardial
remodeling by down-regulating the NF-κB pathway. Tohoku J Exp Med.
227:161–170. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gu Y, Wang X, Wu G, Wang X, Cao H, Tang Y
and Huang C: Artemisinin suppresses sympathetic hyperinnervation
following myocardial infarction via anti-inflammatory effects. J
Mol Histol. 43:737–743. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wen HZ, Jiang H, Li L, Xie P, Li JY, Lu Zb
and He B: Semaphorin 3A attenuates electrical remodeling at infarct
border zones in rats after myocardial infarction. Tohoku J Exp Med.
225:51–57. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xiong Z, Sun G, Zhu C, Cheng B, Zhang C,
Ma Y and Dong Y: Artemisinin, an anti-malarial agent, inhibits rat
cardiac hypertrophy via inhibition of NF-κB signaling. Eur J
Pharmacol. 649:277–284. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ponnappa BC, Dey I, Tu GC, Zhou F, Aini M,
Cao QN and Israel Y: In vivo delivery of antisense oligonucleotides
in pH-sensitive liposomes inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced
production of tumor necrosis factor-α in rats. J Pharmacol Exp
Ther. 297:1129–1136. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wen H, Jiang H, Lu Z, He B, Hu X, Chen J
and Zhao D: Carvedilol ameliorates the decreases in connexin 43 and
ventricular fibrillation threshold in rats with myocardial
infarction. Tohoku J Exp Med. 218:121–127. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lerner DL, Yamada KA, Schuessler RB and
Saffitz JE: Accelerated onset and increased incidence of
ventricular arrhythmias induced by ischemia in Cx43-deficient mice.
Circulation. 101:547–552. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yao JA, Gutstein DE, Liu F, Fishman GI and
Wit AL: Cell coupling between ventricular myocyte pairs from
connexin43-deficient murine hearts. Circ Res. 93:736–743. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Poelzing S and Rosenbaum DS: Altered
connexin43 expression produces arrhythmia substrate in heart
failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 287:H1762–H1770. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Amino M, Yoshioka K, Tanabe T, Tanaka E,
Mori H, Furusawa Y, et al: Heavy ion radiation up-regulates Cx43
and ameliorates arrhythmogenic substrates in hearts after
myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res. 72:412–421. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fernandes S, van Rijen HV, Forest V, Evain
S, Leblond AL, Mérot J, et al: Cardiac cell therapy: overexpression
of connexin43 in skeletal myoblasts and prevention of ventricular
arrhythmias. J Cell and Mol Med. 13:3703–3712. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Peters NS, Coromilas J, Severs NJ and Wit
AL: Disturbed connexin43 gap junction distribution correlates with
the location of reentrant circuits in the epicardial border zone of
healing canine infarcts that cause ventricular tachycardia.
Circulation. 95:988–996. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ohara T, Ohara K, Cao JM, et al: Increased
wave break during ventricular fibrillation in the epicardial border
zone of hearts with healed myocardial infarction. Circulation.
103:1465–1472. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Qiao G, Li S, Yang B and Li B: Inhibitory
effects of artemisinin on voltage-gated ion channels in intact
nodose ganglion neurones of adult rats. Basic Clin Pharmacol
Toxicol. 100:217–224. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang BF, Luo DL, Bao LH, Zhang YC and Wang
HZ: Artemisinin blocks activating and slowly activating
K+ current in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Zhongguo
Yao Li Xue Bao. 19:269–272. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jiang H, Hu X, Lu Z, Wen H, Zhao D, Tang
Q, et al: Effects of sympathetic nerve stimulation on
ischemia-induced ventricular arrhythmias by modulating connexin43
in rats. Arch Med Res. 39:647–654. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ando M, Katare RG, Kakinuma Y, Zhang D,
Yamasaki F, Muramoto K, et al: Efferent vagal nerve stimulation
protects heart against ischemia-induced arrhythmias by preserving
connexin43 protein. Circulation. 112:164–170. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hao JL, Suzuki K, Lu Y, Hirano S, Fukuda
K, Kumagai N, Kimura K and Nishida T: Inhibition of gap
junction-mediated intercellular communication by TNF-alpha in
cultured human corneal fibroblasts. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
46:1195–1200. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|