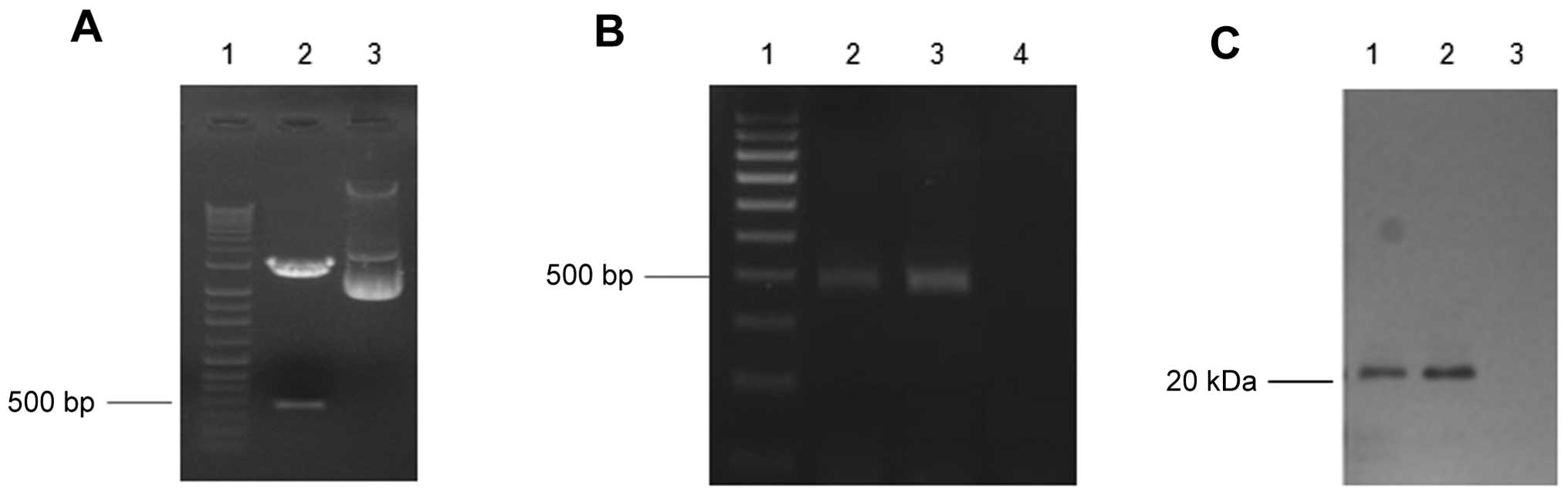
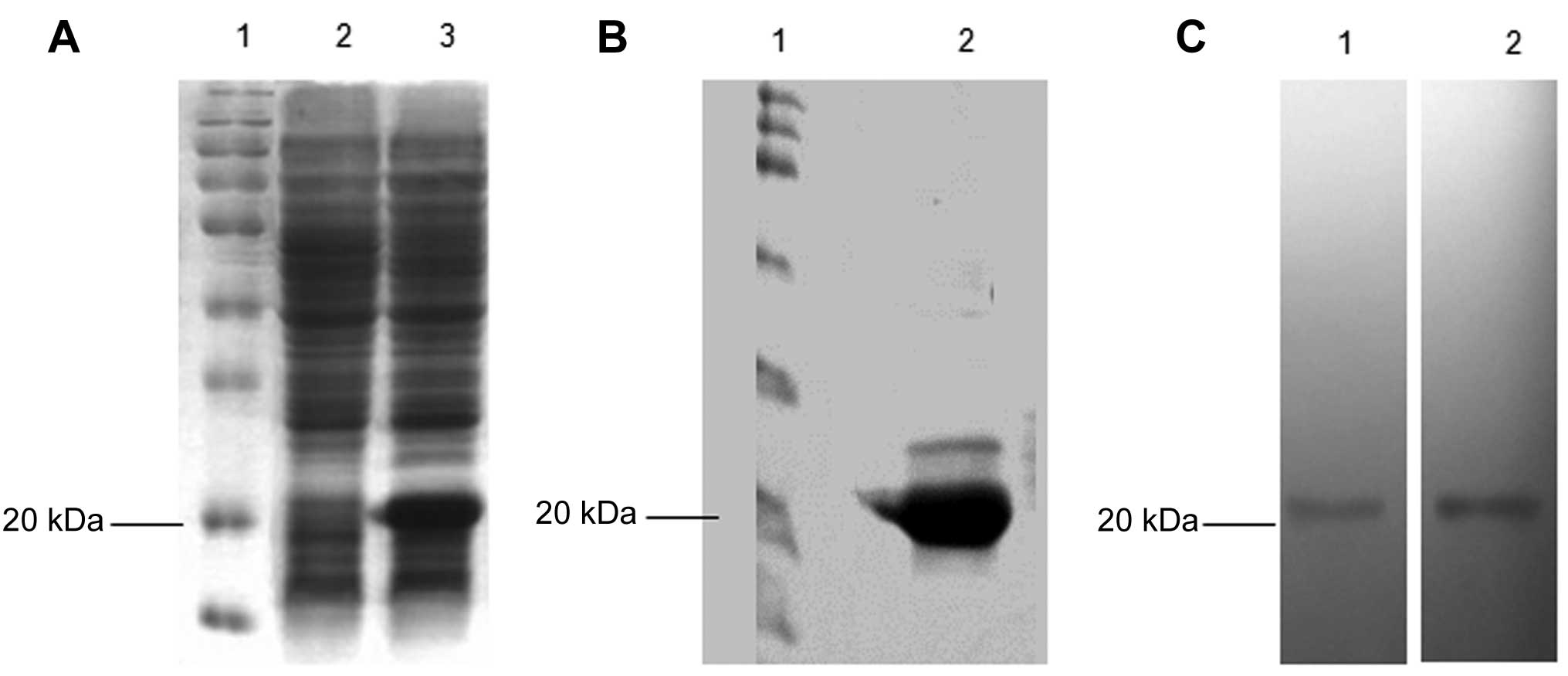
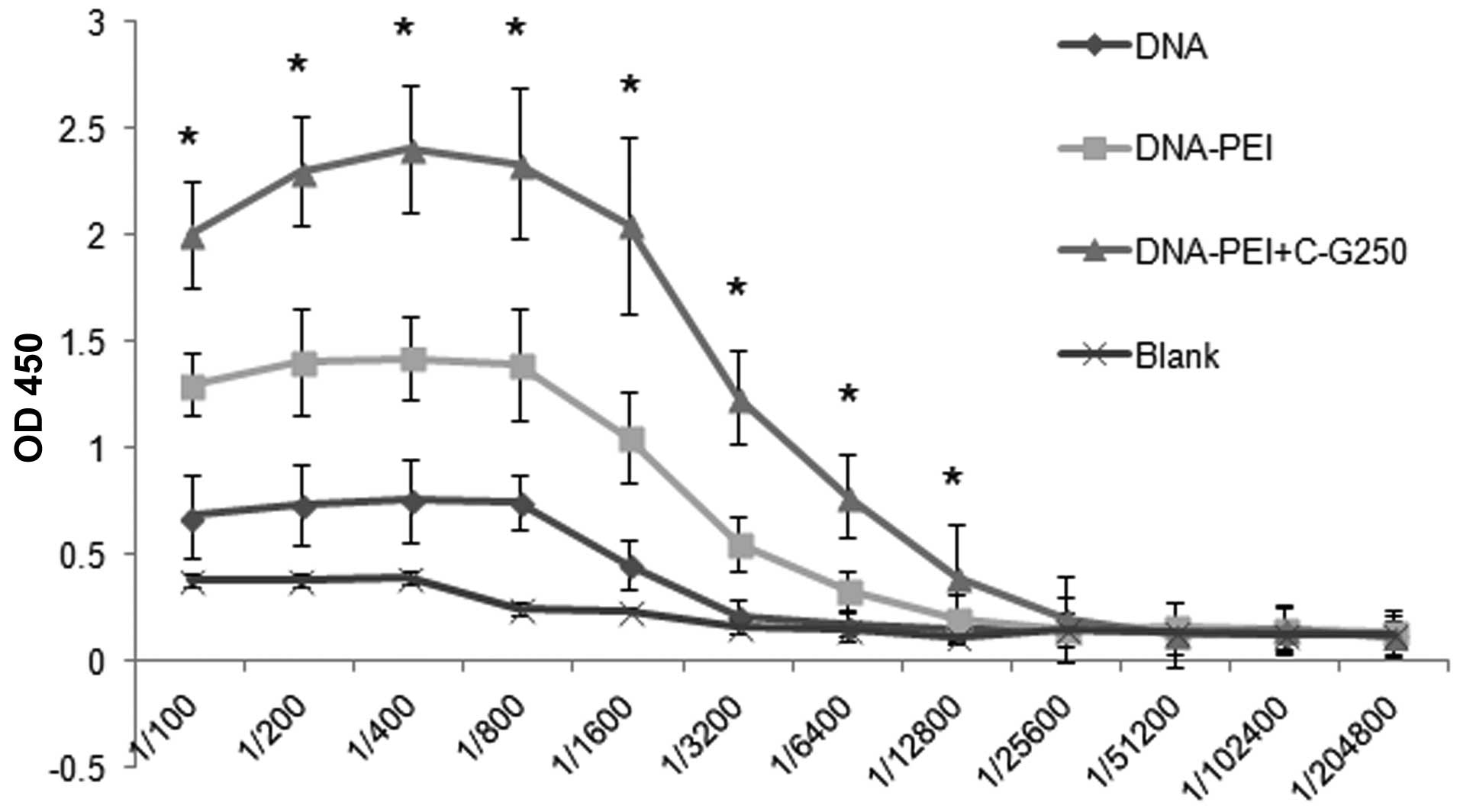
|
1
|
Awakura Y, Ito N, Nakamura E, et al:
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 polymorphisms and renal cell carcinoma
in a Japanese population. Cancer Lett. 241:59–63. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dutcher JP: Recent developments in the
treatment of renal cell carcinoma. Ther Adv Urol. 5:338–353. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tostain J, Li G, Gentil-Perret A and
Gigante M: Carbonic anhydrase 9 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma:
a marker for diagnosis, prognosis and treatment. Eur J Cancer.
46:3141–3148. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stadick H, Stockmeyer B, Kühn R, et al:
Epidermal growth factor receptor and g250: useful target antigens
for antibody mediated cellular cytotoxicity against renal cell
carcinoma? J Urol. 167:707–712. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li G, Feng G, Gentil-Perret A, Genin C and
Tostain J: CA9 gene expression in conventional renal cell
carcinoma: a potential marker for prediction of early metastasis
after nephrectomy. Clin Exp Metastasis. 24:149–155. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Muselaers S, Mulders P, Oosterwijk E, Oyen
W and Boerman O: Molecular imaging and carbonic anhydrase
IX-targeted radioimmunotherapy in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
Immunotherapy. 5:489–495. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vissers JL, De Vries IJ, Engelen LP, et
al: Renal cell carcinoma-associated antigen G250 encodes a
naturally processed epitope presented by human leukocyte antigen-DR
molecules to CD4(+) T lymphocytes. Int J Cancer. 100:441–444. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Vissers JL, De Vries IJ, Schreurs MW, et
al: The renal cell carcinoma-associated antigen G250 encodes a
human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-A2.1-restricted epitope recognized by
cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Cancer Res. 59:5554–5559. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xiao Y, Gao J, Gao K, et al: Prokaryotic
expression, purification and antigenicity identification of human
renal cell carcinoma-associated antigen G250. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian
Yi Xue Za Zhi. 29:269–272. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
10
|
Liu B, Sun Z, Liu Q, et al: Construction
and prokaryotic expression of recombinant gene G250 antigenic
peptide-HBcAg and the immunogenicity analysis of the fusion
protein. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University (Medical Sciences).
1:6–11. 2014.
|
|
11
|
Manoj S, Babiuk LA and van Drunen
Littel-van den Hurk S: Approaches to enhance the efficacy of DNA
vaccines. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 41:1–39. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ada G: Vaccines and vaccination. N Engl J
Med. 345:1042–1053. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Grant EV, Thomas M, Fortune J, Klibanov AM
and Letvin NL: Enhancement of plasmid DNA immunogenicity with
linear polyethylenimine. Eur J Immunol. 42:2937–2948. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Krishnamachari Y, Geary SM, Lemke CD and
Salem AK: Nanoparticle delivery systems in cancer vaccines. Pharm
Res. 28:215–236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Demeneix B and Behr JP: Polyethylenimine
(PEI). Adv Genet. 53PA:215–230. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kichler A, Leborgne C, Coeytaux E and
Danos O: Polyethylenimine-mediated gene delivery: a mechanistic
study. J Gene Med. 3:135–144. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ma YF and Yang YW: Delivery of DNA-based
cancer vaccine with polyethylenimine. Eur J Pharm Sci. 40:75–83.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bivas-Benita M, Bar L, Gillard GO, et al:
Efficient generation of mucosal and systemic antigen-specific CD8+
T-cell responses following pulmonary DNA immunization. J Virol.
84:5764–5774. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gaugler B, Brouwenstijn N, Vantomme V, et
al: A new gene coding for an antigen recognized by autologous
cytolytic T lymphocytes on a human renal carcinoma. Immunogenetics.
44:323–330. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Brossart P, Stuhler G, Flad T, et al:
Her-2/neu-derived peptides are tumor-associated antigens expressed
by human renal cell and colon carcinoma lines and are recognized by
in vitro induced specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Cancer Res.
58:732–736. 1998.
|
|
21
|
Kawagoe N, Shintaku I, Yutani S, et al:
Expression of the SART3 tumor rejection antigen in renal cell
carcinoma. J Urol. 164:2090–2095. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li K, Gao H, Gao L, et al: Enhancement of
humoral and cellular immunity in chickens against
reticuloendotheliosis virus by DNA prime-protein boost vaccination.
Vaccine. 31:1944–1949. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li M, Jiang Y, Xu C, Zhang Z and Sun X:
Enhanced immune response against HIV-1 induced by a heterologous
DNA prime-adenovirus boost vaccination using mannosylated
polyethyleneimine as DNA vaccine adjuvant. Int J Nanomedicine.
8:1843–1854. 2013.
|
|
24
|
Lan J, Gao Z, Xiong H, et al: Generation
of protective immune responses against coxsackievirus B3 challenge
by DNA prime-protein boost vaccination. Vaccine. 29:6894–6902.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang X, Xu J, Qiu C, et al: Mucosal
priming with PEI/DNA complex and systemic boosting with recombinant
TianTan vaccinia stimulate vigorous mucosal and systemic immune
responses. Vaccine. 25:2620–2629. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Goula D, Becker N, Lemkine GF, et al:
Rapid crossing of the pulmonary endothelial barrier by
polyethylenimine/DNA complexes. Gene Ther. 7:499–504. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wegmann F, Gartlan KH, Harandi AM, et al:
Polyethyleneimine is a potent mucosal adjuvant for viral
glycoprotein antigens. Nat Biotechnol. 30:883–888. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|