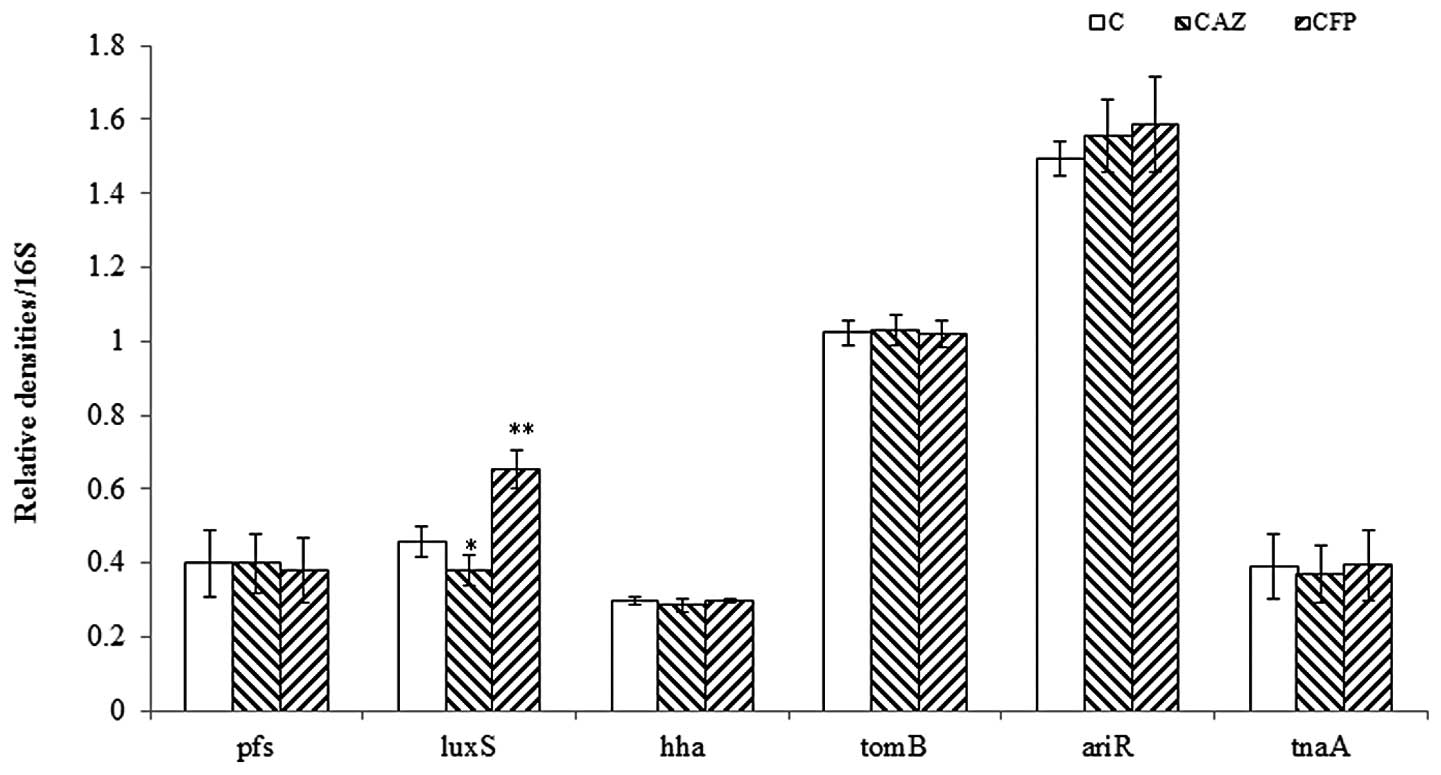
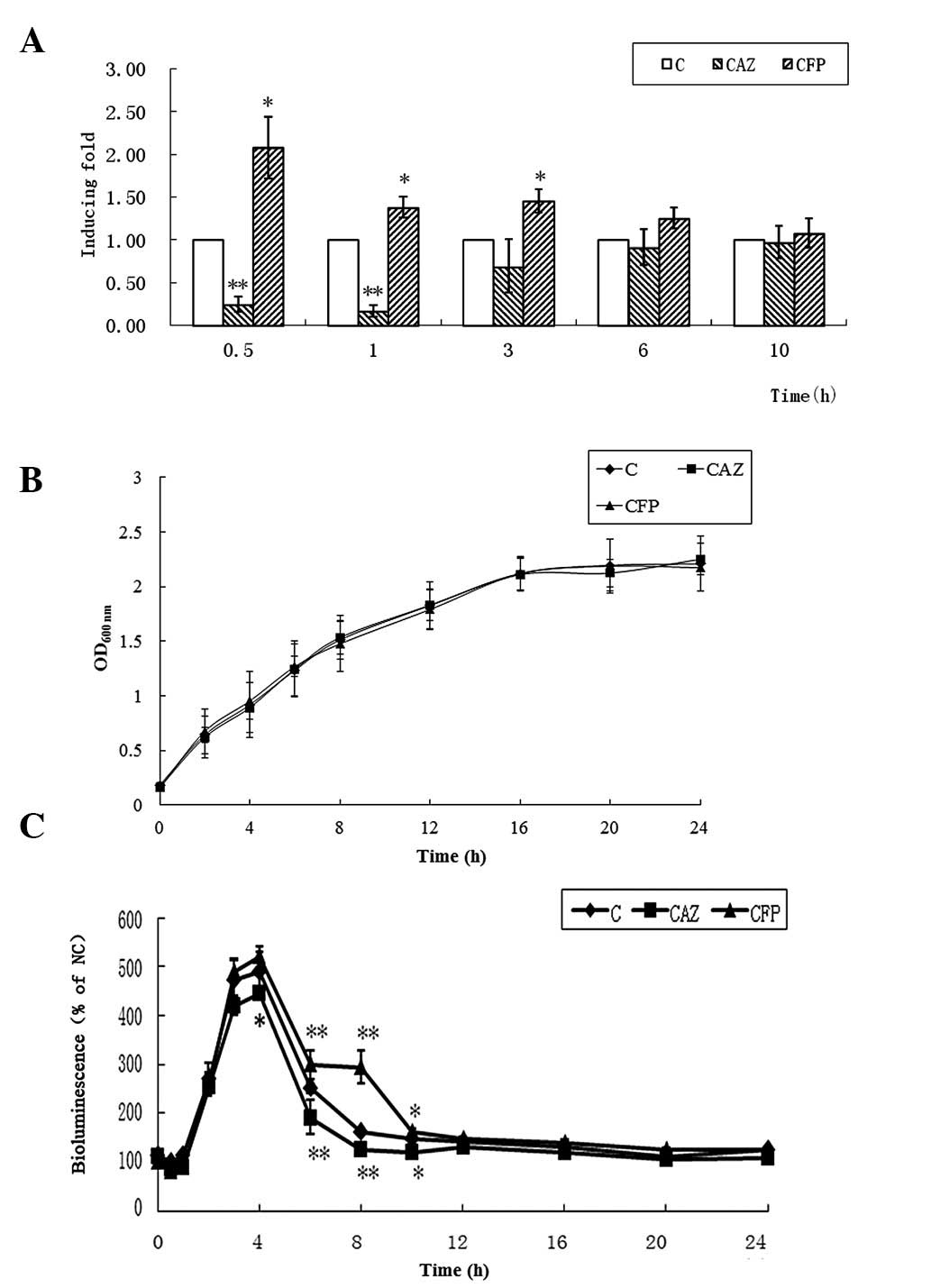
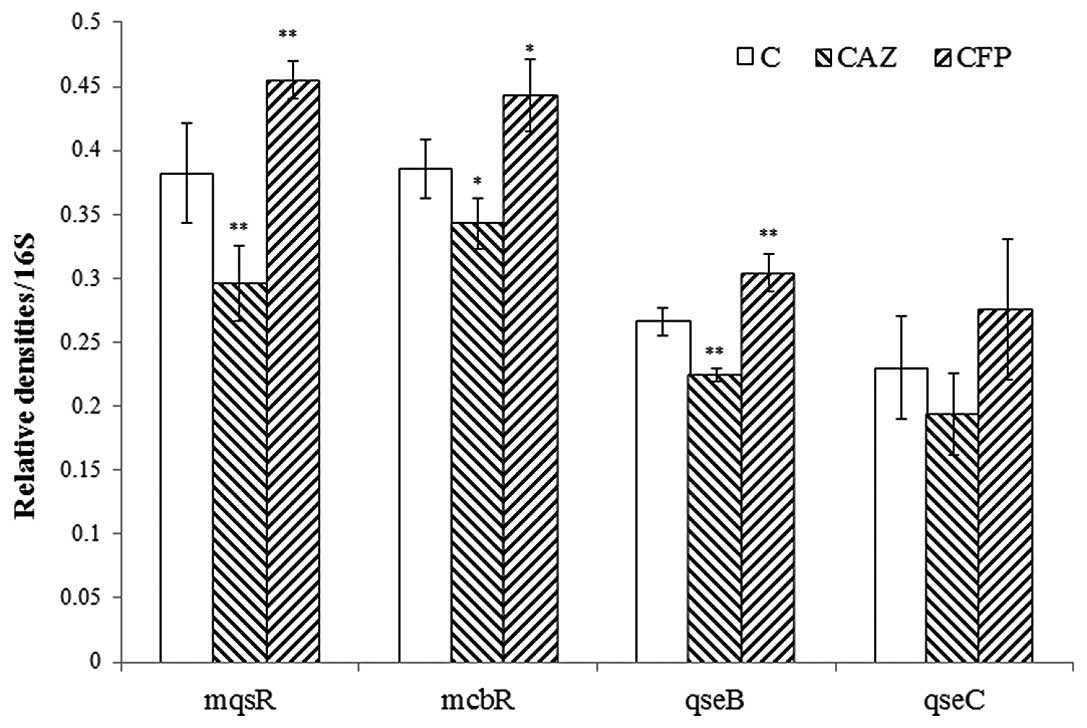
|
1
|
Costerton JW, Stewart PS and Greenberg EP:
Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections.
Science. 284:1318–1322. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Galloway WR, Hodgkinson JT, Bowden SD,
Welch M and Spring DR: Quorum sensing in Gram-negative bacteria:
small-molecule modulation of AHL and AI-2 quorum sensing pathways.
Chem Rev. 111:28–67. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nickel J, Ruseska I, Wright J and
Costerton J: Tobramycin resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
cells growing as a biofilm on urinary catheter material. Antimicrob
Agents Chemother. 27:619–624. 1985.
|
|
4
|
Joly V, Pangon B, Vallois JM, et al: Value
of antibiotic levels in serum and cardiac vegetations for
predicting antibacterial effect of ceftriaxone in experimental
Escherichia coli endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
31:1632–1639. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kaplan JB: Antibiotic-induced biofilm
formation. Int J Artif Organs. 34:737–751. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kanthawong S, Bolscher JG, Veerman EC, et
al: Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity of LL-37 and its
truncated variants against Burkholderia pseudomallei. Int J
Antimicrob Agents. 39:39–44. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Skindersoe ME, Alhede M, Phipps R, et al:
Effects of antibiotics on quorum sensing in Pseudomonas
aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 52:3648–3663. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Song Z, Kong K, Wu H, et al: Panax ginseng
has anti-infective activity against opportunistic pathogen
Pseudomonas aeruginosa by inhibiting quorum sensing, a
bacterial communication process critical for establishing
infection. Phytomedicine. 17:1040–1046. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute.
Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing;
20th informational supplement. CLSI document M100-S20. Clinical
Laboratory Standards Institute; Wayne, PA, USA: 2010
|
|
10
|
Kim YH, Lee Y, Kim S, et al: The role of
periplasmic antioxidant enzymes (superoxide dismutase and thiol
peroxidase) of the Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli
O157: H7 in the formation of biofilms. Proteomics. 6:6181–6193.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li Y, Li Q, Du Y, et al: Prevalence of
plasmid-mediated AmpC beta-lactamases in a Chinese university
hospital from 2003 to 2005: first report of CMY-2-Type AmpC
beta-lactamase resistance in China. J Clin Microbiol. 46:1317–1321.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
|
|
13
|
Surette MG, Miller MB and Bassler BL:
Quorum sensing in Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium,
and Vibrio harveyi: a new family of genes responsible for
autoinducer production. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:1639–1644.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang Y, Zhang W, Wu Z, Zhu X and Lu C:
Functional analysis of luxS in Streptococcus suis reveals a key
role in biofilm formation and virulence. Vet Microbiol.
152:151–160. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li B, Yao Q, Pan XC, et al: Artesunate
enhances the antibacterial effect of β-lactam antibiotics against
Escherichia coli by increasing antibiotic accumulation via
inhibition of the multidrug efflux pump system AcrAB-TolC. J
Antimicrob Chemother. 66:769–777. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Meng J, Wang H, Hou Z, et al: Novel anion
liposome-encapsulated antisense oligonucleotide restores
susceptibility of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus
aureus and rescues mice from lethal sepsis by targeting
mecA. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 53:2871–2878. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Jones MB, Jani R, Ren D, Wood TK and
Blaser MJ: Inhibition of Bacillus anthracis growth and
virulence-gene expression by inhibitors of quorum-sensing. J Infect
Dis. 191:1881–1888. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wood TK: Insights on Escherichia
coli biofilm formation and inhibition from whole-transcriptome
profiling. Environ Microbiol. 11:1–15. 2009.
|
|
19
|
Bala A, Kumar R and Harjai K: Inhibition
of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by azithromycin
and its effectiveness in urinary tract infections. J Med Microbiol.
60:300–306. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Maezono H, Noiri Y, Asahi Y, et al:
Antibiofilm effects of azithromycin and erythromycin on
Porphyromonas gingivalis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
55:5887–5892. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang Q, Sun FJ, Liu Y, et al: Enhancement
of biofilm formation by subinhibitory concentrations of macrolides
in icaADBC-positive and -negative clinical isolates of
Staphylococcus epidermidis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
54:2707–2711. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Garey KW, Vo QP, Lewis RE, et al:
Increased bacterial adherence and biomass in Pseudomonas
aeruginosa bacteria exposed to clarithromycin. Diagn Microbiol
Infect Dis. 63:81–86. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bijie H, Kulpradist S, Manalaysay M and
Soebandrio A: In vitro activity, pharmacokinetics, clinical
efficacy, safety and pharmacoeconomics of ceftriaxone compared with
third and fourth generation cephalosporins: review. J Chemother.
17:3–24. 2005.
|
|
24
|
González Barrios FG, Zuo R, Hashimoto Y,
et al: Autoinducer 2 controls biofilm formation in Escherichia
coli through a novel motility quorum-sensing regulator (MqsR,
B3022). J Bacteriol. 188:305–316. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mandell G and Sande M: Antimicrobial
agents: penicillins, cephalosporins, and other beta-lactam
antibiotics. Goodman and Gilman’s The Pharmacologic Basis of
Therapeutics. Gilman AG, Hardman JG, Limbird L and Ral TR: 9th
edition. McGraw-Hill; New York, NY: pp. 1090–1091. 1996
|
|
26
|
Arndt PA and Garratty G: Cross-reactivity
of cefotetan and ceftriaxone antibodies, associated with hemolytic
anemia, with other: cephalosporins and penicillin. Am J Clin
Pathol. 118:256–262. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|