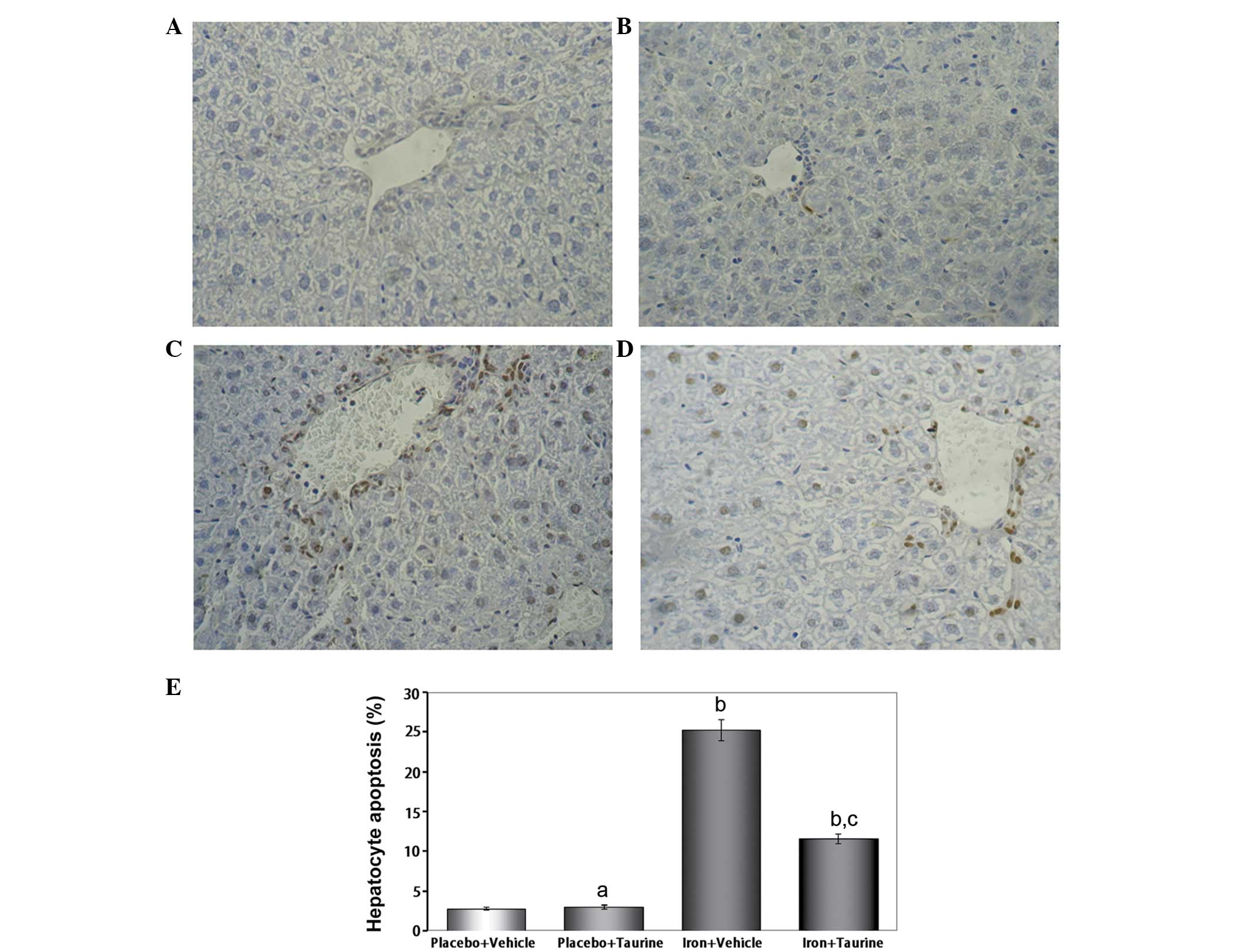
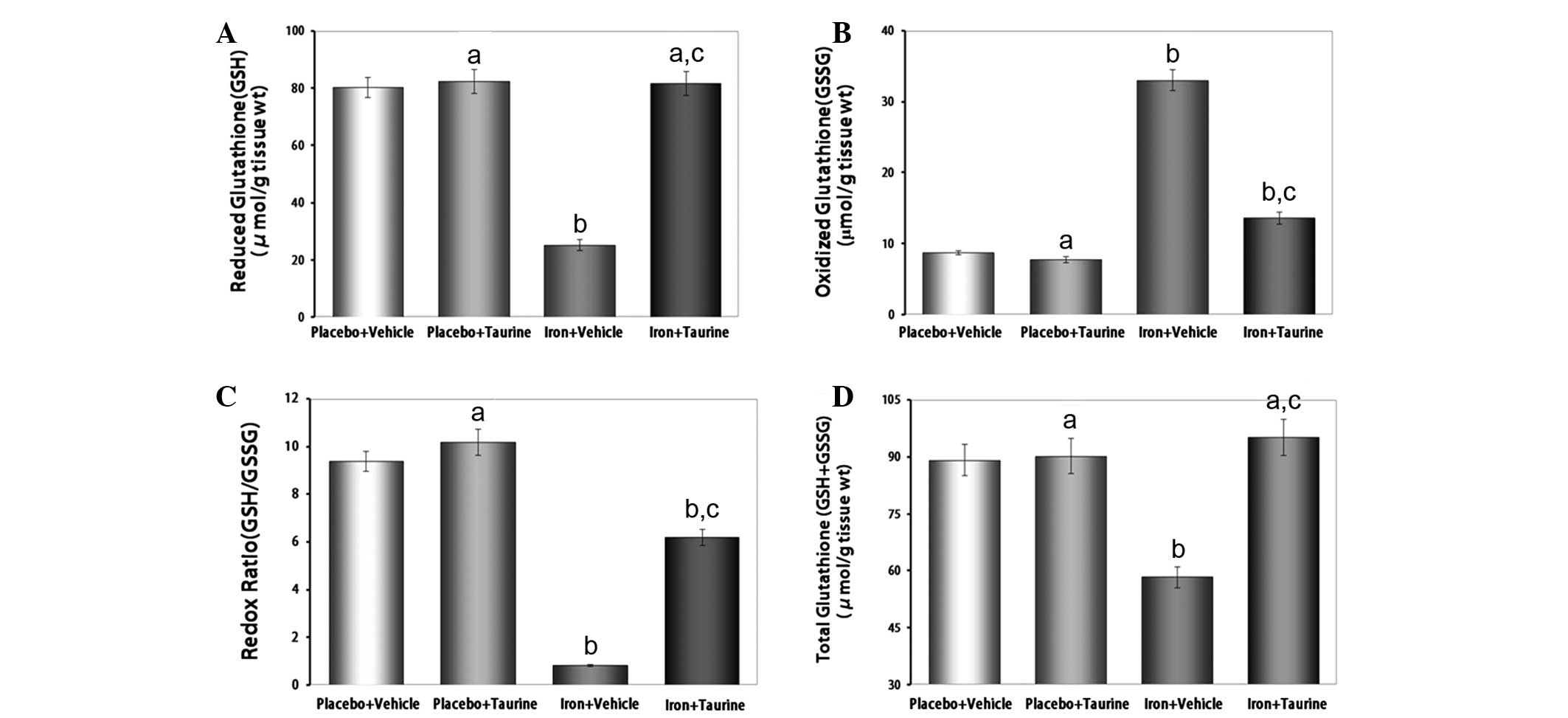
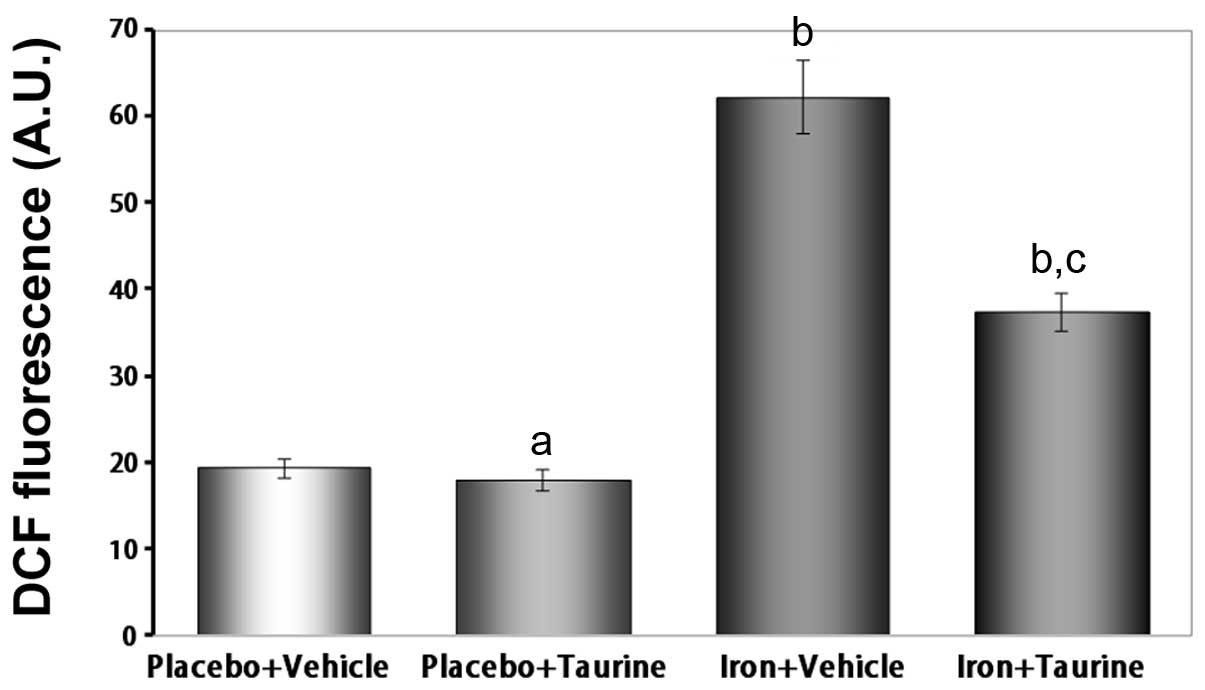
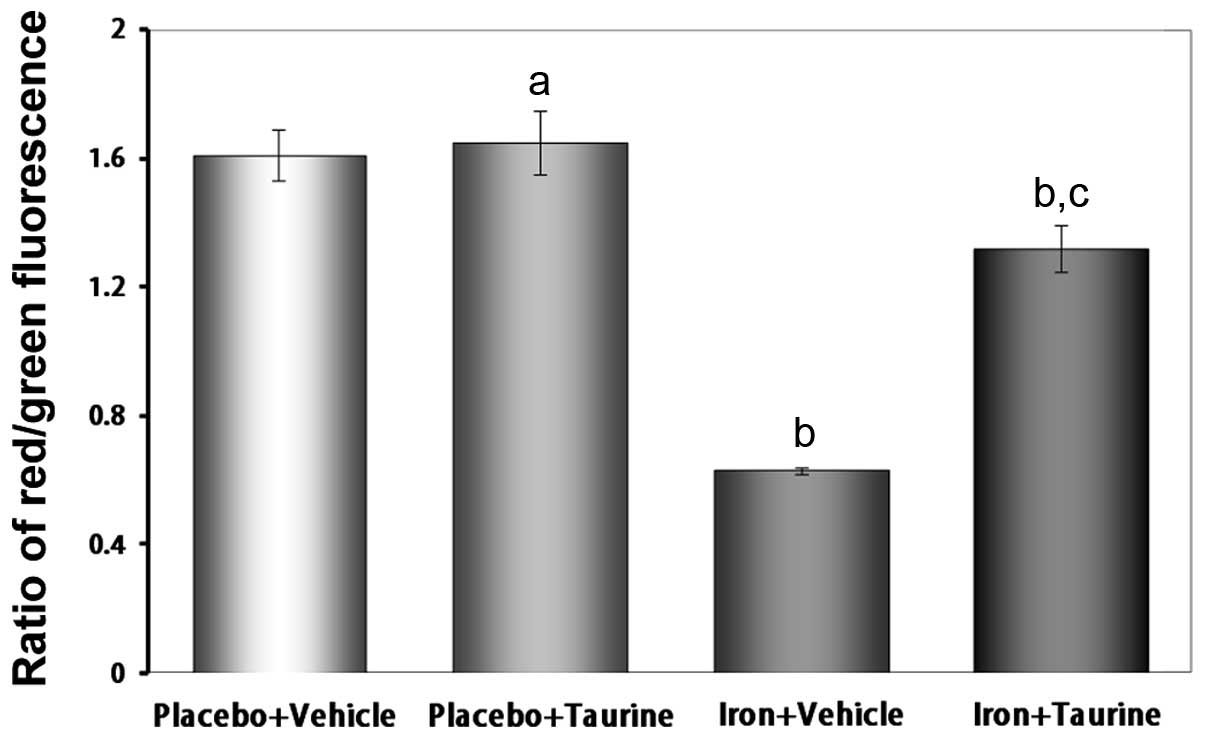
|
1
|
Santos PC, Krieger JE and Pereira AC:
Molecular diagnostic and pathogenesis of hereditary
hemochromatosis. Int J Mol Sci. 13:1497–1511. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Murphy CJ and Oudit GY: Iron-overload
cardiomyopathy: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. J Card
Fail. 16:888–900. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Moretti D, van Doorn GM, Swinkels DW and
Melse-Boonstra A: Relevance of dietary iron intake and
bioavailability in the management of HFE hemochromatosis: a
systematic review. Am J Clin Nutr. 98:468–479. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Alústiza Echeverría JM, Castiella A and
Emparanza JI: Quantification of iron concentration in the liver by
MRI. Insights Imaging. 3:173–180. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee M and Kowdley KV: Alcohol’s effect on
other chronic liver diseases. Clin Liver Dis. 16:827–837. 2012.
|
|
6
|
Hayashi H, Piperno A, Tomosugi N, et al:
Patients with chronic hepatitis C may be more sensitive to iron
hepatotoxicity than patients with HFE-hemochromatosis. Intern Med.
49:2371–2377. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Abdalla MY, Fawzi M, Al-Maloul SR,
El-Banna N, Tayyem RF and Ahmad IM: Increased oxidative stress and
iron overload in Jordanian β-thalassemic children. Hemoglobin.
35:67–79. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li X, Li H, Lu N, Feng Y, Huang Y and Gao
Z: Iron increases liver injury through oxidative/nitrative stress
in diabetic rats: Involvement of nitrotyrosination of glucokinase.
Biochimie. 94:2620–2627. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Serviddio G, Bellanti F, Sastre J,
Vendemiale G and Altomare E: Targeting mitochondria: a new
promising approach for the treatment of liver diseases. Curr Med
Chem. 17:2325–2337. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu D, He H, Yin D, Que A, Tang L, Liao Z,
Huang Q and He M: Mechanism of chronic dietary iron
overload-induced liver damage in mice. Mol Med Rep. 7:1173–1179.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Batista TM, Ribeiro RA, da Silva PM,
Camargo RL, Lollo PC, Boschero AC and Carneiro EM: Taurine
supplementation improves liver glucose control in normal protein
and malnourished mice fed a high-fat diet. Mol Nutr Food Res.
57:423–434. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Heidari R, Babaei H and Eghbal MA:
Cytoprotective effects of taurine against toxicity induced by
isoniazid and hydrazine in isolated rat hepatocytes. Arh Hig Rada
Toksikol. 64:15–24. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hartman JC, Brouwer K, Mandagere A, Melvin
L and Gorczynski R: Evaluation of the endothelin receptor
antagonists ambrisentan, darusentan, bosentan, and sitaxsentan as
substrates and inhibitors of hepatobiliary transporters in
sandwich-cultured human hepatocytes. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
88:682–691. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Liao Y, Lu X, Lu C, Li G, Jin Y and Tang
H: Selection of agents for prevention of cisplatin-induced
hepatotoxicity. Pharmacol Res. 57:125–131. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tabassum H, Rehman H, Banerjee BD,
Raisuddin S and Parvez S: Attenuation of tamoxifen-induced
hepatotoxicity by taurine in mice. Clin Chim Acta. 370:129–136.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang GG, Li W, Lu XH, Zhao X and Xu L:
Taurine attenuates oxidative stress and alleviates cardiac failure
in type I diabetic rats. Croat Med J. 54:171–179. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Higuchi M, Celino FT, Shimizu-Yamaguchi S,
Miura C and Miura T: Taurine plays an important role in the
protection of spermatogonia from oxidative stress. Amino Acids.
43:2359–2369. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Oudit GY, Sun H, Trivieri MG, Koch SE,
Dawood F, Ackerley C, Yazdanpanah M, Wilson GJ, Schwartz A, Liu PP
and Backx PH: L-type Ca2+ channels provide a major
pathway for iron entry into cardiomyocytes in iron-overload
cardiomyopathy. Nat Med. 9:1187–1194. 2003.
|
|
19
|
Galleano M and Puntarulo S: Hepatic
chemiluminescence and lipid peroxidation in mild iron overload.
Toxicology. 76:27–38. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Keith ME, Ball A, Jeejeebhoy KN, Kurian R,
Butany J, Dawood F, Wen WH, Madapallimattam A and Sole MJ:
Conditioned nutritional deficiencies in the cardiomyopathic hamster
heart. Can J Cardiol. 17:449–458. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Okhawa H, Ohishi N and Yagi K: Assay for
lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction.
Anal Biochem. 95:351–358. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Beauchamp C and Fridovich I: Superoxide
dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide
gels. Anal Biochem. 44:276–287. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hill MF and Singal PK: Right and left
myocardial antioxidant responses during heart failure subsequent to
myocardial infarction. Circulation. 96:2414–2420. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Anderson ME: Determination of glutathione
and glutathione disulfide in biological samples. Methods Enzymol.
113:548–555. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kalantari-Dehaghi M, Chen Y, Deng W,
Chernyavsky A, Marchenko S, Wang PH and Grando SA: Mechanisms of
mitochondrial damage in keratinocytes by Pemphigus vulgaris
antibodies. J Biol Chem. 288:16916–16925. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Beavis AD, Brannan RD and Garlid KD:
Swelling and contraction of the mitochondrial matrix. I. A
structural interpretation of the relationship between light
scattering and matrix volume. J Biol Chem. 260:13424–13433.
1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Misra HP and Fridovich I: The role of
superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple
assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem. 247:3170–3175.
1972.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ketterer B: Detoxication reactions of
glutathione and glutathione transferases. Xenobiotica. 16:957–973.
1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu CM, Zheng GH, Ming QL, Sun JM and
Cheng C: Protective effect of quercetin on lead-induced oxidative
stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress in rat liver via the
IRE1/JNK and PI3K/Akt pathway. Free Radic Res. 47:192–201. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Banu S, Bhaskar B and Balasekar P:
Hepatoprotective and antioxidant activity of Leucas aspera
against D-galactosamine induced liver damage in rats. Pharm Biol.
50:1592–1595. 2012.
|
|
31
|
Pompella A, Visvikis A, Paolicchi A, De
Tata V and Casini AF: The changing faces of glutathione, a cellular
protagonist. Biochem Pharmacol. 66:1499–1503. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schaffer SW, Azuma J and Mozaffari M: Role
of antioxidant activity of taurine in diabetes. Can J Physiol
Pharmacol. 87:91–99. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pardo Andreu GL, Inada NM, Vercesi AE and
Curti C: Uncoupling and oxidative stress in liver mitochondria
isolated from rats with acute iron overload. Arch Toxicol.
83:47–53. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tirnitz-Parker JE, Glanfield A, Olynyk JK
and Ramm GA: Iron and hepatic carcinogenesis. Crit Rev Oncog.
18:391–407. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Sorrentino P, Terracciano L, D’Angelo S,
et al: Oxidative stress and steatosis are cofactors of liver injury
in primary biliary cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol. 45:1053–1062. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lalisang TJ: Serum bile acid: an
alternative liver function marker in the obstructive jaundice
patient. Acta Med Indones. 44:233–238. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Manna P, Sinha M and Sil PC: Taurine plays
a beneficial role against cadmium-induced oxidative renal
dysfunction. Amino Acids. 36:417–428. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sinha M, Manna P and Sil PC: Taurine, a
conditionally essential amino acid, ameliorates arsenic-induced
cytotoxicity in murine hepatocytes. Toxicol In Vitro. 21:1419–1428.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Aruoma OI, Halliwell B, Hoey BM and Butler
J: The antioxidant action of taurine, hypotaurine and their
metabolic precursors. Biochem J. 256:251–255. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Budhram R, Pandya KG and Lau-Cam CA:
Protection by taurine and thiotaurine against biochemical and
cellular alterations induced by diabetes in a rat model. Adv Exp
Med Biol. 775:321–343. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kang IS and Kim C: Taurine chloramine
administered in vivo increases NRF2-regulated antioxidant enzyme
expression in murine peritoneal macrophages. Adv Exp Med Biol.
775:259–267. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ghyasi R, Sepehri G, Mohammadi M,
Badalzadeh R and Ghyasi A: Effect of mebudipine on oxidative stress
and lipid peroxidation in myocardial ischemic-reperfusion injury in
male rat. J Res Med Sci. 17:1150–1155. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ramesh B, Karuna R, Sreenivasa RS, Haritha
K, Sai MD, Sasi BR and Saralakumari D: Effect of Commiphora
mukul gum resin on hepatic marker enzymes, lipid peroxidation
and antioxidants status in pancreas and heart of streptozotocin
induced diabetic rats. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2:895–900.
2012.
|
|
44
|
Huxtable RJ: Physiological actions of
taurine. Physiol Rev. 72:101–163. 1992.
|
|
45
|
Woo HA, Chae HZ, Hwang SC, Yang KS, Kang
SW, Kim K and Rhee SG: Reversing the inactivation of peroxiredoxins
caused by cysteine sulfinic acid formation. Science. 300:653–656.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sharma V, Anderson D and Dhawan A: Zinc
oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative DNA damage and ROS-triggered
mitochondria mediated apoptosis in human liver cells (HepG2).
Apoptosis. 17:852–870. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Zhao CY, Liu XY and Shen C: Molecular
mechanisms of mitochondrial damage in the development of liver
failure. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 19:955–957. 2011.(In
Chinese).
|
|
48
|
Gottlieb RA and Gustafsson AB:
Mitochondrial turnover in the heart. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1813.1295–1301. 2011.
|
|
49
|
Bae YS, Oh H, Rhee SG and Yoo YD:
Regulation of reactive oxygen species generation in cell signaling.
Mol Cells. 32:491–509. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|