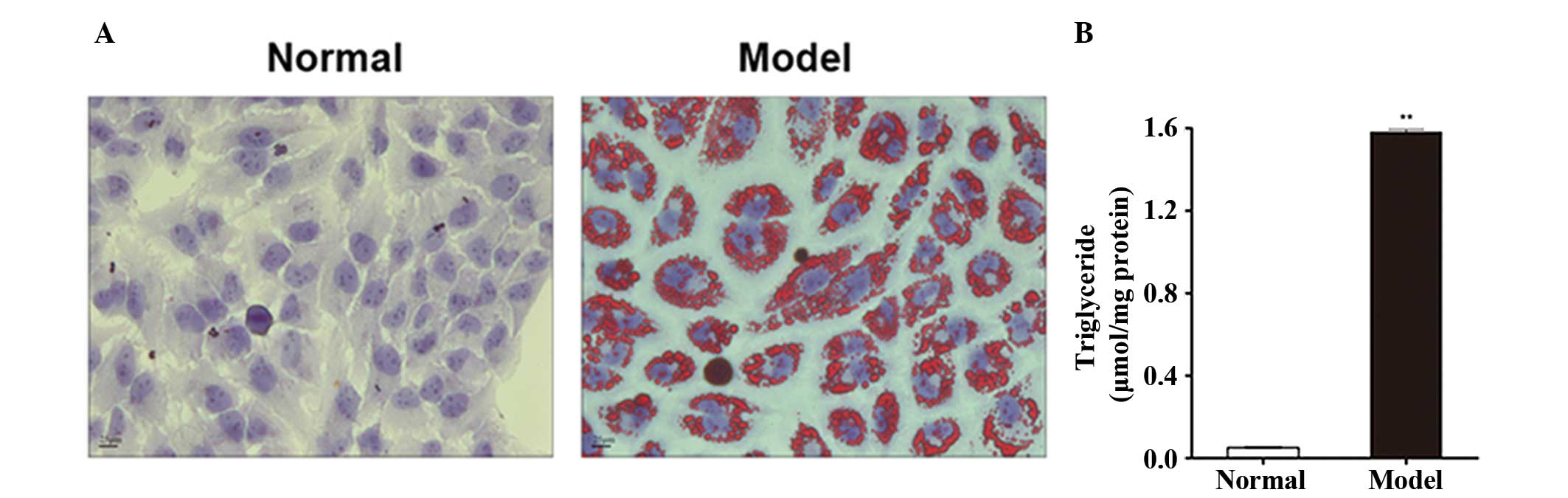
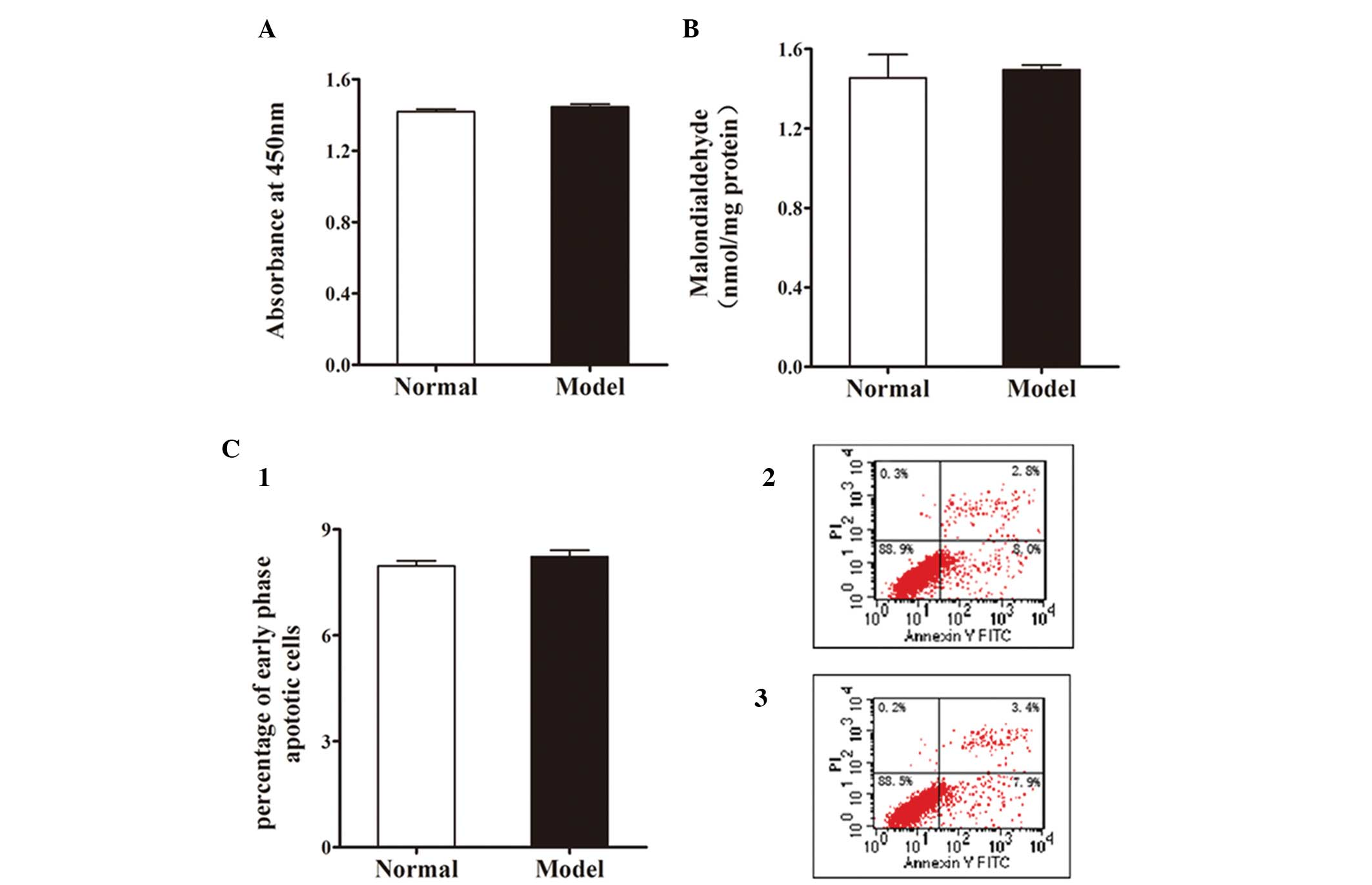
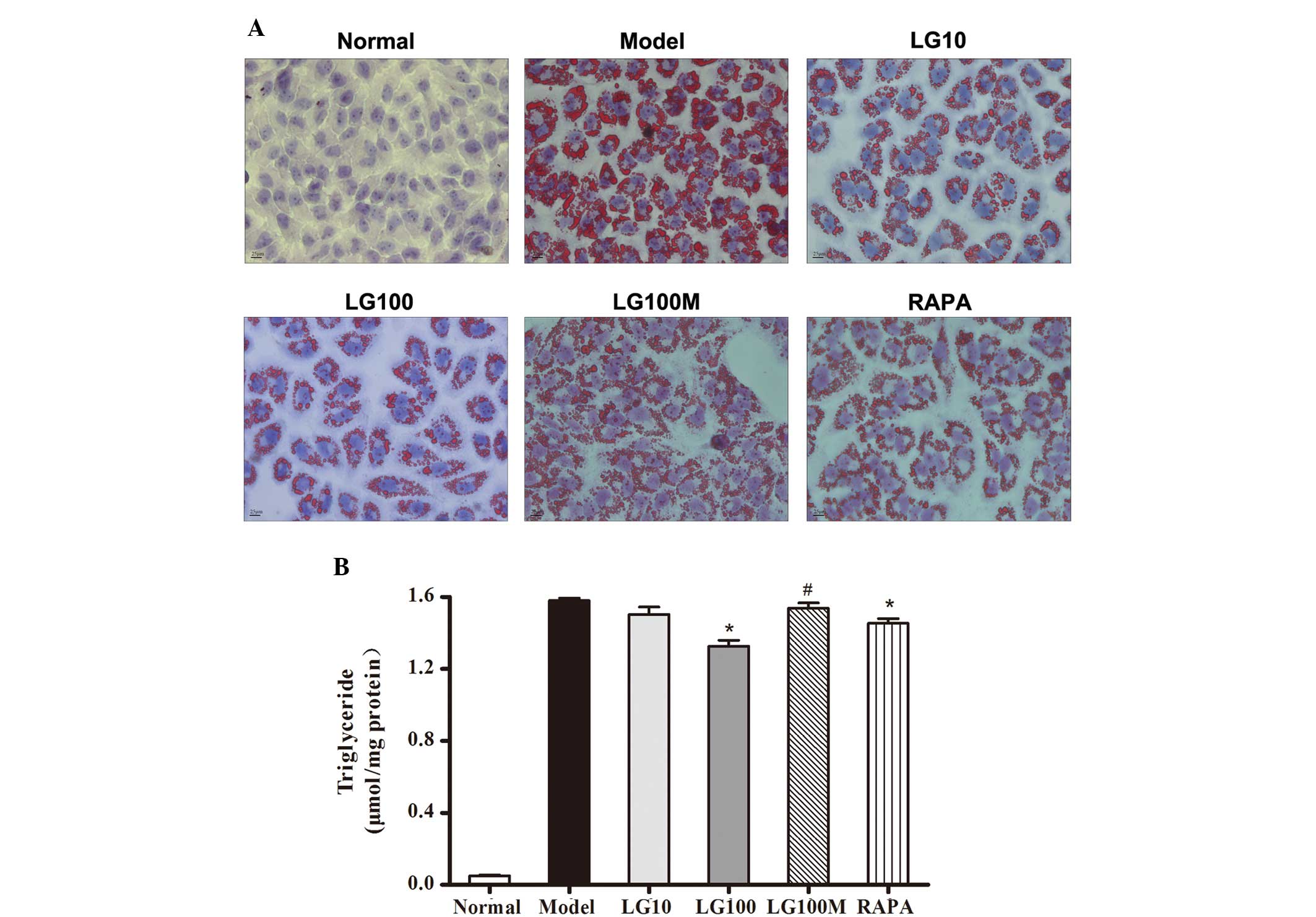
|
1
|
Cohen JC, Horton JD and Hobbs HH: Human
fatty liver disease: old questions and new insights. Science.
332:1519–1523. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferre P and Foufelle F: Hepatic steatosis:
a role for de novo lipogenesis and the transcription factor
SREBP-1c. Diabetes Obes Metab. 12 Suppl 2:83–92. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gentile CL, Frye MA and Pagliassotti MJ:
Fatty acids and the endoplasmic reticulum in nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease. Biofactors. 37:8–16. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
LL and Drucker DJ: Biology of incretins:
GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterology. 132:2131–2157. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Abu-Hamdah R, Rabiee A, Meneilly GS,
Shannon RP, Andersen DK and Elahi D: Clinical review: The
extrapancreatic effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 and related
peptides. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 94:1843–1852. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Svegliati-Baroni G, Saccomanno S,
Rychlicki C, et al: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor activation
stimulates hepatic lipid oxidation and restores hepatic signalling
alteration induced by a high-fat diet in nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis. Liver Int. 31:1285–1297. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Gupta NA, Mells J, Dunham RM, et al:
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor is present on human hepatocytes
and has a direct role in decreasing hepatic steatosis in vitro by
modulating elements of the insulin signaling pathway. Hepatology.
51:1584–1592. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ding X, Saxena NK, Lin S, Gupta NA and
Anania FA: Exendin-4, a glucagon-like protein-1 (GLP-1) receptor
agonist, reverses hepatic steatosis in ob/ob mice. Hepatology.
43:173–181. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sharma S, Mells JE, Fu PP, Saxena NK and
Anania FA: GLP-1 analogs reduce hepatocyte steatosis and improve
survival by enhancing the unfolded protein response and promoting
macroautophagy. PLoS One. 6:e252692011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ben-Shlomo S, Zvibel I, Shnell M, et al:
Glucagon-like peptide-1 reduces hepatic lipogenesis via activation
of AMP-activated protein kinase. J Hepatol. 54:1214–1223. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Samson SL and Bajaj M: Potential of
incretin-based therapies for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J
Diabetes Complications. 27:401–406. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Levine B and Kroemer G: Autophagy in the
pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 132:27–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Singh R, Kaushik S, Wang Y, et al:
Autophagy regulates lipid metabolism. Nature. 458:1131–1135. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ding WX, Li M, Chen X, et al: Autophagy
reduces acute ethanol-induced hepatotoxicity and steatosis in mice.
Gastroenterology. 139:1740–1752. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Choi SE, Lee SM, Lee YJ, et al: Protective
Role of Autophagy in Palmitate-Induced INS-1 beta-Cell Death.
Endocrinology. 150:126–134. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
|
|
17
|
Farrell GC and Larter CZ: Nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease: from steatosis to cirrhosis. Hepatology.
43:S99–S112. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T and Levine B:
Methods in Mammalian Autophagy Research. Cell. 140:313–326. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Day CP and James OF: Steatohepatitis: a
tale of two ‘hits’? Gastroenterology. 114:842–845. 1998.
|
|
20
|
Gomez-Lechon MJ, Donato MT,
Martinez-Romero A, Jimenez N, Castell JV and O’Connor JE: A human
hepatocellular in vitro model to investigate steatosis. Chem Biol
Interact. 165:106–116. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Marathe CS, Rayner CK, Jones KL and
Horowitz M: Glucagon-like peptides 1 and 2 in health and disease: a
review. Peptides. 44:75–86. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Musso G, Gambino R and Cassader M: Recent
insights into hepatic lipid metabolism in non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease (NAFLD). Prog Lipid Res. 48:1–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang L, Yang M, Ren H, et al: GLP-1
analogue prevents NAFLD in ApoE KO mice with diet and Acrp30
knockdown by inhibiting c-JNK. Liver Int. 33:794–804. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mells JE, Fu PP, Sharma S, et al: Glp-1
analog, liraglutide, ameliorates hepatic steatosis and cardiac
hypertrophy in C57BL/6J mice fed a Western diet. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 302:G225–G235. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gupta NA, Kolachala VL, Jiang R, et al:
The glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist Exendin 4 has a
protective role in ischemic injury of lean and steatotic liver by
inhibiting cell death and stimulating lipolysis. Am J Pathol.
181:1693–1701. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Škop V, Cahová M, Papáčková Z, et al:
Autophagy-lysosomal pathway is involved in lipid degradation in rat
liver. Physiol Res. 61:287–297. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|