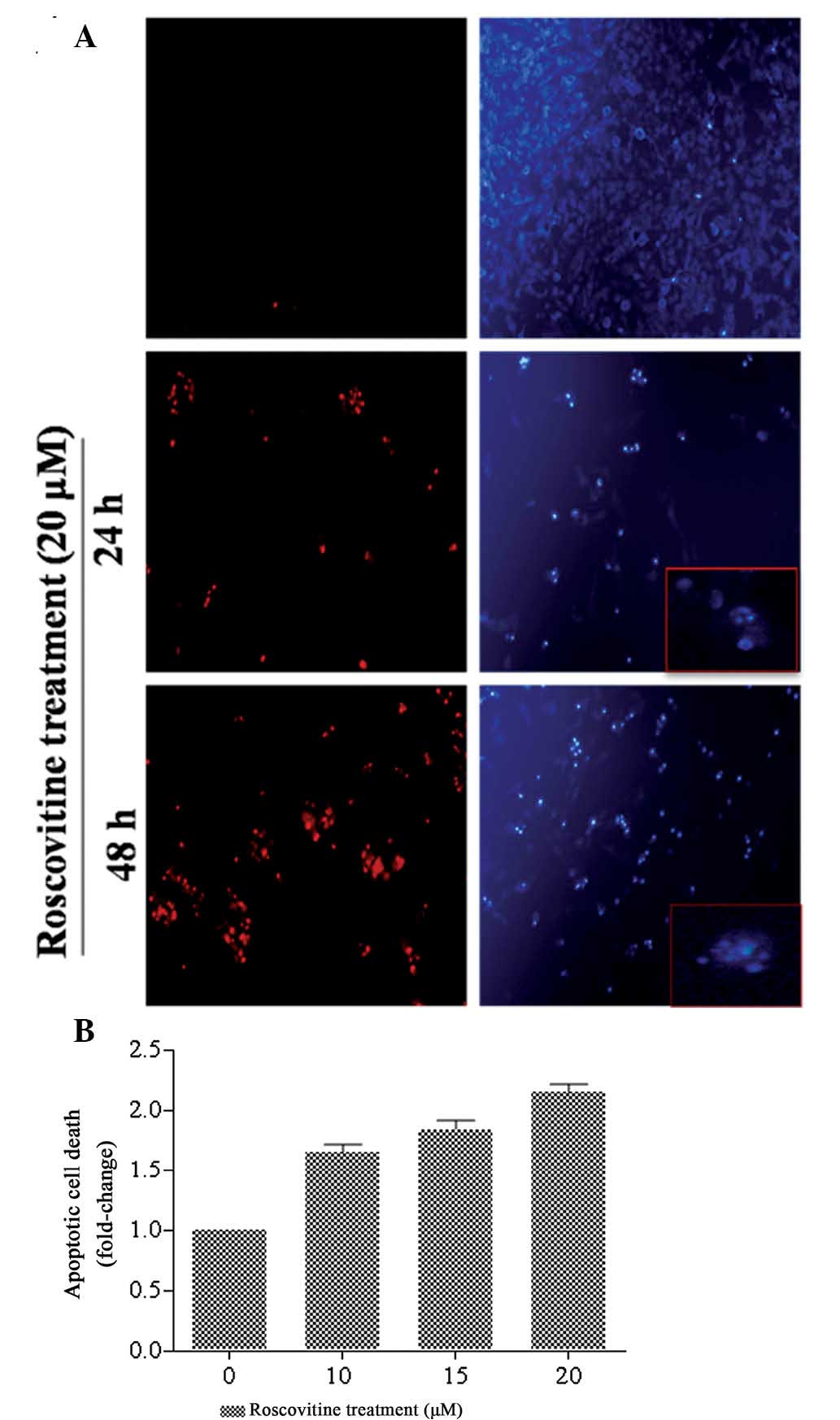
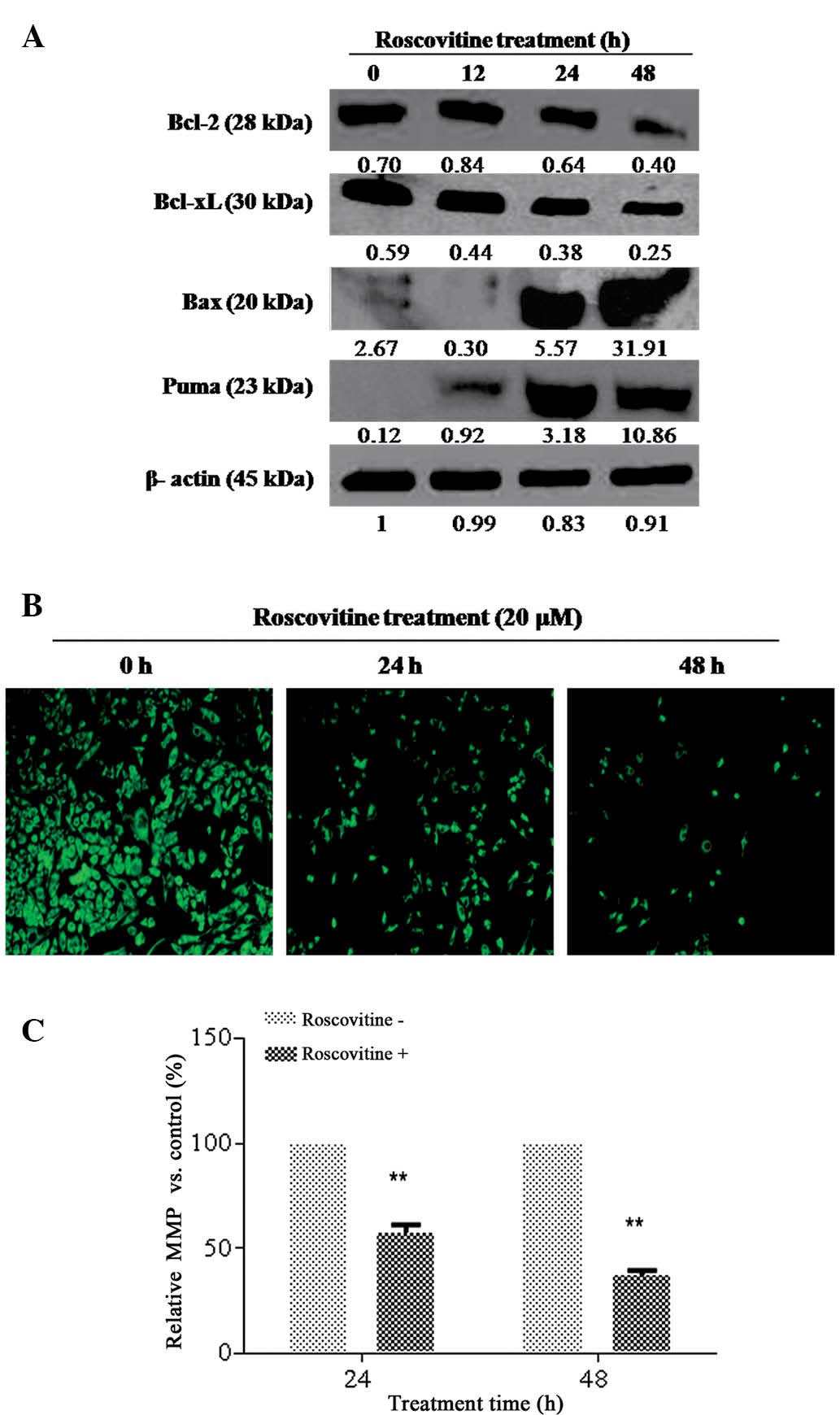
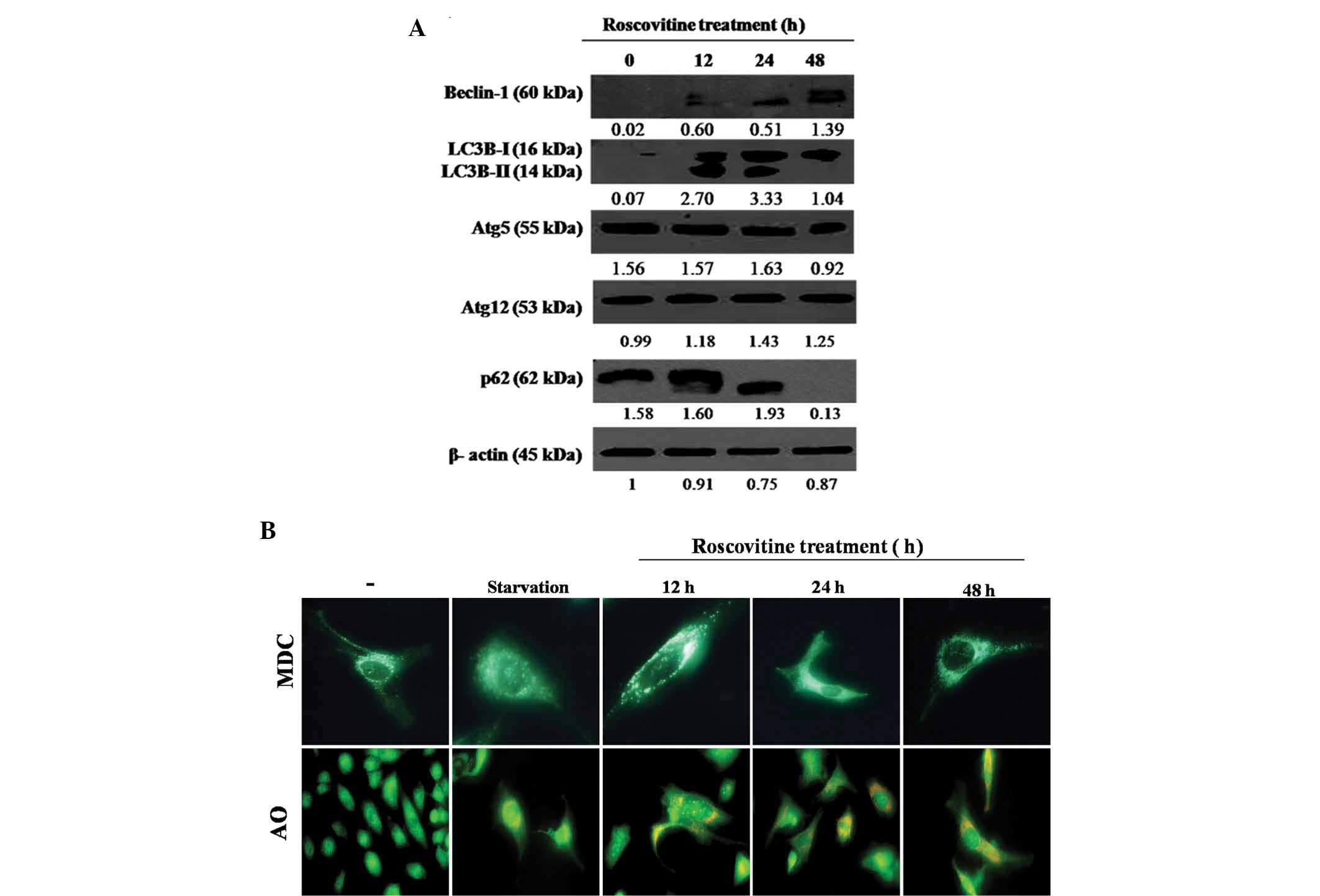
|
1
|
Wesierska-Gadek J, Gueorguieva M,
Wojciechowski J and Horky M: Cell cycle arrest induced in human
breast cancer cells by cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors: a
comparison of the effects exerted by roscovitine and olomoucine.
Pol J Pharmacol. 56:635–641. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang T, Jiang T, Zhang F, et al:
Involvement of p21Waf1/Cip1 cleavage during roscovitine-induced
apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
23:239–245. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wesierska-Gadek J, Wandl S, Kramer MP, et
al: roscovitine up-regulates p53 protein and induces apoptosis in
human HeLaS(3) cervix carcinoma cells. J Cell Biochem.
105:1161–1171. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Arisan ED, Coker A and Palavan-Ünsal N:
Polyamine depletion enhances the roscovitine-induced apoptosis
through the activation of mitochondria in HCT116 colon carcinoma
cells. Amino Acids. 42:655–665. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Appleyard MV, O’Neill MA, Murray KE, et
al: Seliciclib (CYC202, R-roscovitine) enhances the antitumor
effect of doxorubicin in vivo in a breast cancer xenograft model.
Int J Cancer. 124:465–472. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kondo Y, Kanzawa T, Sawaya R and Kondo S:
The role of autophagy in cancer development and response to
therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:726–734. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gozuacik D and Kimchi A: Autophagy and
cell death. Curr Top Dev Biol. 78:217–245. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Maiuri MC, Zalckvar E, Kimchi A and
Kroemer G: Self-eating and self-killing: crosstalk between
autophagy and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:741–752. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang J: Beclin 1 bridges autophagy,
apoptosis and differentiation. Autophagy. 4:947–948. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ku B, Woo JS, Liang C, et al: An insight
into the mechanistic role of Beclin 1 and its inhibition by
prosurvival Bcl-2 family proteins. Autophagy. 4:519–520. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Maiuri MC, Criollo A, Tasdemir E, et al:
BH3-only proteins and BH3 mimetics induce autophagy by
competitively disrupting the interaction between Beclin 1 and
Bcl-2/Bcl-X(L). Autophagy. 3:374–376. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zalckvar E, Berissi H, Eisenstein M and
Kimchi A: Phosphorylation of Beclin 1 by DAP-kinase promotes
autophagy by weakening its interactions with Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL.
Autophagy. 5:720–722. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Anorlu RI: What is the significance of the
HPV epidemic? Can J Urol. 15:3860–3865. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Weinstein LC, Buchanan EM, Hillson C and
Chambers CV: Screening and prevention: cervical cancer. Prim Care.
36:559–574. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Singh KC, Agarwal A, Agarwal S, et al:
‘Quick course’ neoadjuvant chemotherapy with cisplatin, bleomycin
and vincristine in advanced cervical cancer. Gynecol Obstet Invest.
58:109–113. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
van Luijk IF, Coens C, van der Burg ME, et
al: Phase II study of bleomycin, vindesine, mitomycin C and
cisplatin (BEMP) in recurrent or disseminated squamous cell
carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Ann Oncol. 18:275–281. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Benson C, White J, De Bono J, et al: A
phase I trial of the selective oral cyclin-dependent kinase
inhibitor seliciclib (CYC202; R-roscovitine), administered twice
daily for 7 days every 21 days. Br J Cancer. 96:29–37. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sherr CJ: Cancer cell cycles. Science.
274:1672–1677. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guzi T: CYC-202 Cyclacel. Curr Opin
Investig Drugs. 5:1311–1318. 2004.
|
|
20
|
Coley HM, Shotton CF and Thomas H:
Seliciclib (CYC202; r-roscovitine) in combination with cytotoxic
agents in human uterine sarcoma cell lines. Anticancer Res.
27:273–278. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dey A, Wong ET, Cheok CF, Tergaonkar V and
Lane DP: R-roscovitine simultaneously targets both the p53 and
NF-kappaB pathways and causes potentiation of apoptosis:
implications in cancer therapy. Cell Death Differ. 15:263–273.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Duffin R, Leitch AE, Sheldrake TA, et al:
The CDK inhibitor, R-roscovitine, promotes eosinophil apoptosis by
down-regulation of Mcl-1. FEBS Lett. 583:2540–2546. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Goodyear S and Sharma MC: roscovitine
regulates invasive breast cancer cell (MDA-MB231) proliferation and
survival through cell cycle regulatory protein cdk5. Exp Mol
Pathol. 82:25–32. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Maurer M, Komina O and Wesierska-Gadek J:
roscovitine differentially affects asynchronously growing and
synchronized human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Ann NY Acad Sci.
1171:250–256. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mitchell C, Park MA, Zhang G, et al:
Extrinsic pathway- and cathepsin-dependent induction of
mitochondrial dysfunction are essential for synergistic
flavopiridol and vorinostat lethality in breast cancer cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 6:3101–3112. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nair BC, Vallabhaneni S, Tekmal RR and
Vadlamudi RK: roscovitine confers tumor suppressive effect on
therapy-resistant breast tumor cells. Breast Cancer Res.
13:R802011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ribas J, Boix J and Meijer L:
(R)-roscovitine (CYC202, Seliciclib) sensitizes SH-SY5Y
neuroblastoma cells to nutlin-3-induced apoptosis. Exp Cell Res.
312:2394–2400. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zolnierczyk JD, Bloński JZ, Robak T,
Kiliańska ZM and Wesierska-Gadek J: roscovitine triggers apoptosis
in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells with similar
efficiency as combinations of conventional purine analogs with
cyclophosphamide. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1171:124–131. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wesierska-Gadek J, Gueorguieva M and Horky
M: roscovitine-induced up-regulation of p53AIP1 protein precedes
the onset of apoptosis in human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 4:113–124. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lambert LA, Qiao N, Hunt KK, et al:
Autophagy: a novel mechanism of synergistic cytotoxicity between
doxorubicin and roscovitine in a sarcoma model. Cancer Res.
68:7966–7974. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Houel-Renault L, Philippe L, Piquemal M
and Ciapa B: Autophagy is used as a survival program in
unfertilized sea urchin eggs that are destined to die by apoptosis
after inactivation of MAPK1/3 (ERK2/1). Autophagy. 9:1527–1539.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sinha S and Levine B: The autophagy
effector Beclin 1: a novel BH3-only protein. Oncogene. 27(Suppl 1):
S137–S148. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wei Y, Sinha S and Levine B: Dual role of
JNK1-mediated phosphorylation of Bcl-2 in autophagy and apoptosis
regulation. Autophagy. 4:949–951. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zalckvar E, Berissi H, Mizrachy L, et al:
DAP-kinase-mediated phosphorylation on the BH3 domain of beclin 1
promotes dissociation of beclin 1 from Bcl-XL and induction of
autophagy. EMBO Rep. 10:285–292. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, et al: LC3,
a mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome
membranes after processing. Embo J. 19:5720–5728. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|