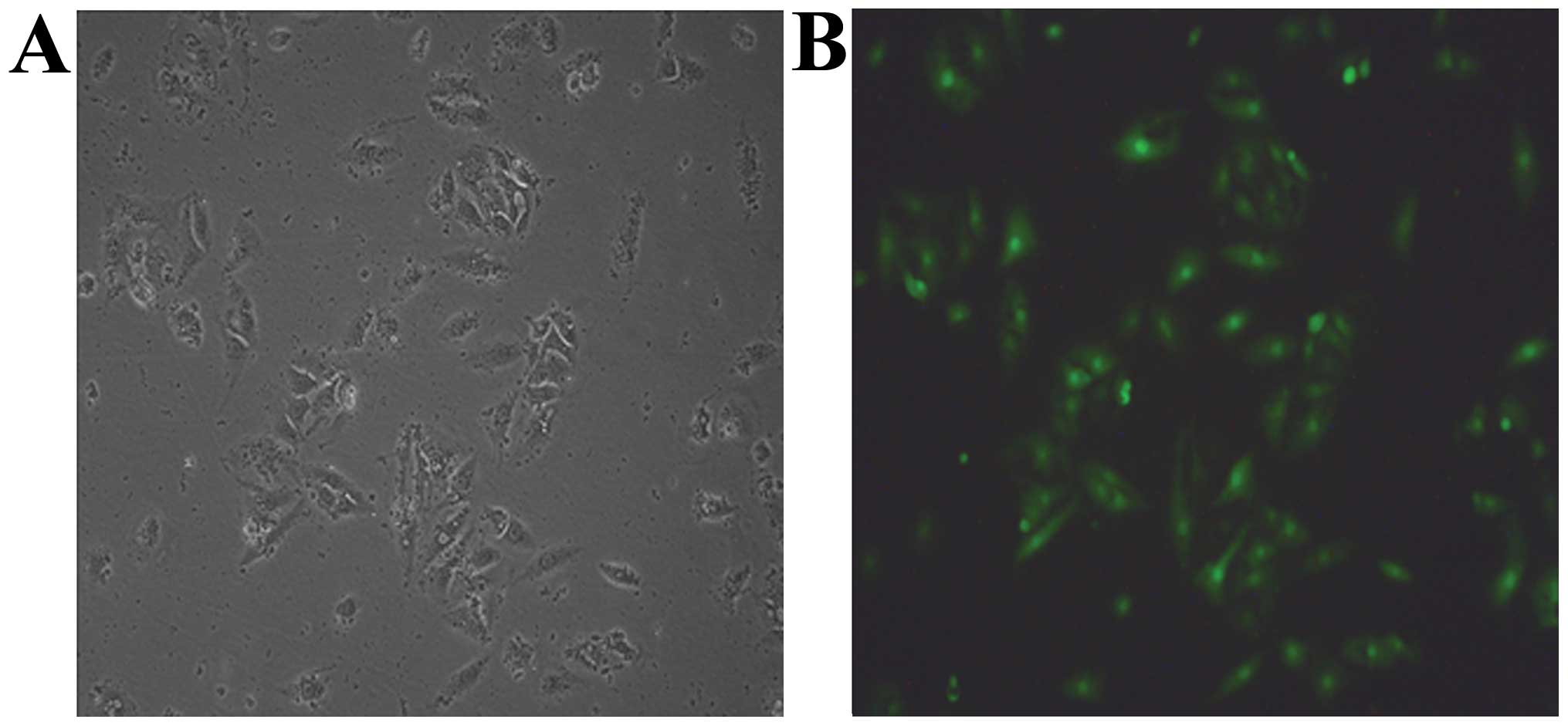
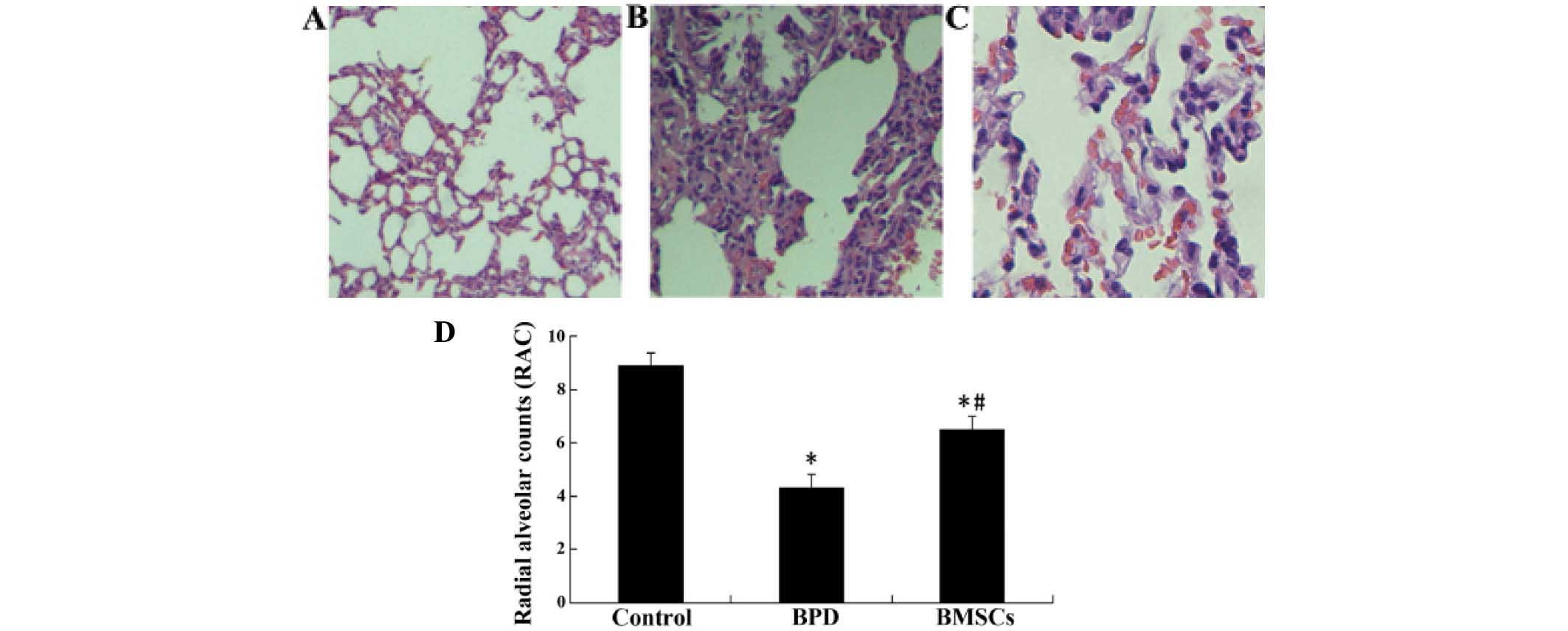
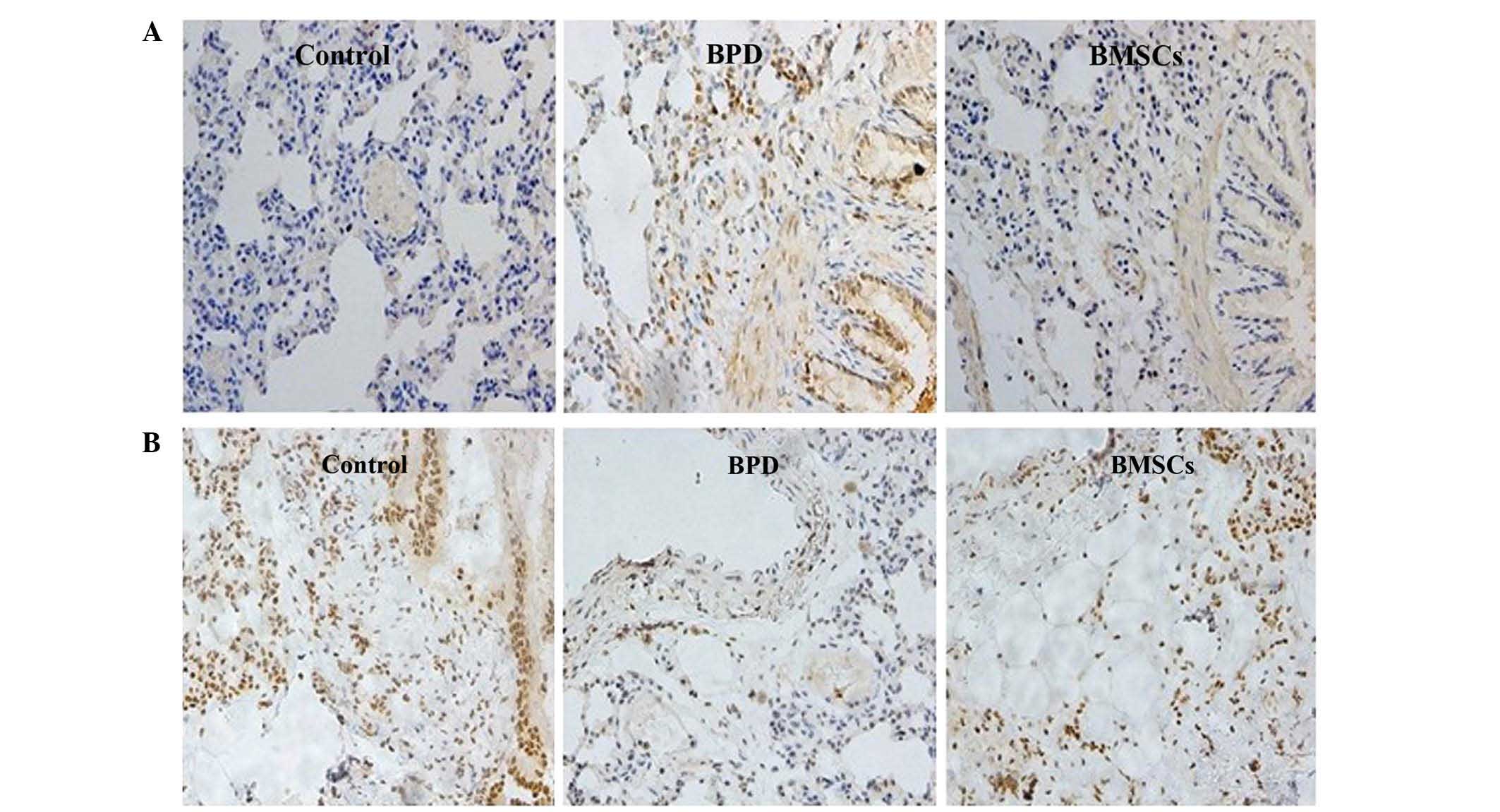
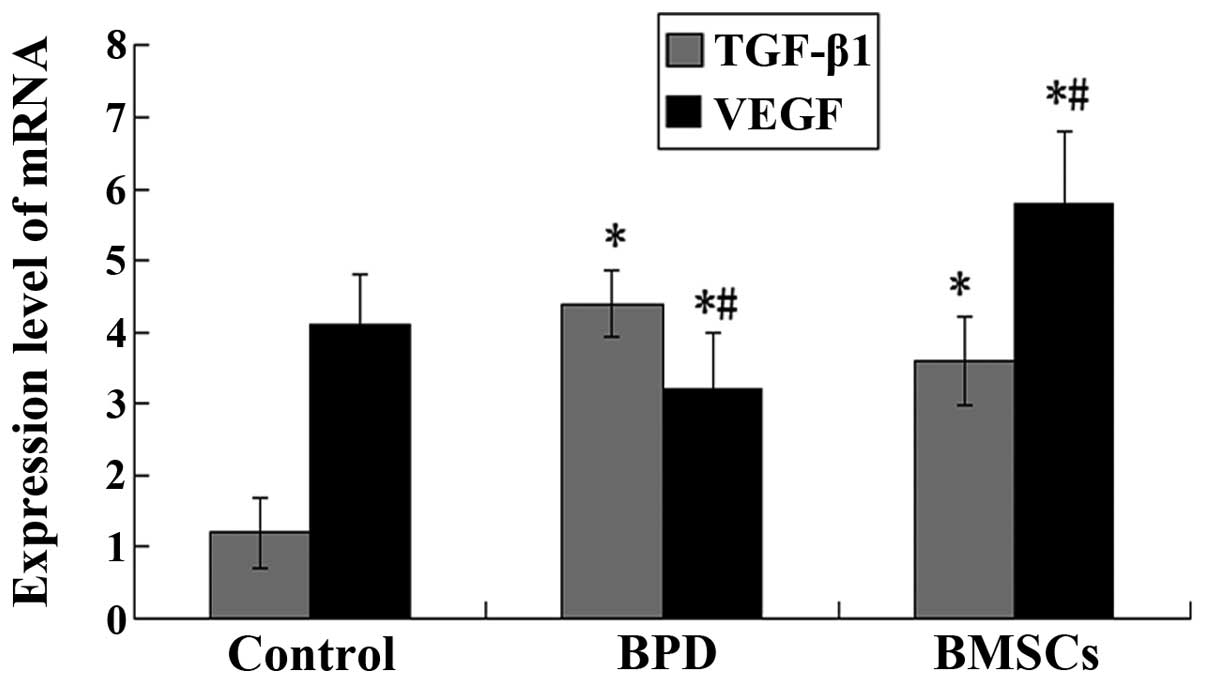
|
1
|
Rezvani M, Wilde J, Vitt P, et al:
Association of a FGFR-4 gene polymorphism with bronchopulmonary
dysplasia and neonatal respiratory distress. Dis Markers.
35:633–640. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sakurai R, Li Y, Torday JS and Rehan VK:
Curcumin augments lung maturation, preventing neonatal lung injury
by inhibiting TGF-β signaling. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
301:L721–L730. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xu J, Woods CR, Mora AL, et al: Prevention
of endotoxin-induced systemic response by bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stem cells in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
293:L131–L141. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ortiz LA, Gambelli F, McBride C, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cell engraftment in lung is enhanced in response
to bleomycin exposure and ameliorates its fibrotic effects. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:8407–8411. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
van Haaften T, Byrne R, Bonnet S, et al:
Airway delivery of mesenchymal stem cells prevents arrested
alveolar growth in neonatal lung injury in rats. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 180:1131–1142. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Aslam M, Baveja R, Liang OD, et al: Bone
marrow stromal cells attenuate lung injury in a murine model of
neonatal chronic lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
180:1122–1130. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee JW, Fang X, Krasnodembskaya A, Howard
JP and Matthay MA: Concise review: Mesenchymal stem cells for acute
lung injury: role of paracrine soluble factors. Stem Cells.
29:913–919. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gauldie J, Galt T, Bonniaud P, et al:
Transfer of the active form of transforming growth factor-beta 1
gene to newborn rat lung induces changes consistent with
bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Pathol. 163:2575–2584. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vicencio AG, Lee CG, Cho SJ, et al:
Conditional overexpression of bioactive transforming growth
factor-beta1 in neonatal mouse lung: a new model for
bronchopulmonary dysplasia? Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 31:650–656.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Monz D, Tutdibi E, Mildau C, et al: Human
umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells in a double-hit model of
bronchopulmonary dysplasia in neonatal mice. PLoS One.
8:e747402013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Abman SH: Impaired vascular endothelial
growth factor signaling in the pathogenesis of neonatal pulmonary
vascular disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 661:323–335. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jakkula M, Le Cras TD, Gebb S, et al:
Inhibition of angiogenesis decreases alveolarization in the
developing rat lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
279:L600–L607. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Acarregui MJ, Penisten ST, Goss KL,
Ramirez K and Snyder JM: Vascular endothelial growth factor gene
expression in human fetal lung in vitro. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
20:14–23. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Okabe M, Ikawa M, Kominami K, et al:
‘Green mice’ as a source of ubiquitous green cells. FEBS Lett.
407:313–319. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Peng C, Yang K, Xiang P, et al: Effect of
transplantation with autologous bone marrow stem cells on acute
myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 162:158–165. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Balasubramaniam V, Mervis CF, Maxey AM,
Markham NE and Abman SH: Hyperoxia reduces bone marrow, circulating
and lung endothelial progenitor cells in the developing lung:
implications for the pathogenesis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am
J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 292:L1073–L1084. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kunig AM, Balasubramaniam V, Markham NE,
Seedorf G, Gien J and Abman SH: Recombinant human VEGF treatment
transiently increases lung edema but enhances lung structure after
neonatal hyperoxia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
291:L1068–L1078. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Luan Y, Zhang ZH, Wei DE, Lu Y and Wang
YB: Effects of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells
implantation in canine model of pulmonary hypertension. Circ J.
76:977–985. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rojas M, Xu J, Woods CR, et al: Bone
marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells in repair of the injured
lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 33:145–152. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ortiz LA, Gambelli F, McBride C, et al:
MSC engraftment in lung is enhanced in response to bleomycin
exposure and ameliorates its fibroproliferative effects. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 100:8407–8011. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Abman SH and Matthay MA: Mesenchymal stem
cells for the prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia: delivering
the secretome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 180:1039–1041. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hennrick KT, Keeton AG, Nanua S, et al:
Lung cells from neonates show a mesenchymal stem cell phenotype. Am
J Respir Crit Care Med. 175:1158–1164. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL, et
al: Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult
marrow. Nature. 418:41–49. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Krause DS, Theise ND, Collector MI, et al:
Multi-organ, multi-lineage engraftment by a single bone
marrow-derived stem cell. Cell. 105:369–377. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wen ST, Chen W, Chen HL, et al: Amniotic
fluid stem cells from EGFP transgenic mice attenuate
hyperoxia-induced acute lung injury. PLoS One. 8:e753832013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Collins JJ, Kallapur SG, Knox CL, et al:
Repeated intrauterine exposures to inflammatory stimuli attenuated
transforming growth factor-β signaling in the ovine fetal lung.
Neonatology. 104:49–55. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Collins JJ, Kunzmann S, Kuypers E, et al:
Antenatal glucocorticoids counteract LPS changes in TGF-β pathway
and caveolin-1 in ovine fetal lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 304:L438–L444. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Abman SH: Impaired vascular endothelial
growth factor signaling in the pathogenesis of neonatal pulmonary
vascular disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 661:323–335. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
De Paepe ME, Mao Q, Powell J, et al:
Growth of pulmonary microvasculature in ventilated preterm infants.
Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 173:204–211. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Maniscalco WM, Watkins RH, Pryhuber GS,
Bhatt A, Shea C and Huyck H: Angiogenic factors and alveolar
vasculature: development and alterations by injury in very
premature baboons. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
282:L811–L823. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Acarregui MJ, Penisten ST, Goss KL,
Ramirez K and Snyder JM: Vascular endothelial growth factor gene
expression in human fetal lung in vitro. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
20:14–23. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Jakkula M, Le Cras TD, Gebb S, et al:
Inhibition of angiogenesis decreases alveolarization in the
developing rat lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
279:L600–L607. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hosford GE and Olson DM: Effects of
hyperoxia on VEGF, its receptors and HIF-2alpha in the newborn rat
lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 285:L161–L168.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Le Cras TD, Markham NE, Tuder RM, Voelkel
NF and Abman SH: Treatment of newborn rats with a VEGF receptor
inhibitor causes pulmonary hypertension and abnormal lung
structure. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 283:L555–L562.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|