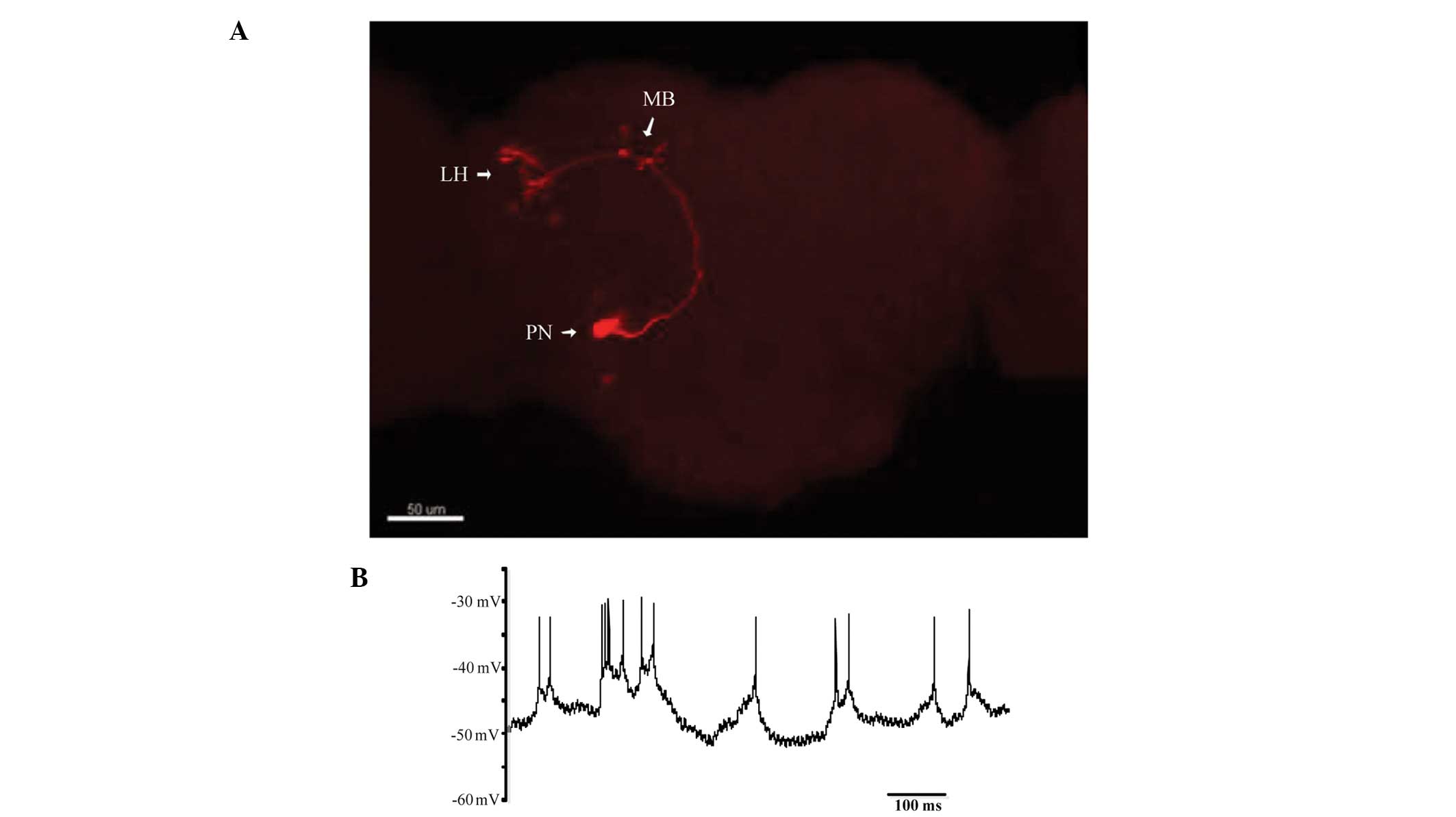
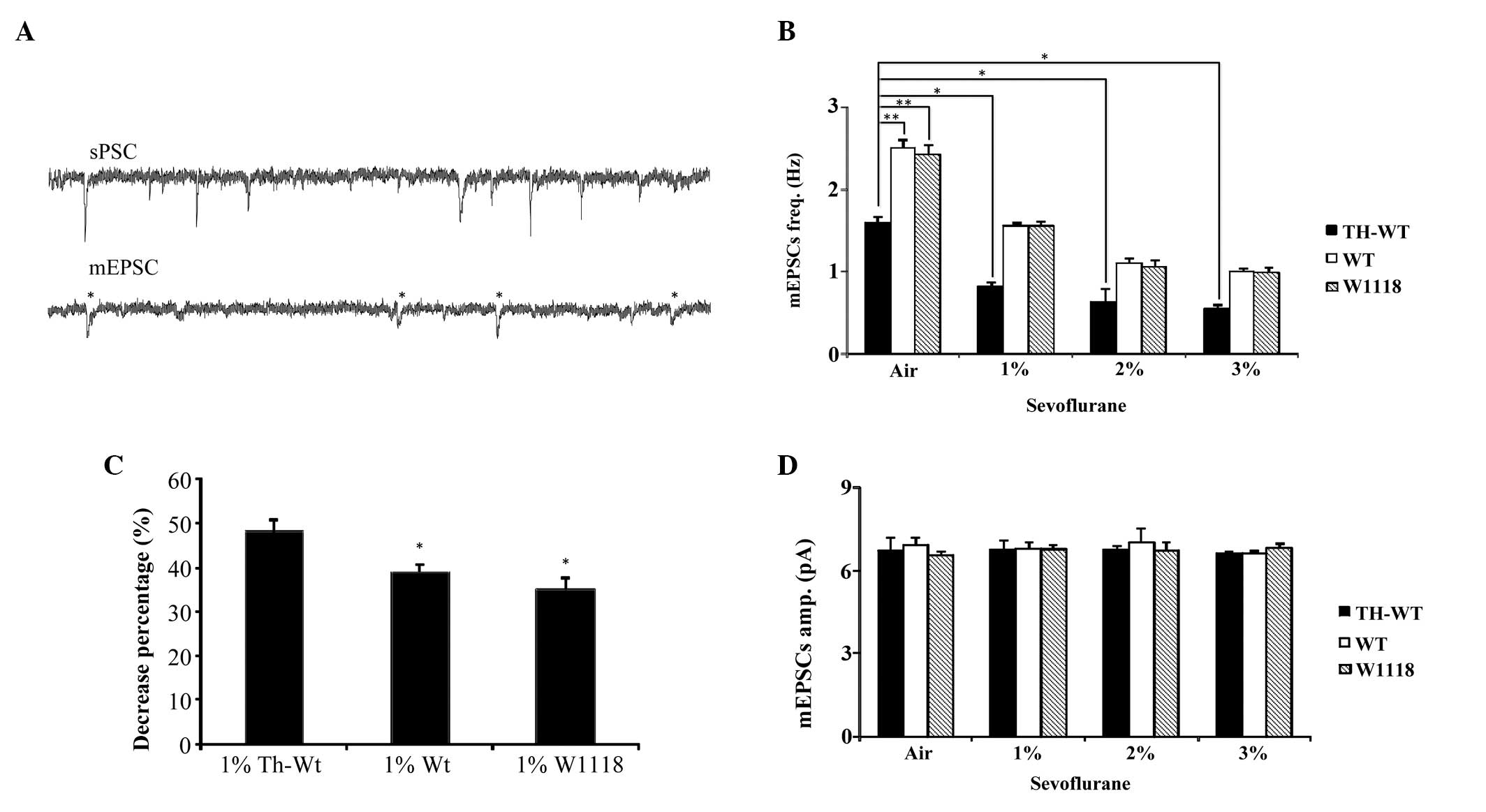
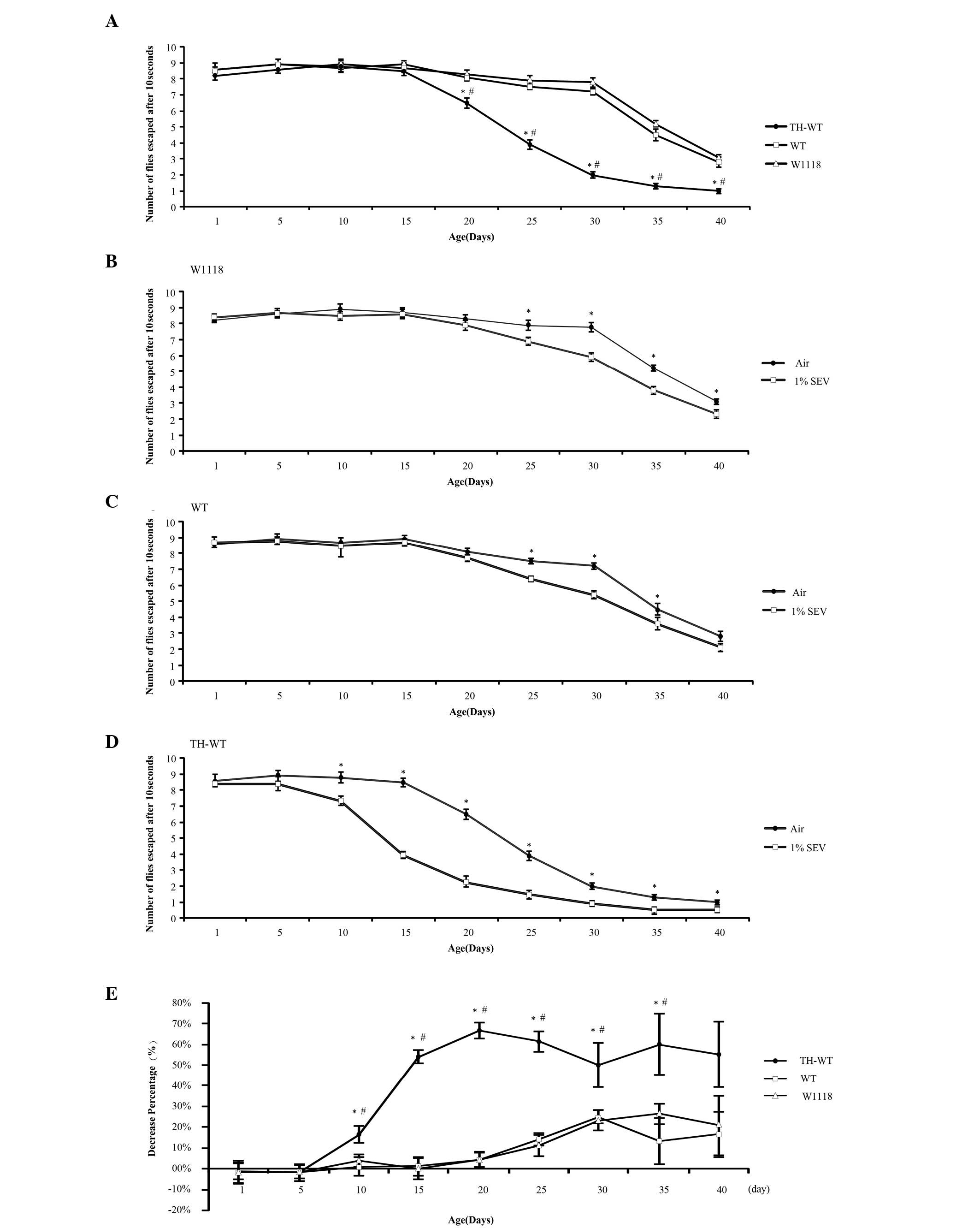
|
1
|
Nicholson G, Pereira AC and Hall GM:
Parkinson’s disease and anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth. 89:904–916.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Belin AC and Westerlund M: Parkinson’s
disease: a genetic perspective. FEBS J. 275:1377–1383. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
García-Pérez L, Linertová R, Lorenzo-Riera
A, Vázquez-Díaz JR, Duque-González B and Sarría-Santamera A: Risk
factors for hospital readmissions in elderly patients: a systematic
review. QJM. 104:639–651. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang X, Xue Z and Sun A: Subclinical
concentration of sevoflurane potentiates neuronal apoptosis in the
developing C57BL/6 mouse brain. Neurosci Lett. 447:109–114. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Culley DJ, Baxter MG, Yukhananov R and
Crosby G: Long-term impairment of acquisition of a spatial memory
task following isoflurane-nitrous oxide anesthesia in rats.
Anesthesiology. 100:309–314. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Satomoto M, Satoh Y, Terui K, et al:
Neonatal exposure to sevoflurane induces abnormal social behaviors
and deficits in fear conditioning in mice. Anesthesiology.
110:628–637. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Haseneder R, Kratzer S, von Meyer L, Eder
M, Kochs E and Rammes G: Isoflurane and sevoflurane
dose-dependently impair hippocampal long-term potentiation. Eur J
Pharmacol. 623:47–51. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ishizeki J, Nishikawa K, Kubo K, Saito S
and Goto F: Amnestic concentrations of sevoflurane inhibit synaptic
plasticity of hippocampal CA1 neurons through gamma-aminobutyric
acid-mediated mechanisms. Anesthesiology. 108:447–456. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mason LJ, Cojocaru TT and Cole DJ:
Surgical intervention and anesthetic management of the patient with
Parkinson’s disease. Int Anesth Clin. 34:133–150. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ng M, Roorda RD, Lima SQ, Zemelman BV,
Morcillo P and Miesenböck G: Transmission of olfactory information
between three populations of neurons in the antennal lobe of the
fly. Neuron. 36:463–474. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zimprich A, Biskup S, Leitner P, et al:
Mutations in LRRK2 cause autosomal-dominant parkinsonism with
pleomorphic pathology. Neuron. 44:601–607. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu Z, Wang X, Yu Y, et al: A Drosophila
model for LRRK2-linked parkinsonism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:2693–2698. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Choi DC, Chae YJ, Kabaria S, et al:
MicroRNA-7 Protects against 1-Methyl-4-Phenylpyridinium-Induced
Cell Death by Targeting RelA. J Neuroscience. 34:12725–12737. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
White KE, Humphrey DM and Hirth F: The
dopaminergic system in the aging brain of Drosophila. Front
Neurosci. 4:2052010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Braak H and Del Tredici K: Invited
Article: Nervous system pathology in sporadic Parkinson disease.
Neurology. 70:1916–1925. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Obeso JA, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Goetz CG, et
al: Missing pieces in the Parkinson’s disease puzzle. Nat Med.
16:653–661. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Friggi-Grelin F, Coulom H, Meller M, Gomez
D, Hirsh J and Birman S: Targeted gene expression in Drosophila
dopaminergic cells using regulatory sequences from tyrosine
hydroxylase. J Neurobiol. 54:618–627. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ueno K, Naganos S, Hirano Y, Horiuchi J
and Saitoe M: Long-term enhancement of synaptic transmission
between antennal lobe and mushroom body in cultured Drosophila
brain. Physiology. 591:287–302. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
D’Souza RD, Parsa PV and Vijayaraghavan S:
Nicotinic receptors modulate olfactory bulb external tufted cells
via an excitation-dependent inhibitory mechanism. J
Neurophysiology. 110:1544–1553. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ran D, Cai S, Wu H and Gu H: Di
(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate modulates cholinergic mini-presynaptic
transmission of projection neurons in Drosophila antennal lobe.
Food Chem Toxicol. 50:3291–3297. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Brand AH and Perrimon N: Targeted gene
expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating
dominant phenotypes. Development. 118:401–15. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gu H and O’Dowd DK: Cholinergic synaptic
transmission in adult Drosophila Kenyon cells in situ. J Neurosci.
26:265–272. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gu H and O’Dowd DK: Whole cell recordings
from brain of adult Drosophila. J Vis Exp. (6): 2482007.
|
|
24
|
Yan Y, Yang Y, You J, et al: Permethrin
modulates cholinergic mini-synaptic currents by partially blocking
the calcium channel. Toxicol Lett. 201:258–263. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Venderova K, Kabbach G, Abdel-Messih E, et
al: Leucine-Rich Repeat Kinase 2 interacts with Parkin, DJ-1 and
PINK-1 in a Drosophila melanogaster model of Parkinson’s disease.
Hum Mol Genet. 18:4390–4404. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tai Y, Chen L, Huang E, et al: Protective
effect of alpha-synuclein knockdown on methamphetamine-induced
neurotoxicity in dopaminergic neurons. Neural regeneration
research. 9:951–958. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
Feany MB and Bender WW: A Drosophila model
of Parkinson’s disease. Nature. 404:394–398. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dauer W and Przedborski S: Parkinson’s
disease: mechanisms and models. Neuron. 39:889–909. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Forno LS: Neuropathology of Parkinson’s
disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 55:259–272. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mouradian MM: Recent advances in the
genetics and pathogenesis of Parkinson disease. Neurology.
58:179–185. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yamasaki M, Hashimoto K and Kano M:
Miniature synaptic events elicited by presynaptic Ca2+
rise are selectively suppressed by cannabinoid receptor activation
in cerebellar Purkinje cells. J Neurosci. 26:86–95. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang J, Yang Y, Li H, Cao J and Xu L:
Amplitude/frequency of spontaneous mEPSC correlates to the degree
of long-term depression in the CA1 region of the hippocampal slice.
Brain Res. 1050:110–117. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Talantova M, Sanz-Blasco S, Zhang X, et
al: Aβ induces astrocytic glutamate release, extrasynaptic NMDA
receptor activation, and synaptic loss. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:E2518–E2527. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yasuyama K, Meinertzhagen IA and Schürmann
FW: Synaptic organization of the mushroom body calyx in Drosophila
melanogaster. J Comp Neurol. 445:211–226. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Su H and O’Dowd DK: Fast synaptic currents
in Drosophila mushroom body Kenyon cells are mediated by
alpha-bungarotoxin-sensitive nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and
picrotoxin-sensitive GABA receptors. J Neurosci. 23:9246–9253.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Simkus CR and Stricker C: The contribution
of intracellular calcium stores to mEPSCs recorded in layer II
neurones of rat barrel cortex. J Physiol. 545:521–535. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kato R, Tachibana K, Nishimoto N, et al:
Neonatal exposure to sevoflurane causes significant suppression of
hippocampal long-term potentiation in postgrowth rats. Anesth
Analg. 117:1429–1435. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shaltiel-Karyo R, Davidi D, Menuchin Y, et
al: A novel, sensitive assay for behavioral defects in Parkinson’s
disease model Drosophila. Parkinsons Dis. 2012:6975642012.
|
|
38
|
Kwon Y, Kim JW, Ho Y, et al: Analysis of
antagonistic co-contractions with motorized passive movement device
in patients with parkinson’s disease. Bio-medical materials and
engineering. 24:2291–2297. 2014.
|
|
39
|
Oxenkrug GF: The extended life span of
Drosophila melanogaster eye-color (white and vermilion) mutants
with impaired formation of kynurenine. J Neural Transm. 117:23–26.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Jenner P and Olanow CW: The pathogenesis
of cell death in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology. 66:S24–S36. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Reynolds NP, Soragni A, Rabe M, et al:
Mechanism of membrane interaction and disruption by α-synuclein. J
Am Chem Soc. 133:19366–19375. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Rajput A, Dickson DW, Robinson CA, et al:
Parkinsonism, Lrrk2 G2019S, and tau neuropathology. Neurology.
67:1506–1508. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ross OA, Toft M, Whittle AJ, et al: Lrrk2
and Lewy body disease. Ann Neurol. 59:388–393. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|