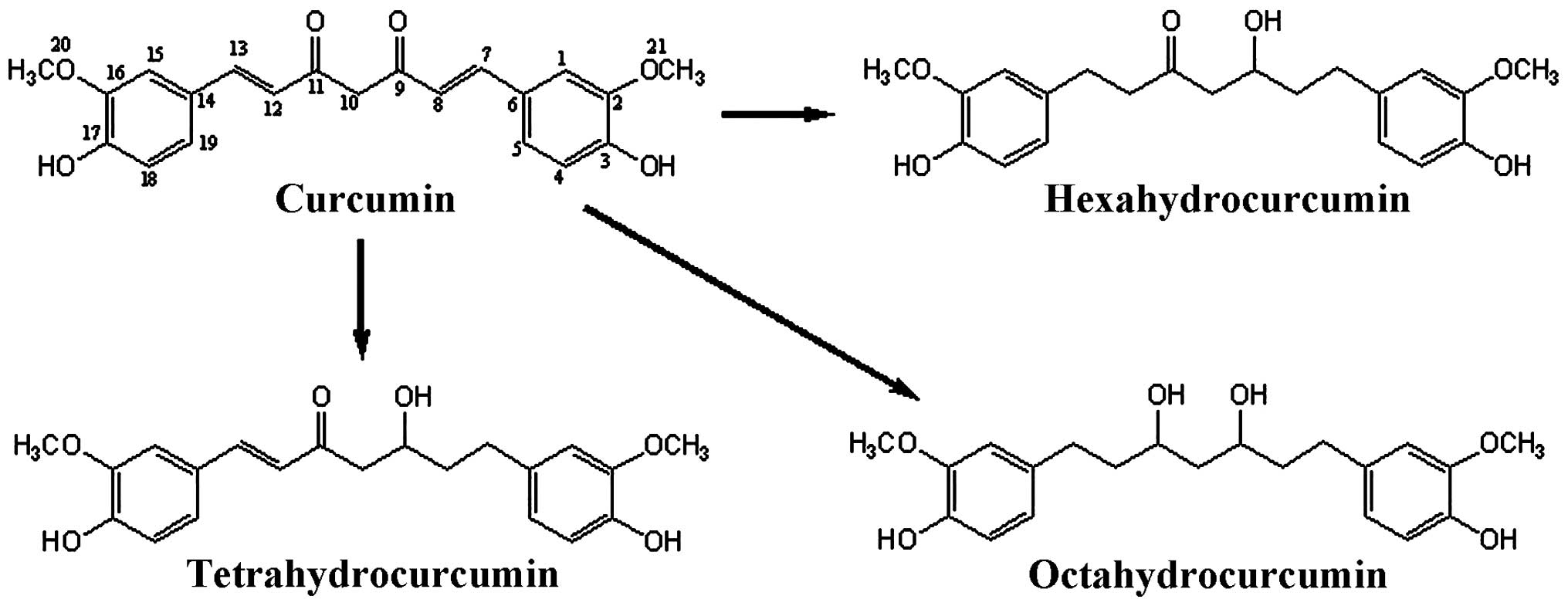
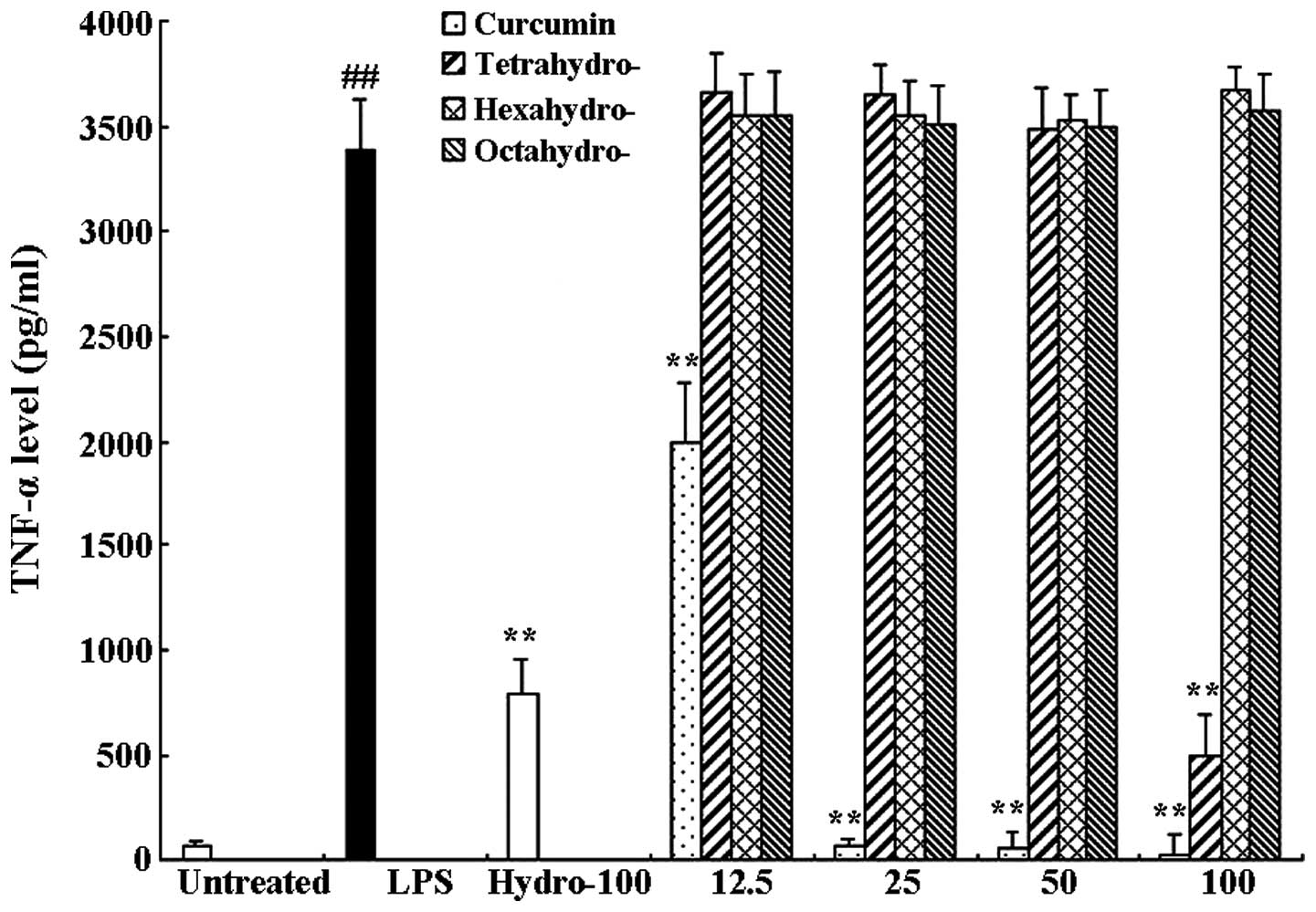
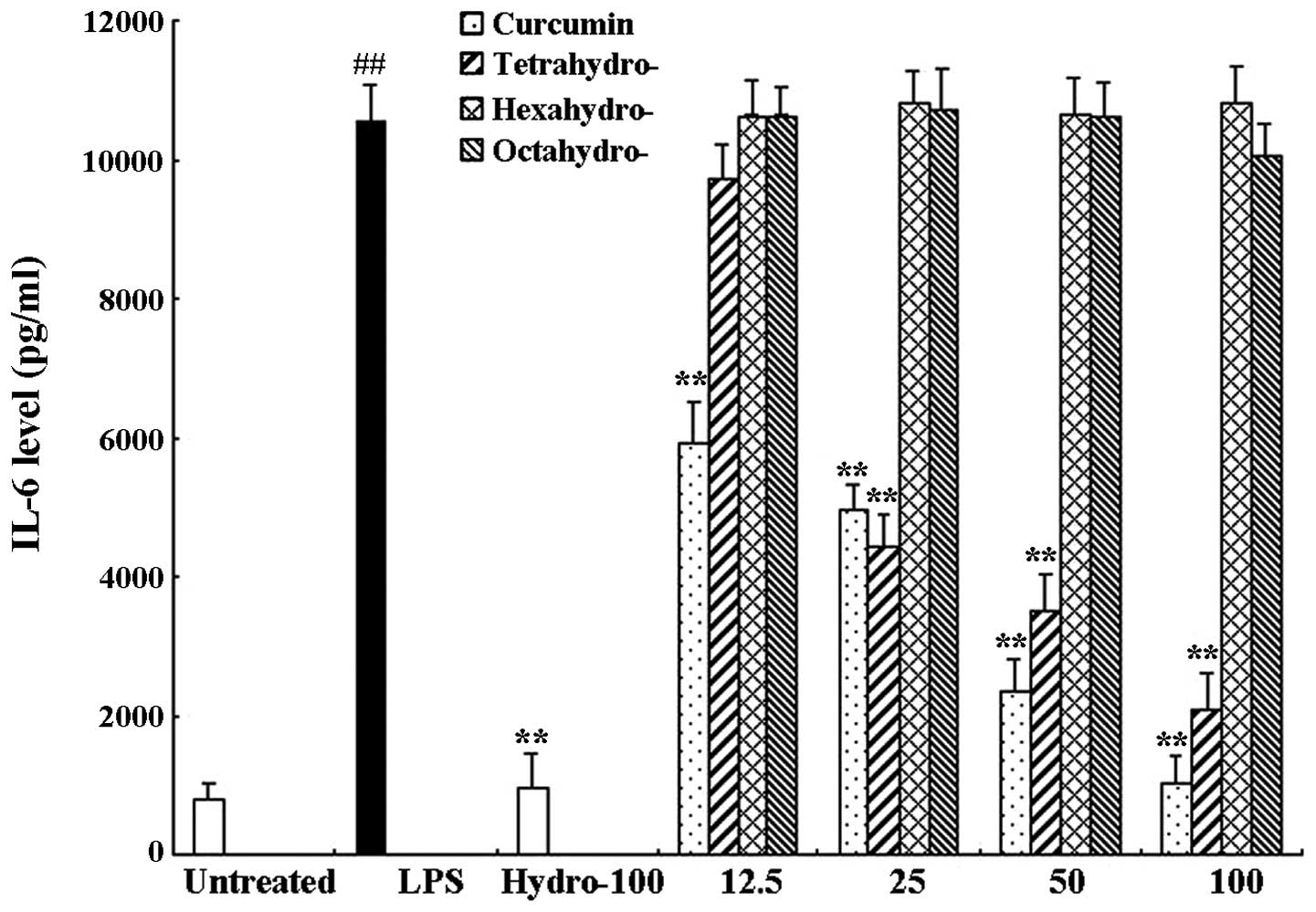
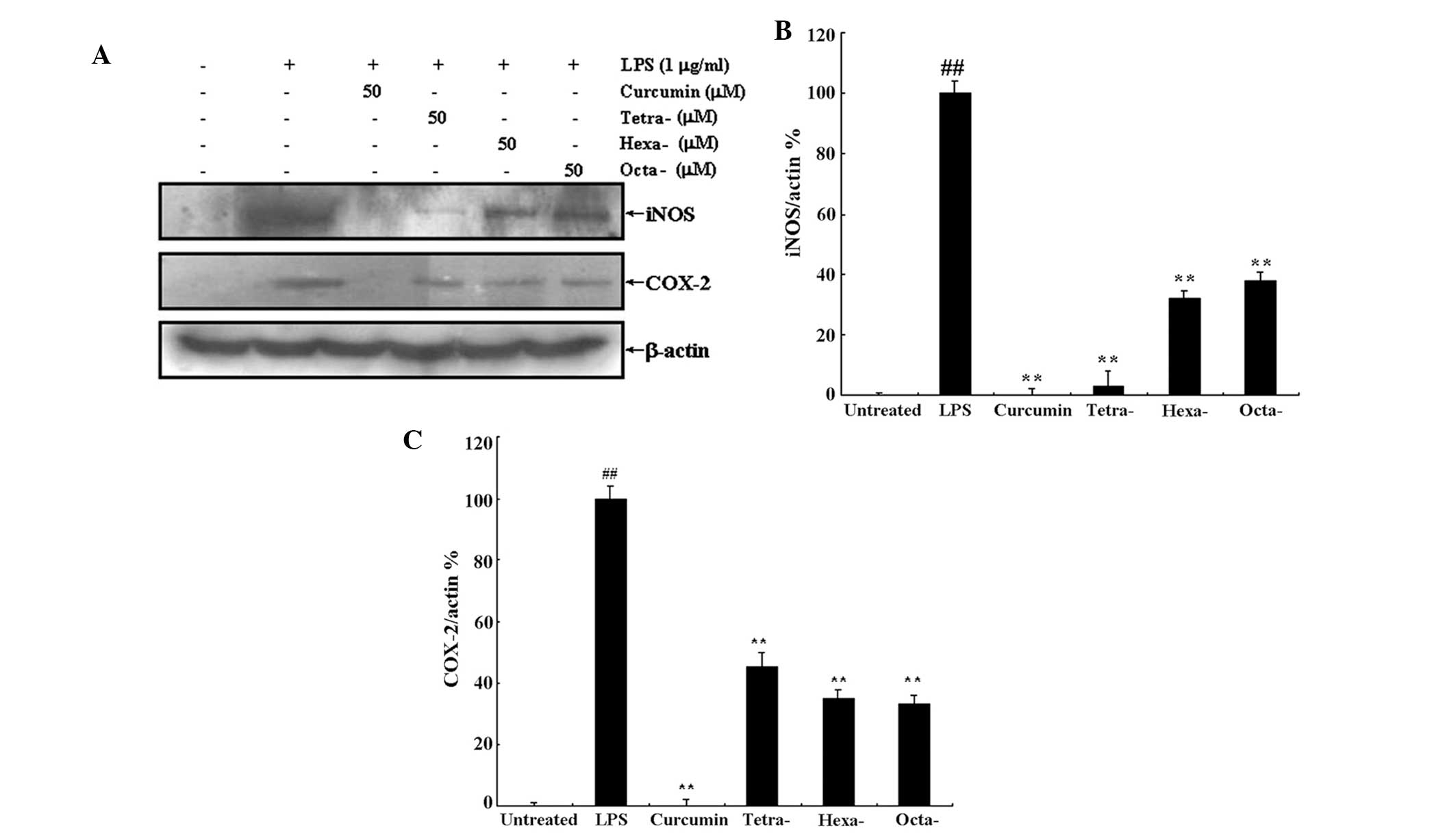
|
1
|
Nandal S, Dhir A, Kuhad A, Sharma S and
Chopra K: Curcumin potentiates the anti-inflammatory activity of
cyclooxygenase inhibitors in the cotton pellet granuloma pouch
model. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 31:89–93. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Adapala N and Chan MM: Long-term use of an
antiinflammatory, curcumin, suppressed type 1 immunity and
exacerbated visceral leishmaniasis in a chronic experimental model.
Lab Invest. 88:1329–1339. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tian F, Fan T, Zhang Y, Jiang Y and Zhang
X: Curcumin potentiates the antitumor effects of 5-FU in treatment
of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells through downregulating the
activation of NF-κB signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. Acta
Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 44:847–855. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wang K, Zhang T, Liu L, Wang X, Wu P, Chen
Z, Ni C, Zhang J, Hu F and Huang J: Novel micelle formulation of
curcumin for enhancing antitumor activity and inhibiting colorectal
cancer stem cells. Int J Nanomedicine. 7:4487–4497. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sadzuka Y, Nagamine M, Toyooka T, Ibuki Y
and Sonobe T: Beneficial effects of curcumin on antitumor activity
and adverse reactions of doxorubicin. Int J Pharm. 432:42–49. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang H, Geng QR, Wang L and Lu Y: Curcumin
potentiates antitumor activity of L-asparaginase via inhibition of
the AKT signaling pathway in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk
Lymphoma. 53:1376–1382. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Aftab N and Vieira A: Antioxidant
activities of curcumin and combinations of this curcuminoid with
other phytochemicals. Phytother Res. 24:500–502. 2010.
|
|
8
|
Masuda T, Hidaka K, Shinohara A, Maekawa
T, Takeda Y and Yamaguchi H: Chemical studies on antioxidant
mechanism of curcuminoid: analysis of radical reaction products
from curcumin. J Agric Food Chem. 47:71–77. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jordan WC and Drew CR: Curcumin - a
natural herb with anti-HIV activity. J Natl Med Assoc.
88:3331996.
|
|
10
|
Kim MK, Choi GJ and Lee HS: Fungicidal
property of Curcuma longa L. rhizome-derived curcumin against
phytopathogenic fungi in a greenhouse. J Agric Food Chem.
51:1578–1581. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Deters M, Siegers C, Muhl P and Hänsel W:
Choleretic effects of curcuminoids on an acute cyclosporin-induced
cholestasis in the rat. Planta Med. 65:610–613. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu H, Li Z, Qiu D, Gu Q, Lei Q and Mao L:
The inhibitory effects of different curcuminoids on β-amyloid
protein, β-amyloid precursor protein and β-site amyloid precursor
protein cleaving enzyme 1 in swAPP HEK293 cells. Neurosci Lett.
485:83–88. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhao J, Zhao Y, Zheng W, Lu Y, Feng G and
Yu S: Neuroprotective effect of curcumin on transient focal
cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 1229:224–232. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shukla Y, Arora A and Taneja P:
Antimutagenic potential of curcumin on chromosomal aberrations in
Wistar rats. Mutat Res. 515:197–202. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Volak LP, Ghirmai S, Cashman JR and Court
MH: Curcuminoids inhibit multiple human cytochromes P450,
UDP-glucuronosyltransferase, and sulfotransferase enzymes, whereas
piperine is a relatively selective CYP3A4 inhibitor. Drug Metab
Dispos. 36:1594–1605. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Graber-Maier A, Büter KB, Aeschlimann J,
Bittel C, Kreuter M, Drewe J and Gutmann H: Effects of Curcuma
extracts and curcuminoids on expression of P-glycoprotein and
cytochrome P450 3A4 in the intestinal cell culture model LS180.
Planta Med. 76:1866–1870. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lao CD, Ruffin MT IV, Normolle D, Heath
DD, Murray SI, Bailey JM, Boggs ME, Crowell J, Rock CL and Brenner
DE: Dose escalation of a curcuminoid formulation. BMC Complement
Altern Med. 6:102006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cheng AL, Hsu CH, Lin JK, et al: Phase I
clinical trial of curcumin, a chemopreventive agent, in patients
with high-risk or pre-malignant lesions. Anticancer Res.
21:2895–2900. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Anand P, Kunnumakkara AB, Newman RA and
Aggarwal BB: Bioavailability of curcumin: problems and promises.
Mol Pharm. 4:807–818. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhongfa L, Chiu M, Wang J, Chen W, Yen W,
Fan-Havard P, Yee LD and Chan KK: Enhancement of curcumin oral
absorption and pharmacokinetics of curcuminoids and curcumin
metabolites in mice. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 69:679–689. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Wu JC, Lai CS, Badmaev V, Nagabhushanam K,
Ho CT and Pan MH: Tetrahydrocurcumin, a major metabolite of
curcumin, induced autophagic cell death through coordinative
modulation of PI3K/Akt-mTOR and MAPK signaling pathways in human
leukemia HL-60 cells. Mol Nutr Food Res. 55:1646–1654. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yodkeeree S, Garbisa S and Limtrakul P:
Tetrahydrocurcumin inhibits HT1080 cell migration and invasion via
downregulation of MMPs and uPA. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 29:853–860.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yoysungnoen P, Wirachwong P, Changtam C,
Suksamrarn A and Patumraj S: Anti-cancer and anti-angiogenic
effects of curcumin and tetrahydrocurcumin on implanted
hepatocellular carcinoma in nude mice. World J Gastroenterol.
14:2003–2009. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lai CS, Wu JC, Yu SF, Badmaev V,
Nagabhushanam K, Ho CT and Pan MH: Tetrahydrocurcumin is more
effective than curcumin in preventing azoxymethane-induced colon
carcinogenesis. Mol Nutr Food Res. 55:1819–1828. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pan MH, Lin-Shiau SY and Lin JK:
Comparative studies on the suppression of nitric oxide synthase by
curcumin and its hydrogenated metabolites through down-regulation
of IkappaB kinase and NFkappaB activation in macrophages. Biochem
Pharmacol. 60:1665–1676. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li J, Liu Y, Wei JQ, Wang K, Chen LX, Yao
XS and Qiu F: Isolation and identification of phase 1 metabolites
of curcuminoids in rats. Planta Med. 78:1351–1356. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao F, Wang L and Liu K: In vitro
anti-inflammatory effects of arctigenin, a lignan from Arctium
lappa L., through inhibition on iNOS pathway. J Ethnopharmacol.
122:457–462. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ishihara T, Kohno K, Ushio S, Iwaki K,
Ikeda M and Kurimoto M: Tryptanthrin inhibits nitric oxide and
prostaglandin E(2) synthesis by murine macrophages. Eur J
Pharmacol. 407:197–204. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao F, Gao Z, Jiao W, Chen L, Chen L and
Yao X: In vitro anti-inflammatory effects of beta-carboline
alkaloids, isolated from Picrasma quassioides, through inhibition
of the iNOS pathway. Planta Med. 78:1906–1911. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao F, Chen L, Zhang M, Bi C, Li L, Zhang
Q, Shi C, Li M, Zhou S and Kong L: Inhibition of
lipopolysaccharide-induced iNOS and COX-2 expression by indole
alkaloid,
3-(hydroxymethyl)-6,7-dihydroindolo[2,3-a]quinolizin-(12H)-one, via
NF-κB inactivation in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Planta Med.
79:782–787. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pursley J, Shen JX, Schuster A, Dang OT,
Lehman J, Buonarati MH, Song Y, Aubry AF and Arnold ME: LC-MS/MS
determination of apixaban (BMS-562247) and its major metabolite in
human plasma: an application of polarity switching and monolithic
HPLC column. Bioanalysis. 6:2071–2082. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|