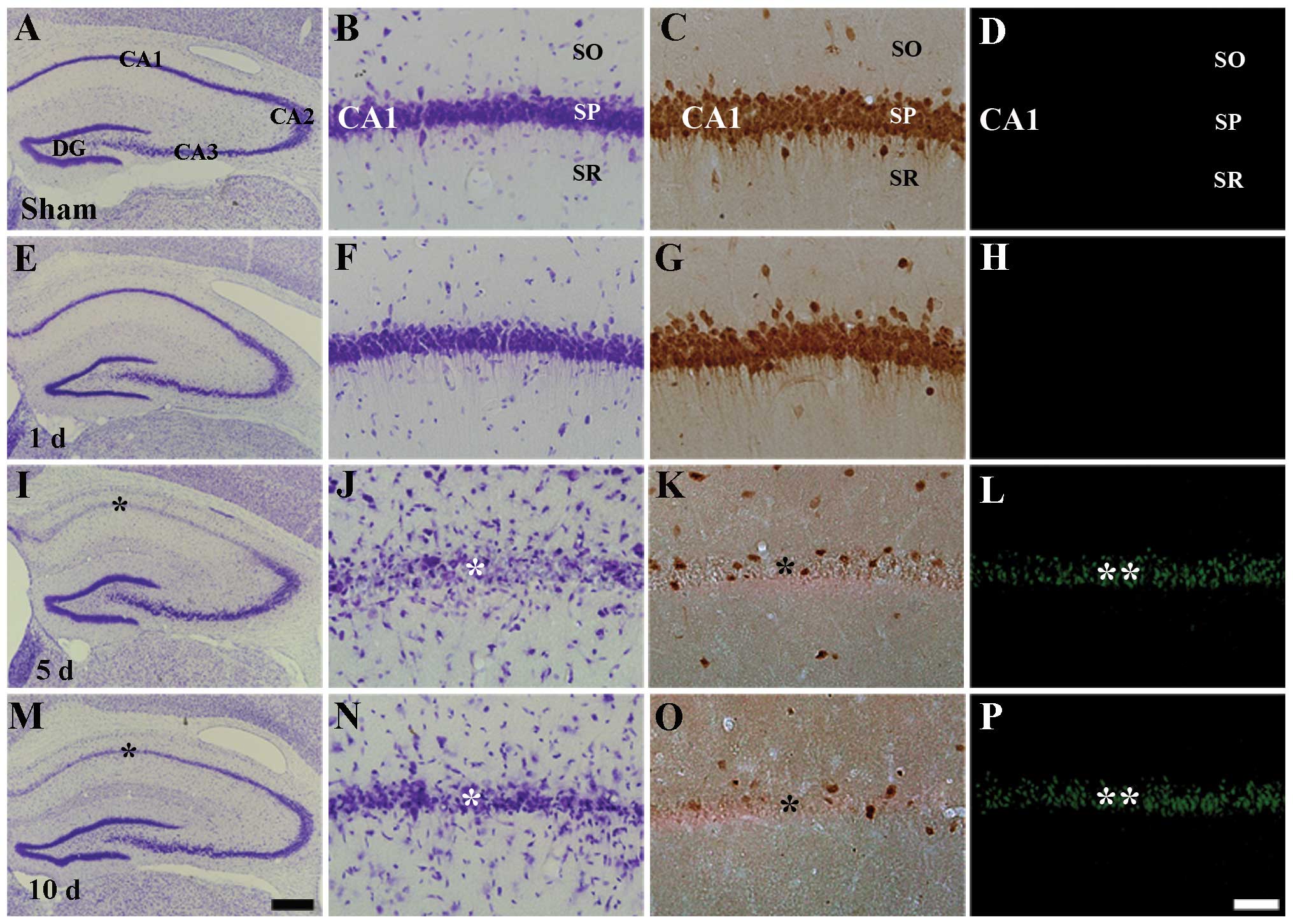
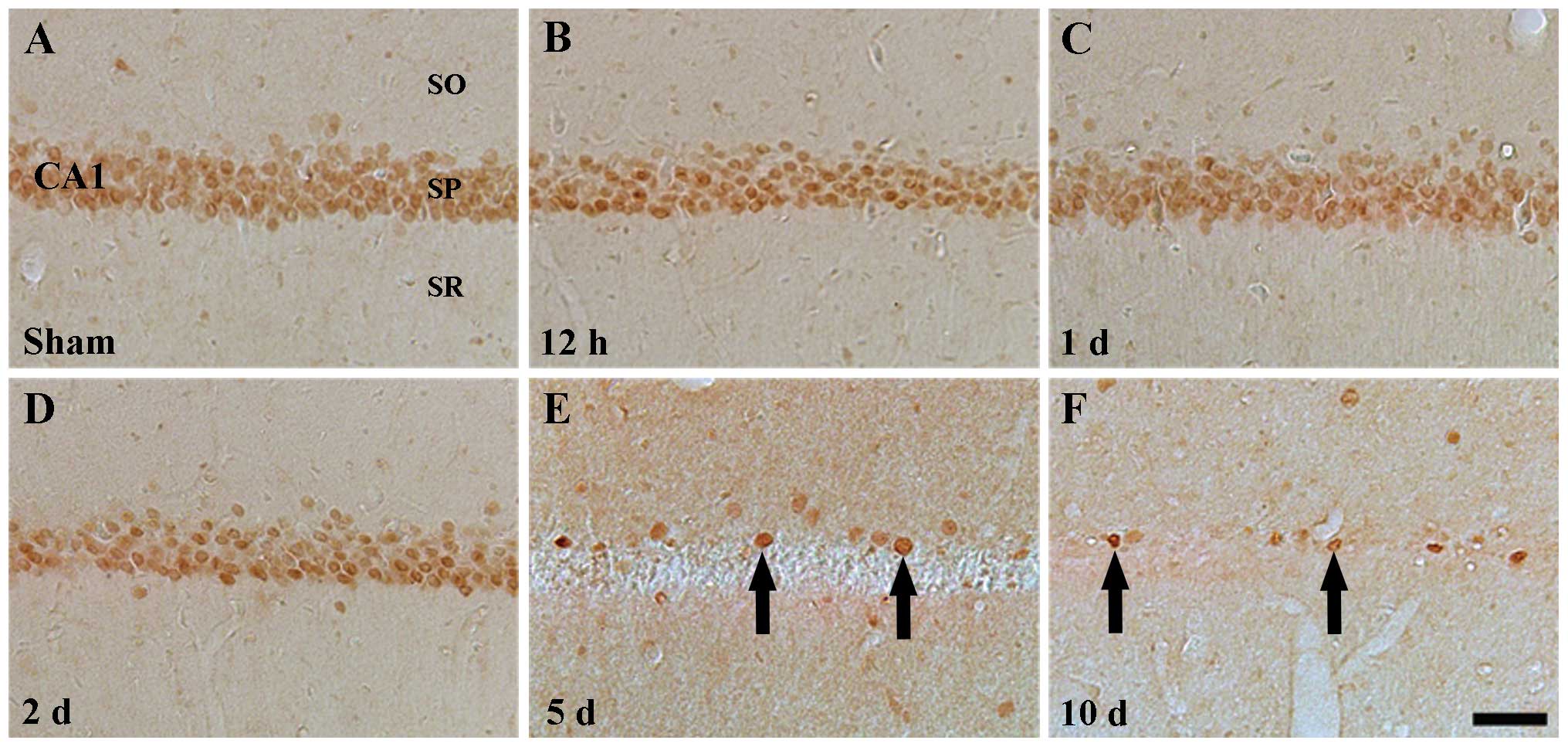
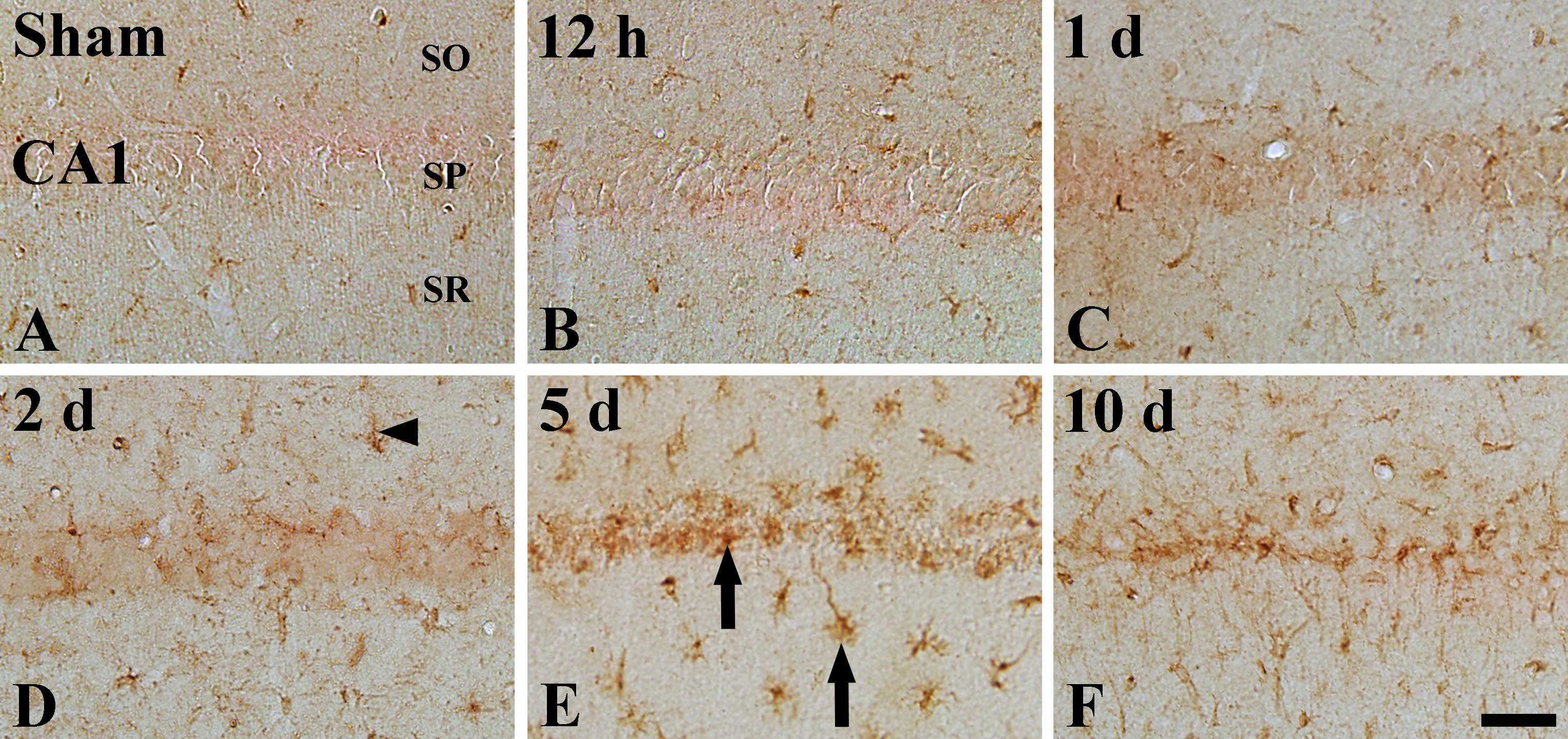
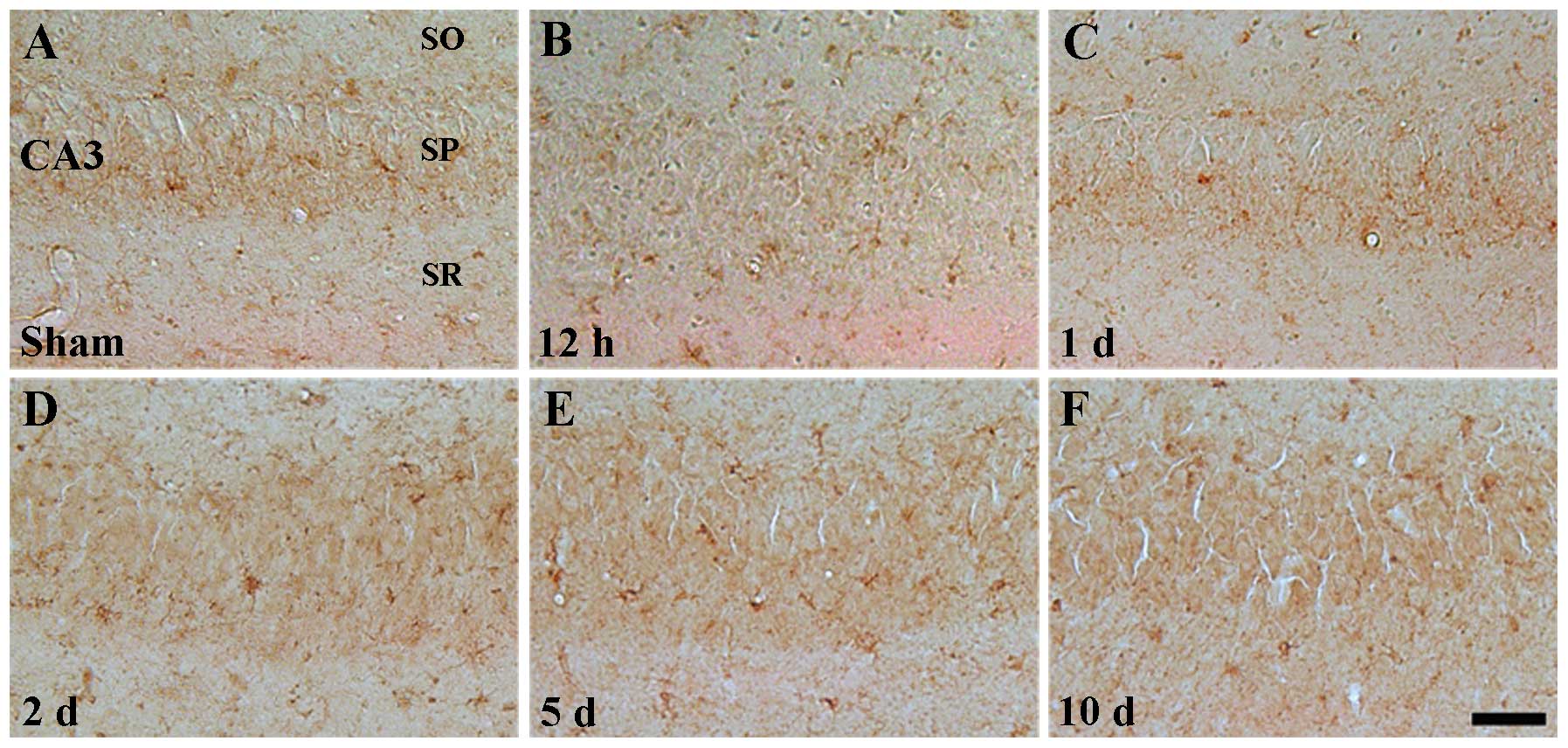
|
1
|
Kirino T: Delayed neuronal death in the
gerbil hippocampus following ischemia. Brain Res. 239:57–69. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lin CS, Polsky K, Nadler JV and Crain BJ:
Selective neocortical and thalamic cell death in the gerbil after
transient ischemia. Neuroscience. 35:289–299. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pulsinelli WA, Brierley JB and Plum F:
Temporal profile of neuronal damage in a model of transient
forebrain ischemia. Ann Neurol. 11:491–498. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Won MH, Kang T, Park S, et al: The
alterations of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor expressions and
oxidative DNA damage in the CA1 area at the early time after
ischemia-reperfusion insult. Neurosci Lett. 301:139–142. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rastogi L, Godbole MM, Ray M, et al:
Reduction in oxidative stress and cell death explains
hypothyroidism induced neuroprotection subsequent to
ischemia/reperfusion insult. Exp Neurol. 200:290–300. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Candelario-Jalil E, Alvarez D, Merino N
and Leon OS: Delayed treatment with nimesulide reduces measures of
oxidative stress following global ischemic brain injury in gerbils.
Neurosci Res. 47:245–253. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kee Y and Bronner-Fraser M: To proliferate
or to die: role of Id3 in cell cycle progression and survival of
neural crest progenitors. Genes Dev. 19:744–755. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Massari ME and Murre C: Helix-loop-helix
proteins: regulators of transcription in eucaryotic organisms. Mol
Cell Biol. 20:429–440. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Perk J, Iavarone A and Benezra R: Id
family of helix-loop-helix proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:603–614. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ruzinova MB and Benezra R: Id proteins in
development, cell cycle and cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 13:410–418.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kremer D, Aktas O, Hartung HP and Kury P:
The complex world of oligodendroglial differentiation inhibitors.
Ann Neurol. 69:602–618. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Norton JD: ID helix-loop-helix proteins in
cell growth, differentiation and tumorigenesis. J Cell Sci.
113:3897–3905. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jen Y, Manova K and Benezra R: Each member
of the Id gene family exhibits a unique expression pattern in mouse
gastrulation and neurogenesis. Dev Dyn. 208:92–106. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Neuman T, Keen A, Zuber MX, Kristjansson
GI, Gruss P and Nornes HO: Neuronal expression of regulatory
helix-loop-helix factor Id2 gene in mouse. Dev Biol. 160:186–195.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Riechmann V and Sablitzky F: Mutually
exclusive expression of two dominant-negative helix-loop-helix
(dnHLH) genes, Id4 and Id3, in the developing brain of the mouse
suggests distinct regulatory roles of these dnHLH proteins during
cellular proliferation and differentiation of the nervous system.
Cell Growth Differ. 6:837–843. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Andres-Barquin PJ, Hernandez MC and Israel
MA: Id genes in nervous system development. Histol Histopathol.
15:603–618. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Elliott RC, Khademi S, Pleasure SJ, Parent
JM and Lowenstein DH: Differential regulation of basic
helix-loop-helix mRNAs in the dentate gyrus following status
epilepticus. Neuroscience. 106:79–88. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rubenstein JL, Anderson S, Shi L,
Miyashita-Lin E, Bulfone A and Hevner R: Genetic control of
cortical regionalization and connectivity. Cereb Cortex. 9:524–532.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tzeng SF and de Vellis J: Id1, Id2 and Id3
gene expression in neural cells during development. Glia.
24:372–381. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fukuchi T, Katayama Y, Kamiya T, McKee A,
Kashiwagi F and Terashi A: The effect of duration of cerebral
ischemia on brain pyruvate dehydrogenase activity, energy
metabolites and blood flow during reperfusion in gerbil brain.
Brain Res. 792:59–65. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lorrio S, Negredo P, Roda JM, Garcia AG
and Lopez MG: Effects of memantine and galantamine given separately
or in association, on memory and hippocampal neuronal loss after
transient global cerebral ischemia in gerbils. Brain Res.
1254:128–137. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhang YB, Kan MY, Yang ZH, et al:
Neuroprotective effects of N-stearoyltyrosine on transient global
cerebral ischemia in gerbils. Brain Res. 1287:146–156. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang Q, Sun AY, Pardeike J, Muller RH,
Simonyi A and Sun GY: Neuroprotective effects of a nanocrystal
formulation of sPLA2 inhibitor PX-18 in cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion in gerbils. Brain Res. 1285:188–195. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hwang IK, Eum WS, Yoo KY, et al: Copper
chaperone for Cu,Zn-SOD supplement potentiates the Cu,Zn-SOD
function of neuroprotective effects against ischemic neuronal
damage in the gerbil hippocampus. Free Radic Biol Med. 39:392–402.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Park OK, Yoo KY, Lee CH, et al:
Arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase (AANAT) is expressed in
astrocytes and melatonin treatment maintains AANAT in the gerbil
hippocampus induced by transient cerebral ischemia. J Neurol Sci.
294:7–17. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schmued LC and Hopkins KJ: Fluoro-Jade B:
A high affinity fluorescent marker for the localization of neuronal
degeneration. Brain Res. 874:123–130. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Loskota WJ, Lomax LP and Verity MA: A
stereotaxic atlas of the Mongolian gerbil brain (Meriones
unguiculatus). Loskota William James, Lomax Peter and Verity M
Anthony: Ann Arbor Science; Ann Arbor, MI: 1974
|
|
28
|
Lee CH, Park JH, Choi JH, Yoo KY, Ryu PD
and Won MH: Heat shock protein 90 and its cochaperone, p23, are
markedly increased in the aged gerbil hippocampus. Exp Gerontol.
46:768–772. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee CH, Moon SM, Yoo KY, et al: Long-term
changes in neuronal degeneration and microglial activation in the
hippocampal CA1 region after experimental transient cerebral
ischemic damage. Brain Res. 1342:138–149. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nguyen MD, Boudreau M, Kriz J,
Couillard-Despres S, Kaplan DR and Julien JP: Cell cycle regulators
in the neuronal death pathway of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
caused by mutant superoxide dismutase 1. J Neurosci. 23:2131–2140.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vincent I, Rosado M and Davies P: Mitotic
mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease? J Cell Biol. 132:413–425. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Byrnes KR and Faden AI: Role of cell cycle
proteins in CNS injury. Neurochem Res. 32:1799–1807. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Broughton BR, Reutens DC and Sobey CG:
Apoptotic mechanisms after cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 40:e331–e339.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rashidian J, Iyirhiaro GO and Park DS:
Cell cycle machinery and stroke. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1772:484–493. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wen Y, Yang S, Liu R, Brun-Zinkernagel AM,
Koulen P and Simpkins JW: Transient cerebral ischemia induces
aberrant neuronal cell cycle re-entry and Alzheimer’s disease-like
tauopathy in female rats. J Biol Chem. 279:22684–22692. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang F, Corbett D, Osuga H, et al:
Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases improves CA1 neuronal
survival and behavioral performance after global ischemia in the
rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 22:171–182. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yokota Y and Mori S: Role of Id family
proteins in growth control. J Cell Physiol. 190:21–28. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hara E, Yamaguchi T, Nojima H, et al:
Id-related genes encoding helix-loop-helix proteins are required
for G1 progression and are repressed in senescent human
fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 269:2139–2145. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Barone MV, Pepperkok R, Peverali FA and
Philipson L: Id proteins control growth induction in mammalian
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 91:4985–4988. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fukuda T, Nakano S, Yoshiya I and
Hashimoto PH: Persistent degenerative state of non-pyramidal
neurons in the CA1 region of the gerbil hippocampus following
transient forebrain ischemia. Neuroscience. 53:23–38. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tortosa A and Ferrer I: Parvalbumin
immunoreactivity in the hippocampus of the gerbil after transient
forebrain ischaemia: a qualitative and quantitative sequential
study. Neuroscience. 55:33–43. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Benezra R, Davis RL, Lockshon D, Turner DL
and Weintraub H: The protein Id: a negative regulator of
helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 61:49–59. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nagata Y and Todokoro K: Activation of
helix-loop-helix proteins Id1, Id2 and Id3 during neural
differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 199:1355–1362. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lyden D, Young AZ, Zagzag D, et al: Id1
and Id3 are required for neurogenesis, angiogenesis and
vascularization of tumour xenografts. Nature. 401:670–677. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Fontemaggi G, Dell’Orso S, Trisciuoglio D,
et al: The execution of the transcriptional axis mutant p53, E2F1
and ID4 promotes tumor neo-angiogenesis. Nat Struct Mol Biol.
16:1086–1093. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sugawara T, Lewen A, Noshita N, Gasche Y
and Chan PH: Effects of global ischemia duration on neuronal,
astroglial, oligodendroglial and microglial reactions in the
vulnerable hippocampal CA1 subregion in rats. J Neurotrauma.
19:85–98. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hailer NP, Jarhult JD and Nitsch R:
Resting microglial cells in vitro: analysis of morphology and
adhesion molecule expression in organotypic hippocampal slice
cultures. Glia. 18:319–331. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hwang IK, Yoo KY, Kim DW, et al: Ionized
calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 immunoreactive cells change in
the gerbil hippocampal CA1 region after ischemia/reperfusion.
Neurochem Res. 31:957–965. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Schwartz M, Butovsky O, Bruck W and
Hanisch UK: Microglial phenotype: is the commitment reversible?
Trends Neurosci. 29:68–74. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Colton CA and Gilbert DL: Production of
superoxide anions by a CNS macrophage, the microglia. FEBS Lett.
223:284–288. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Han HS, Qiao Y, Karabiyikoglu M, Giffard
RG and Yenari MA: Influence of mild hypothermia on inducible nitric
oxide synthase expression and reactive nitrogen production in
experimental stroke and inflammation. J Neurosci. 22:3921–3928.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Suzuki S, Tanaka K, Nogawa S, et al:
Temporal profile and cellular localization of interleukin-6 protein
after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
19:1256–1262. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hashimoto M, Nitta A, Fukumitsu H, Nomoto
H, Shen L and Furukawa S: Involvement of glial cell line-derived
neurotrophic factor in activation processes of rodent macrophages.
J Neurosci Res. 79:476–487. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Laurenzi MA, Arcuri C, Rossi R, Marconi P
and Bocchini V: Effects of microenvironment on morphology and
function of the microglial cell line BV-2. Neurochem Res.
26:1209–1216. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Lu YZ, Lin CH, Cheng FC and Hsueh CM:
Molecular mechanisms responsible for microglia-derived protection
of Sprague-Dawley rat brain cells during in vitro ischemia.
Neurosci Lett. 373:159–164. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|