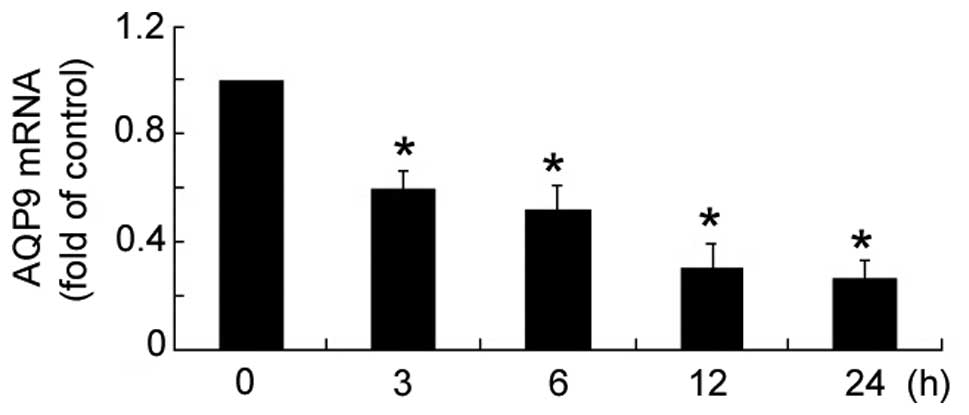
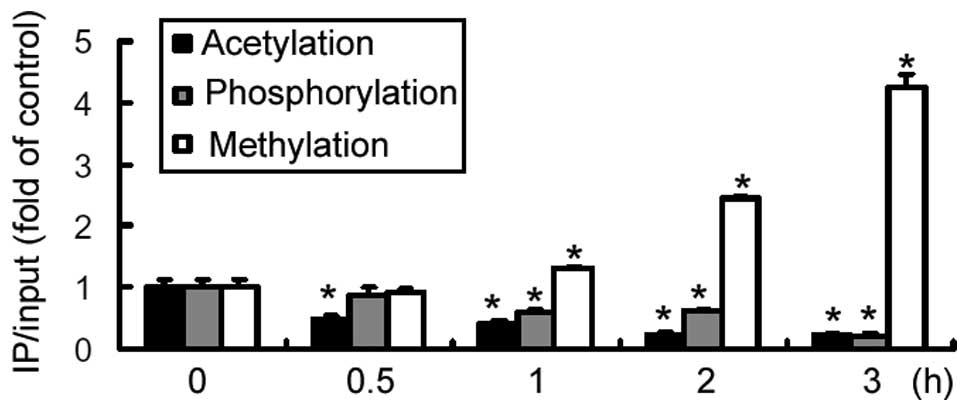
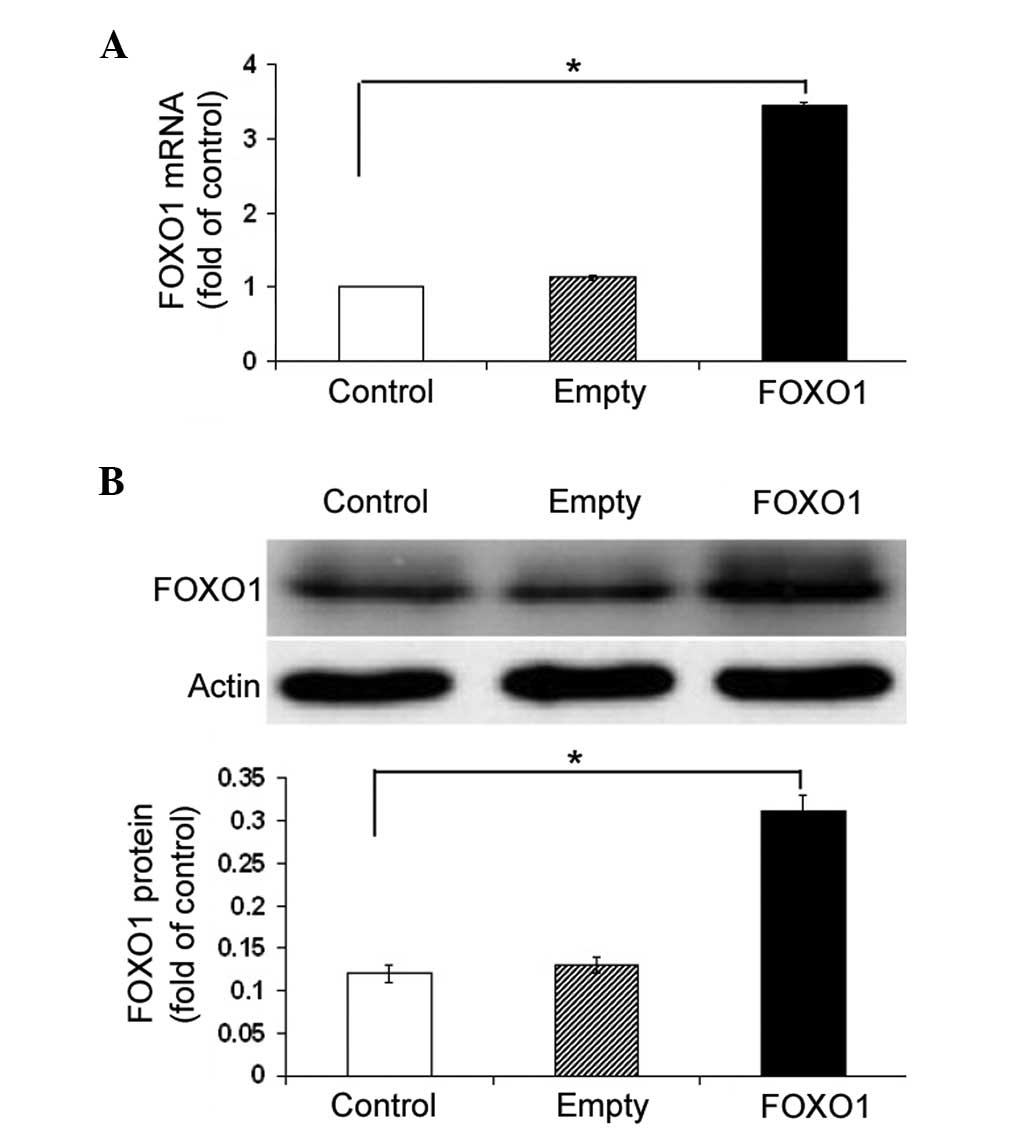
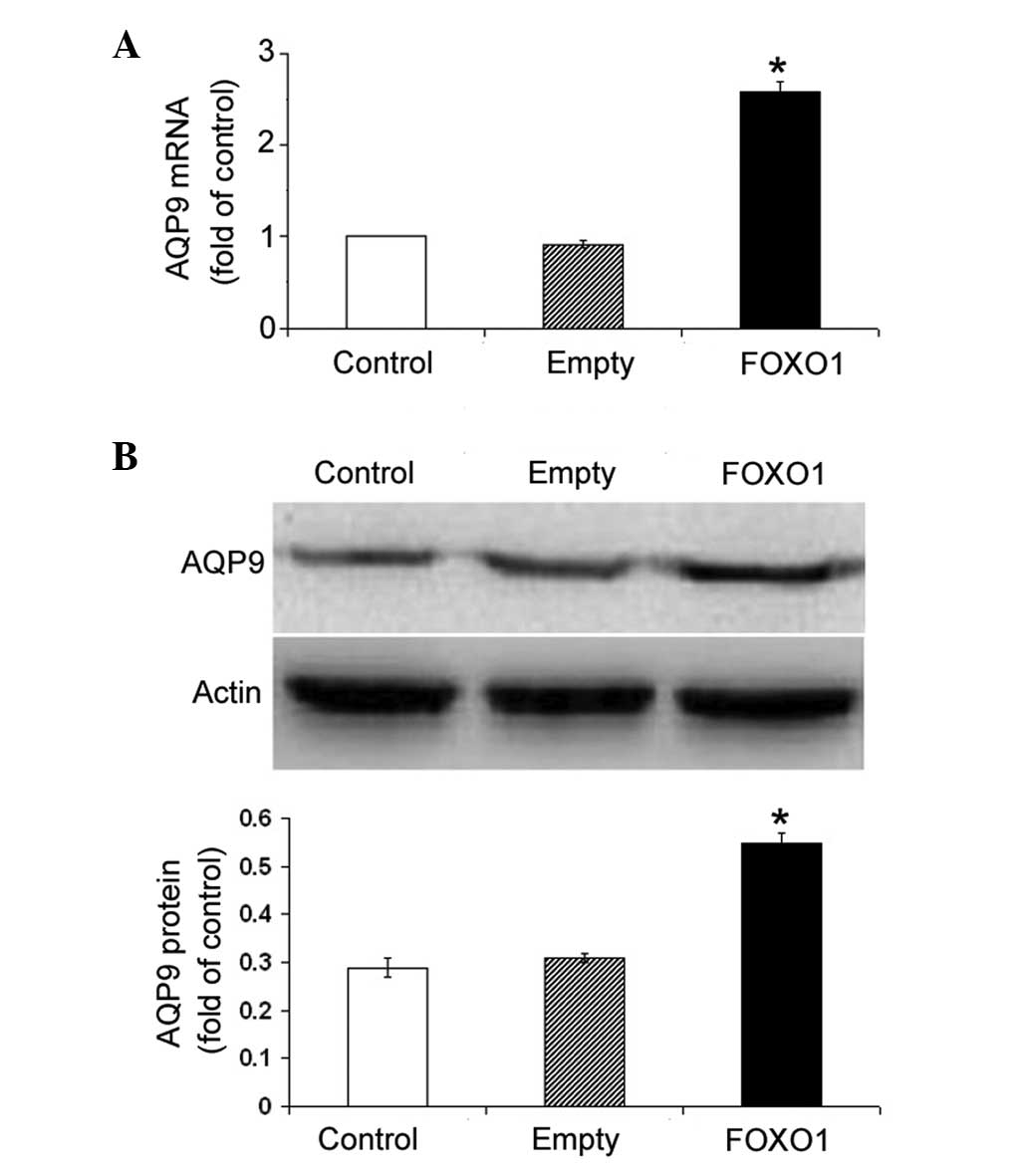
|
1
|
Verkman AS: Aquaporins. Curr Biol.
23:R52–R55. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Buffoli B: Aquaporin biology and nervous
system. Curr Neuropharmacol. 8:97–104. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Maeda N: Implications of aquaglyceroporins
7 and 9 in glycerol metabolism and metabolic syndrome. Mol Aspects
Med. 33:665–675. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rojek AM, Skowronski MT, Füchtbauer EM, et
al: Defective glycerol metabolism in aquaporin 9 (AQP9) knockout
mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:3609–3614. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jelen S, Wacker S, Aponte-Santamaría C, et
al: Aquaporin-9 protein is the primary route of hepatocyte glycerol
uptake for glycerol gluconeogenesis in mice. J Biol Chem.
286:44319–44325. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kuriyama H, Shimomura I, Kishida K, et al:
Coordinated regulation of fat-specific and liver-specific glycerol
channels, aquaporin adipose and aquaporin 9. Diabetes.
51:2915–2921. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Castro Parodi M, Farina M, Dietrich V,
Abán C, Szpilbarg N, Zotta E and Damiano AE: Evidence for
insulin-mediated control of AQP9 expression in human placenta.
Placenta. 32:1050–1056. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rodríguez A, Catalán V, Gómez-Ambrosi J,
et al: Insulin- and leptin-mediated control of aquaglyceroporins in
human adipocytes and hepatocytes is mediated via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR
signaling cascade. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 96:E586–E597. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Carbrey JM, Gorelick-Feldman DA, Kozono D,
Praetorius J, Nielsen S and Agre P: Aquaglyceroporin AQP9: solute
permeation and metabolic control of expression in liver. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 100:2945–2950. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kamagate A, Qu S, Perdomo G, et al: FoxO1
mediates insulin-dependent regulation of hepatic VLDL production in
mice. J Clin Invest. 118:2347–2364. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Matsumoto M, Pocai A, Rossetti L, Depinho
RA and Accili D: Impaired regulation of hepatic glucose production
in mice lacking the forkhead transcription factor Foxo1 in liver.
Cell Metab. 6:208–216. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tsuchida A, Yamauchi T, Ito Y, et al:
Insulin/Foxo1 pathway regulates expression levels of adiponectin
receptors and adiponectin sensitivity. J Biol Chem.
279:30817–30822. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xiao X, Mei ZC, Qiu LW, et al: Effect of
forkhead transcription factor 1 gene silencing on expression of
aquaporin 9 in normal human liver cells. Chin J Biologicals.
10:1157–1161. 2011.
|
|
14
|
Sharma S, Kelly TK and Jones PA:
Epigenetics in cancer. Carcinogenesis. 31:27–36. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Gräff J, Kim D, Dobbin MM and Tsai LH:
Epigenetic regulation of gene expression in physiological and
pathological brain processes. Physiol Rev. 91:603–649. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kabra DG, Gupta J and Tikoo K: Insulin
induced alteration in post-translational modifications of histone
H3 under a hyperglycemic condition in L6 skeletal muscle myoblasts.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1792:574–583. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gupta J and Tikoo K: Involvement of
insulin-induced reversible chromatin remodeling in altering the
expression of oxidative stress-responsive genes under hyperglycemia
in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Gene. 504:181–191. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hatta M and Cirillo LA: Chromatin opening
and stable perturbation of core histone: DNA contacts by FoxO1. J
Biol Chem. 282:35583–35593. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ornskov D, Nexo E and Sorensen BS: Insulin
induces a transcriptional activation of epiregulin, HB-EGF and
amphiregulin, by a PI3K-dependent mechanism: identification of a
specific insulin-responsive promoter element. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 354:885–891. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ge J, Zhai W, Cheng B, et al: Insulin
induces human acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase1 gene
expression via MAP kinases and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α. J
Cell Biochem. 114:2188–2198. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yan C and Boyd DD: Histone H3 acetylation
and H3 K4 methylation define distinct chromatin regions permissive
for transgene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 26:6357–6371. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fischle W, Wang YM and Allis CD: Histone
and chromatin cross-talk. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 15:172–183. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cheung P, Tanner KG, Cheung WL,
Sassone-Corsi P, Denu JM and Allis CD: Synergistic coupling of
histone H3 phosphorylation and acetylation in response to epidermal
growth factor stimulation. Mol Cell. 5:905–915. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Matsuzaki H, Daitoku H, Hatta M, Tanaka K
and Fukamizu A: Insulin-induced phosphorylation of FKHR (Foxo1)
targets to proteasomal degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:11285–11290. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Miao H, Zhang Y, Lu Z, Liu Q and Gan L:
FOXO1 involvement in insulin resistance-related pro-inflammatory
cytokine production in hepatocytes. Inflamm Res. 61:349–358. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Durham SK, Suwanichkul A, Scheimann AO,
Yee D, Jackson JG, Barr FG and Powell DR: FKHR binds the insulin
response element in the insulin-like growth factor binding
protein-1 promoter. Endocrinology. 140:3140–3146. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|