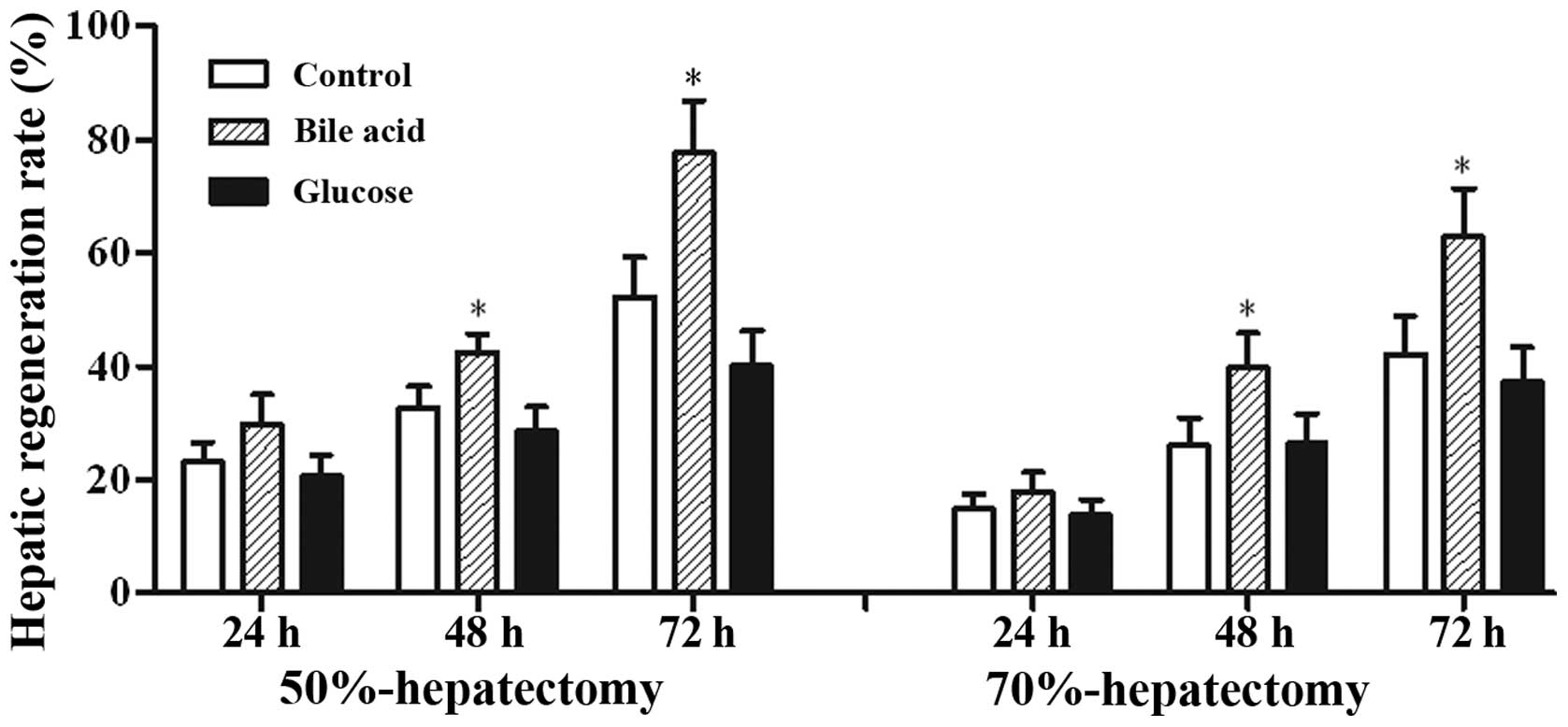
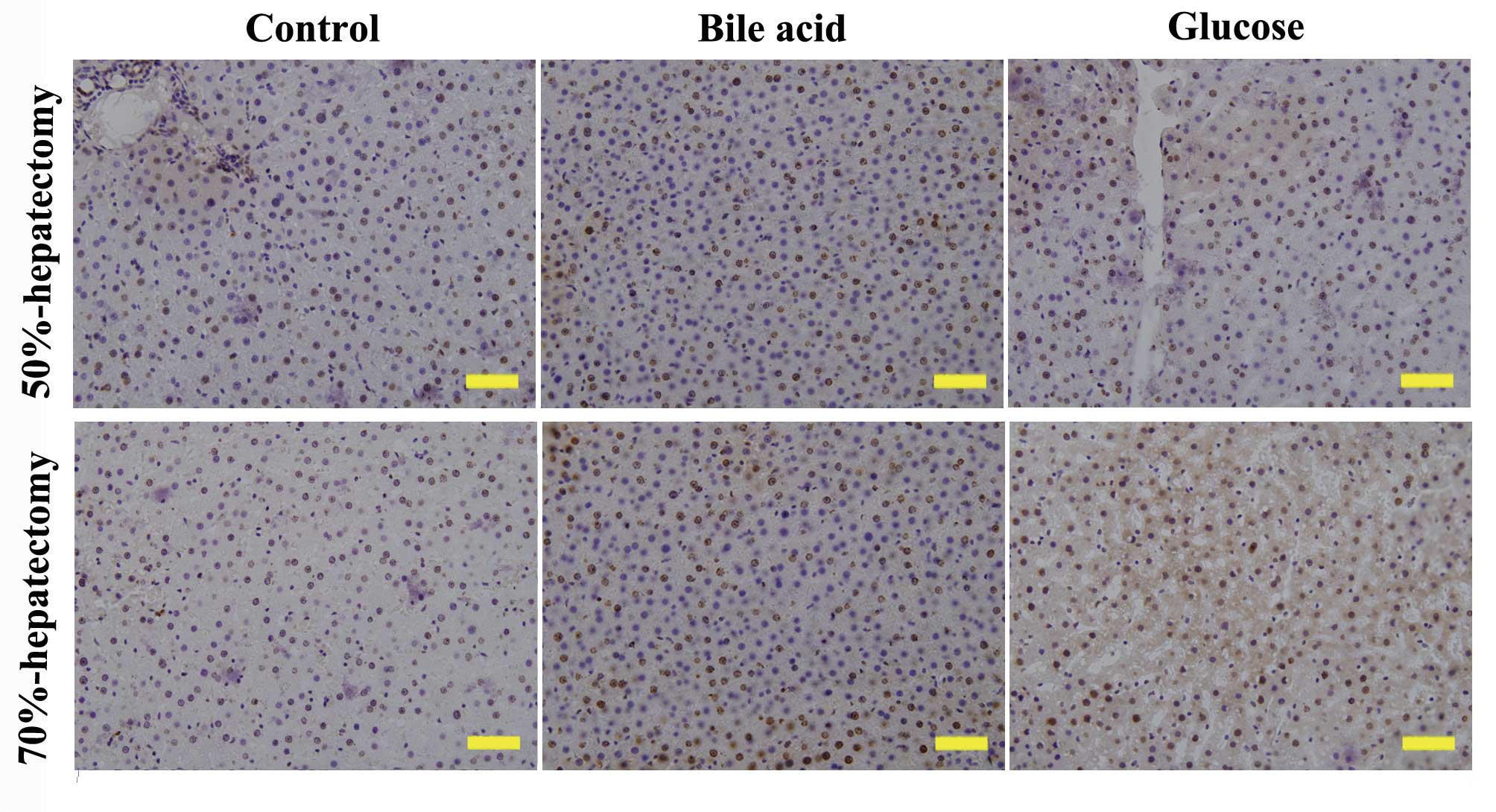
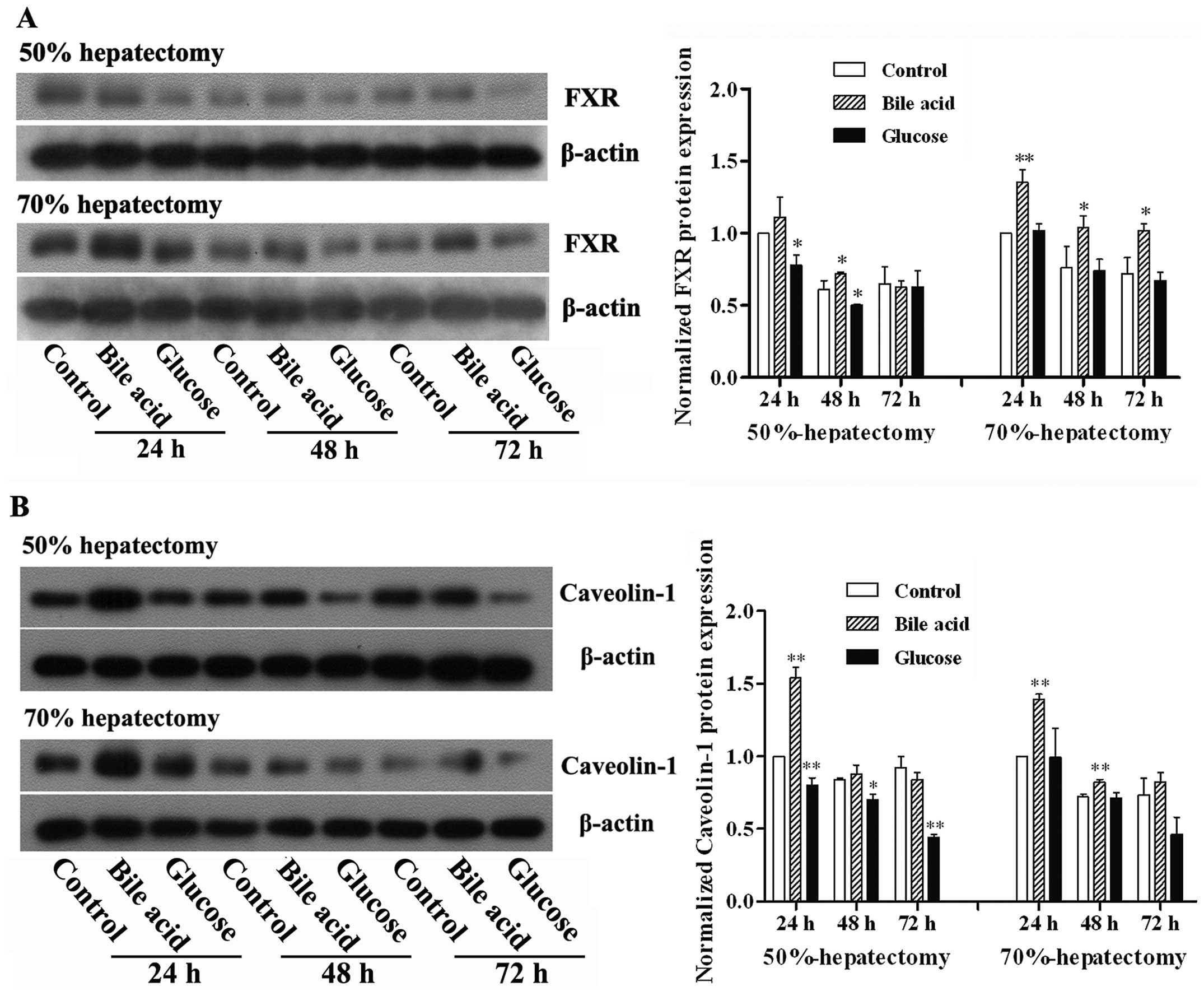
|
1
|
Fausto N, Campbell JS and Riehle KJ: Liver
regeneration. Hepatology. 43(2 Suppl 1): S45–S53. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mohammed FF and Khokha R: Thinking outside
the cell: proteases regulate hepatocyte division. Trends Cell Biol.
15:555–563. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gerbino A, Ranieri M, Lupo S, et al:
Ca2+-dependent K+ efflux regulates
deoxycholate-induced apoptosis of BHK-21 and Caco-2 cells.
Gastroenterology. 137:955–964. e951–e952. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Drudi Metalli V, Mancino MG, Mancino A, et
al: Bile salts regulate proliferation and apoptosis of liver cells
by modulating the IGF1 system. Dig Liver Dis. 39:654–662. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Staudinger JL, Woody S, Sun M and Cui W:
Nuclear-receptor-mediated regulation of drug- and
bile-acid-transporter proteins in gut and liver. Drug Metab Rev.
45:48–59. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Carlberg C and Seuter S: Dynamics of
nuclear receptor target gene regulation. Chromosoma. 119:479–484.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Forman BM, Goode E, Chen J, et al:
Identification of a nuclear receptor that is activated by farnesol
metabolites. Cell. 81:687–693. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang YD, Chen WD, Moore DD and Huang W:
FXR: a metabolic regulator and cell protector. Cell Res.
18:1087–1095. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gadaleta RM, van Mil SW, Oldenburg B,
Siersema PD, Klomp LW and van Erpecum KJ: Bile acids and their
nuclear receptor FXR: Relevance for hepatobiliary and
gastrointestinal disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1801:683–692. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Peterson DF, Coote JH, Gilbey MP and
Futuro-Neto HA: Differential pattern of sympathetic outflow during
upper airway stimulation with smoke. Am J Physiol. 245:R433–R437.
1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xing X, Burgermeister E, Geisler F, et al:
Hematopoietically expressed homeobox is a target gene of farnesoid
X receptor in chenodeoxycholic acid-induced liver hypertrophy.
Hepatology. 49:979–988. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lefebvre P, Cariou B, Lien F, Kuipers F
and Staels B: Role of bile acids and bile acid receptors in
metabolic regulation. Physiol Rev. 89:147–191. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
El-Shenawy NS: Effects of insecticides
fenitrothion, endosulfan and abamectin on antioxidant parameters of
isolated rat hepatocytes. Toxicol In Vitro. 24:1148–1157. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Matsubara T, Li F and Gonzalez FJ: FXR
signaling in the enterohepatic system. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
368:17–29. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Fernández MA, Albor C, Ingelmo-Torres M,
et al: Caveolin-1 is essential for liver regeneration. Science.
313:1628–1632. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hoekstra LT, van Lienden KP, Schaap FG,
Chamuleau RA, Bennink RJ and van Gulik TM: Can plasma bile salt,
triglycerides, and apoA-V levels predict liver regeneration? World
J Surg. 36:2901–2908. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Csanaky IL, Aleksunes LM, Tanaka Y and
Klaassen CD: Role of hepatic transporters in prevention of bile
acid toxicity after partial hepatectomy in mice. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 297:G419–G433. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Otao R, Beppu T, Isiko T, et al: External
biliary drainage and liver regeneration after major hepatectomy. Br
J Surg. 99:1569–1574. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Perez MJ and Briz O: Bile-acid-induced
cell injury and protection. World J Gastroenterol. 15:1677–1689.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kren BT, Rodrigues CM, Setchell KD and
Steer CJ: Modulation of steady-state messenger RNA levels in the
regenerating rat liver with bile acid feeding. Liver Transpl.
7:321–334. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang L, Huang X, Meng Z, et al:
Significance and mechanism of CYP7a1 gene regulation during the
acute phase of liver regeneration. Mol Endocrinol. 23:137–145.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Chen WD, Wang YD, Zhang L, et al:
Farnesoid X receptor alleviates age-related proliferation defects
in regenerating mouse livers by activating forkhead box m1b
transcription. Hepatology. 51:953–962. 2010.
|
|
23
|
Meng Z, Wang Y, Wang L, et al: FXR
regulates liver repair after CCl4-induced toxic injury. Mol
Endocrinol. 24:886–897. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Borude P, Edwards G, Walesky C, et al:
Hepatocyte-specific deletion of farnesoid X receptor delays but
does not inhibit liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in
mice. Hepatology. 56:2344–2352. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang L, Wang YD, Chen WD, et al:
Promotion of liver regeneration/repair by farnesoid X receptor in
both liver and intestine in mice. Hepatology. 56:2336–2343. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dionne I, Brown NJ, Woodgate R and Bell
SD: On the mechanism of loading the PCNA sliding clamp by RFC. Mol
Microbiol. 68:216–222. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hlinkova V, Xing G, Bauer J, et al:
Structures of monomeric, dimeric and trimeric PCNA: PCNA-ring
assembly and opening. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr.
64:941–949. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Woudenberg J, Rembacz KP, van den Heuvel
FA, et al: Caveolin-1 is enriched in the peroxisomal membrane of
rat hepatocytes. Hepatology. 51:1744–1753. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fernández-Rojo MA, Restall C, Ferguson C,
et al: Caveolin-1 orchestrates the balance between glucose and
lipid-dependent energy metabolism: implications for liver
regeneration. Hepatology. 55:1574–1584. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Meyer C, Liu Y, Kaul A, Peipe I and Dooley
S: Caveolin-1 abrogates TGF-beta mediated hepatocyte apoptosis.
Cell Death Dis. 4:e4662013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Li G, Thomas AM, Hart SN, Zhong X, Wu D
and Guo GL: Farnesoid X receptor activation mediates head-to-tail
chromatin looping in the Nr0b2 gene encoding small heterodimer
partner. Mol Endocrinol. 24:1404–1412. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Anakk S, Watanabe M, Ochsner SA, McKenna
NJ, Finegold MJ and Moore DD: Combined deletion of FXR and SHP in
mice induces Cyp17a1 and results in juvenile onset cholestasis. J
Clin Invest. 121:86–95. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Kerr TA, Matsumoto Y, Matsumoto H, et al:
Cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase regulation: A role for
farnesoid X receptor and small heterodimer partner in murine
hepatic taurine metabolism. Hepatol Res. 44:E218–E228. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Matsui S, Yamane T, Takita T, Oishi Y and
Kobayashi-Hattori K: The hypocholesterolemic activity of Momordica
charantia fruit is mediated by the altered cholesterol- and bile
acid-regulating gene expression in rat liver. Nutr Res. 33:580–585.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhu QN, Xie HM, Zhang D, Liu J and Lu YF:
Hepatic bile acids and bile acid-related gene expression in
pregnant and lactating rats. Peer J. 1:e1432013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Miura T, Kimura N, Yamada T, et al:
Sustained repression and translocation of Ntcp and expression of
Mrp4 for cholestasis after rat 90% partial hepatectomy. J Hepatol.
55:407–414. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hoang MH, Houng SJ, Jun HJ, et al: Barley
intake induces bile acid excretion by reduced expression of
intestinal ASBT and NPC1L1 in C57BL/6 J mice. J Agric Food Chem.
59:6798–6805. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|