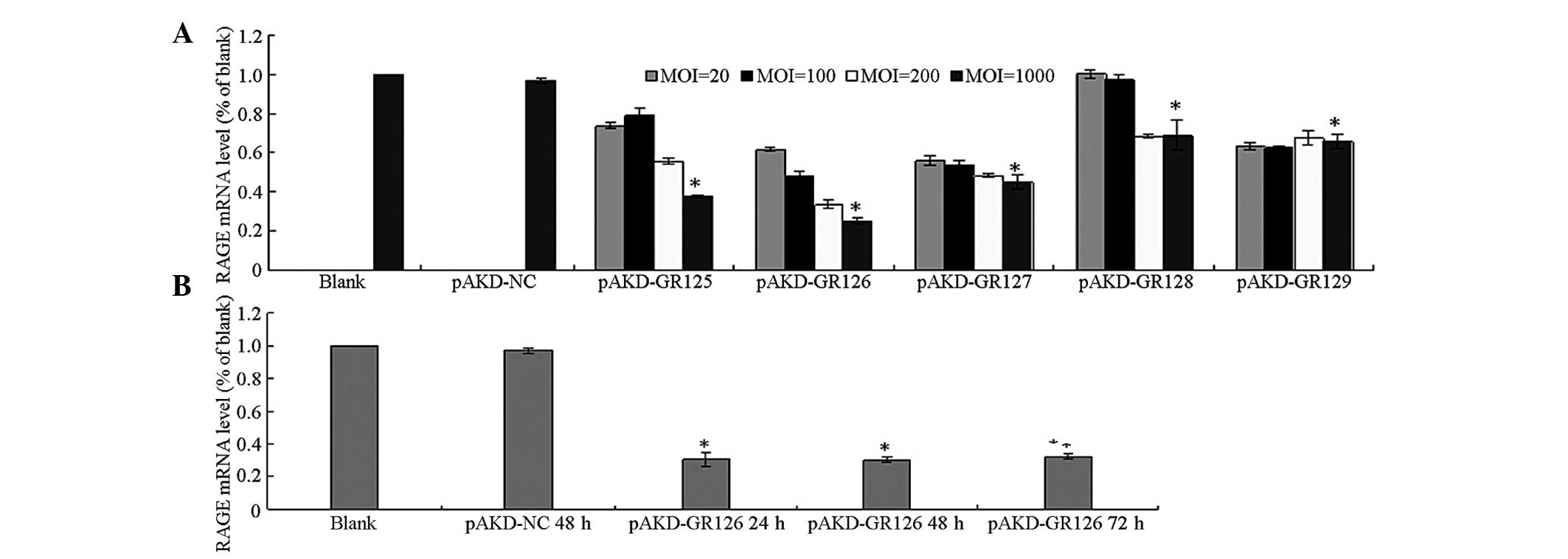
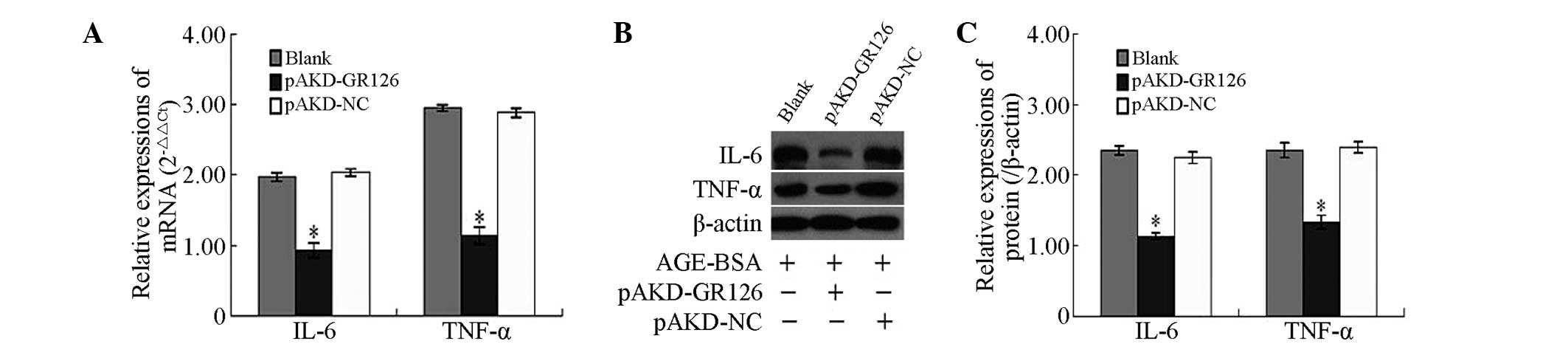
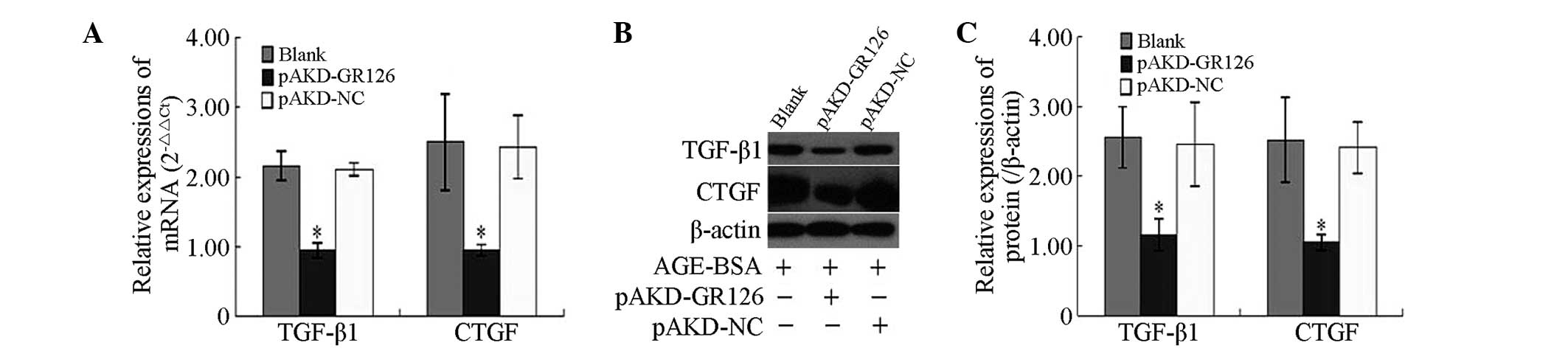
|
1
|
Bierhaus A, Humpert PM, Morcos M, et al:
Nawroth, Understanding RAGE, the receptor for advanced glycation
end products. J Mol Med (Berl). 83:876–886. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hegab Z, Gibbons S, Neyses L and Mamas MA:
Role of advanced glycation end products in cardiovascular disease.
World J Cardiol. 4:90–102. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yan SD, Bierhaus A, Nawroth PP and Stern
DM: RAGE and Alzheimer’s disease: a progression factor for
amyloid-beta-induced cellular perturbation? J Alzheimers Dis.
16:833–843. 2009.
|
|
4
|
Oleniuc M, Secara I, Onofriescu M, Hogas
S, et al: Consequences of advanced glycation end products
accumulation in chronic kidney disease and clinical usefulness of
their assessment using a non-invasive technique-skin
autofluorescence. Maedica (Buchar). 6:298–307. 2011.
|
|
5
|
Barlovic DP, Soro-Paavonen A and
Jandeleit-Dahm KA: RAGE biology, atherosclerosis and diabetes. Clin
Sci (Lond). 211:43–55. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Schwenger V, Morath C, Salava A, et al:
Damage to the peritoneal membrane by glucose degradation products
is mediated by the receptor for advanced glycation end-products. J
Am Soc Nephrol. 17:199–207. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Vlassara H, Striker LJ, Teichberg S, et
al: Advanced glycation end products induce glomerular sclerosis and
albuminuria in normal rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 91:11704–11708.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fehrenbach H, Weiskirchen R, Kasper M and
Gressner AM: Up-regulated expression of the receptor for advanced
glycation end products in cultured rat hepatic stellate cells
during transdifferentiation to myofibroblasts. Hepatology.
34:943–952. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Guimarães EL, Empsen C, Geerts A and van
Grunsven LA: Advanced glycation end products induce production of
reactive oxygen species via the activation of NADPH oxidase in
murine hepatic stellate cells. J Hepatol. 52:389–397. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Iwamoto K, Kanno K, Hyogo H, et al:
Advanced glycation end products enhance the proliferation and
activation of hepatic stellate cells. J Gastroenterol. 43:298–304.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xia JR, Liu NF and Zhu NX: Specific siRNA
targeting the receptor for advanced glycation end products inhibits
experimental hepatic fibrosis in rats. Int J Mol Sci. 9:638–661.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lohwasser C, Neureiter D, Popov Y, Bauer M
and Schuppan D: Role of the receptor for advanced glycation end
products in hepatic fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol. 15:5789–5798.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Friedman SL and Roll FJ: Isolation and
culture of hepatic lipocytes, Kuper cells, and sinusoidal
endothelial cells by density gradient centreifugation with
Stractan. Anal Biochem. 161:207–218. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PRC and
the 2 (− Delta Delta C(T) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Xie X, Zhao R and Shen GX: Impact of
cyanidin-3-glucoside on glycated LDL-induced NADPH oxidase
activation, mitochondrial dysfunction and cell viability in
cultured vascular endothelial cells. Int J Mol Sci. 13:15867–15880.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Sangle GV, Zhao R, Mizuno TM and Shen GX:
Involvement of RAGE, NADPH oxidase, and Ras/Raf-1 pathway in
glycated LDL-induced expression of heat shock factor-1 and
plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in vascular endothelial cells.
Endocrinology. 151:4455–4466. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Willems S, Verleden SE, Vanaudenaerde BM,
et al: Multiplex protein profiling of bronchoalveolar lavage in
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Ann
Thorac Med. 8:38–45. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cheng A, Dong Y, Zhu F, et al: AGE-LDL
activates Toll like receptor 4 pathway and promotes inflammatory
cytokines production in renal tubular epithelial cells. Int J Biol
Sci. 9:94–107. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Honsawek S, Vejchapipat P, Payungporn S,
et al: Soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products and
liver stiffness in postoperative biliary atresia. Clin Biochem.
46:214–218. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Goodwin M, Herath C, Jia Z, et al:
Advanced glycation end products augment experimental hepatic
fibrosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 28:369–376. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sebeková K, Kupcová V, Schinzel R and
Heidland A: Markedly elevated levels of plasma advanced glycation
end products in patients with liver cirrhosis-amelioration by liver
transplantation. J Hepatol. 36:66–71. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Ahmed N, Lüthen R, Häussinger D, et al:
Increased protein glycation in cirrhosis and therapeutic strategies
to prevent it. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1043:718–724. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yagmur E, Tacke F, Weiss C, et al:
Elevation of Nepsilon-(carboxymethyl) lysine-modified advanced
glycation end products in chronic liver disease is an indicator of
liver cirrhosis. Clin Biochem. 39:39–45. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Oldfield MD, Bach LA, Forbes JM, et al:
Advanced glycation end products cause epithelial-myofibroblast
transdifferentiation via the receptor for advanced glycation end
products (RAGE). J Clin Invest. 108:1853–1863. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lin J, Tang Y, Kang Q, Feng Y and Chen A:
Curcumin inhibits gene expression of receptor for advanced
glycation end-products (RAGE) in hepatic stellate cells in vitro by
elevating PPARγ activity and attenuating oxidative stress. Br J
Pharmacol. 166:2212–2227. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Reynaert H, Thompson MG, Thomas T and
Geerts A: Hepatic stellate cells: role in microcirculation and
pathophysiology of portal hypertension. Gut. 50:571–581. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shi GF and Li Q: Effects of oxymatrine on
experimental hepatic fibrosis and its mechanism in vivo. World J
Gastroenterol. 11:268–271. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Reeves HL and Friedman SL: Activation of
hepatic stellate ceils-a key issue in liver fibrosis. Front Biosci.
7:d808–d826. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Campbell JS, Hughes SD, Gilbertson DG, et
al: Pletelet-derived growth factor C induces liver fibrosis,
steatosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:3389–3394. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Sakaida I, Hironaka K, Kimura T, et al:
Herbal medicine sho-saiko-to(TJ-9) increases expression matrix
metalloproteinases (MMPs) with reduced expression of tissue
inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMPs) in rat stellate cell. Life
Sci. 74:2251–2263. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Iredale JP: Hepatic stellate cell behavior
during resolution of liver injury. Semin Liver Dis. 21:427–436.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Benyon RC and Arthur MJ: Extracellular
matrix degradation and the role of hepatic stellate cells. Semin
Liver Dis. 21:373–384. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Borkham-Kamphorst E, Herrmann J, Stoll D,
et al: Dominent-negative solute PDGF-beta receptor inhibits hepatic
stellate cell activation and attenuates liver fibrosis. Lab Invest.
84:766–777. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Novosyadlyy R, Tron K, Dudas J, Ramadori G
and Scharf JG: Expression and regulation of the insulin-like growth
factor axis components in rat liver myofibroblasts. J Cell Physiol.
199:388–398. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Simeonova PP, Gallucci RM, Hulderman T, et
al: The role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in liver toxicity,
inflammation, and fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 177:112–120. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
da Silva FM, Guimarães EL, Grivicich I, et
al: Hepatic stellate cell activation in vitro: cell cycle arrest at
G2/M and modification of cell motility. J Cell Biochem. 90:387–396.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Huang G and Brigstock DR: Integrin
expression and function in the response of primary culture hepatic
stellate cells to connective tissue growth factor (CCN2). J Cell
Mol Med. 15:1087–1095. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Galicia-Moreno M, Rodríguez-Rivera A,
Reyes-Gordillo K, et al: Trolox down-regulates transforming growth
factor-beta and prevents experimental cirrhosis. Basic Clin
Pharmacol Toxicol. 103:476–481. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen A: Acetaldehyde stimulates the
activation of latent transforming growth factor-betal and induces
expression of the type II receptor of the cytokine in rat cultured
hepatic stellate cells. Biochem J. 368:683–693. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sedlaczek N, Jia JD, Bauer M, et al:
Proliferating bile duct epithelial cells are a major source of
connective tissue growth factor in rat bilinry fibrosis. Am J
Pathol. 158:1239–1244. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Faouzi S, Le Bail B, Neaud V, et al:
Myofibroblasts are responsible for collagen synthesis in the stroma
of human hepatocellular carcinoma: an in vivo and in vitro study. J
Hepatol. 30:275–284. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Friedman SL: Molecular regulation of
hepatic fibrosis, an integrated cellular response to tissue injury.
J Biol Chem. 275:2247–2250. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pinzani M and Marra F: Cytokine receptors
and signaling in hepatic stellate cells. Semin Liver Dis.
21:397–416. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|