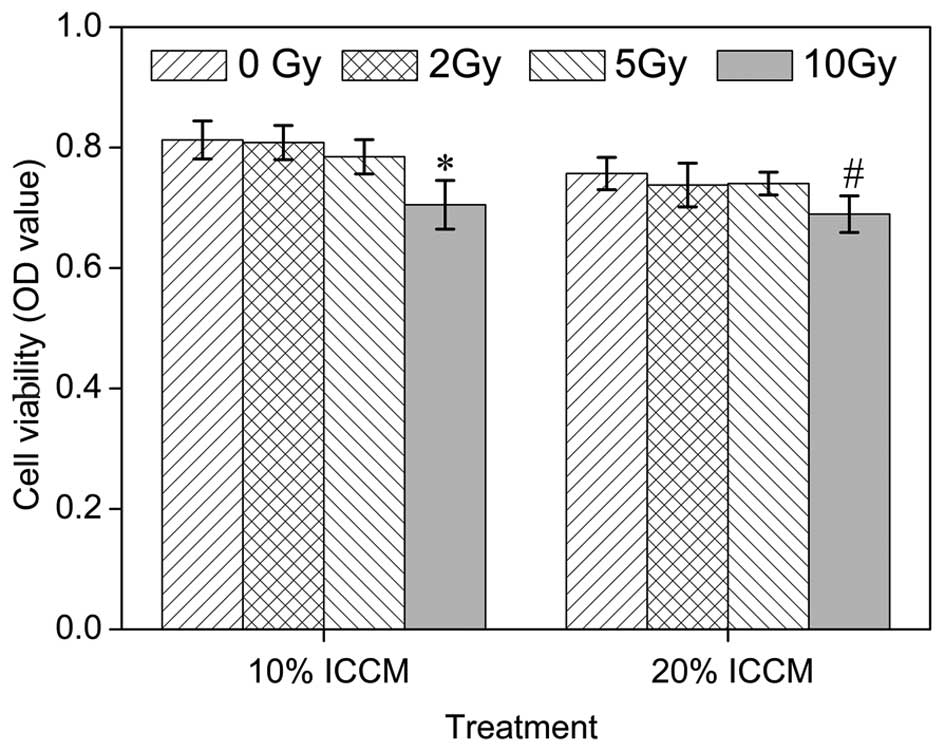
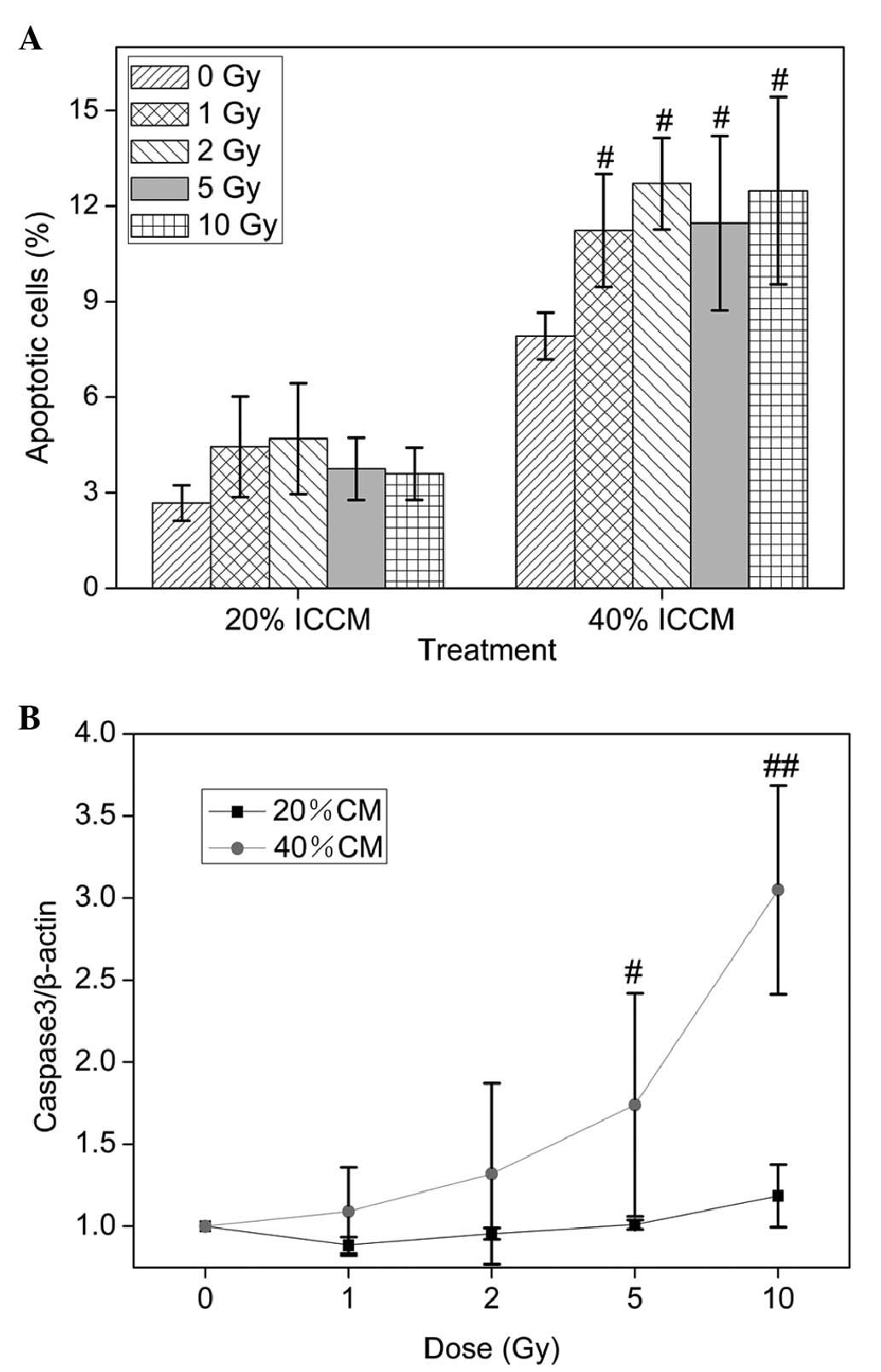
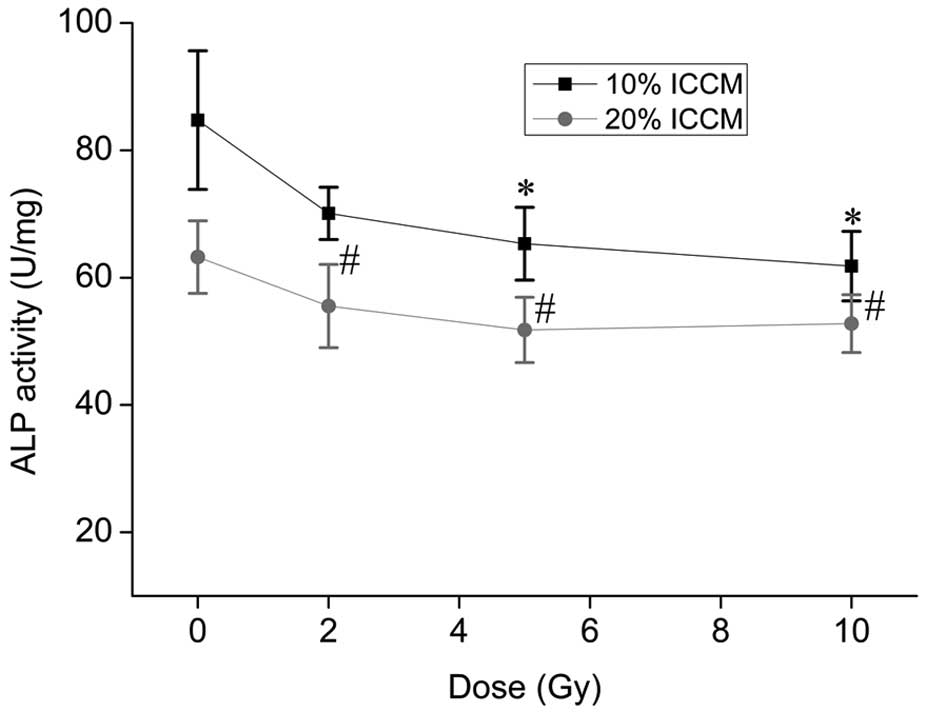
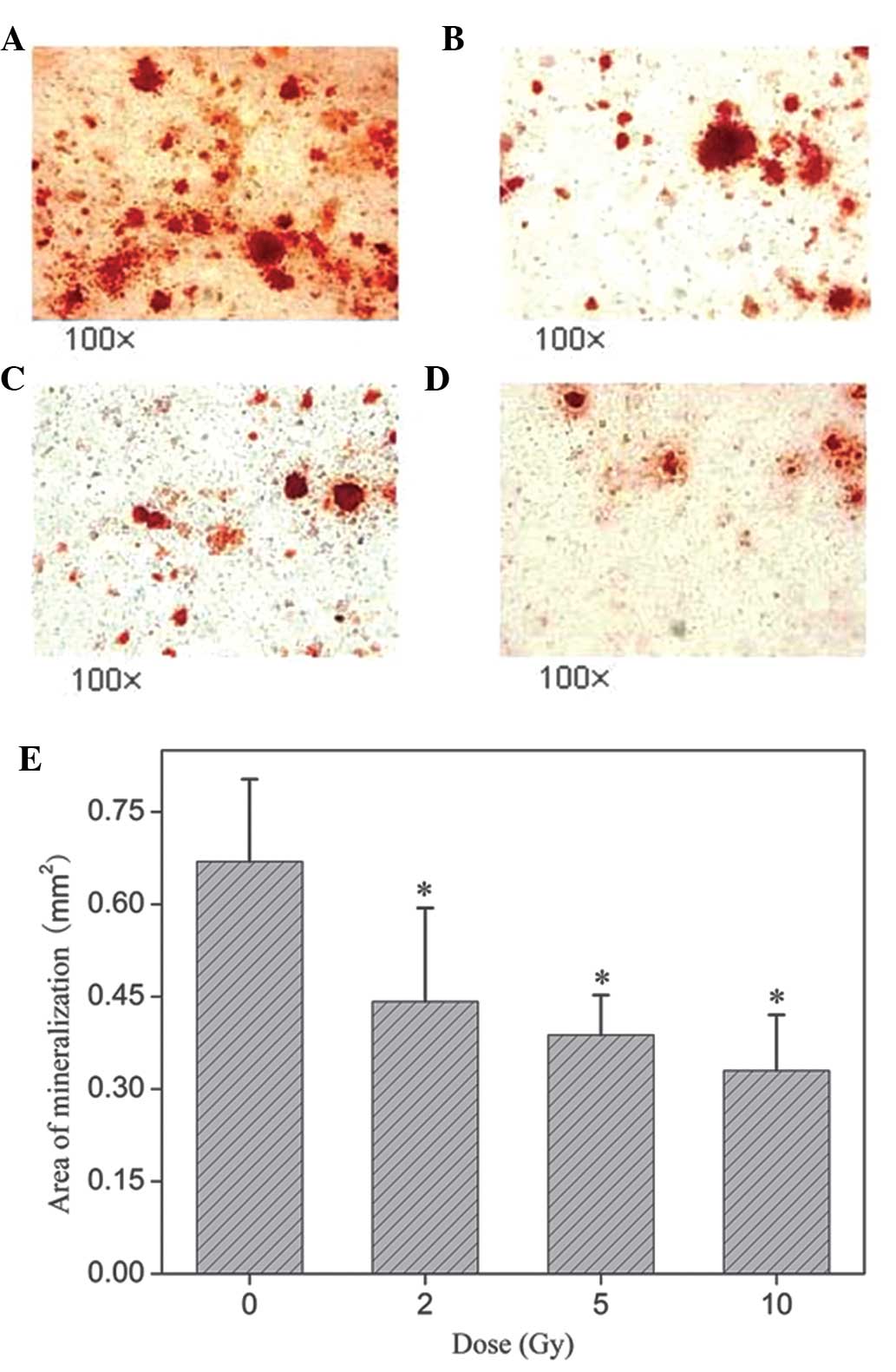
|
1
|
Bentzen SM: Preventing or reducing late
side effects of radiation therapy: radiobiology meets molecular
pathology. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:702–713. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Robbins ME and Zhao W: Chronic oxidative
stress and radiation-induced late normal tissue injury: a review.
Int J Radiat Biol. 80:251–259. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Baxter NN, Habermann EB, Tepper JE, Durham
SB and Virnig BA: Risk of pelvic fractures in older women following
pelvic irradiation. JAMA. 294:2587–2593. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Abe H, Nakamura M, Takahashi S, Maruoka S,
Ogawa Y and Sakamoto K: Radiation-induced insufficiency fractures
of the pelvis: evaluation with 99mTc-methylene diphosphonate
scintigraphy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 158:599–602. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Blomlie V, Rofstad EK, Talle K, Sundfør K,
Winderen M and Lien HH: Incidence of radiation-induced
insufficiency fractures of the female pelvis: evaluation with MR
imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 167:1205–1210. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Van Staa TP, Leufkens HG, Abenhaim L,
Zhang B and Cooper C: Use of oral corticosteroids and risk of
fractures. June, 2000. J Bone Miner Res. 20:1487–1494. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nelson HD, Helfand M, Woolf SH and Allan
JD: Screening for postmenopausal osteoporosis: a review of the
evidence for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann Intern
Med. 137:529–541. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zuppinger A and Minder W: Calcium uptake
in irradiated bone. United Nations International Conference on the
Peaceful Uses of Atomic Energy; United Nations, Geneva,
Switzerland. 22. pp. p2471959
|
|
9
|
Pappas AM and Cohen J: The abscopal effect
of X-irradiation on bone growth in rats. J Bone Joint Surg.
45A:765–772. 1963.
|
|
10
|
Jia D, Gaddy D, Suva LJ and Corry PM:
Rapid loss of bone mass and strength in mice after abdominal
irradiation. Radiat Res. 176:624–635. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen Z, Maricic M, Aragaki AK, et al:
Fracture risk increases after diagnosis of breast or other cancers
in postmenopausal women: results from the Women’s Health
Initiative. Osteoporos Int. 20:527–536. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hinoi E, Fujimori S, Takemori A and Yoneda
Y: Cell death by pyruvate deficiency in proliferative cultured
calvarial osteoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 294:1177–1183.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hansen MB, Nielsen SE and Berg K:
Re-examination and further development of a precise and rapid dye
method for measuring cell growth/cell kill. J Immunol Methods.
119:203–210. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kirsch T, Nah HD, Shapiro IM and Pacifici
M: Regulated production of mineralization-competent matrix vesicles
in hypertrophic chondrocytes. J Cell Biol. 137:1149–1160. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dare A, Hachisu R, Yamaguchi A, Yokose S,
Yoshiki S and Okano T: Effects of ionizing radiation on
proliferation and differentiation of osteoblast-like cells. J Dent
Res. 76:658–664. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Aksnes LH and Bruland ØS: Some
musculo-skeletal sequelae in cancer survivors. Acta Oncol.
46:490–496. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jia D, Koonce NA, Griffin RJ, Jackson C
and Corry PM: Prevention and mitigation of acute death of mice
after abdominal irradiation by the antioxidant N-acetyl-cysteine
(NAC). Radiat Res. 173:579–589. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Travis EL: The sequence of histological
changes in mouse lungs after single doses of x-rays. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 6:345–347. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hopewell JW: Radiation-therapy effects on
bone density. Med Pediatr Oncol. 41:208–211. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhou G, Gu G, Li Y, et al: Effects of
cerium oxide nanoparticles on the proliferation, differentiation,
and mineralization function of primary osteoblasts in vitro. Biol
Trace Elem Res. 153:411–418. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lyng FM, Seymour CB and Mothersill C:
Early events in the apoptotic cascade initiated in cells treated
with medium from the progeny of irradiated cells. Radiat Prot
Dosimetry. 99:169–172. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lehnert BE, Goodwin EH and Deshpande A:
Extracellular factor(s) following exposure to alpha particles can
cause sister chromatid exchanges in normal human cells. Cancer Res.
57:2164–2171. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lyng FM, Seymour CB and Mothersill C:
Production of a signal by irradiated cells which leads to a
response in unirradiated cells characteristic of initiation of
apoptosis. Br J Cancer. 83:1223–1230. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, et al:
Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9
complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell. 91:479–489.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Collett WK, Watson JA and Wald N: Abscopal
and direct effects on calcium mobilization, alkaline phosphatase
levels, and dentin formation following x-irradiation of either the
rat incisor or the thyroid-parathyroid region. J Dent Res.
45:1529–1538. 1966. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Montour JL: Abscopal radiation damage to
chick thymus and bursa of Fabricius. Acta Radiol Ther Phys Biol.
10:150–160. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nobler MP: The abscopal effect in
malignant lymphoma and its relationship to lymphocyte circulation.
Radiology. 93:410–412. 1969. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Van der Meeren A, Monti P, Vandamme M,
Squiban C, Wysocki J and Griffiths N: Abdominal radiation exposure
elicits inflammatory responses and abscopal effects in the lungs of
mice. Radiat Res. 163:144–152. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kurnick NB and Nokay N: Abscopal effects
and bone-marrow repop-ulation in man and mouse. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
114:528–537. 1964. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Conard RA: Indirect Effect of X-radiation
on bone growth in rats. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 114:335–338. 1964.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mothersill C, Rea D, Wright EG, et al:
Individual variation in the production of a ‘bystander signal’
following irradiation of primary cultures of normal human
urothelium. Carcinogenesis. 22:1465–1471. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Azzam EI, de Toledo SM, Gooding T and
Little JB: Intercellular communication is involved in the bystander
regulation of gene expression in human cells exposed to very low
fluences of alpha particles. Radiat Res. 150:497–504. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Azzam EI, de Toledo SM, Waker AJ and
Little JB: High and low fluences of alpha-particles induce a G1
checkpoint in human diploid fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 60:2623–2631.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ghandhi SA, Yaghoubian B and Amundson SA:
Global gene expression analyses of bystander and alpha particle
irradiated normal human lung fibroblasts: synchronous and
differential responses. BMC Med Genomics. 1:632008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Belyakov OV, Folkard M, Mothersill C,
Prise KM and Michael BD: A proliferation-dependent bystander effect
in primary porcine and human urothelial explants in response to
targeted irradiation. Br J Cancer. 88:767–774. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lyng FM, Howe OL and McClean B: Reactive
oxygen species-induced release of signalling factors in irradiated
cells triggers membrane signalling and calcium influx in bystander
cells. Int J Radiat Biol. 87:683–695. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lyng FM, Maguire P, McClean B, Seymour C
and Mothersill C: The involvement of calcium and MAP kinase
signaling pathways in the production of radiation-induced bystander
effects. Radiat Res. 165:400–409. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shao C, Folkard M and Prise KM: Role of
TGF-beta1 and nitric oxide in the bystander response of irradiated
glioma cells. Oncogene. 27:434–440. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Facoetti A, Ballarini F, Cherubini R, et
al: Gamma ray-induced bystander effect in tumour glioblastoma
cells: a specific study on cell survival, cytokine release and
cytokine receptors. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 122:271–274. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Facoetti A, Mariotti L, Ballarini F, et
al: Experimental and theoretical analysis of cytokine release for
the study of radiation-induced bystander effect. Int J Radiat Biol.
85:690–699. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mothersill C and Seymour CB: Cell-cell
contact during gamma irradiation is not required to induce a
bystander effect in normal human keratinocytes: evidence for
release during irradiation of a signal controlling survival into
the medium. Radiat Res. 149:256–262. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mothersill C, Saroya R, Smith RW, Singh H
and Seymour CB: Serum serotonin levels determine the magnitude and
type of bystander effects in medium transfer experiments. Radiat
Res. 174:119–123. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|