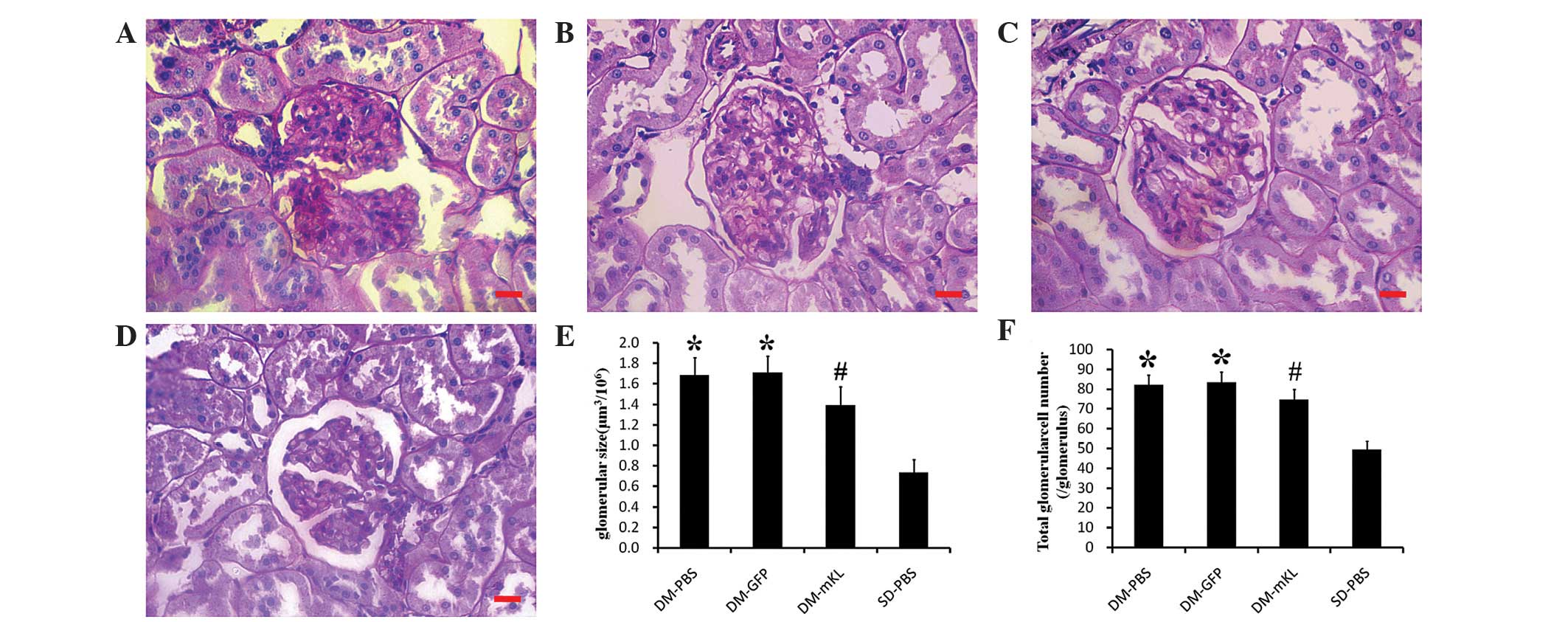
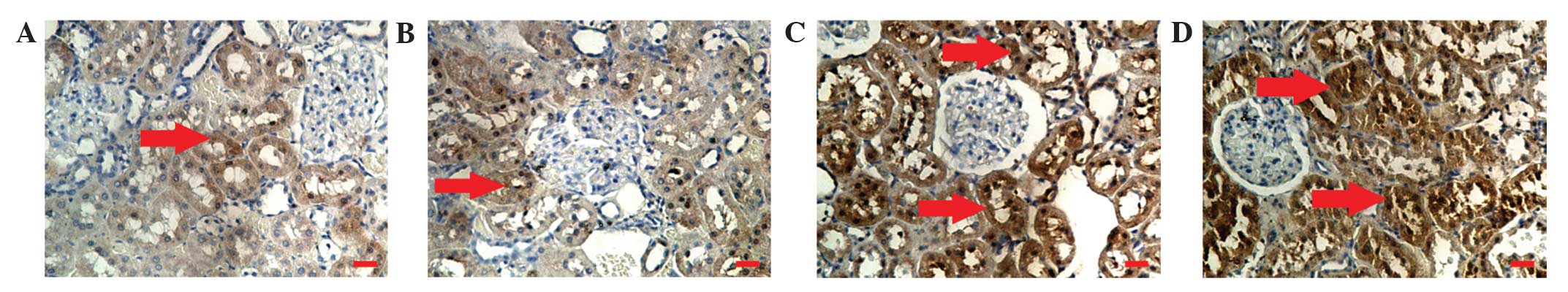
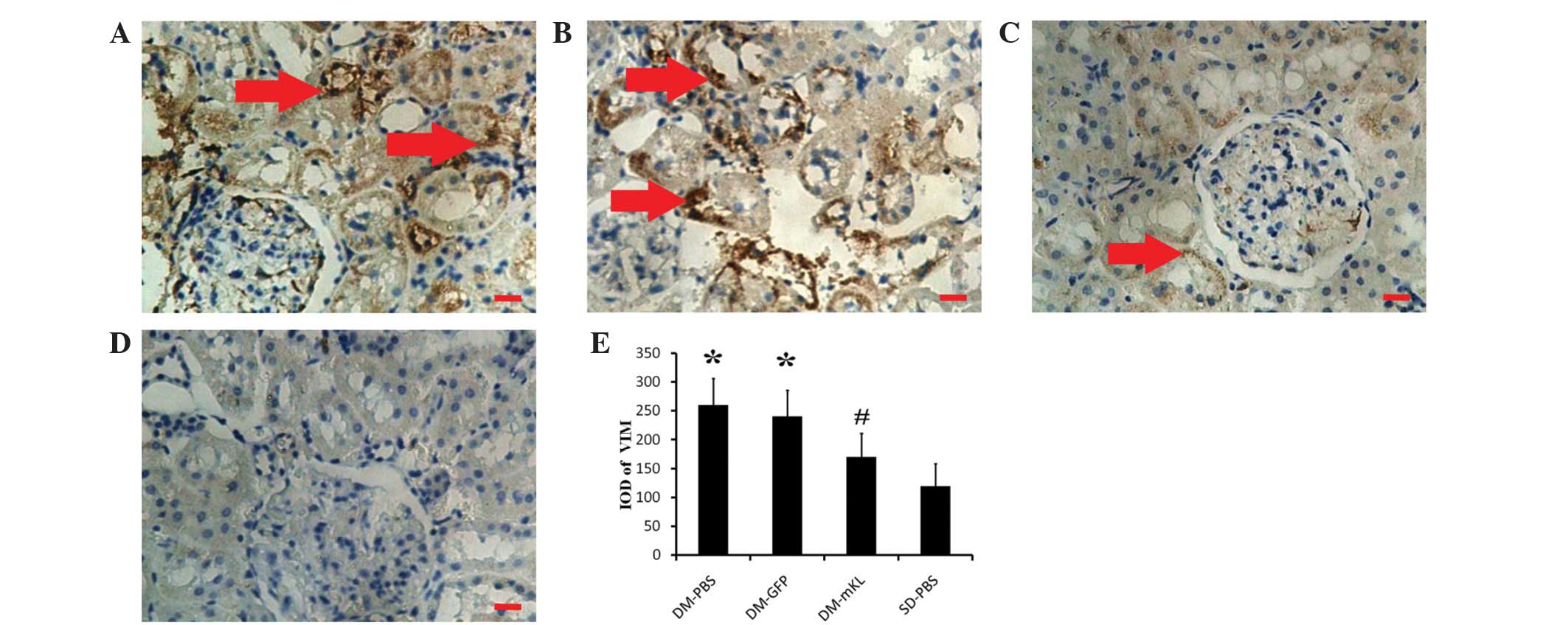
|
1
|
Kuro-o M, Matsumura Y, Aizawa H, et al:
Mutation of the mouse klotho gene leads to a syndrome resembling
ageing. Nature. 390:45–51. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Masuda H, Chikuda H, Suga T, Kawaguchi H
and Kuro-o M: Regulation of multiple ageing-like phenotypes by
inducible klotho gene expression in klotho mutant mice. Mech Ageing
Dev. 126:1274–1283. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kurosu H, Yamamoto M, Clark JD, et al:
Suppression of aging in mice by the hormone Klotho. Science.
309:1829–1833. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ishizaka N, Matsuzaki G, Saito K, Furuta
K, Mori I and Nagai R: Downregulation of klotho gene expression in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Geriatr Gerontol Int.
7:285–292. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Cheng MF, Chen LJ and Cheng JT: Decrease
of Klotho in the kidney of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J
Biomed Biotechnol. 2010:5138532012.
|
|
6
|
Nagasu H, Satoh M, Kuwabara A, et al:
Overexpression of klotho protein modulates uninephrectomy-induced
compensatory renal hypertrophy by suppressing IGF-I signals.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 407:39–43. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Haruna Y, Kashihara N, Satoh M, et al:
Amelioration of progressive renal injury by genetic manipulation of
Klotho gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:2331–2336. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sugiura H, Yoshida T, Shiohira S, et al:
Reduced klotho expression level in kidney aggravates renal
interstitial fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 302:1252–1264.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Doi S, Zou Y, Togao O, et al: Klotho
inhibits transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) signaling and
suppresses renal fibrosis and cancer metastasis in mice. J Biol
Chem. 286:8655–8665. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Satoh M, Nagasu H, Morita Y, Yamaguchi TP,
Kanwar YS and Kashihara N: Klotho protects against mouse renal
fibrosis by inhibiting Wnt signaling. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
303:F1641–F1651. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shimokawa H and Takeshita A: Rho-kinase is
an important therapeutic target in cardiovascular medicine.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 25:1767–1775. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Uehata M, Ishizaki T, Satoh H, et al:
Calcium sensitization of smooth muscle mediated by a Rho-associated
protein kinase in hypertension. Nature. 389:990–994. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kikuchi Y, Yamada M, Imakiire T, et al: A
Rho-kinase inhibitor, fasudil, prevents development of diabetes and
nephropathy in insulin-resistant diabetic rats. J Endocrinol.
192:595–603. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kawamura H, Yokote K, Asaumi S, et al:
High glucose-induced upregulation of osteopontin is mediated via
Rho/Rho kinase pathway in cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 24:276–281. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Reiniger N, Lau K, McCalla D, et al:
Deletion of the receptor for advanced glycation end products
reduces glomerulosclerosis and preserves renal function in the
diabetic OVE26 mouse. Diabetes. 59:2043–2054. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang Y, Peng F, Gao B, et al: Mechanical
strain-induced RhoA activation requires NADPH oxidase-mediated ROS
generation in caveolae. Antioxid Redox Signal. 13:959–973. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Seibold S, Schürle D, Heinloth A, et al:
Oxidized LDL induces proliferation and hypertrophy in human
umbilical vein endothelial cells via regulation of p27Kip1
expression: role of RhoA. J Am Soc Nephrol. 15:3026–3034. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Komers R: Rho kinase inhibition in
diabetic nephropathy. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 20:77–83. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kolavennu V, Zeng L, Peng H, Wang Y and
Danesh FR: Targeting of RhoA/ROCK signaling ameliorates progression
of diabetic nephropathy independent of glucose control. Diabetes.
57:714–723. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Peng F, Wu D, Gao B, Ingram AJ, Zhang B,
Chorneyko K, McKenzie R and Krepinsky JC: RhoA/Rho-kinase
contribute to the pathogenesis of diabetic renal disease. Diabetes.
57:1683–1692. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Komers R, Oyama TT, Beard DR, Tikellis C,
Xu B, Lotspeich DF and Anderson S: Rho kinase inhibition protects
kidneys from diabetic nephropathy without reducing blood pressure.
Kidney Int. 79:432–442. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Patel S, Takagi KI, Suzuki J, Imaizumi A,
Kimura T, Mason RM, Kamimura T and Zhang Z: RhoGTPase activation is
a key step in renal epithelial mesenchymal transdifferentiation. J
Am Soc Nephrol. 16:1977–1984. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rodrigues-Díez R, Carvajal-González G,
Sánchez-López E, Rodríguez-Vita J, Rodrigues Díez R, Selgas R,
Ortiz A, Egido J, Mezzano S and Ruiz-Ortega M: Pharmacological
modulation of epithelial mesenchymal transition caused by
angiotensin II. Role of ROCK and MAPK pathways. Pharm Res.
25:2447–2461. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lin G, Craig GP, Zhang L, Yuen VG, Allard
M, McNeill JH and MacLeod KM: Acute inhibition of Rho-kinase
improves cardiac contractile function in streptozotocin-diabetic
rats. Cardiovasc Res. 75:51–58. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sharma V, Parsons H, Allard MF and McNeill
JH: Metoprolol increases the expression of β3-adrenoceptors in the
diabetic heart: effects on nitric oxide signaling and forkhead
transcription factor-3. Eur J Pharmacol. 595:44–51. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ziyadeh EF: The extracellular matrix in
diabetic nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis. 22:736–744. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wolf G and Ziyadeh FN: Molecular
mechanisms of diabetic renal hypertrophy. Kidney Int. 56:393–405.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen JK, Chen J, Neilson EG and Harris RC:
Role of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in compensatory
renal hypertrophy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:1384–1391. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen JK, Chen J, Thomas G, Kozma SC and
Harris RC: S6 kinase 1 knockout inhibits uninephrectomy- or
diabetes-induced renal hypertrophy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
297:585–593. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ozeki M, Nagasu H, Satoh M, Namikoshi T,
Haruna Y, Tomita N, Sasaki T and Kashihara N: Reactive oxygen
species mediate compensatory glomerular hypertrophy in rat
uninephrectomized kidney. J Physiol Sci. 59:397–373. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mauer SM, Lane P, Zhu D, Fioretto P and
Steffes MW: Renal structure and function in insulin-dependent
diabetes mellitus in man. J Hypertens Suppl. 10:S17–S20. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Van Vliet A, Baelde HJ, Vleming LJ, de
Heer E and Bruijn JA: Distribution of fibronectin isoforms in human
renal disease. J Pathol. 193:256–262. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Carew RW, Wang B and Kantharidis P: The
role of EMT in renal fibrosis. Cell Tissue Res. 347:103–116. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kalluri R and Neilson EG:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for
fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 112:1776–1784. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Moeller MJ, Soofi A, Hartmann I, Le Hir M,
Wiggins R, Kriz W and Holzman LB: Podocytes populate cellular
crescents in a murine model of inflammatory glomerulonephritis. J
Am Soc Nephrol. 15:61–67. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zeisberg EM, Potenta SE, Sugimoto H,
Zeisberg M and Kalluri R: Fibroblasts in kidney fibrosis emerge via
endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Am Soc Nephrol.
19:2282–2287. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Galichon P and Hertig A: Epithelial to
mesenchymal transition as a biomarker in renal fibrosis: are we
ready for the bedside? Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 4:112011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Guan SJ, Ma ZH, Wu YL, Zhang JP, Liang F,
Weiss JW, Guo QY, Wang JY, Ji ES and Chu L: Long-term
administration of fasudil improves cardiomyopathy in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Food Chem Toxicol.
50:1874–1882. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Narumiya H, Sasaki S, Kuwahara N, et al:
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors up-regulate anti-aging klotho mRNA via
RhoA inactivation in IMCD3 cells. Cardiovasc Res. 64:331–336. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Oi K, Shimokawa H, Hiroki J, et al:
Remnant lipoproteins from patients with sudden cardiac death
enhance coronary vasospastic activity through upregulation of
Rho-kinase. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 24:918–922. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hiroki J, Shimokawa H, Higashi M, et al:
Inflammatory stimuli upregulate Rho-kinase in human coronary
vascular smooth muscle cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 37:537–546. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhao Y, Banerjee S, Dey N, et al: Klotho
depletion contributes to increased inflammation in kidney of the
db/db mouse model of diabetes via RelA (serine) 536
phosphorylation. Diabetes. 60:1907–1916. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Urakawa I, Yamazaki Y, Shimada T, et al:
Klotho converts canonical FGF receptor into a specific receptor for
FGF23. Nature. 444:770–774. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang Y and Sun Z: Current understanding of
klotho. Ageing Res Rev. 8:43–51. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
45
|
Hu MC, Kuro-o M and Moe OW: Renal and
extrarenal actions of Klotho. Semin Nephrol. 33:118–129. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Koh N, Fujimori T, Nishiguchi S, Tamori A
and Shiomi S: Severely reduced production of klotho in human
chronic renal failure kidney. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
280:1015–1020. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Weroha SJ and Haluska P: IGF-1 Receptor
Inhibitors in Clinical Trials-Early Lessons. J Mammary Gland Biol
Neoplasia. 13:471–483. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Huang SM, Mishina YM, Liu S, et al:
Tankyrase inhibition stabilizes axin and antagonizes Wnt
signalling. Nature. 461:614–620. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yingling JM, Blanchard KL and Sawyer JS:
Development of TGF-β signalling inhibitors for cancer therapy. Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 3:1011–1022. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Prud’homme GJ: Pathobiology of
transforming growth factor β in cancer, fibrosis and immunologic
disease, and therapeutic considerations. Lab Invest. 7:1077–1091.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|