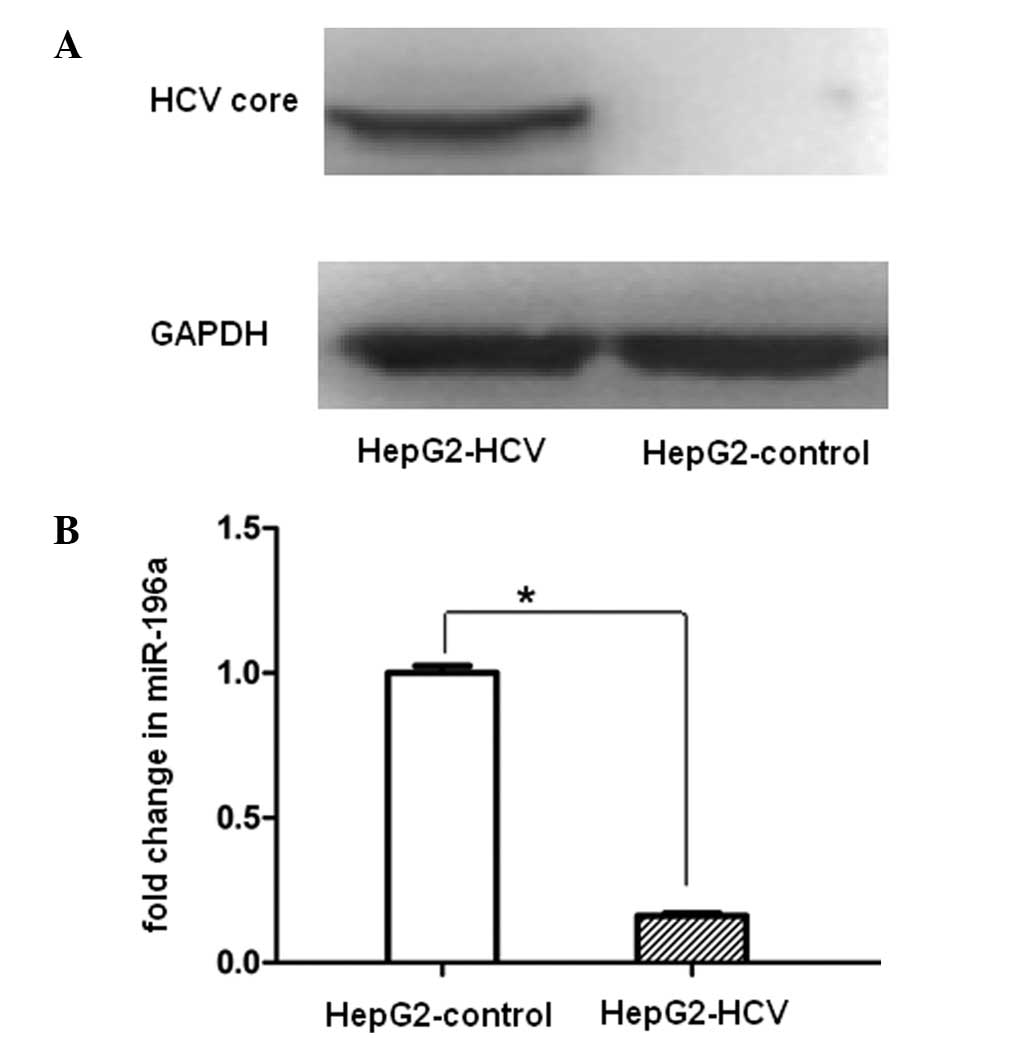
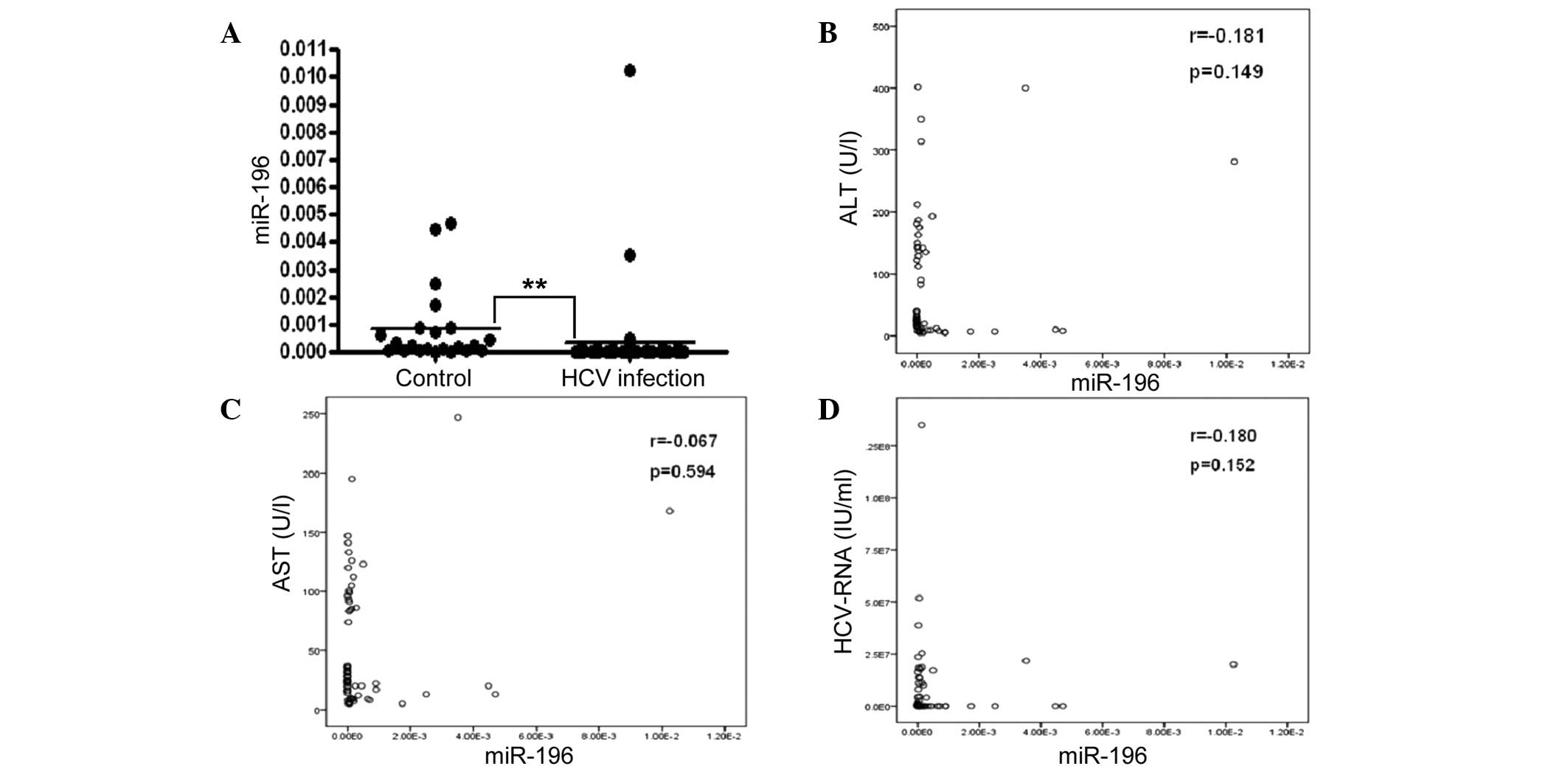
|
1
|
Eckman MH, Talal AH, Gordon SC, Schiff E
and Sherman KE: Cost-effectiveness of screening for chronic
hepatitis C infection in the United States. Clin Infect Dis.
56:1382–1393. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Saludes V, González V, Planas R, et al:
Tools for the diagnosis of hepatitis C virus infection and hepatic
fibrosis staging. World J Gastroenterol. 20:3431–3442. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sarrazin C, Wedemeyer H, Cloherty G, et
al: Importance of very early HCV RNA kinetics for prediction of
treatment outcome of highly effective all oral direct acting
antiviral combination therapy. J Virol Methods. 214C:29–32.
2014.
|
|
4
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Eulalio A, Huntzinger E and Izaurralde E:
Getting to the root of miRNA-mediated gene silencing. Cell.
132:9–14. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Carthew RW and Sontheimer EJ: Origins and
Mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell. 136:642–655. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Williams AE: Functional aspects of animal
microRNAs. Cell Mol Life Sci. 65:545–562. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Jopling CL, Yi M, Lancaster AM, Lemon SM
and Sarnow P: Modulation of hepatitis C virus RNA abundance by a
liver-specific MicroRNA. Science. 309:1577–1581. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bandyopadhyay S, Friedman RC, Marquez RT,
et al: Hepatitis C virus infection and hepatic stellate cell
activation downregulate miR-29: miR-29 overexpression reduces
hepatitis C viral abundance in culture. J Infect Dis.
203:1753–1762. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ishida H, Tatsumi T, Hosui A, et al:
Alterations in microRNA expression profile in HCV-infected hepatoma
cells: Involvement of miR-491 in regulation of HCV replication via
the PI3 kinase/Akt pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 412:92–97.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Henke JI, Goergen D, Zheng J, Song Y,
Schüttler CG, Fehr C, Jünemann C and Niepmann M: microRNA-122
stimulates translation of hepatitis C virus RNA. EMBO J.
27:3300–3310. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pedersen IM, Cheng G, Wieland S, Volinia
S, Croce CM, Chisari FV and David M: Interferon modulation of
cellular microRNAs as an antiviral mechanism. Nature. 449:919–922.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hou W, Tian Q, Zheng J and Bonkovsky HL:
MicroRNA-196 represses Bach1 protein and hepatitis C virus gene
expression in human hepatoma cells expressing hepatitis C viral
proteins. Hepatology. 51:1494–1504. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sarasin-Filipowicz M, Krol J, Markiewicz
I, Heim MH and Filipowicz W: Decreased levels of microRNA miR-122
in individuals with hepatitis C responding poorly to interferon
therapy. Nat Med. 15:31–33. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Weiland M, Gao XH, Zhou L and Mi QS: Small
RNAs have a large impact: Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for
human diseases. RNA Biol. 9:850–859. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang S, Xie Y, Yang P, Chen P and Zhang
L: HCV core protein-induced down-regulation of microRNA-152
promoted aberrant proliferation by regulating Wnt1 in HepG2 cells.
PLoS One. 9:e817302014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jardim MJ, Dailey L, Silbajoris R and
Diaz-Sanchez D: Distinct microRNA expression in human airway cells
of asthmatic donors identifies a novel asthma-associated gene. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 47:536–542. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kowala-Piaskowska A, Słuzewski W,
Figlerowicz M and Mozer-Lisewska I: Factors influencing early
virological response in children with chronic hepatitis C treated
with pegylated interferon and ribavirin. Hepatol Res. 32:224–226.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hollingsworth RC, Sillekens P, van Deursen
P, Neal KR and Irving WL: Serum HCV RNA levels assessed by
quantitative NASBA: stability of viral load over time, and lack of
correlation with liver disease. The Trent HCV Study Group. J
Hepatol. 25:301–306. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hornstein E, Mansfield JH, Yekta S, Hu JK,
Harfe BD, McManus MT, Baskerville S, Bartel DP and Tabin CJ: The
microRNA miR-196 acts upstream of Hoxb8 and Shh in limb
development. Nature. 438:671–674. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ronshaugen M, Biemar F, Piel J, Levine M
and Lai EC: The Drosophila microRNA iab-4 causes a dominant
homeotic transformation of halteres to wings. Genes Dev.
19:2947–2952. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qiu R, Liu Y, Wu JY, Liu K, Mo W and He R:
Misexpression of miR-196a induces eye anomaly in Xenopus laevis.
Brain Res Bull. 79:26–31. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bloomston M, Frankel WL, Petrocca F,
Volinia S, Alder H, Hagan JP, Liu CG, Bhatt D, Taccioli C and Croce
CM: MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic
adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. JAMA.
297:1901–1908. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schotte D, Chau JC, Sylvester G, Liu G,
Chen C, van der Velden VH, Broekhuis MJ, Peters TC, Pieters R and
den Boer ML: Identification of new microRNA genes and aberrant
microRNA profiles in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Leukemia. 23:313–322. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Maru DM, Singh RR, Hannah C, et al:
MicroRNA-196a is a potential marker of progression during Barrett’s
metaplasia-dysplasia-invasive adenocarcinoma sequence in esophagus.
Am J Pathol. 174:1940–1948. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schimanski CC, Frerichs K, Rahman F,
Berger M, Lang H, Galle PR, Moehler M and Gockel I: High miR-196a
levels promote the oncogenic phenotype of colorectal cancer cells.
World J Gastroenterol. 15:2089–2096. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ye L, Wang X, Wang S, Wang Y, Song L, Hou
W, Zhou L, Li H and Ho W: CD56+ T cells inhibit hepatitis C virus
replication in human hepatocytes. Hepatology. 49:753–762. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Sonkoly E, Ståhle M and Pivarcsi A:
MicroRNAs and immunity: Novel players in the regulation of normal
immune function and inflammation. Semin Cancer Biol. 18:131–140.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Witwer KW: Circulating microRNA biomarker
studies: Pitfalls and potential solutions. Clin Chem. 61:56–63.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhong J, He Y, Chen W, et al: Circulating
microRNA-19a as a potential novel biomarker for diagnosis of acute
myocardial infarction. Int J Mol Sci. 15:20355–20364. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shifeng H, Danni W, Pu C, et al:
Circulating liver-specific miR-122 as a novel potential biomarker
for diagnosis of cholestatic liver injury. PLoS One. 8:e731332013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li H, Wang Z, Fu Q and Zhang J: Plasma
miRNA levels correlate with sensitivity to bone mineral density in
postmenopausal osteoporosis patients. Biomarkers. 19:553–556. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Resnick KE, Alder H, Hagan JP, Richardson
DL, Croce CM and Cohn DE: The detection of differentially expressed
microRNAs from the serum of ovarian cancer patients using a novel
real-time PCR platform. Gynecol Oncol. 112:55–59. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhu W, Qin W, Atasoy U and Sauter ER:
Circulating microRNAs in breast cancer and healthy subjects. BMC
Res Notes. 2:892009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|