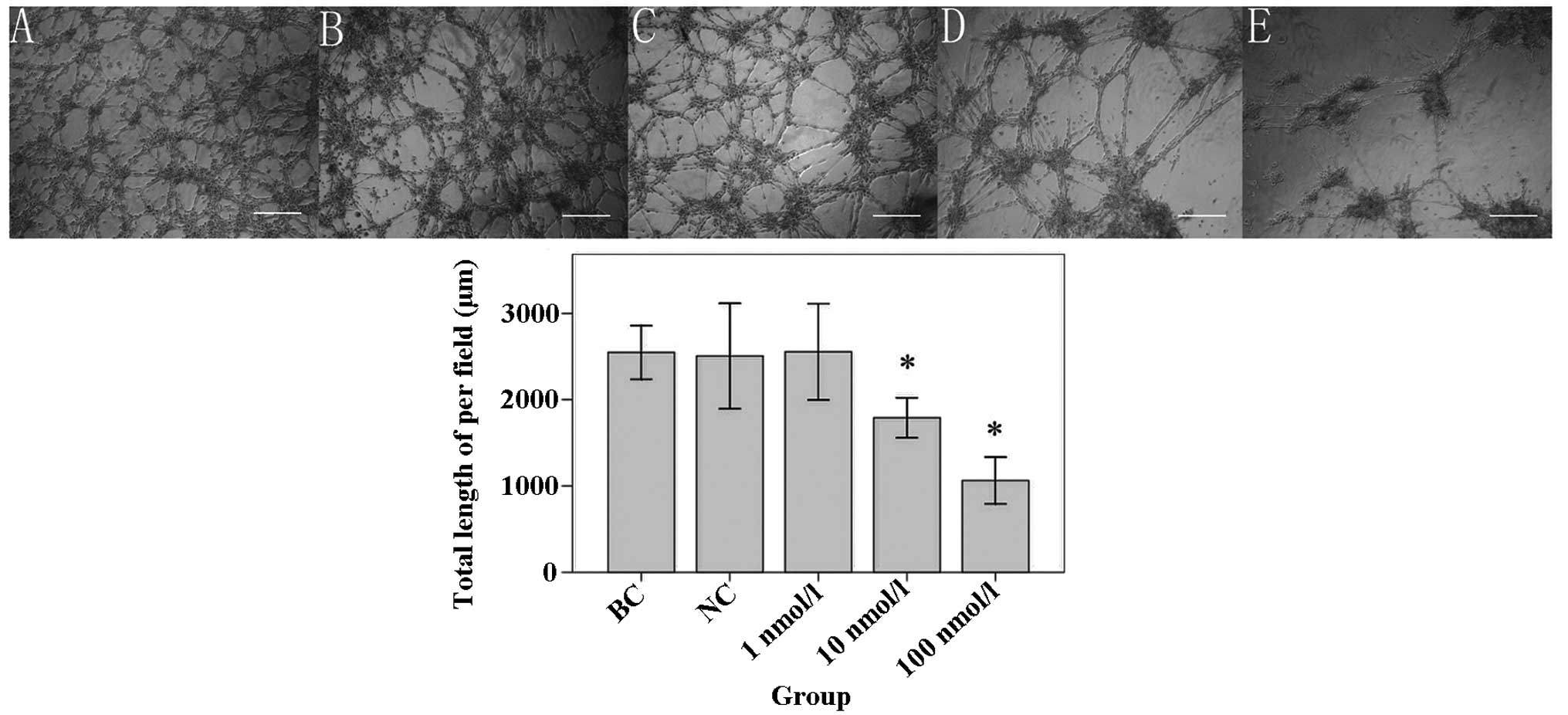
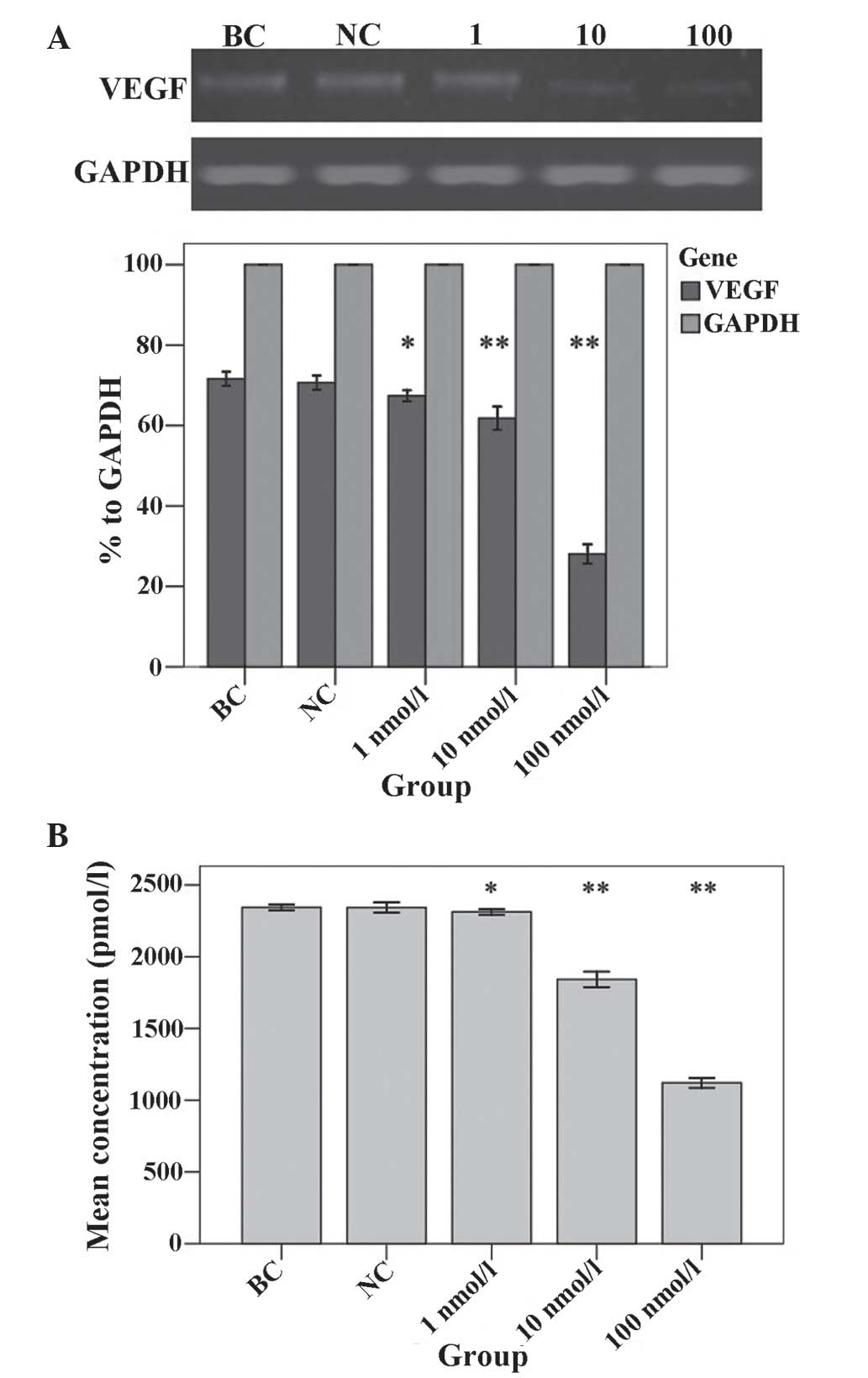
|
1
|
Omuro A and DeAngelis LM: Glioblastoma and
other malignant gliomas: a clinical review. JAMA. 310:1842–1850.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hardee ME and Zagzag D: Mechanisms of
glioma-associated neovascularization. Am J Pathol. 181:1126–1141.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vredenburgh JJ, Desjardins A, Herndon JE
II, et al: Phase II trial of bevacizumab and irinotecan in
recurrent malignant glioma. Clin Cancer Res. 13:1253–1259. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bergers G and Hanahan D: Modes of
resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:592–603.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Soda Y, Myskiw C, Rommel A and Verma IM:
Mechanisms of neovascularization and resistance to anti-angiogenic
therapies in glioblastoma multiforme. J Mol Med. 91:439–448. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Maniotis AJ, Folberg R, Hess A, et al:
Vascular channel formation by human melanoma cells in vivo and in
vitro: vasculogenic mimicry. Am J Pathol. 155:739–752. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang SY, Ke YQ, Lu GH, et al: Vasculogenic
mimicry is a prognostic factor for postoperative survival in
patients with glioblastoma. J Neurooncol. 112:339–345. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen LX, He YJ, Zhao SZ, et al: Inhibition
of tumor growth and vasculogenic mimicry by curcumin through
down-regulation of the EphA2/PI3K/MMP pathway in a murine choroidal
melanoma model. Cancer Biol Ther. 11:229–235. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hu A, Huang JJ, Jin XJ, et al: Curcumin
suppresses invasiveness and vasculogenic mimicry of squamous cell
carcinoma of the larynx through the inhibition of JAK-2/STAT-3
signaling pathway. Am J Cancer Res. 5:278–288. 2014.
|
|
10
|
Liu TJ, Sun BC, Zhao XL, et al: CD133+
cells with cancer stem cell characteristics associates with
vasculogenic mimicry in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncogene.
32:544–553. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Jordan CT, Guzman ML and Noble M: Cancer
stem cells. N Engl J Med. 355:1253–1261. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Charles N, Ozawa T, Squatrito M, et al:
Perivascular nitric oxide activates notch signaling and promotes
stem-like character in PDGF-induced glioma cells. Cell Stem Cell.
6:141–152. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Eyler CE and Rich JN: Survival of the
fittest: cancer stem cells in therapeutic resistance and
angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol. 26:2839–2845. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cao Z, Shang B, Zhang G, et al: Tumor
cell-mediated neovascularization and lymphan-giogenesis contrive
tumor progression and cancer metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1836:273–286. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Campos B, Wan F, Farhadi M, et al:
Differentiation therapy exerts antitumor effects on stem-like
glioma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 16:2715–2728. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ling G, Wang S, Song Z, et al:
Transforming growth factor-β is required for vasculogenic mimicry
formation in glioma cell line U251MG. Cancer Biol Ther. 12:978–988.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang M, Song T, Yang L, et al: Nestin and
CD133: valuable stem cell-specific markers for determining clinical
outcome of glioma patients. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 27:852008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Singh SK, Hawkins C, Clarke ID, et al:
Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature.
432:396–401. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, et al:
Identification of a cancer stem cell in human brain tumors. Cancer
Res. 63:5821–5828. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Galli R, Binda E, Orfanelli U, et al:
Isolation and characterization of tumorigenic, stem-like neural
precursors from human glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 64:7011–7021. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xiao ZY, Tang H, Xu ZM, et al: An
experimental study of dendritic cells transfected with cancer
stem-like cells RNA against 9L brain tumors. Cancer Biol Ther.
11:974–980. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu Y, Richard JP, Wang SD, et al:
Regulation of glioblastoma multiforme stem-like cells by inhibitor
of DNA binding proteins and oligodendroglial lineage-associated
transcription factors. Cancer Sci. 103:1028–1037. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gupta PB, Chaffer CL and Weinberg RA:
Cancer stem cells: mirage or reality? Nat Med. 15:1010–1012. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang R, Chadalavada K, Wilshire J, et al:
Glioblastoma stem-like cells give rise to tumor endothelium.
Nature. 468:829–833. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ricci-Vitiani L, Pallini R, Biffoni M, et
al: Tumor vascularization via endothelial differentiation of
glioblastoma stem-like cells. Nature. 468:824–828. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
El Hallani S, Boisselier B, Peglion F, et
al: A new alternative mechanism in glioblastoma vascularization:
Tubular vasculogenic mimicry. Brain. 133:973–982. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ma JL, Han SX, Zhu Q, et al: Role of Twist
in vasculogenic mimicry formation in hypoxic hepatocellular
carcinoma cells in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 408:686–691.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ping YF and Bian XW: Concise review:
Contribution of cancer stem cells to neovascularization. Stem
Cells. 29:888–894. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang JY, Sun T, Zhao XL, et al: Functional
significance of VEGF-a in human ovarian carcinoma: role in
vasculogenic mimicry. Cancer Biol Ther. 7:758–766. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen Y, Jing Z, Luo C, et al: Vasculogenic
mimicry-potential target for glioblastoma therapy: an in vitro and
in vivo study. Med Oncol. 29:324–331. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Mei J, Gao Y, Zhang L, et al: VEGF-siRNA
silencing induces apoptosis, inhibits proliferation and suppresses
vasculogenic mimicry in osteosarcoma in vitro. Exp Oncol. 30:29–34.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shi Z, Lou M, Zhao Y, et al: Effect of
all-trans retinoic acid on the differentiation of U87 glioma
stem/progenitor cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 33:943–951. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Karsy M, Albert L, Tobias ME, et al:
All-trans retinoic acid modulates cancer stem cells of glioblastoma
multiforme in an MAPK-dependent manner. Anticancer Res.
30:4915–4920. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee J, Kotliarova S, Kotliarov Y, et al:
Tumor stem cells derived from glioblastomas cultured in bFGF and
EGF more closely mirror the phenotype and genotype of primary
tumors than do serum-cultured cell lines. Cancer Cell. 9:391–403.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kaba SE, Kyritsis AP, Conrad C, et al: The
treatment of recurrent cerebral gliomas with all-trans-retinoic
acid tretinoin. J Neurooncol. 34:145–151. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Phuphanich S, Scott C, Fischbach AJ, et
al: All-trans-retinoic acid: a phase II Radiation Therapy Oncology
Group study (RTOG 91-13) in patients with recurrent malignant
astrocytoma. J Neurooncol. 34:193–200. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Charoenputtakhun P, Opanasopit P,
Rojanarata T and Ngawhirunpat T: All-trans retinoic acid-loaded
lipid nanoparticles as a transdermal drug delivery carrier. Pharm
Dev Technol. 19:164–172. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Hattori M, Shimizu K, Katsumura K, et al:
Effects of all-trans retinoic acid nanoparticles on corneal
epithelial wound healing. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol.
250:557–563. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|