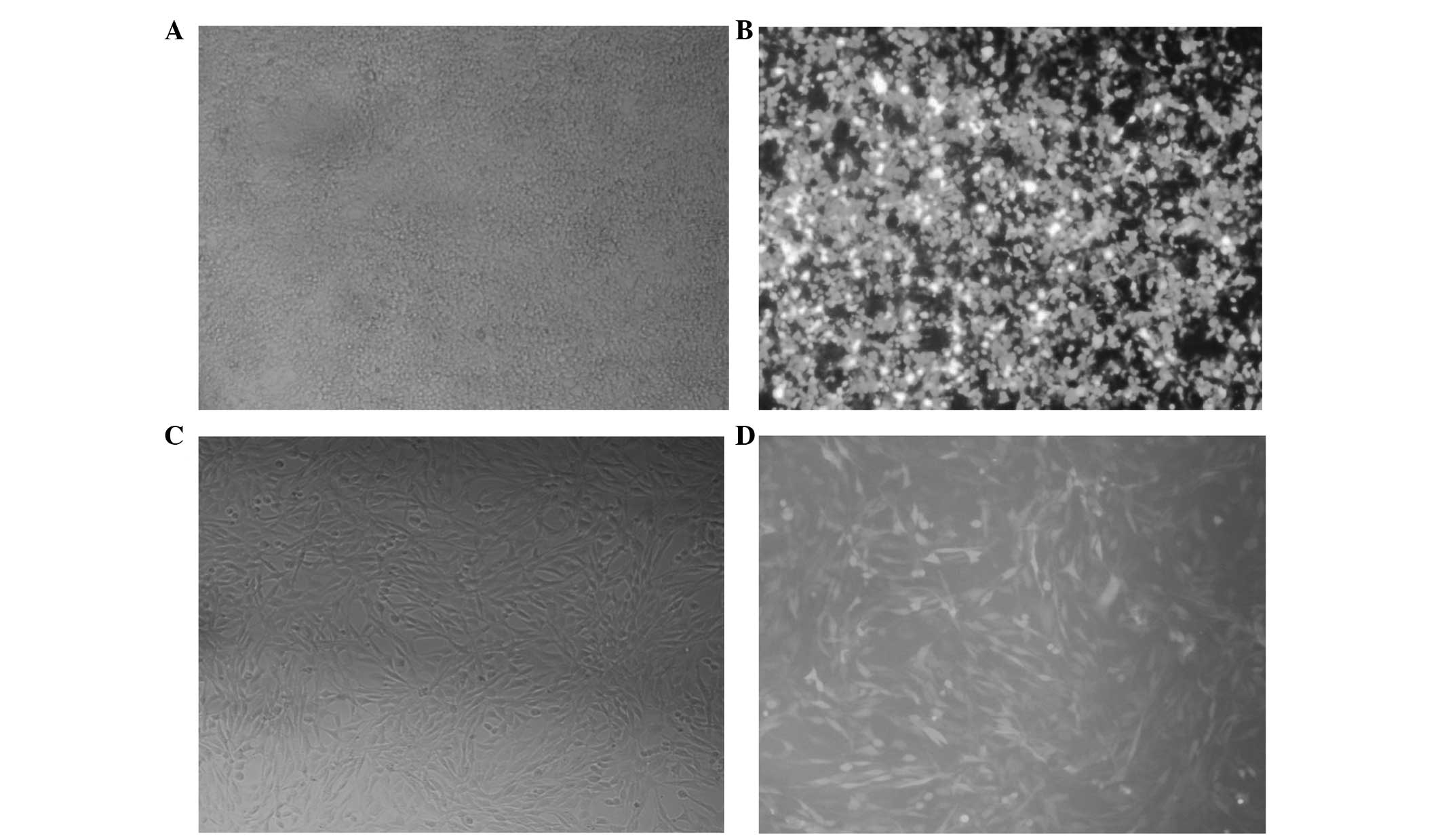
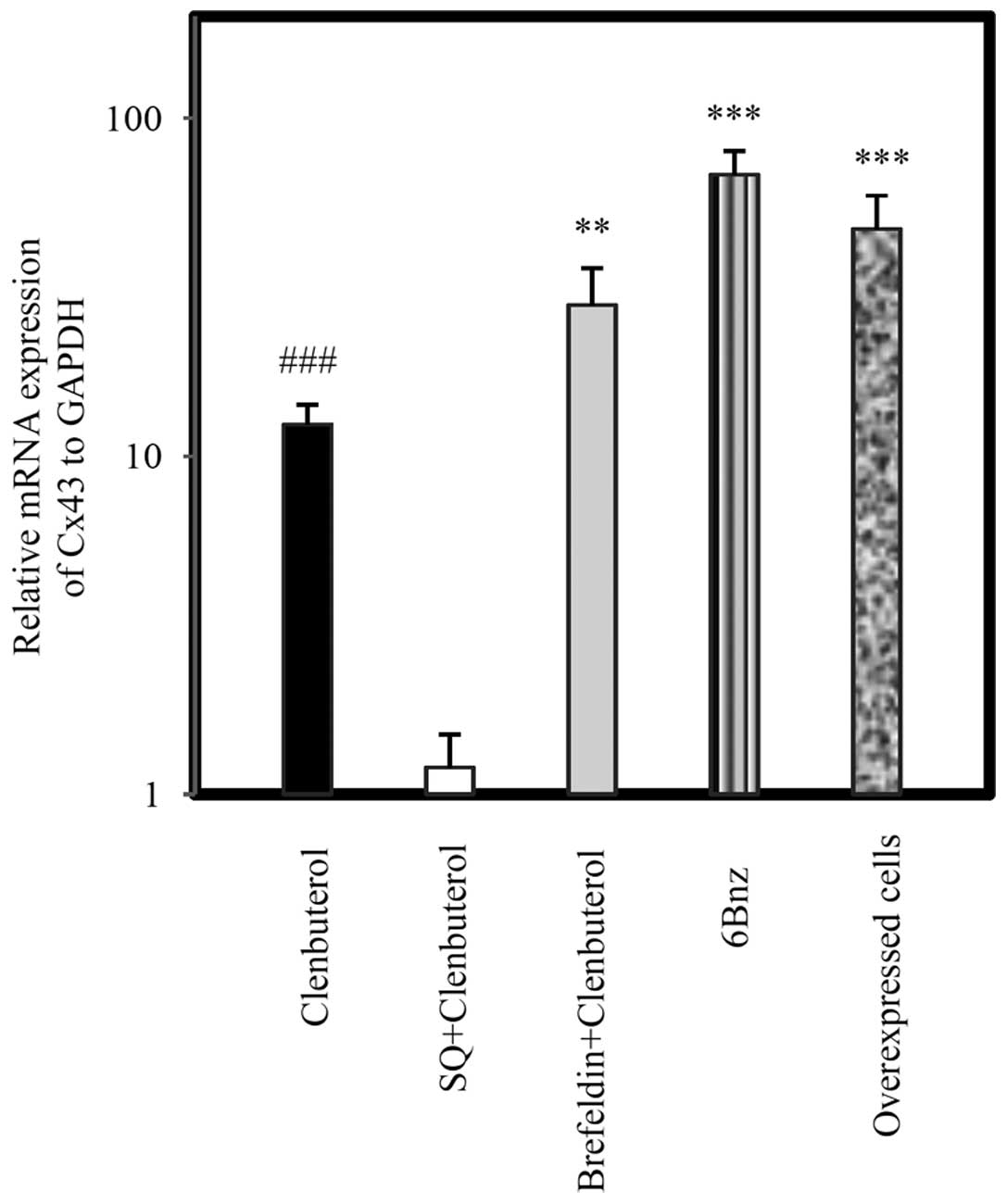
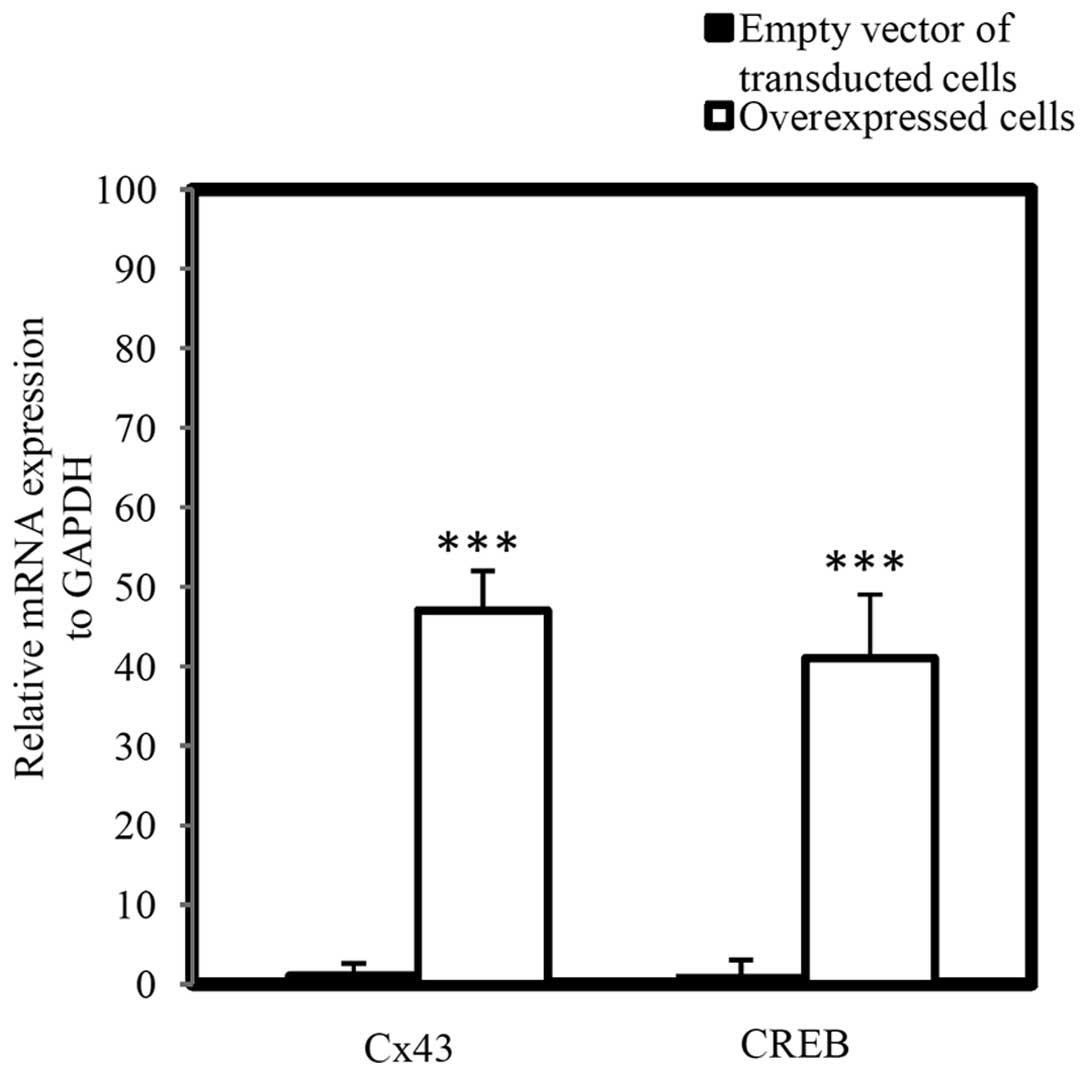
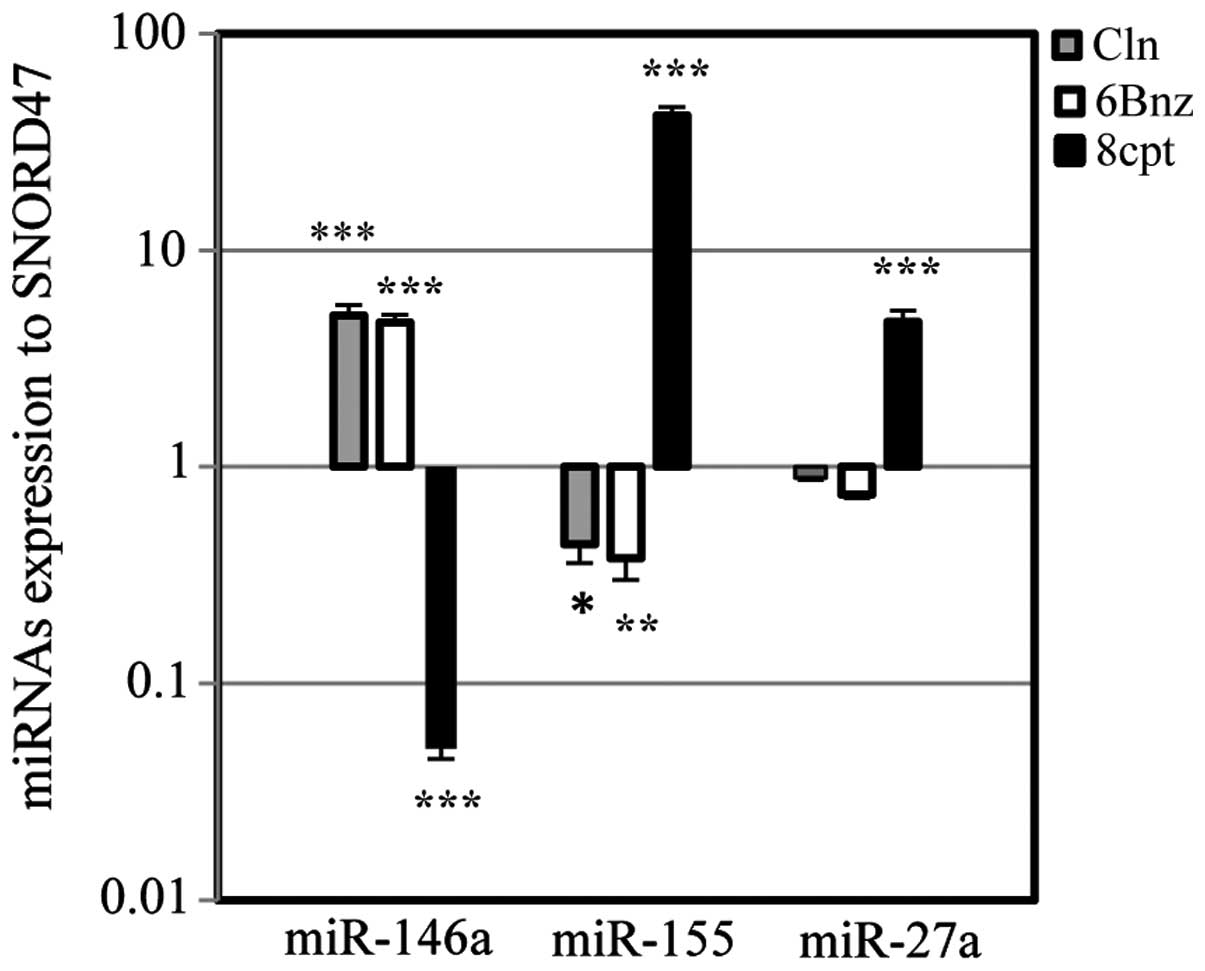
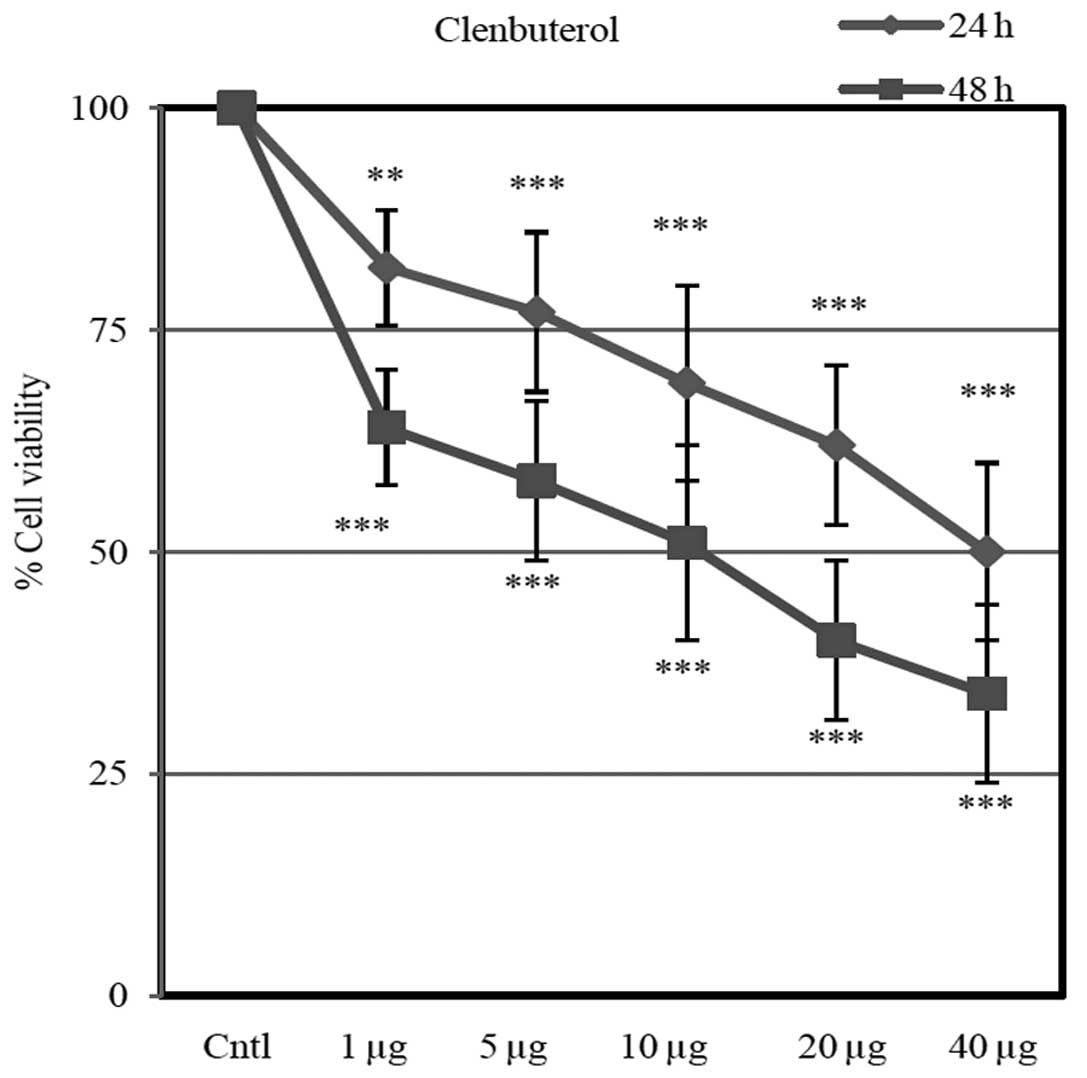
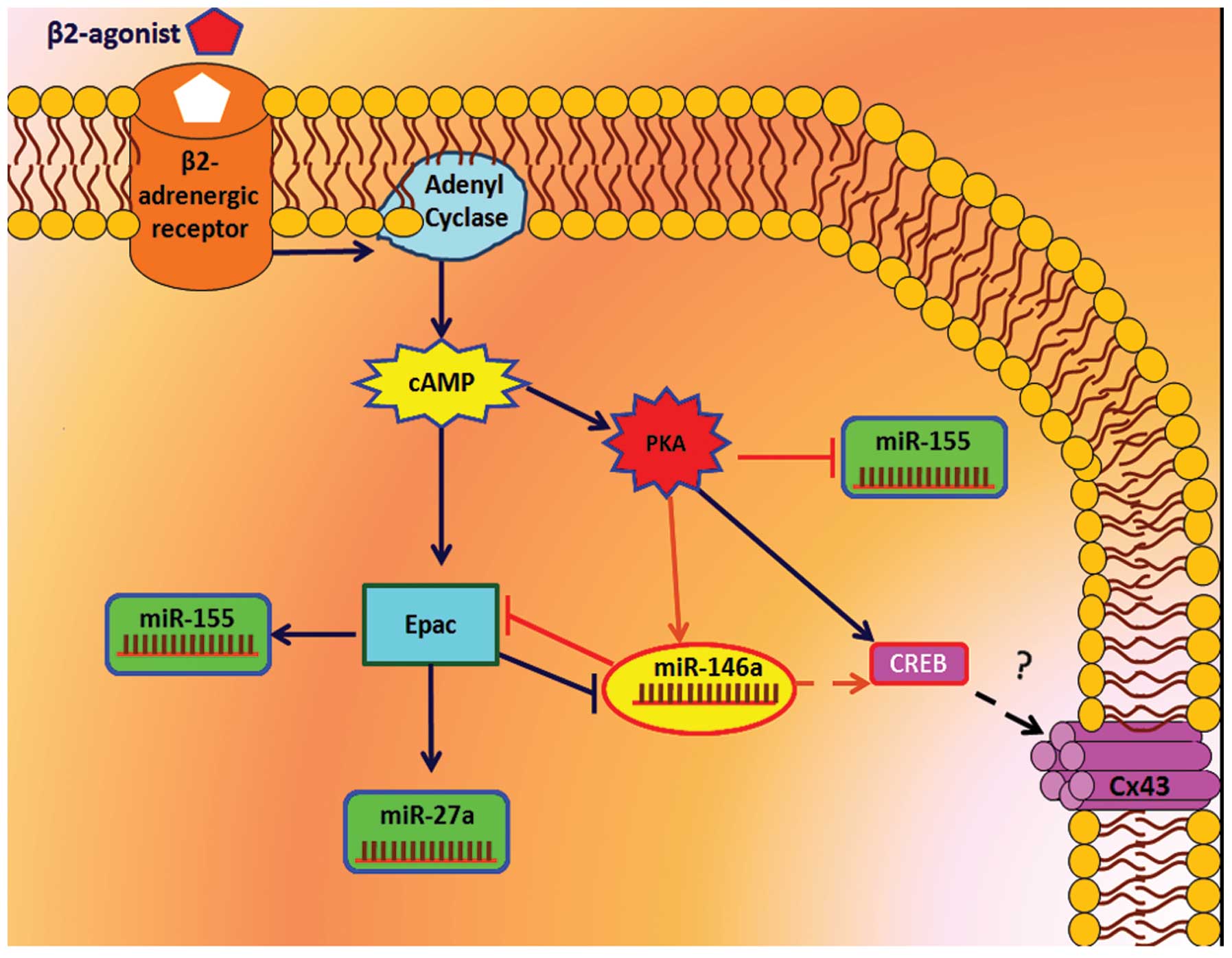
|
1
|
Toll L, Jimenez L, Waleh N, et al:
β2-adrenergic receptor agonists inhibit the proliferation of 1321N1
astrocytoma cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 336:524–532. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
2
|
Vinken M, Decrock E, De Vuyst E, et al:
Connexins: sensors and regulators of cell cycling. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1815:13–25. 2011.
|
|
3
|
Gabriely G, Yi M, Narayan RS, et al: Human
glioma growth is controlled by microRNA-10b. Cancer Res.
71:3563–3572. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Castro MG, Cowen R, Williamson IK, et al:
Current and future strategies for the treatment of malignant brain
tumors. Pharmacol Ther. 98:71–108. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lin JH, Takano T, Cotrina ML, et al:
Connexin 43 enhances the adhesivity and mediates the invasion of
malignant glioma cells. J Neurosci. 22:4302–4311. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sin WC, Crespin S and Mesnil M: Opposing
roles of connexin43 in glioma progression. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1818:2058–2067. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Huang RP, Hossain MZ, Huang R, Gano J, Fan
Y and Boynton AL: Connexin 43 (cx43) enhances chemotherapy-induced
apoptosis in human glioblastoma cells. Int J Cancer. 92:130–138.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huang R, Liu YG, Lin Y, Fan Y, Boynton A,
Yang D and Huang RP: Enhanced apoptosis under low serum conditions
in human glioblastoma cells by connexin 43 (Cx43). Mol Carcinog.
32:128–138. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pu P, Xia Z, Yu S and Huang Q: Altered
expression of Cx43 in astrocytic tumors. Clin Neurol Neurosurg.
107:49–54. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Soroceanu L, Manning TG Jr and Sontheimer
H: Reduced expression of connexin-43 and functional gap junction
coupling in human gliomas. Glia. 33:107–117. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mesnil M: Connexins and cancer. Biol Cell.
94:493–500. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Sánchez-Alvarez R, Paíno T,
Herrero-González S, Medina JM and Tabernero A: Tolbutamide reduces
glioma cell proliferation by increasing connexin43, which promotes
the upregulation of p21 and p27 and subsequent changes in
retinoblastoma phosphorylation. Glia. 54:125–134. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Maatouk D and Harfe B: MicroRNAs in
development. ScientificWorldJournal. 6:1828–1840. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Novakova J, Slaby O, Vyzula R and Michalek
J: MicroRNA involvement in glioblastoma pathogenesis. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 386:1–5. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jin Z, Xu S, Yu H, Yang B, Zhao H and Zhao
G: miR-125b inhibits Connexin43 and promotes glioma growth. Cell
Mol Neurobiol. 33:1143–1148. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Somekawa S, Fukuhara S, Nakaoka Y, Fujita
H, Saito Y and Mochizuki N: Enhanced functional gap junction
neoformation by protein kinase A-dependent and Epac-dependent
signals downstream of cAMP in cardiac myocytes. Circ Res.
97:655–662. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shu M, Zhou Y, Zhu W, et al: MicroRNA 335
is required for differentiation of malignant glioma cells induced
by activation of cAMP/protein kinase A pathway. Mol Pharmacol.
81:292–298. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Mei J, Bachoo R and Zhang CL:
MicroRNA-146a inhibits glioma development by targeting Notch1. Mol
Cell Biol. 31:3584–3592. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Barde I, Salmon P and Trono D: Production
and titration of lentiviral vectors. Curr Protoc Neurosci.
2010.Chapter 4. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, et al:
Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic
Acids Res. 33:e1792005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mohammadi-Yeganeh S, Paryan M and Mirab
Samiee S: Development of a robust, low cost stem-loop real-time
quantification PCR technique for miRNA expression analysis. Mol
Biol Rep. 40:3665–3674. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Takano S, Yamashita T and Ohneda O:
Molecular therapeutic targets for glioma angiogenesis. J Oncol.
2010:3519082010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bai RY, Staedtke V and Riggins GJ:
Molecular targeting of glioblastoma: Drug discovery and therapies.
Trends Mol Med. 17:301–312. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ling N, Gu J, Lei Z, et al: microRNA-155
regulates cell proliferation and invasion by targeting FOXO3a in
glioma. Oncol Rep. 30:2111–2118. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lages E, Guttin A, El Atifi M, et al:
MicroRNA and target protein patterns reveal physiopathological
features of glioma subtypes. PLoS One. 6:e206002011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chaudhry MA, Sachdeva H and Omaruddin RA:
Radiation-induced micro-RNA modulation in glioblastoma cells
differing in DNA-repair pathways. DNA Cell Biol. 29:553–561. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Poltronieri P, D’Urso PI, Mezzolla V and
D’Urso OF: Potential of anti-cancer therapy based on anti-miR-155
oligonucleotides in glioma and brain tumours. Chem Biol Drug Des.
81:79–84. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Feng SY, Dong CG, Wu WK, Wang XJ, Qiao J
and Shao JF: Lentiviral expression of anti-microRNAs targeting
miR-27a inhibits proliferation and invasiveness of U87 glioma
cells. Mol Med Rep. 6:275–281. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang S, Wang K, Qian C, et al: A predicted
miR-27a-mediated network identifies a signature of glioma. Oncol
Rep. 28:1249–1256. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Blum AE, Walsh BC and Dubyak GR:
Extracellular osmolarity modulates G protein-coupled
receptor-dependent ATP release from 1321N1 astrocytoma cells. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 298:C386–C396. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Racagni G, Pezzotta S, Giordana MT, et al:
Cyclic nucleotides in experimental and human brain tumors. J
Neurooncol. 1:61–67. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mostafavi H, Khaksarian M, Joghataei MT,
et al: Selective β2 adrenergic agonist increases Cx43 and miR-451
expression via cAMP-Epac. Mol Med Rep. 9:2405–2410. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Salameh A, Krautblatter S, Karl S, et al:
The signal transduction cascade regulating the expression of the
gap junction protein connexin43 by beta-adrenoceptors. Br J
Pharmacol. 158:198–208. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lu Y, Zhang Y, Shan H, et al: MicroRNA-1
downregulation by propranolol in a rat model of myocardial
infarction: a new mechanism for ischaemic cardioprotection.
Cardiovasc Res. 84:434–441. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hanstein R, Trotter J, Behl C and Clement
AB: Increased connexin 43 expression as a potential mediator of the
neuro-protective activity of the corticotropin-releasing hormone.
Mol Endocrinol. 23:1479–1493. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Curcio A, Torella D, Iaconetti C, et al:
MicroRNA-1 down-regulation increases connexin 43 displacement and
induces ventricular tachyarrhythmias in rodent hypertrophic hearts.
PLoS One. 8:e701582013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hegi ME, Rajakannu P and Weller M:
Epidermal growth factor receptor: a re-emerging target in
glioblastoma. Curr Opin Neurol. 25:774–779. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Katakowski M, Zheng X, Jiang F, Rogers T,
Szalad A and Chopp M: MiR-146b-5p suppresses EGFR expression and
reduces in vitro migration and invasion of glioma. Cancer Invest.
28:1024–1030. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ueki T, Fujita M, Sato K, Asai K, Yamada K
and Kato T: Epidermal growth factor down-regulates connexin-43
expression in cultured rat cortical astrocytes. Neurosci Lett.
313:53–56. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shi J, Zhang L, Shen A, et al: Clinical
and biological significance of forkhead class box O 3a expression
in glioma: mediation of glioma malignancy by transcriptional
regulation of p27kip1. J Neurooncol. 98:57–69. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
D’Urso PI, D’Urso OF, Storelli C, et al:
miR-155 is up-regulated in primary and secondary glioblastoma and
promotes tumour growth by inhibiting GABA receptors. Int J Oncol.
41:228–234. 2012.
|
|
42
|
Qiu S, Lin S, Hu D, Feng Y, Tan Y and Peng
Y: Interactions of miR-323/miR-326/miR-329 and
miR-130a/miR-155/miR-210 as prognostic indicators for clinical
outcome of glioblastoma patients. J Transl Med. 11:102013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu S, Yang Y and Wu J: TNFα-induced
up-regulation of miR-155 inhibits adipogenesis by down-regulating
early adipogenic transcription factors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
414:618–624. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Johnstone SR, Best AK, Wright CS, Isakson
BE, Errington RJ and Martin PE: Enhanced connexin 43 expression
delays intra-mitotic duration and cell cycle traverse independently
of gap junction channel function. J Cell Biochem. 110:772–782.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Huang RP, Fan Y, Hossain MZ, Peng A, Zeng
ZL and Boynton AL: Reversion of the neoplastic phenotype of human
glioblastoma cells by connexin 43 (cx43). Cancer Res. 58:5089–5096.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|