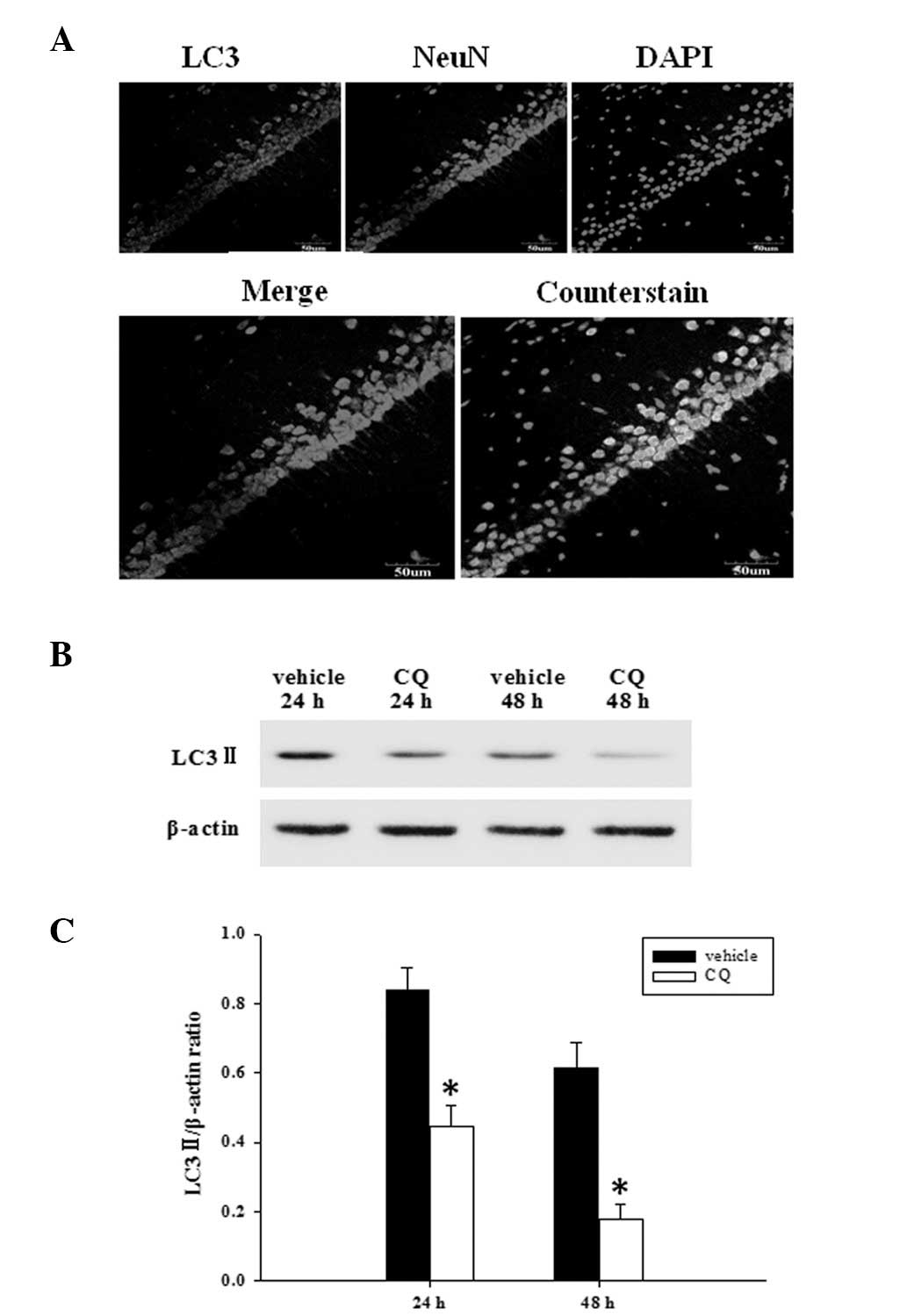
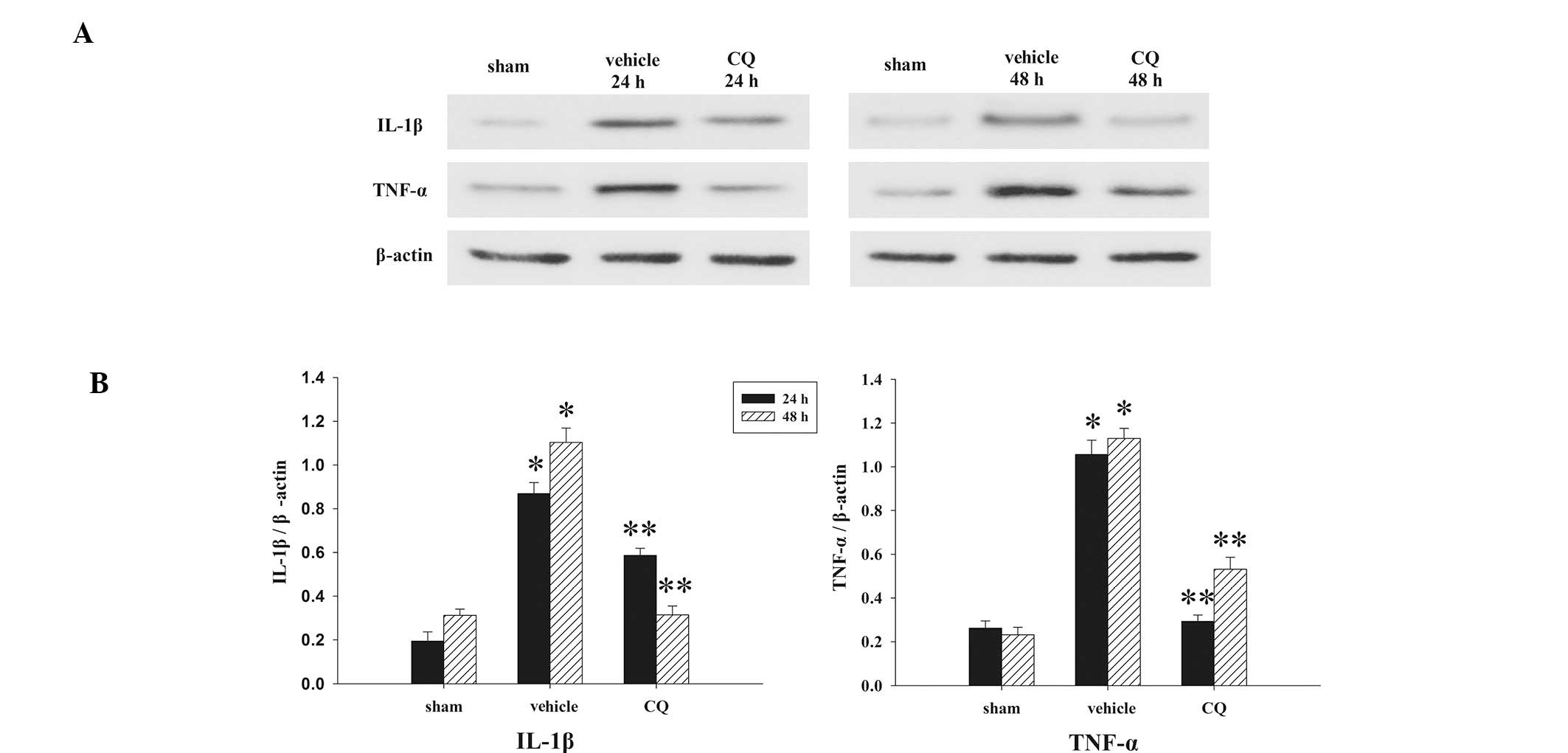
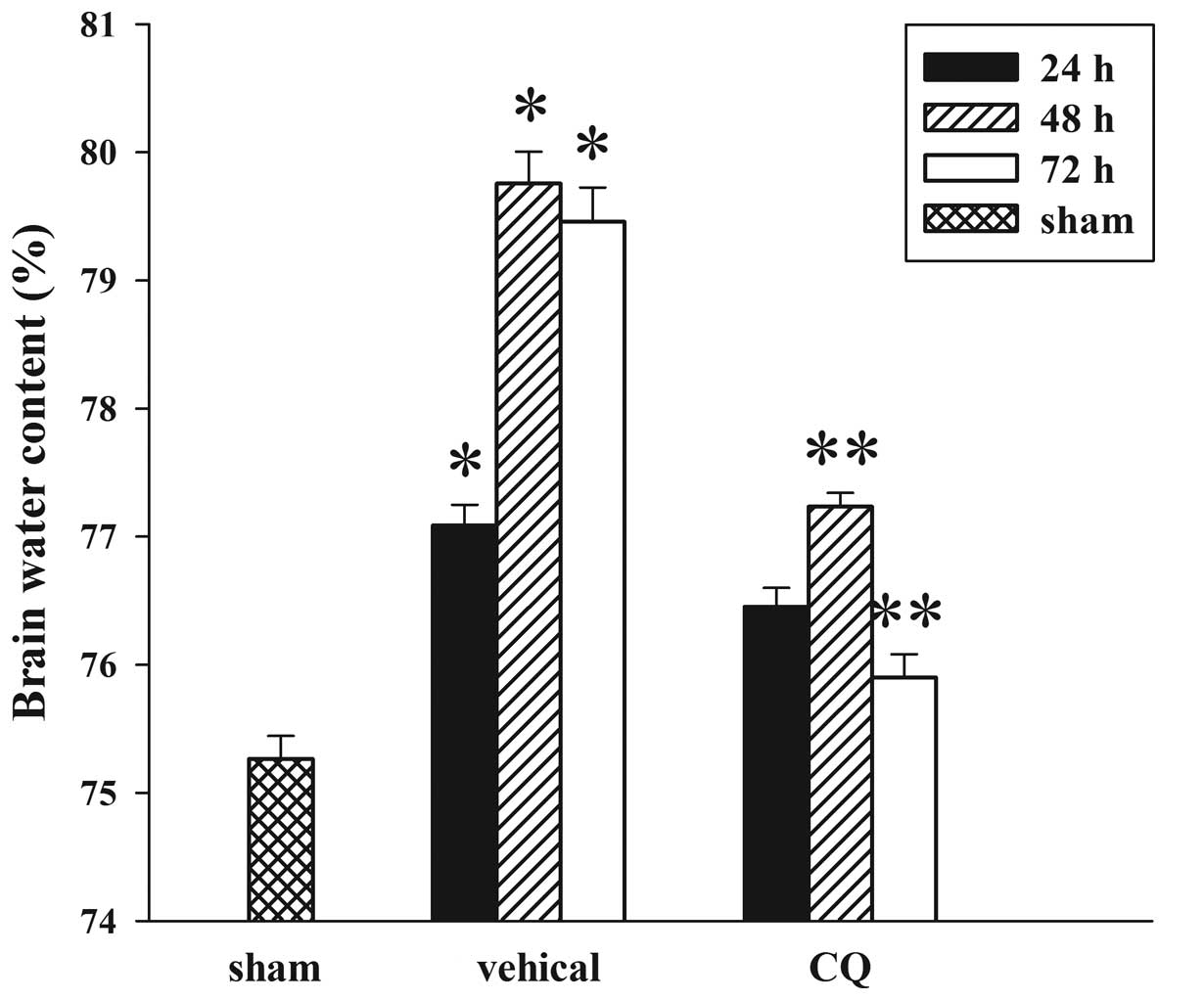
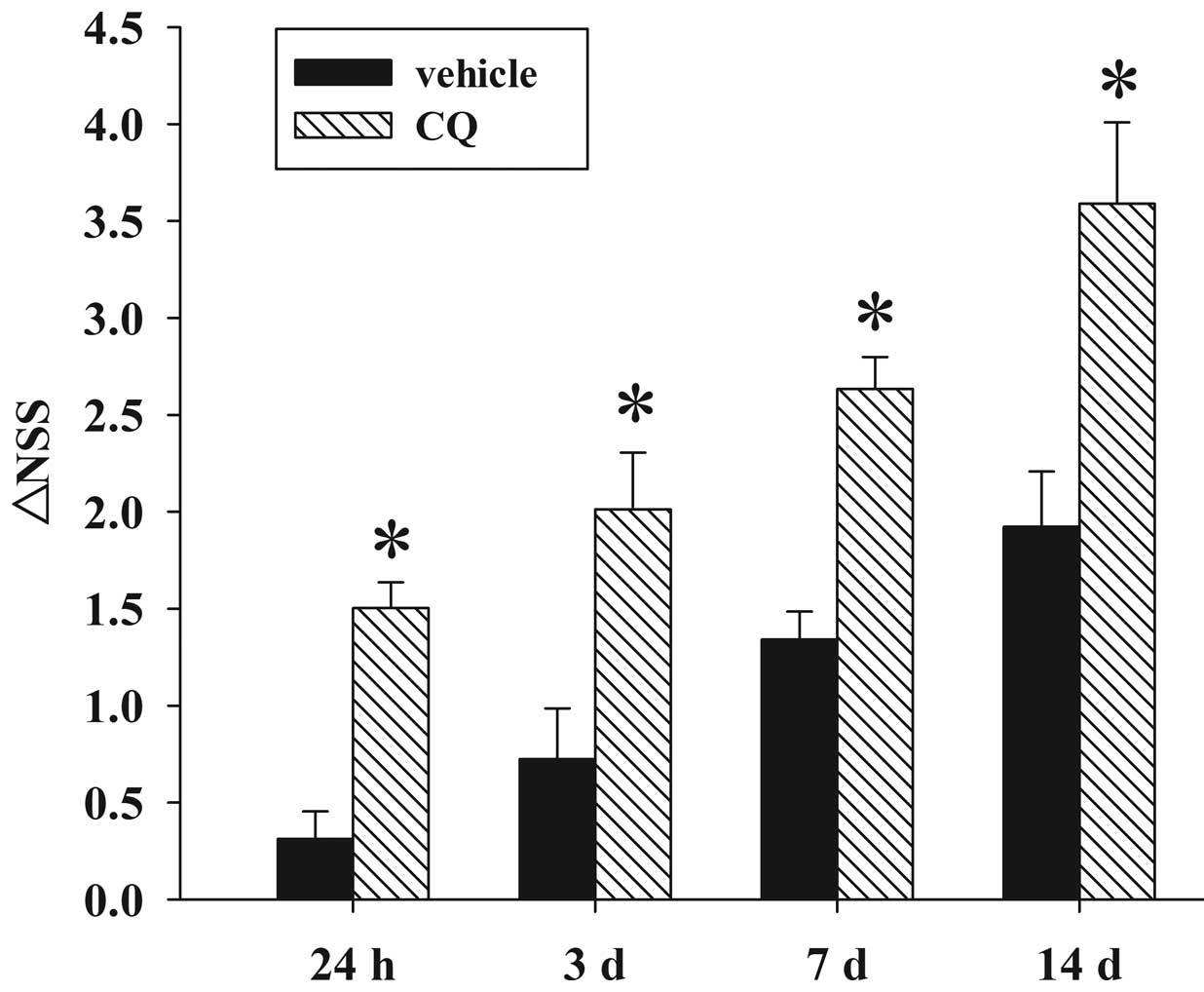
|
1
|
Thurman DJ, Alverson C, Dunn KA, Guerrero
J and Sniezek JE: Traumatic brain injury in the United States: a
public health perspective. J Head Trauma Rehabil. 14:602–615. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Davis AE: Mechanisms of traumatic brain
injury: biomechanical, structural and cellular considerations. Crit
Care Nurs Q. 23:1–13. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wang YQ, Wang L, Zhang MY, et al:
Necrostatin-1 suppresses autophagy and apoptosis in mice traumatic
brain injury model. Neurochem Res. 37:1849–1858. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Luo CL, Chen XP, Yang R, et al: Cathepsin
B contributes to traumatic brain injury-induced cell death through
a mitochondria-mediated apoptotic pathway. J Neurosci Res.
88:2847–2858. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shintani T and Klionsky DJ: Autophagy in
health and disease: a double-edged sword. Science. 306:990–995.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mizushima N: Autophagy: process and
function. Genes Dev. 21:2861–2873. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Galluzzi L, Aaronson SA, Abrams J, et al:
Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring
cell death in higher eukaryotes. Cell Death Differ. 16:1093–1107.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lai Y, Hickey RW, Yaming Chen Y, et al:
Autophagy is increased after traumatic brain injury in mice and is
partially inhibited by the antioxidant gamma-glutamylcysteinyl
ethyl ester. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 28:540–550. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Puyal J, Vaslin A, Mottier V and Clarke
PG: Postischemic treatment of neonatal cerebral ischemia should
target autophagy. Ann Neurol. 66:378–389. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Caro LH, Plomp PJ, Wolvetang EJ, Kerkhof C
and Meijer AJ: 3-Methyladenine, an inhibitor of autophagy, has
multiple effects on metabolism. Eur J Biochem. 175:325–329. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Homewood CA, Warhurst DC, Peters W and
Baggaley VC: Lysosomes, pH and the anti-malarial action of
chloroquine. Nature. 235:50–52. 1972. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Slater AF: Chloroquine: mechanism of drug
action and resistance in Plasmodium falciparum. Pharmacol Ther.
57:203–235. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Janku F, McConkey DJ, Hong DS and Kurzrock
R: Autophagy as a target for anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 8:528–539. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lopez G, Torres K and Lev D: Autophagy
blockade enhances HDAC inhibitors’ pro-apoptotic effects: potential
implications for the treatment of a therapeutic-resistant
malignancy. Autophagy. 7:440–441. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sotelo J, Briceño E and López-González MA:
Adding chloroquine to conventional treatment for glioblastoma
multiforme: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
Ann Intern Med. 144:337–343. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kimura T, Takabatake Y, Takahashi A and
Isaka Y: Chloroquine in cancer therapy: a double-edged sword of
autophagy. Cancer Res. 73:3–7. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu C, Gao Y, Barrett J and Hu B:
Autophagy and protein aggregation after brain ischemia. J
Neurochem. 115:68–78. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang JY, Peng C, Shi H, Wang S, Wang Q
and Wang JZ: Inhibition of autophagy causes tau proteolysis by
activating calpain in rat brain. J Alzheimers Dis. 16:39–47.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Marmarou A, Foda MA, van den Brink W,
Campbell J, Kita H and Demetriadou K: A new model of diffuse brain
injury in rats. J Neurosurg. 80:291–300. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tang J, Liu J, Zhou C, et al: Mmp-9
deficiency enhances collagenase-induced intracerebral hemorrhage
and brain injury in mutant mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
24:1133–1145. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Beni-Adani L, Gozes I, Cohen Y, et al: A
peptide derived from activity-dependent neuroprotective protein
(ADNP) ameliorates injury response in closed head injury in mice. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 296:57–63. 2001.
|
|
22
|
Hui-guo L, Kui L, Yan-ning Z and Yong-jian
X: Apocynin attenuate spatial learning deficits and oxidative
responses to intermittent hypoxia. Sleep Med. 11:205–212. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yi JH and Hazell AS: Excitotoxic
mechanisms and the role of astrocytic glutamate transporters in
traumatic brain injury. Neurochem Int. 48:394–403. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tyurin VA, Tyurina YY, Borisenko GG, et
al: Oxidative stress following traumatic brain injury in rats. J
Neurochem. 75:2178–2189. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Frugier T, Morganti-Kossmann MC, O’Reilly
D and McLean CA: In situ detection of inflammatory mediators in
post mortem human brain tissue after traumatic injury. J
Neurotrauma. 27:497–507. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Raghupathi R: Cell death mechanisms
following traumatic brain injury. Brain Pathol. 14:215–222. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
O’Connor WT, Smyth A and Gilchrist MD:
Animal models of traumatic brain injury: a critical evaluation.
Pharmacol Ther. 130:106–113. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Diskin T, Tal-Or P, Erlich S, et al:
Closed head injury induces upregulation of Beclin 1 at the cortical
site of injury. J Neurotrauma. 22:750–762. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Erlich S, Alexandrovich A, Shohami E and
Pinkas-Kramarski R: Rapamycin is a neuroprotective treatment for
traumatic brain injury. Neurobiol Dis. 26:86–93. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
van den Borne BE, Dijkmans BA, de Rooij H,
le Cessie S and Verweij CL: Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine
equally affect tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin 6, and
interferon-gamma production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
J Rheumatol. 24:55–60. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jang CH, Choi JH, Byun MS and Jue DM:
Chloroquine inhibits production of TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and IL-6
from lipopolysac-charide-stimulated human monocytes/macrophages by
different modes. Rheumatology (Oxford). 45:703–710. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Fullerton HJ, Ditelberg JS, Chen SF, et
al: Copper/zinc superoxide dismutase transgenic brain accumulates
hydrogen peroxide after perinatal hypoxia ischemia. Ann Neurol.
44:357–364. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sehgal S, Baker H and Vézina C: Rapamycin
(AY-22,989), a new antifungal antibiotic. II Fermentation,
isolation and characterization. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 28:727–732.
1975. View Article : Google Scholar
|