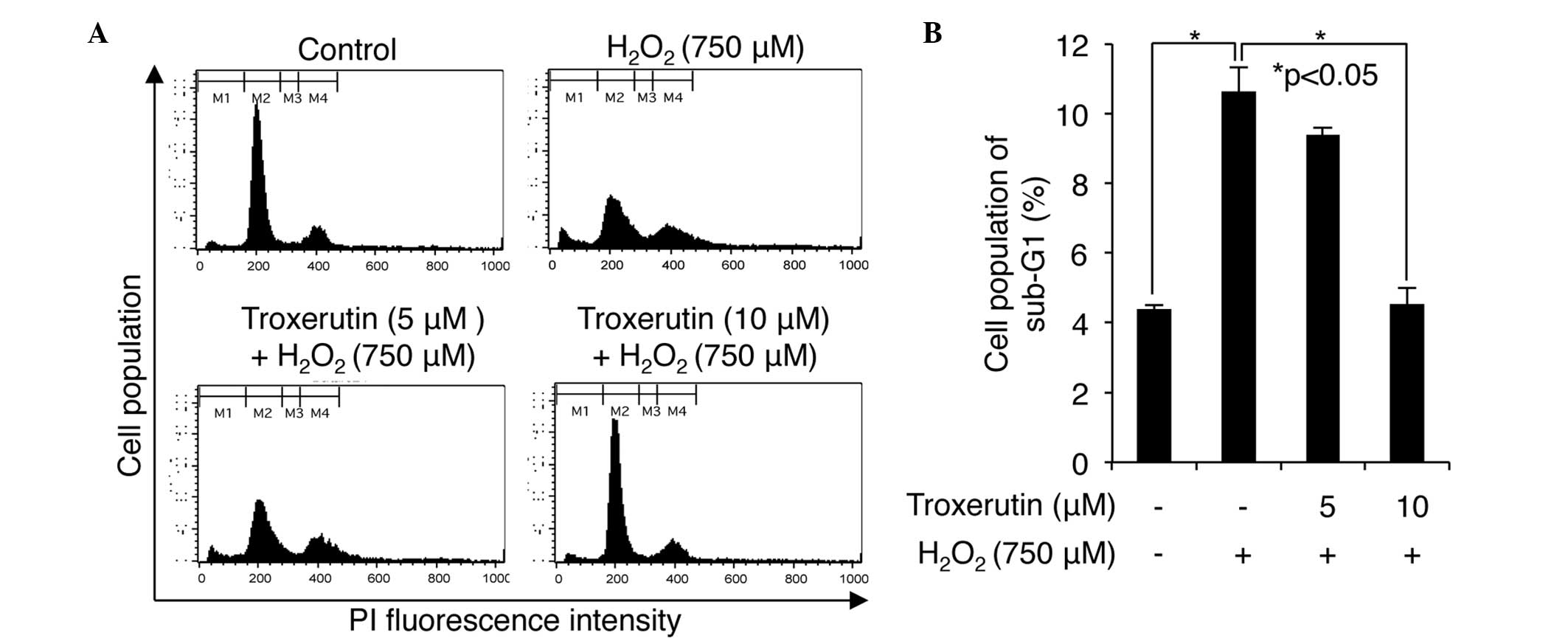
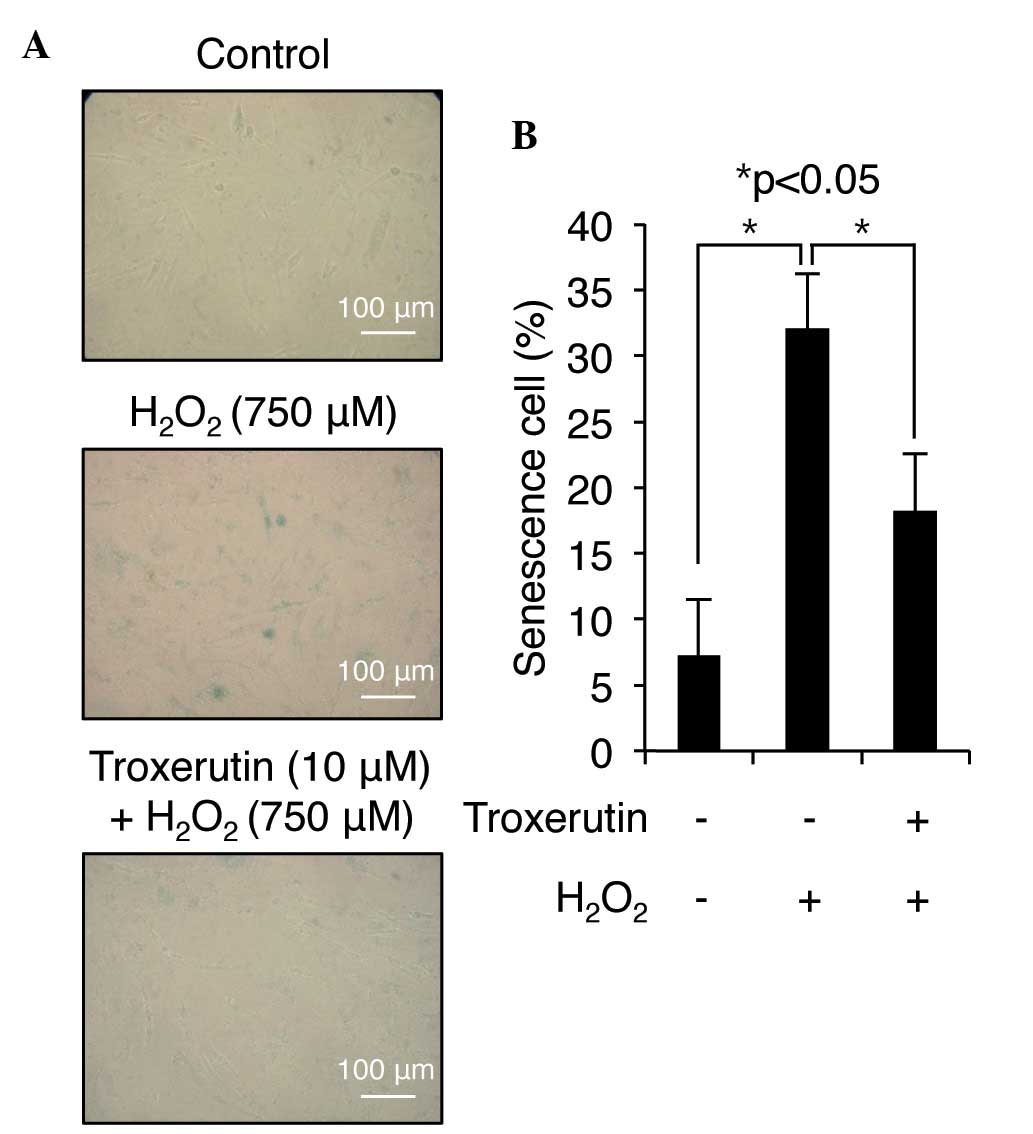
|
1
|
Marzin D, Phi HV, Olivier P and Sauzieres
J: Study of mutagenic activity of troxerutin, a flavonoid
derivative. Toxicol Lett. 35:297–305. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Boisseau MR, Taccoen A, Garreau C, Vergnes
C, Roudaut MF and Garreau-Gomez B: Fibrinolysis and hemorheology in
chronic venous insufficiency: a double blind study of troxerutin
efficiency. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 36:369–374. 1995.
|
|
3
|
Lu J, Wu DM, Zheng ZH, Zheng YL, Hu B and
Zhang ZF: Troxerutin protects against high cholesterol-induced
cognitive deficits in mice. Brain. 134:783–797. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lu J, Wu DM, Zheng YL, et al: Troxerutin
counteracts domoic acid induced memory deficits in mice by
inhibiting CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta-mediated
inflammatory response and oxidative stress. J Immunol.
190:3466–3479. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Babri S, Amani M, Mohaddes G, Alihemmati A
and Ebrahimi H: Protective effects of troxerutin on beta-amyloid
(1–42)-induced impairments of spatial learning and memory in rats.
Neurophysiology. 44:387–393. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lee KS, Cha HJ, Lee GT, et al: Troxerutin
induces protective effects against ultraviolet B radiation through
the alteration of microRNA expression in human HaCaT keratinocyte
cells. Int J Mol Med. 33:934–942. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cha HJ, Lee KS, Lee GT, et al: Altered
miRNA expression profiles are involved in the protective effects of
troxerutin against ultraviolet B radiation in normal human dermal
fibroblasts. Int J Mol Med. 33:957–963. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ping X, Junqing J, Junfeng J and Enjin J:
Radioprotective effects of troxerutin against gamma irradiation in
V79 cells and mice. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 12:2593–2596.
2011.
|
|
9
|
Maurya DK, Salvi VP and Krishnan Nair CK:
Radioprotection of normal tissues in tumor bearing mice by
troxerutin. J Radiat Res. 45:221–228. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Flore R, Gerardino L, Santoliquido A, et
al: Enhanced oxidative stress in workers with a standing
occupation. Occup Environ Med. 61:548–550. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hladovec J: Protective effect of
oxygen-derived free radical scavengers on the endothelium in vivo.
Physiol Bohemoslov. 35:97–103. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lu J, Wu DM, Hu B, Zheng YL, Zhang ZF and
Wang YJ: NGF-Dependent activation of TrkA pathway: A mechanism for
the neuroprotective effect of troxerutin in D-galactose-treated
mice. Brain Pathol. 20:952–965. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Heck DE, Vetrano AM, Mariano TM and Laskin
JD: UVB light stimulates production of reactive oxygen species:
unexpected role for catalase. J Biol Chem. 278:22432–22436. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Leach JK, Van Tuyle G, Lin PS,
Schmidt-Ullrich R and Mikkelsen RB: Ionizing radiation induced,
mitochondria-dependent generation of reactive oxygen/nitrogen.
Cancer Res. 61:3894–3901. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Driskell RR, Clavel C, Rendl M and Watt
FM: Hair follicle dermal papilla cells at a glance. J Cell Sci.
124:1179–1182. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hibberts NA, Howell AE and Randall VA:
Balding hair follicle dermal papilla cells contain higher levels of
androgen receptors than those from non balding scalp. J Endocrinol.
156:59–65. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Trüeb RM: Oxidative stress in ageing of
hair. Int J Trichology. 1:6–14. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ripple MO, Henry WF, Rago RP and Wilding
G: Prooxidant-antioxidant shift induced by androgen treatment of
human prostate carcinoma cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 89:40–48. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Naito A, Midorikawa T, Yoshino T and
Ohdera M: Lipid peroxides induce early onset of catagen phase in
murine hair cycles. Int J Mol Med. 22:725–729. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bahta AW, Farjo N, Farjo B and Philpott
MP: Premature senescence of balding dermal papilla cells in vitro
is associated with p16 (INK4a) expression. J Invest Dermatol.
128:1088–1094. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lee EJ, Cha HJ, Ahn KJ, An IS, An S and
Bae S: Oridonin exerts protective effects against hydrogen
peroxideinduced damage by altering microRNA expression profiles in
human dermal fibroblasts. Int J Mol Med. 32:1345–1354.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, et al: The
DAVID Gene Functional Classification Tool: a novel biological
module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large gene lists.
Genome Biol. 8:R1832007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Luanpitpong S, Nimmannit U, Chanvorachote
P, et al: Hydroxyl radical mediates cisplatin-induced apoptosis in
human hair follicle dermal papilla cells and keratinocytes through
Bcl-2-dependent mechanism. Apoptosis. 16:769–782. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shin H, Yoo HG, Inui S, et al: Induction
of transforming growth factor-beta 1 by androgen is mediated by
reactive oxygen species in hair follicle dermal papilla cells. BMB
Rep. 46:460–464. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Colavitti R and Finkel T: Reactive oxygen
species as mediators of cellular senescence. IUBMB Life.
57:277–281. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Baehrecke EH: miRNAs: micro managers of
programmed cell death. Curr Biol. 13:R473–R475. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang Z, Liu Y, Han N, et al: Profiles of
oxidative stress-related microRNA and mRNA expression in auditory
cells. Brain Res. 1346:14–25. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Faraonio R, Salerno P, Passaro F, et al: A
set of miRNAs participates in the cellular senescence program in
human diploid fibroblasts. Cell Death Differ. 19:713–721. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Bakry OA, Elshazly RM, Shoeib MA and Gooda
A: Oxidative stress in alopecia areata: a case-control study. Am J
Clin Dermatol. 15:57–64. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Seo JA, Bae IH, Jang WH, et al: Hydrogen
peroxide and monoethanolamine are the key causative ingredients for
hair dye-induced dermatitis and hair loss. J Dermatol Sci.
66:12–19. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Trüeb RM: Is androgenetic alopecia a
photoaggravated dermatosis? Dermatology. 207:343–348. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Camacho F, Moreno JC and García-Hernández
MJ: Telogen alopecia from UV rays. Arch Dermatol. 132:1398–1399.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Johnsson A, Kjeldstad B and Melø TB:
Fluorescence from pilosebaceous follicles. Arch Dermatol Res.
279:190–193. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang L, Ma Z, Wang D, Zhao W, Chen L and
Wang G: MicroRNA-602 regulating tumor suppressive gene RASSF1A is
overexpressed in hepatitis B virus-infected liver and
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 9:803–808. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Singh M, Sharma H and Singh N: Hydrogen
peroxide induces. apoptosis in HeLa cells through mitochondrial
pathway. Mitochondrion. 7:367–373. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Surendiran A, Balamurugan N, Gunaseelan K,
Akhtar S, Reddy KS and Adithan C: Adverse drug reaction profile of
cisplatin-based chemotherapy regimen in a tertiary care hospital in
India: An evaluative study. Indian J Pharmacol. 42:40–43. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Casares C, Ramírez-Camacho R, Trinidad A,
Roldán A, Jorge E and García-Berrocal JR: Reactive oxygen species
in apoptosis induced by cisplatin: review of physiopathological
mechanisms in animal models. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol.
269:2455–2459. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gong JG, Costanzo A, Yang HQ, et al: The
tyrosine kinase c-Abl regulates p73 in apoptotic response to
cisplatin-induced DNA damage. Nature. 399:806–809. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang Z, Cui M, Sun L, et al:
Angiopoietin-1 protects H9c2 cells from
H2O2-induced apoptosis through AKT signaling.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 359:685–690. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mora A, Komander D, van Aalten DM and
Alessi DR: PDK1, the master regulator of AGC kinase signal
transduction. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 15:161–170. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Finkel T: Signal transduction by reactive
oxygen species. J Cell Biol. 194:7–15. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shin SY, Kim CG, Jho EH, et al: Hydrogen
peroxide negatively modulates Wnt signaling through downregulation
of beta-catenin. Cancer Lett. 212:225–231. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Korswagen HC: Regulation of the
Wnt/beta-catenin pathway by redox signaling. Dev Cell. 10:687–688.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Song X, Xu A, Pan W, et al: Minocycline
protects melanocytes against H2O2-induced
cell death via JNK and p38 MAPK pathways. Int J Mol Med. 22:9–16.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ismail NS, Pravda EA, Li D, Shih SC and
Dallabrida SM: Angiopoietin-1 reduces
H2O2-induced increases in reactive oxygen
species and oxidative damage to skin cells. J Invest Dermatol.
130:1307–1317. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|