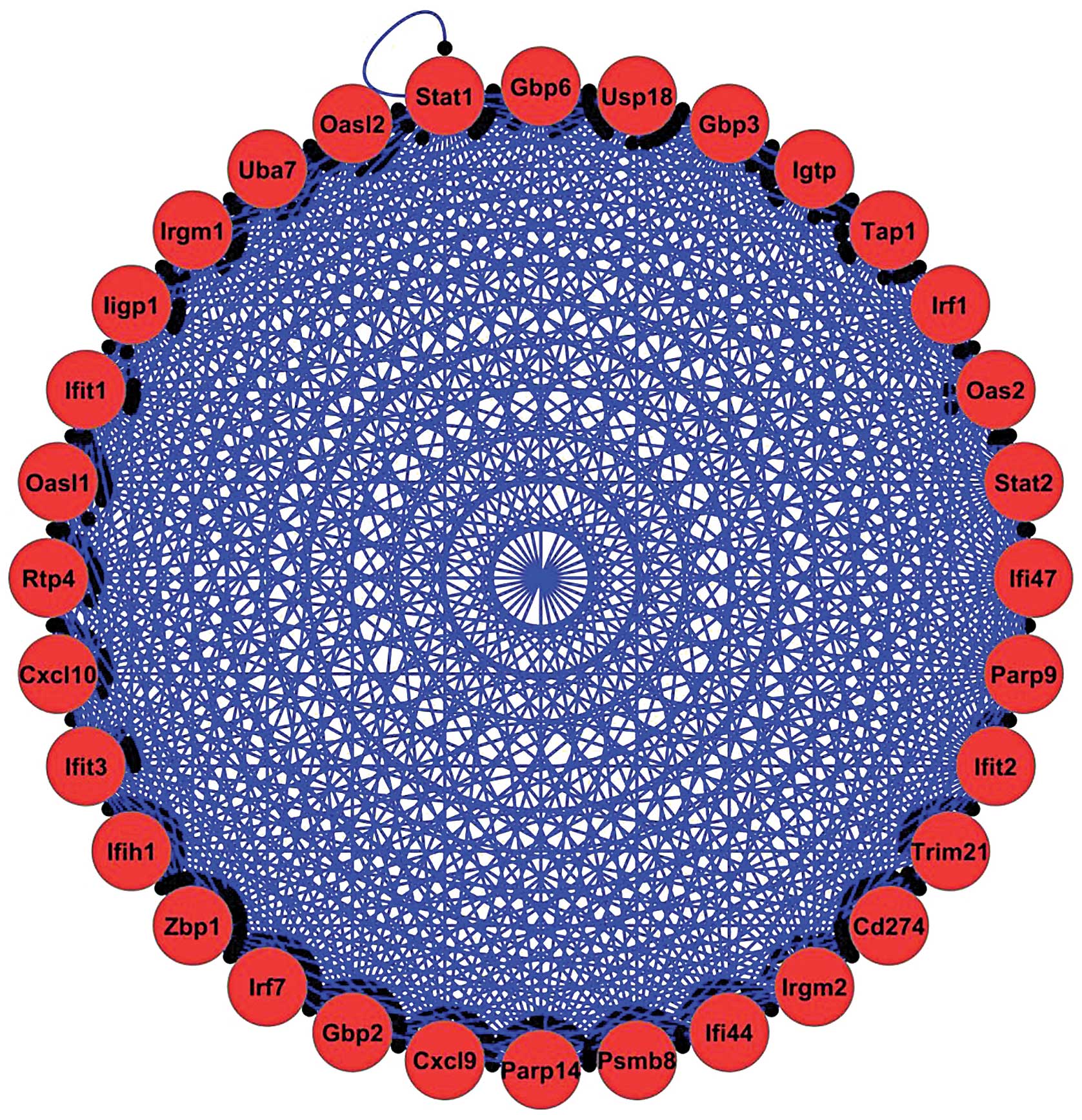
|
1
|
World Health Organisation: Tuberculosis
Fact Sheet. World Health Organization; Geneva Switzerland: 2012
|
|
2
|
Leveton C, Barnass S, Champion B, Lucas S,
De Souza B, Nicol M, Banerjee D and Rook G: T-cell-mediated
protection of mice against virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Infect Immun. 57:390–395. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kaufmann SH: Immunity to intracellular
bacteria. Annu Rev Immunol. 11:129–163. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schluger NW and Rom WN: The host immune
response to tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 157(3 Pt 1):
679–691. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mogues T, Goodrich ME, Ryan L, LaCourse R
and North RJ: The relative importance of T cell subsets in immunity
and immunopathology of airborne Mycobacterium tuberculosis
infection in mice. J Exp Med. 193:271–280. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sugawara I, Yamada H and Mizuno S:
Relative importance of STAT4 in murine tuberculosis. J Med
Microbiol. 52:29–34. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Via LE, Tsytsykova AV, Rajsbaum R, Falvo
JV and Goldfeld AE: The transcription factor NFATp plays a key role
in susceptibility to TB in mice. PLoS One. 7:e414272012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Marquis JF, LaCourse R, Ryan L, North RJ
and Gros P: Disseminated and rapidly fatal tuberculosis in mice
bearing a defective allele at IFN regulatory factor 8. J Immunol.
182:3008–3015. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Keller C, Hoffmann R, Lang R, Brandau S,
Hermann C and Ehlers S: Genetically determined susceptibility to
tuberculosis in mice causally involves accelerated and enhanced and
recruitment of granulocytes. Infect Immun. 74:4295–4309. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Marquis JF, Kapoustina O, Langlais D,
Ruddy R, Dufour CR, Kim BH, MacMicking JD, Giguère V and Gros P:
Interferon regulatory factor 8 regulates pathways for antigen
presentation in myeloid cells and during tuberculosis. PLoS Genet.
7:e10020972011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Corn RA, Hunter C, Liou HC, Siebenlist U
and Boothby MR: Opposing roles for RelB and Bcl-3 in regulation of
T-box expressed in T cells, GATA-3 and Th effector differentiation.
J Immunol. 175:2102–2110. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Szabo SJ, Sullivan BM, Peng SL and
Glimcher LH: Molecular mechanisms regulating Th1 immune responses.
Annu Rev Immunol. 21:713–758. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang X, Wang H and Xie J: Genes and
regulatory networks involved in persistence of Mycobacterium
tuberculosis. Sci China Life Sci. 54:300–310. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sambarey A, Prashanthi K and Chandra N:
Mining large-scale response networks reveals ‘topmost activities’
in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Sci Rep. 3:23022013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kumar D, Nath L, Kamal MA, Varshney A,
Jain A, Singh S and Rao KV: Genome-wide analysis of the host
intracellular network that regulates survival of Mycobacterium
tuberculosis. Cell. 140:731–743. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kang DD, Lin Y, Moreno JR, Randall TD and
Khader SA: Profiling early lung immune responses in the mouse model
of tuberculosis. PLoS One. 6:e161612011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F,
Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ, Scherf U and Speed TP:
Exploration, normalization and summaries of high density
oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics. 4:249–264.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Blazejczyk M, Miron M and Nadon R:
FlexArray: Statistical data analysis software for gene expression
microarrays, made with life scientists in mind. McGill University
and Génome Québec Innovation Centre; Montréal, QC: 2007
|
|
19
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lachmann A, Xu H, Krishnan J, Berger SI,
Mazloom AR and Ma’ayan A: ChEA: transcription factor regulation
inferred from integrating genome-wide ChIP-X experiments.
Bioinformatics. 26:2438–2444. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Essaghir A, Toffalini F, Knoops L, Kallin
A, van Helden J and Demoulin JB: Transcription factor regulation
can be accurately predicted from the presence of target gene
signatures in microarray gene expression data. Nucleic Acids Res.
38:e1202010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stark C, Breitkreutz BJ, Reguly T, Boucher
L, Breitkreutz A and Tyers M: BioGRID: a general repository for
interaction datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 34(Database Issue):
D535–539. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering C
and Jensen LJ: STRING v9.1: protein-protein interaction networks,
with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41(Database Issue): D808–D815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Saito R, Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J,
Wang PL, Lotia S, Pico AR, Bader GD and Ideker T: A travel guide to
Cytoscape plugins. Nat Methods. 9:1069–1076. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bindea G, Mlcenik B, Hackl H, Charoentong
P, Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Fridman WH, Pagès F, Trajanoski Z and
Galon J: ClueGO: a Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally
grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks.
Bioinformatics. 25:1091–1093. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Scardoni G, Petterlini M and Laudanna C:
Analyzing biological network parameters with CentiScaPe.
Bioinformatics. 25:2857–2859. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bader GD and Hogue CW: An automated method
for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction
networks. BMC Bioinformatics. 4:22003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ideker T, Ozier O, Schwikowski B and
Siegel AF: Discovering regulatory and signalling circuits in
molecular interaction networks. Bioinformatics. 18(Suppl 1):
233–240. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Rengarajan J, Szabo SJ and Glimcher LH:
Transcriptional regulation of Th1/Th2 polarization. Immunol Today.
21:479–483. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wurster AL, Tanaka T and Grusby MJ: The
biology of Stat4 and Stat6. Oncogene. 19:2577–2584. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Raju B, Hoshino Y, Belitskaya-Lévy I,
Dawson R, Ress S, Gold JA, Condos R, Pine R, Brown S, Nolan A, et
al: Gene expression profiles of bronchoalveolar cells in pulmonary
TB. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 88:39–51. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhao J, Kong HJ, Li H, Huang B, Yang M,
Zhu C, Bogunovic M, Zheng F, Mayer L, Ozato K, et al:
IRF-8/interferon (IFN) consensus sequence-binding protein is
involved in Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling and contributes to
the cross-talk between TLR and IFN-gamma signaling pathways. J Biol
Chem. 281:10073–10080. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
McKercher SR, Torbett BE, Anderson KL,
Henkel GW, Vestal DJ, Baribault H, Klemsz M, Feeney AJ, Wu GE,
Paige CJ and Maki RA: Targeted disruption of the PU. 1 gene results
in multiple hematopoietic abnormalities. EMBO J. 15:5647–5658.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Spain LM, Guerriero A, Kunjibettu S and
Scott EW: T cell development in PU. 1-deficient mice. J Immunol.
163:2681–2687. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chang HC, Han L, Jabeen R, Carotta S, Nutt
SL and Kaplan MH: PU. 1 regulates TCR expression by modulating
GATA-3 activity. J Immunol. 183:4887–4894. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
He S, Tong Q, Bishop DK and Zhang Y:
Histone methyltrans-ferase and histone methylation in inflammatory
T-cell responses. Immunotherapy. 5:989–1004. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jacob E, Hod-Dvorai R, Ben-Mordechai OL,
Boyko Y and Avni O: Dual function of polycomb group proteins in
differentiated murine T helper (CD4+) cells. J Mol Signal. 6:52011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Koyanagi M, Baguet A, Martens J, Margueron
R, Jenuwein T and Bix M: EZH2 and histone 3 trimethyl lysine 27
associated with II4 and II13 gene silencing in Th1 cells. J Biol
Chem. 280:31470–31477. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lee GR, Kim ST, Spilianakis CG, Fields PE
and Flavell RA: T helper cell differentiation: regulation by cis
elements and epigenetics. Immunity. 24:369–379. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
An J, Golech S, Klaewsongkram J, Zhang Y,
Subedi K, Huston GE, Wood WH III, Wersto RP, Becker KG, Swain SL
and Weng N: Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) directly regulates
proliferation in thymocyte development and IL-17 expression during
Th17 differentiation. FASEB J. 25:3634–3645. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Subbian S, O’Brien P, Kushner NL, Yang G,
Tsenova L, Peixoto B, Bandyopadhyay N, Bader JS, Karakousis PC,
Fallows D and Kaplan G: Molecular immunologic correlates of
spontaneous latency in a rabbit model of pulmonary tuberculosis.
Cell Commun Signal. 11:162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|