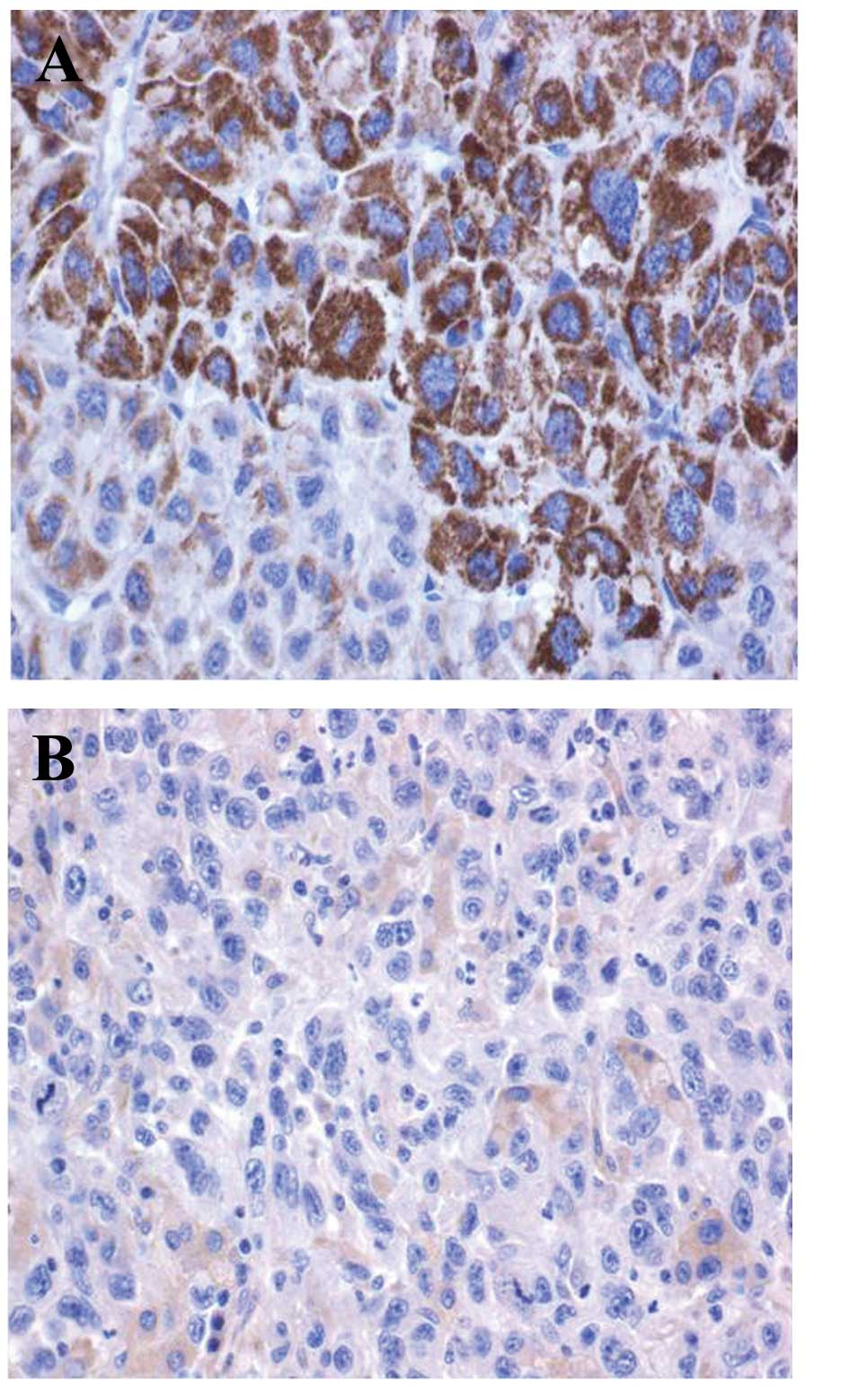
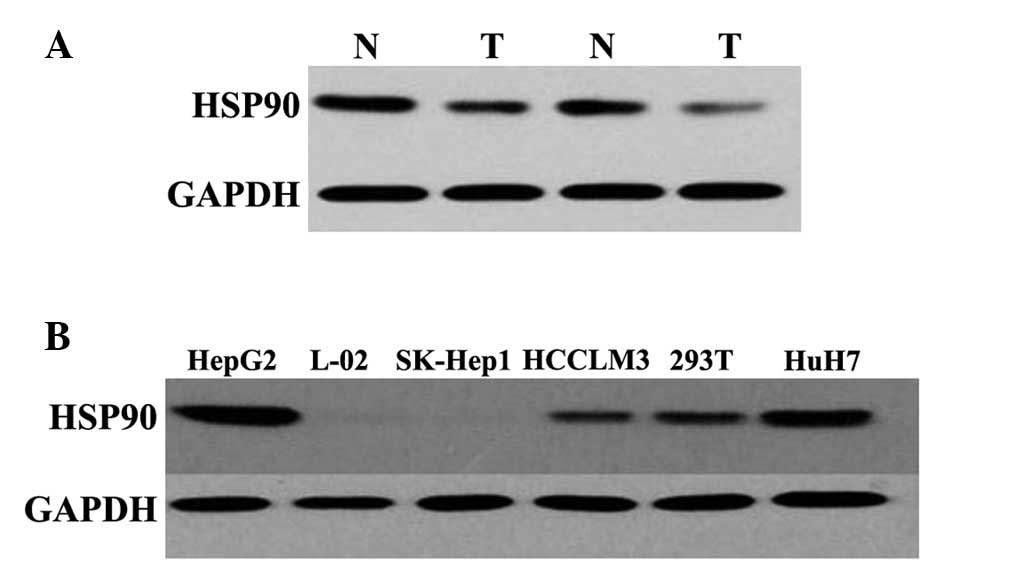
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ades S: Adjuvant chemotherapy for colon
cancer in the elderly: moving from evidence to practice. Oncology
(Williston Park). 23:162–167. 2009.
|
|
3
|
Frangov T, Gaĭdarski R, Dimitrova V, Popov
V, Grozeva K and Rusenov D: Prognostic factors for survival in
primary liver cancer. Khirurgiia (Sofiia). 6:36–39. 2007.In
Bulgarian.
|
|
4
|
Folkman J: Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic
implications. N Engl J Med. 285:1182–1186. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fidler IJ and Ellis LM: The implications
of angiogenesis for the biology and therapy of cancer metastasis.
Cell. 79:185–188. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ferrara N: Role of vascular endothelial
growth factor in regulation of physiological angiogenesis. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 280:C1358–C1366. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Weidner N: Intratumor microvessel density
as a prognostic factor in cancer. Am J Pathol. 147:9–19.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu YZ, Zhu Y, Shen ZJ, Sheng JY, He HC, Ma
G, et al: Significance of heparanase-1 and vascular endothelial
growth factor in adrenocortical carcinoma angiongenesis: Potential
for therapy. Endocrine. 40:445–451. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Trepel J, Mollapour M, Giaccone G and
Neckers L: Targeting the dynamic HSP90 complex in cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 10:537–549. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee KH, Lee JH, Han SW, Im SA, Kim TY, Oh
DY and Bang YJ: Antitumor activity of NVP-AUY922, a novel heat
shock protein 90 inhibitor, in human gastric cancer cells is
mediated through proteasomal degradation of client proteins. Cancer
Sci. 102:1388–1395. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Eccles SA, Massey A, Raynaud FI, Sharp SY,
Box G, Valenti M, Patterson L, de Haven Brandon A, Gowan S, Boxall
F, Aherne W, et al: NVP-AUY922: A novel heat shock protein 90
inhibitor active against xenograft tumor growth, angiogenesis and
metastasis. Cancer Res. 68:2850–2860. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu Y, Zhang C, Chen D, Zhao J, Shen Z, Wu
Y and Zhu Y: Effect of HSP90 inhibitor in pheochromocytoma PC12
cells: an experimental investigation. Tumour Biol. 34:4065–4071.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Laforga JB and Aranda FI: Angiogenic
Index: A new method for assessing microvascularity in breast
carcinoma with possible prognostic implications. Breast J.
6:103–107. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Geng J, Li X, Zhou Z, Wu CL, Dai M and Bai
X: EZH2 promotes tumor progression via regulating VEGF-A/AKT
signaling in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 359:275–287.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pearl LH, Prodromou C and Workman P: The
Hsp90 molecular chaperone: an open and shut case for treatment.
Biochem J. 410:439–453. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pratt WB and Toft DO: Regulation of
signaling protein function and trafficking by the hsp90/hsp70-based
chaperone machinery. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 228:111–133. 2003.
|
|
17
|
Powers MV and Workman P: Targeting of
multiple signalling pathways by heat shock protein 90 molecular
chaperone inhibitors. Endocr Relat Cancer. 13(Suppl 1): 125–135.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Gartner EM, Silverman P, Simon M, Flaherty
L, Abrams J, Ivy P and Lorusso PM: A phase II study of
17-allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin in metastatic or locally
advanced, unresectable breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
131:933–937. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Eiseman JL, Lan J, Lagattuta TF, et al:
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of 17-demethoxy
17-[[(2-dimethylamino) ethyl]amino]geldanamycin (17DMAG, NSC
707545) in C.B-17 SCID mice bearing MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer
xenografts. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 55:21–32. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Moulick K, Ahn JH, Zong H, Rodina A,
Cerchietti L, Gomes DaGama EM, Caldas-Lopes E, Beebe K, Perna F,
Hatzi K, Vu LP, et al: Affinity-based proteomics reveal
cancer-specific networks coordinated by Hsp90. Nat Chem Biol.
7:818–826. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nguyen DM, Lorang D, Chen GA, Stewart JH
IV, Tabibi E and Schrump DS: Enhancement of paclitaxel-mediated
cytotoxicity in lung cancer cells by 17-allylamino geldanamycin: in
vitro and in vivo analysis. Ann Thorac Surg. 72:371–378; discussion
378–379. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hur E, Kim HH, Choi SM, et al: Reduction
of hypoxia-induced transcription through the repression of
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha/aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear
translocator DNA binding by the 90-kDa heat-shock protein inhibitor
radicicol. Mol Pharmacol. 62:975–982. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pacey S, Gore M, Chao D, Banerji U, Larkin
J, Sarker S, et al: A Phase II trial of 17-allylamino,
17-demethoxygeldanamycin (17-AAG, tanespimycin) in patients with
metastatic melanoma. Invest New Drugs. 30:341–349. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Eccles SA, Massey A, Raynaud FI, Sharp SY,
Box G, Valenti M, et al: NVP-AUY922: a novel heat shock protein 90
inhibitor active against xenograft tumor growth, angiogenesis and
metastasis. Cancer Res. 68:2850–2860. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jensen MR, Schoepfer J, Radimerski T,
Massey A, Guy CT, Brueggen J, et al: NVP-AUY922: a small molecule
HSP90 inhibitor with potent antitumor activity in preclinical
breast cancer models. Breast Cancer Res. 10:R332008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Moser C, Lang SA, Hackl C, Wagner C,
Scheiffert E, Schlitt HJ, et al: Targeting HSP90 by the novel
inhibitor NVP-AUY922 reduces growth and angiogenesis of pancreatic
cancer. Anticancer Res. 32:2551–2561. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chatterjee M, Andrulis M, Stuhmer T,
Müller E, Hofmann C, Steinbrunn T, et al: The PI3K/Akt signalling
pathway regulates the expression of Hsp70, which critically
contributes to Hsp90-chaperone function and tumor cell survival in
multiple myeloma. Haematologica. 98:1132–1141. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Ueno T, Tsukuda K, Toyooka S, Ando M,
Takaoka M, Soh J, et al: Strong anti-tumor effect of NVP-AUY922, a
novel Hsp90 inhibitor, on non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer.
76:26–31. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|