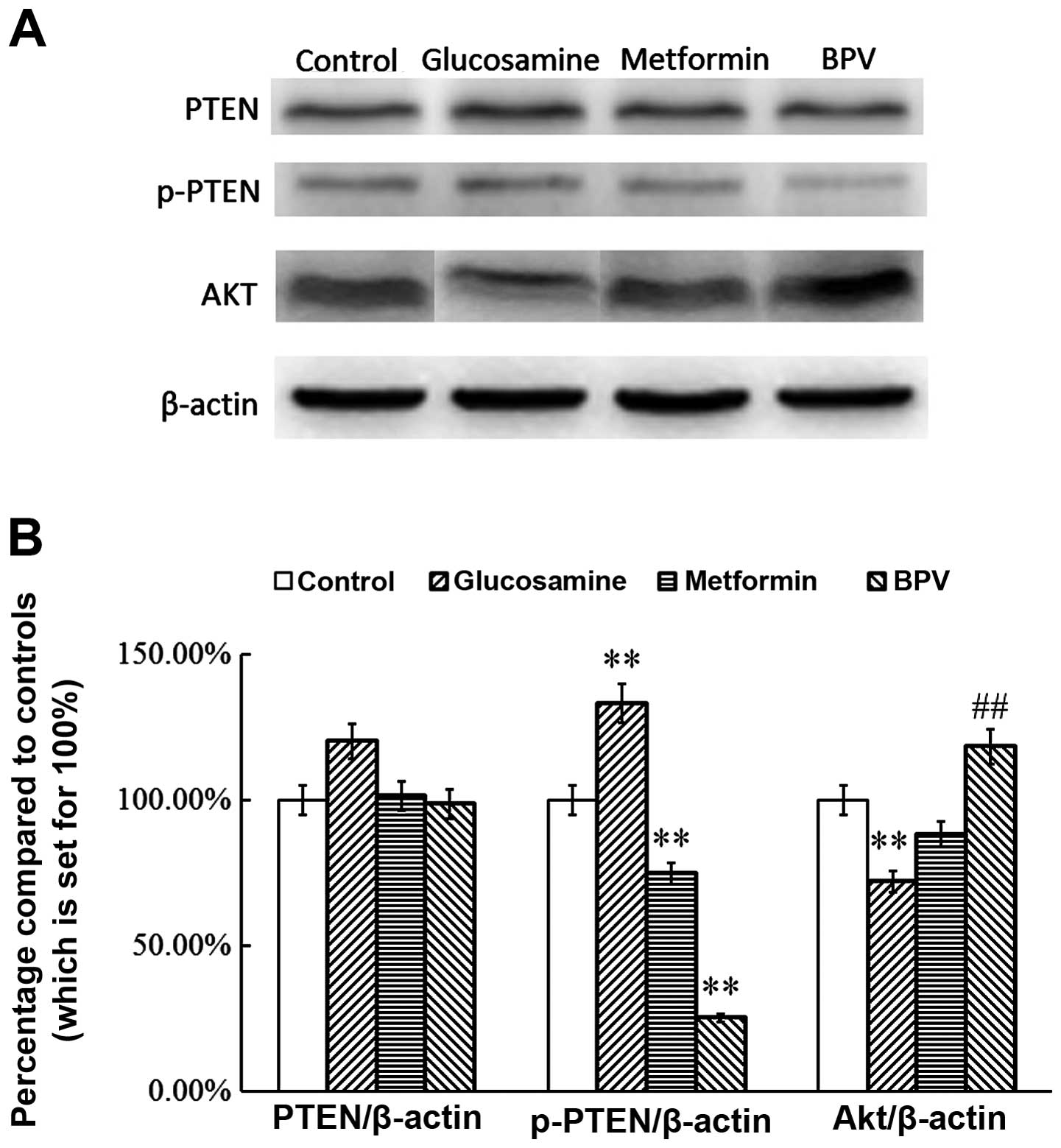
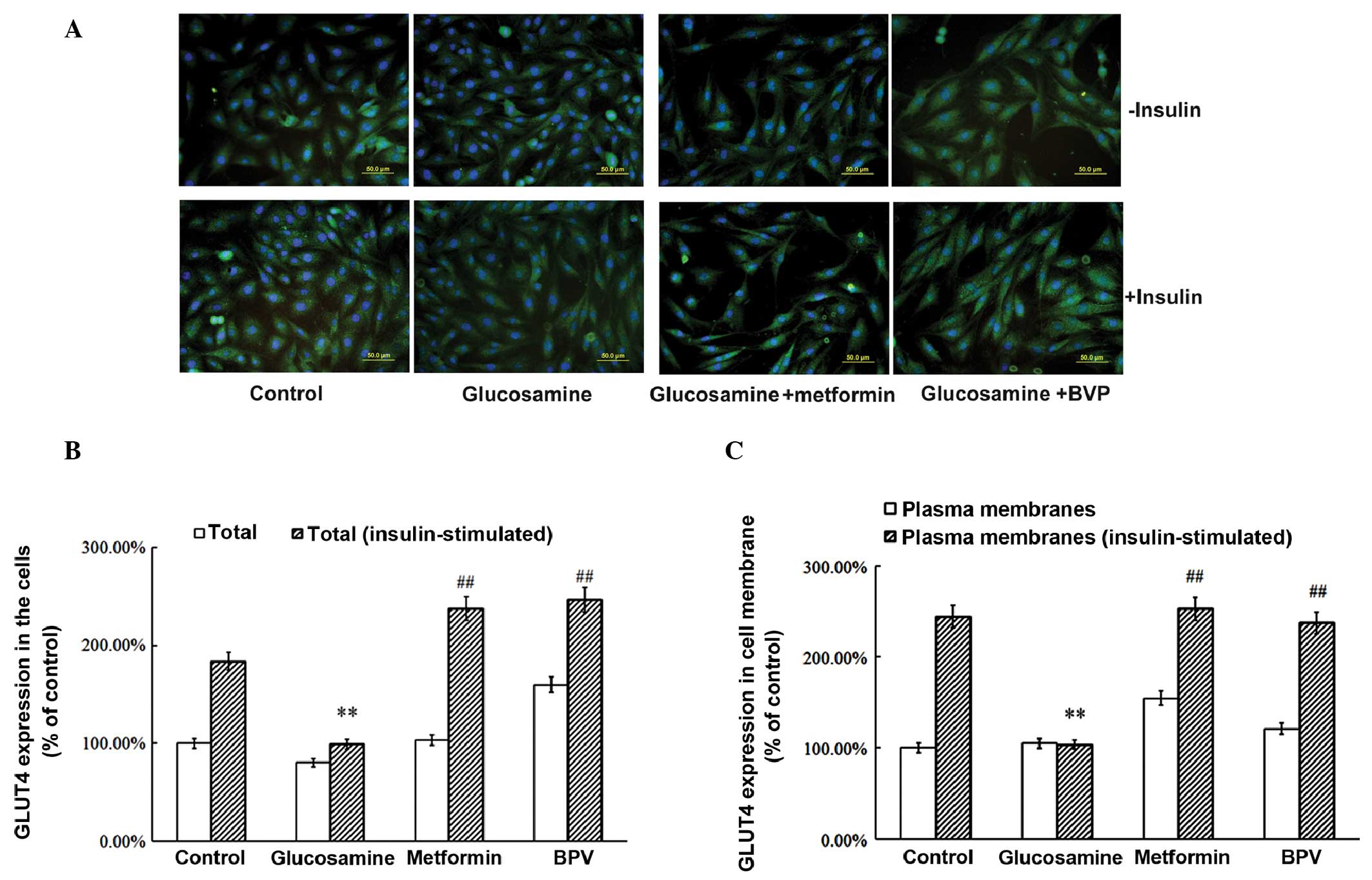
|
1
|
McCarthy AM, Spisak KO, Brozinick JT and
Elmendorf JS: Loss of cortical actin filaments in insulin-resistant
skeletal muscle cells impairs GLUT4 vesicle trafficking and glucose
transport. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 291:C860–C868. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Habegger KM, Penque BA, Sealls W, Tackett
L, Bell LN, Blue EK, Gallagher PJ, Sturek M, Alloosh MA, Steinberg
HO, Considine RV and Elmendorf JS: Fat-induced membrane cholesterol
accrual provokes cortical filamentous actin destabilisation and
glucose transport dysfunction in skeletal muscle. Diabetologia.
55:457–467. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Rando TA and Blau HM: Primary mouse
myoblast purification, characterization and transplantation for
cell-mediated gene therapy. J Cell Biol. 125:1275–1287. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dostrovsky NR, Towheed TE, Hudson RW and
Anastassiades TP: The effect of glucosamine on glucose metabolism
in humans: a systematic review of the literature. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 19:375–380. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chien CS, Cheng SC, Wu HT, Tsao CW and
Cheng JT: Insulin resistance induced by glucosamine in fructose-fed
rats. Horm Metab Res. 41:542–547. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kang L, Chen CH, Cheng YC, Chang CH, Lee
CT, Chang JK, Cheng JT and Chang FM: Glucosamine-induced insulin
resistance in ovariectomized rats is relevant to decreasing the
expression of glucose transport protein subtype 4 in the skeletal
muscle and in increasing the size of pancreatic islets. Menopause.
19:496–502. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sakai K and Clemmons DR: Glucosamine
induces resistance to insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and
insulin in Hep G2 cell cultures: biological significance of
IGF-I/insulin hybrid receptors. Endocrinology. 144:2388–2395. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee JO, Lee SK, Kim JH, Kim N, You GY,
Moon JW, Kim SJ, Park SH and Kim HS: Metformin regulates glucose
transporter 4 (GLUT4) translocation through AMP-activated protein
kinase (AMPK)-Mediated Cbl/CAP Signaling in 3T3-L1
Preadipocytecells. J Biol Chem. 287:44121–44129. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Meshkani R and Adeli K: Hepatic insulin
resistance, metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease. Clin
Biochem. 42:1331–1346. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Joshi A and Ellenson LH: Adenovirus
mediated homozygous endometrial epithelial Pten deletion results in
aggressive endometrial carcinoma. Exp Cell Res. 317:1580–1589.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li J, Yen C, Liaw D, Podsypanina K, Bose
S, Wang SI, Puc J, Miliaresis C, Rodgers L, McCombie R, et al:
PTEN, a putative protein tyrosine phosphatase gene mutated in human
brain, breast and prostate cancer. Science. 275:1943–1947. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nyåkern M, Tazzari PL, Finelli C, Bosi C,
Follo MY, Grafone T, Piccaluga PP, Martinelli G, Cocco L and
Martelli AM: Frequent elevation of Akt kinase phosphorylation in
blood marrow and peripheral blood mononuclear cells from high-risk
myelodysplastic syndrome patients. Leukemia. 20:230–238. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kim SA and Choi HC: Metformin inhibits
inflammatory response via AMPK-PTEN pathway in vascular smooth
muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 425:866–872. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dimchev GA, Al-Shanti N and Stewart CE:
Phospho-tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor Bpv (Hopic) enhances C2C12
myoblast migration in vitro. Requirement of PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK
pathways. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 34:125–136. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li B, Takeda T, Tsuiji K, Kondo A,
Kitamura M, Wong TF and Yaegashi N: The antidiabetic drug metformin
inhibits uterine leiomyoma cell proliferation via an AMP-activated
protein kinase signaling pathway. Gynecol Endocrinol. 29:87–90.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zorzano A, Fandos C and Palacin M: Role of
plasma membrane transporters in muscle metabolism. Biochem J.
349:667–688. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Alkhateeb H, Chabowski C, Glatz JFC,
Luiken JFA and Bonen A: Two phases of palmitate-induced insulin
resistance in skeletal muscle: impaired GLUT4 translocation is
followed by a reduced GLUT4 intrinsic activity. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 293:E783–E793. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zierath JR, Krook A and
Wallberg-Henriksson H: Insulin action in skeletal muscle from
patients with NIDDM. Mol Cell Biochem. 182:153–160. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qu W, Zhao L, Peng X, Yang X, Ying C, Hao
L and Sun X: Biphasic effects of chronic ethanol exposure on
insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in primary cultured rat skeletal
muscle cells: role of the Akt pathway and GLUT4. Diabetes Metab Res
Rev. 47–53. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou QL, Jiang Z, Mabardy AS, Del Campo
CM, Lambright DG, Holik J, Fogarty KE, Straubhaar J, Nicoloro S,
Chawla A and Czech MP: A novel pleckstrin homology
domain-containing protein enhances insulin-stimulated Akt
phosphorylation and GLUT4 translocation in adipocytes. J Biol Chem.
285:27581–27589. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sugimoto N, Miwa S, Ohno-Shosaku T,
Tsuchiya H, Hitomi Y, Nakamura H, Tomita K, Yachie A and Koizumi S:
Activation of tumor suppressor protein PTEN and induction of
apoptosis are involved in cAMP-mediated inhibition of cell number
in B92 glial cells. Neurosci Lett. 497:55–59. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|