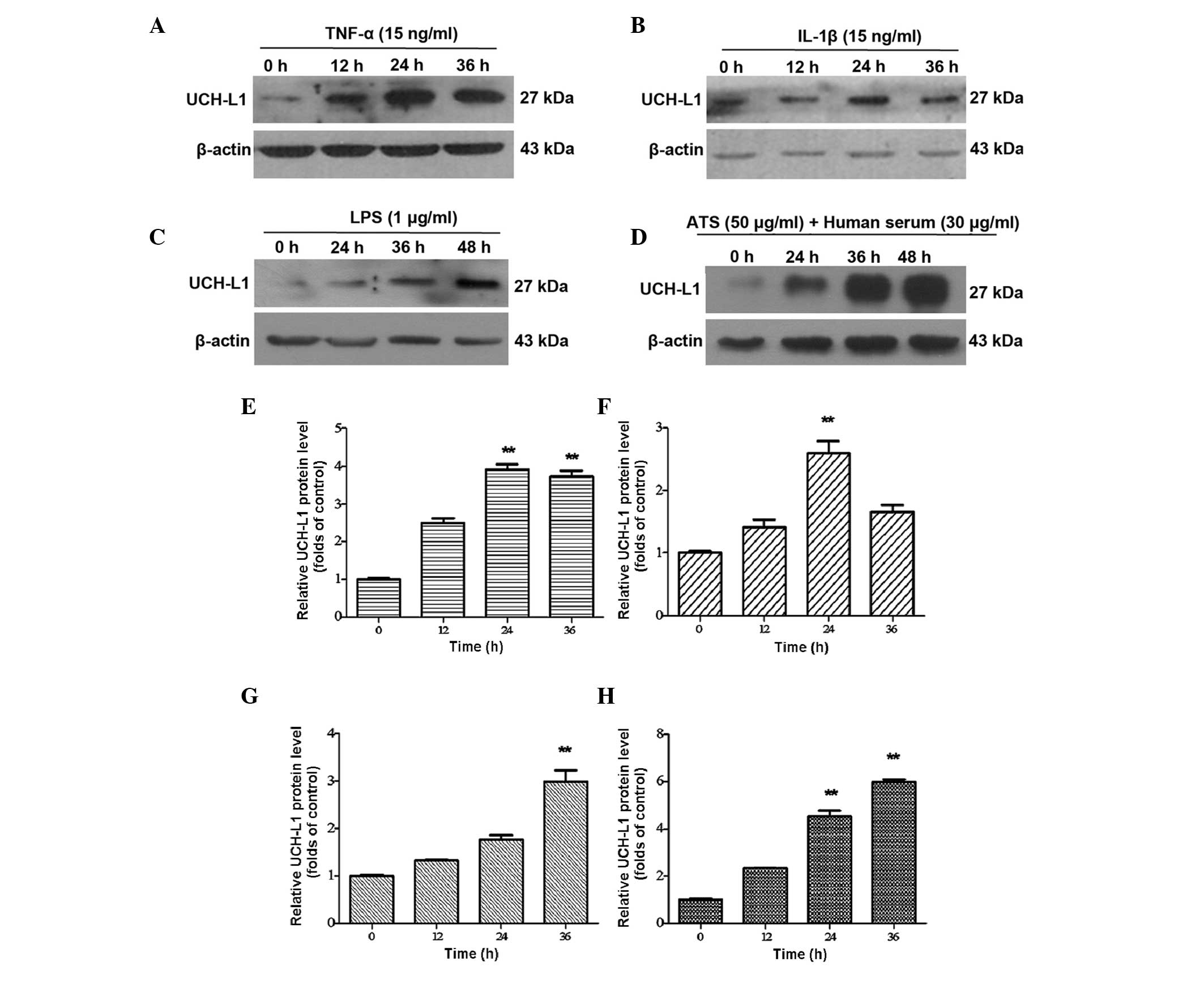
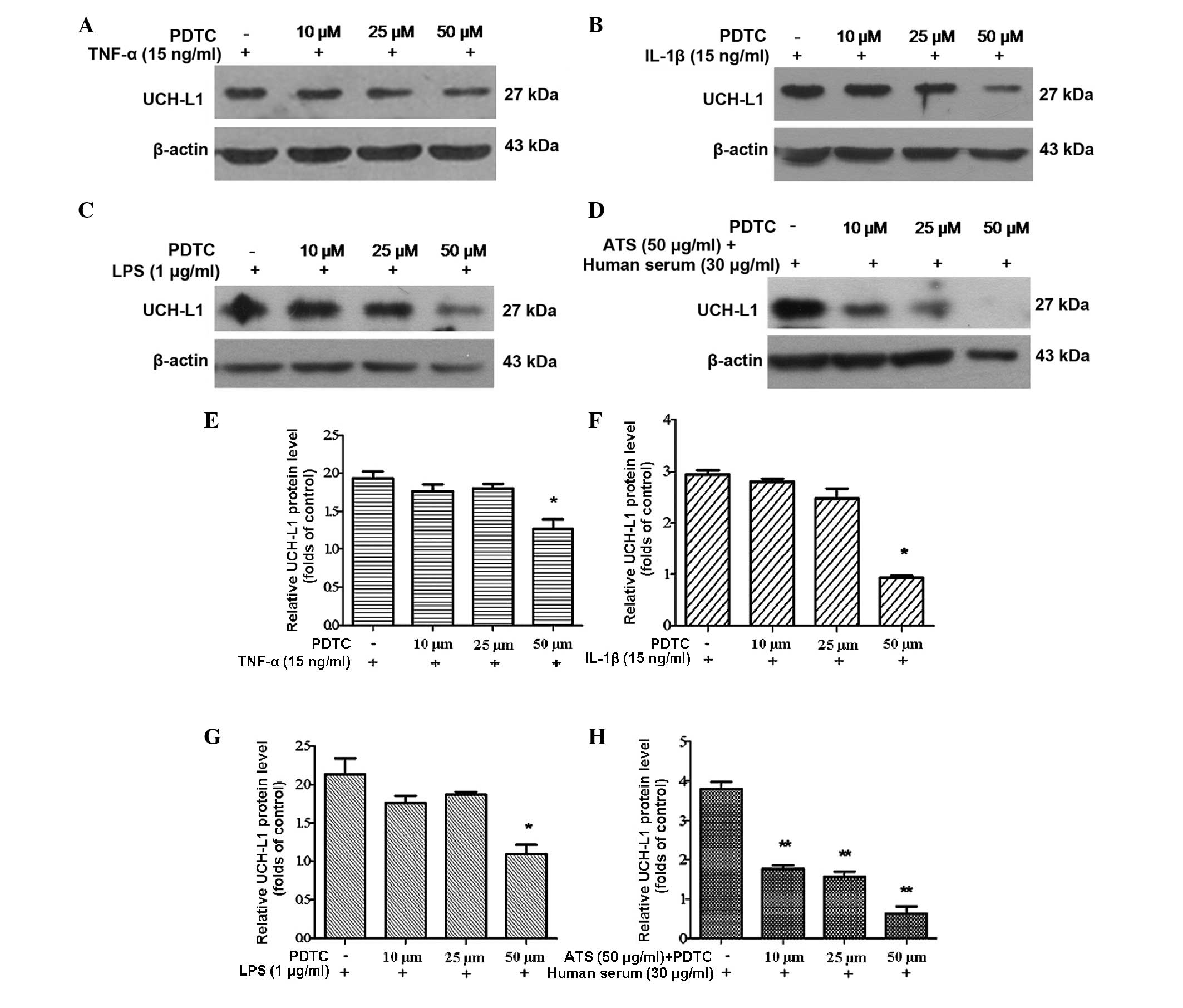
|
1
|
Meyer-Schwesinger C, Meyer TN, Sievert H,
Hoxha E, Sachs M, Klupp EM, Münster S, Balabanov S, Carrier L,
Helmchen U, et al: Ubiquitin c-terminal hydrolase-l1 activity
induces polyubiquitin accumulation in podocytes and increases
proteinuria in rat membranous nephropathy. Am J Pathol.
178:2044–2057. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu Y, Wu J, Wu H, Wang T, Gan H, Zhang X,
Liu Y, Li RX, Zhao Z, Chen Q, Guo MY and Zhang Z: Uch-l1 expression
of podocytes in diseased glomeruli and in vitro. J Pathol.
217:642–653. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Greka A and Mundel P: Cell biology and
pathology of podocytes. Annu Rev Physiol. 74:299–323. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Liu X, Ye L, Christianson G, Yang JQ,
Roopenian DC and Zhu X: Nf-kappab signaling regulates functional
expression of the MHC class I-related neonatal FC receptor for IgG
via intronic binding sequences. J Immunol. 179:2999–3011. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Guijarro C and Egido J: Transcription
factor-kB (NF-kB) and renal disease. Kidney Int. 59:415–424. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Baeuerle PA: Pro-inflammatory signaling:
last pieces in the NF-kappaB puzzle? Curr Biol. 8:R19–R22. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sakurai H, Shigemori N, Hisada Y, Ishizuka
T, Kawashima K and Sugita T: Suppression of NF-kappa B and AP-1
activation by glucocorticoids in experimental glomerulonephritis in
rats: molecular mechanisms of anti-nephritic action. Biochim Biophs
Acta. 1362:252–262. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Massy ZA, Guijarro C, O’Donnell MP, Kim Y,
Kashtan CE, Egido J, Kasiske BL and Keane WF: The central role of
nuclear factor-kappa B in mesangial cell activation. Kidney Int.
(Suppl 71): 76–79. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Rovin BH, Dickerson JA, Tan LC and Hebert
CA: Activation of nuclear factor-kB correlates with MCP-1
expression by human mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 48:1263–1271.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ashizawa M, Miyazaki M, Abe K, Furusu A,
Isomoto H, Harada T, Ozono Y, Sakai H, Koji T and Kohno S:
Detection of nuclear factor-kappaB in IgA nephropathy using
southwestern histochemistry. Am J Kidney Dis. 42:76–86. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zheng L, Sinniah R and Hsu SI: In situ
glomerular expression of activated NF-kappaB in human lupus
nephritis and other non-proliferative proteinuric glomerulopathy.
Virchows Arch. 448:172–183. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bruggeman LA, Drawz PE, Kahoud N, Lin K,
Barisoni L and Nelson PJ: TNFR2 interposes the proliferative and
NF-kappaB-mediated inflammatory response by podocytes to TNF-alpha.
Lab Invest. 91:413–425. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Palanisamy N, Kannappan S and Anuradha CV:
Genistein modulates NF-kappaB-associated renal inflammation,
fibrosis and podocyte abnormalities in fructose-fed rats. Eur J
Pharmacol. 667:355–364. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mudge SJ, Paizis K, Auwardt RB, Thomas RJ
and Power DA: Activation of nuclear factor-kappa B by podocytes in
the autologous phase of passive heymann nephritis. Kidney Int.
59:923–931. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Morigi M, Buelli S, Angioletti S, Zanchi
C, Longaretti L, Zoja C, Galbusera M, Gastoldi S, Mundel P, Remuzzi
G and Benigni A: In response to protein load podocytes reorganize
cytoskeleton and modulate endothelin-1 gene: implication for
permselective dysfunction of chronic nephropathies. Am J Pathol.
166:1309–1320. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Morigi M, Buelli S, Zanchi C, Longaretti
L, Macconi D, Benigni A, Moioli D, Remuzzi G and Zoja C:
Shigatoxin-induced endothelin-1 expression in cultured podocytes
autocrinally mediates actin remodeling. Am J Pathol. 169:1966–1975.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Bondeva T, Roger T and Wolf G:
Differential regulation of toll-like receptor 4 gene expression in
renal cells by angiotensin II: dependency on AP1 and PU.1
transcriptional sites. Am J Nephrol. 27:308–314. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu LX, Lin QX, Liao H, Feng JH, Dong XH
and Ye JM: Tgf-beta1 induces podocyte injury through
SMAD3-ERK-NF-kappaB pathway and FYN-dependent TRPC6
phosphorylation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 26:869–878. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang H, Sun Y, Hu R, Luo W, Mao X, Zhao
Z, Chen Q and Zhang Z: The regulation of the UCH-l1 gene by
transcription factor NF-kB in podocytes. Cell Signal. 25:1574–1585.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fukasawa H: The role of the
ubiquitin-proteasome system in kidney diseases. Clin Exp Nephrol.
16:507–517. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Amerik AY and Hochstrasser M: Mechanism
and function of deubiquitinating enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1695:189–207. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wilson PO, Barber PC, Day IN, Thompson RJ
and Polak JM: The immunolocalization of protein gene product 9.5
using rabbit polyclonal and mouse monoclonal antibodies. Br J Exp
Pathol. 69:91–104. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
D’Andrea V, Malinovsky L, Berni A,
Biancari F, Biassoni L, Di Matteo FM, Corbellini L, Falvo L,
Santoni F, Spyrou M and De Antoni E: The immunolocalization of PGP
9.5 in normal human kidney and renal cell carcinoma. G Chir.
18:521–524. 1997.
|
|
24
|
Shirato I, Asanuma K and Takeda Y: Protein
gene product 9.5 is selectively localized in parietal epithelial
cells of Bowman’s capsule in the rat kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol.
11:2381–2386. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Meyer-Schwesinger C, Meyer TN, Munster S,
Klug P, Saleem M, Helmchen U and Stahl RA: A new role for the
neuronal ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase-l1 (UCH-l1) in podocyte
process formation and podocyte injury in human glomerulopathies. J
Pathol. 217:452–464. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhang M, Guo MY, Chen Q and M JH: The
culture of rat glomerular mesangial cells. J Shanghai Med Univ.
207–209. 1995.
|
|
27
|
Chen GP, Guo MY and Zhang YE: Preparation
of anti-thy1 serum and establishment of mesangioproliferative
glomerulonephritis model in rat. J Clin Exp Pathol. 241–243.
1996.
|
|
28
|
Chiang ML, Hawkins EP, Berry PL, Barrish J
and Hill LL: Diagnostic and prognostic significance of glomerular
epithelial cell vacuolization and podocyte effacement in children
with minimal lesion nephrotic syndrome and focal segmental
glomerulosclerosis: An ultrastructural study. Clin Nephrol.
30:8–14. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang D, Dai C, Li Y and Liu Y: Canonical
WNT/β-catenin signaling mediates transforming growth
factor-β1-driven podocyte injury and proteinuria. Kidney Int.
80:1159–1169. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ghayur A, Liu L, Kolb M, Chawla A, Lambe
S, Kapoor A and Margetts PJ: Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of
TGF-β1 to the renal glomeruli leads to proteinuria. Am J Pathol.
180:940–951. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Shankland SJ: The podocyte’s response to
injury: role in proteinuria and glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int.
69:2131–2147. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Borza DB, Zhang JJ, Beck LH Jr, C M and
Luo W: Mouse models of membranous nephropathy: the road less
travelled by. Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2:135–145. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Meyer-Schwesinger C, Dehde S, Sachs M,
Mathey S, Arefi K, Gatzemeier S, Balabanov S, Becker JU, Thaiss F
and Meyer TN: Rho-kinase inhibition prevents proteinuria in
immune-complex-mediated antipodocyte nephritis. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 303:F1015–F1025. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kato T, Mizuno S and Kamimoto M: The
decreases of nephrin and nuclear WT1 in podocytes may cause
albuminuria during the experimental sepsis in mice. Biomed Res.
31:363–369. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Greka A and Mundel P: Cell biology and
pathology of podocytes. Annu Rev Physiol. 74:299–323. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Hirota M, Watanabe K, Hamada S, Sun Y,
Strizzi L, Mancino M, Nagaoka T, Gonzales M, Seno M, Bianco C and
Salomon D: SMAD2 functions as a co-activator of canonical
WNT/beta-catenin signaling pathway independent of SMAD4 through
histone acetyltransferase activity of p300. Cell Signal.
20:1632–1641. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rangan G, Wang Y and Harris D: NF-kappaB
signalling in chronic kidney disease. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed).
14:3496–3522. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Li QI and Verma M: NF-κB regulation in the
immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2:725–734. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Schjerven H, Brandtzaeg P and Johansen FE:
A novel NF-κB/Rel site in intron 1 cooperates with proximal
promoter elements to mediate TNF-α-induced transcription of the
human polymeric Ig receptor. J Immunol. 167:6412–6420. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nangaku M, Shankland SJ and Couser WG:
Cellular response to injury in membranous nephropathy. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 16:1195–1204. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Rus HG, Niculescu FI and Shin ML: Role of
the c5b-9 complement complex in cell cycle and apoptosis. Immunol
Rev. 180:49–55. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kazatchkine MD, Fearon DT, Appay MD,
Mandet C and Bariety J: Immunohistochemical study of the human
glomerular c3b receptor in normal kidney and in seventy-five cases
of renal diseases: loss of c3b receptor antigen in focal hyalinosis
and in proliferative nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J
Clin Invest. 69:900–912. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|