|
1
|
Chen G, Gharib TG, Wang H, Huang CC, Kuick
R, Thomas DG, Shedden KA, Misek DE, Taylor JMG, Giordano TJ, Kardia
SLR, Iannettoni MD, Yee J, Hogg PJ, Orringer MB, Hanash SM and Beer
DG: Protein profiles associated with survival in lung
adenocarcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:13537–13542. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Brambilla E, Travis WD, Colby TV, Corrin B
and Shimosato Y: The new World Health Organization classification
of lung tumours. Eur Respir J. 18:1059–1068. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Dalton WS and Friend SH: Cancer biomarkers
- an invitation to the table. Science. 312:1165–1168. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fung ET, Wright GL Jr and Dalmasso EA:
Proteomic strategies for biomarker identification: progress and
challenges. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2:643–650. 2000.
|
|
5
|
Sung HJ and Cho JY: Biomarkers for the
lung cancer diagnosis and their advances in proteomics. BMB Rep.
41:615–625. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Druker BJ: Imatinibmesylate in the
treatment of chronic myeloid leukaemia. Expert Opin Pharmaco ther.
4:963–971. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kang SM, Sung HJ, Ahn JM, Park JY, Lee SY,
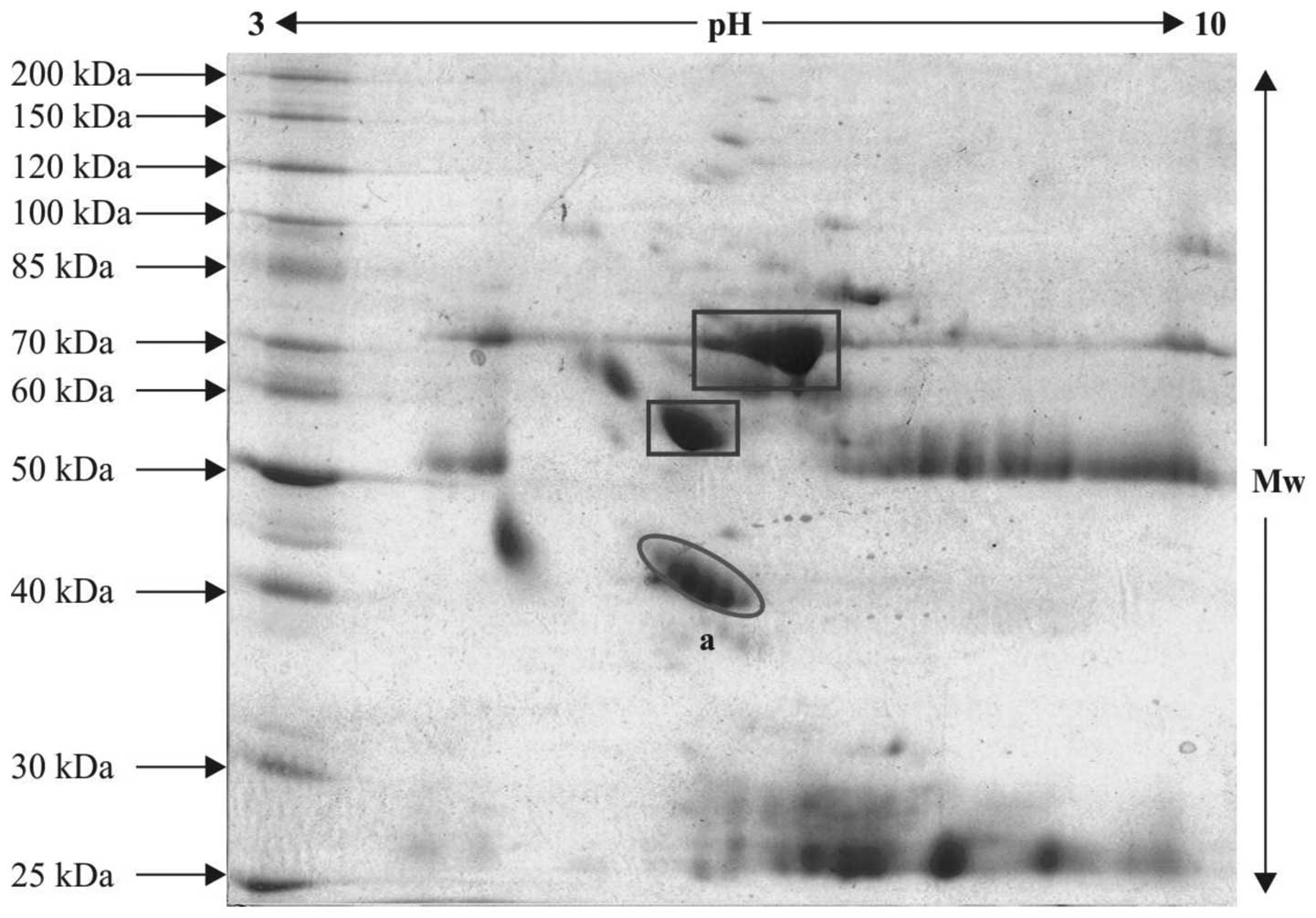
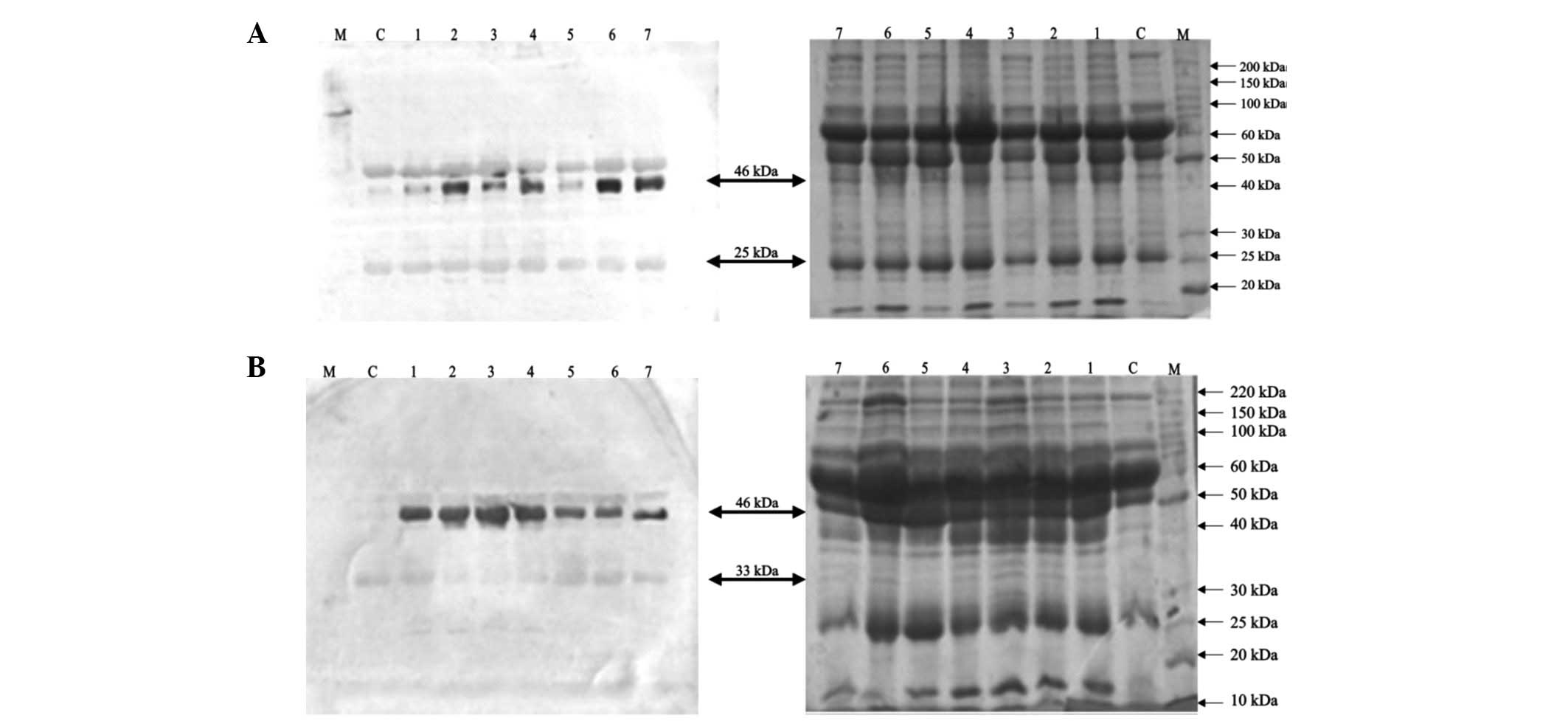
Park CS and Cho JY: The Haptoglobin β chain as a supportive
biomarker for human lung Cancer. J Mol Bio Syst. 7:1167–1175.
2011.
|
|
8
|
Maciel CM, Junqueira M, Paschoal ME,
Kawamura MT, Duarte RL, CarvalhoMda G and Domont GB: Differential
proteomic serum pattern of low molecular weight proteins expressed
by adenocarcinoma lung cancer patients. J Exp Ther Oncl. 5:31–38.
2005.
|
|
9
|
Gruys E, Toussaint MJM, Niewold TA and
Koopmans SJ: Acute phase reaction and acute phase proteins. J
Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 6:1045–1056. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kasprzyk M, Dyszkiewicz W, Zwarun D,
Lesniewska K and Wiktorowicz K: The assessment of acute phase
proteins as prognostic factors in patients surgically treated for
non-small cell lung cancer. Pneumonol Alergol Pol. 76:321–326.
2008.In Polish.
|
|
11
|
Andersen MN, Mouritzen CV and Gabrielli
ER: Mechanisms of plasma hemoglobin clearance after acute hemolysis
in dogs: serum haptoglobin levels and selective deposition in liver
and kidney. Ann Surg. 164:905–912. 1966. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kurosky A, Barnett DR, Lee TH, Touchstone
B, Hay RE, Arnott MS, Bowman BH and Fitch WM: Covalent structure of
human haptoglobin: a serine protease homolog. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 77:3388–3392. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Patzelt D, Geserick G and Schroder H: The
genetic haptoglobin polymorphism: relevance of paternity
assessment. Electrophoresis. 9:393–397. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Judd RC: Purification of outer membrane
proteins of the gram-negative bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Anal
Biochem. 173:307–316. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural
proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.
Nature. 227:680–685. 1970. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Towbin HK, Staehelin T and Gordon J:
Elerophoretic transfer of protein from polyacrylamide gels to
nitrocellulose membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 76:4350–4359.
1979. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics. J Clin. 55:74–108. 2002, 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J,
Smigal C and Thun MJ: Cancer statistics. J Clin. 56:106–130. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ludwig JA and Weinstein JN: Biomarkers in
cancer staging, prognosis and treatment selection. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:845–856. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hanley JM, Haugen TH and Heath EC: Studies
on the biosynthesis of rabbit Haptoglobin. J Biol Chem.
258:7858–7869. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Langlois MR and Delanghe JR: Biological
and clinical significance of haptoglobin polymorphism in humans.
Clin Chem. 42:1589–1600. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Oda K, Miki K, Hirose S, Takami N, Misumi
Y and Ikehara Y: Immunoblotting analysis of plasma protein
processing in the secretory pathway of rat liver: identification of
proteolytic conversion sites of complement pro-C3 and
prohaptoglobin. J Biochem. 100:1669–1675. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hoagland L, Campa M, Gottlin E, Herndon J
and Patz E: Haptoglobin and post-translational glycan-modified
derivatives as serum biomarkers for the diagnosis of non-small cell
lung cancer. 110:2260–2268. 2007.
|