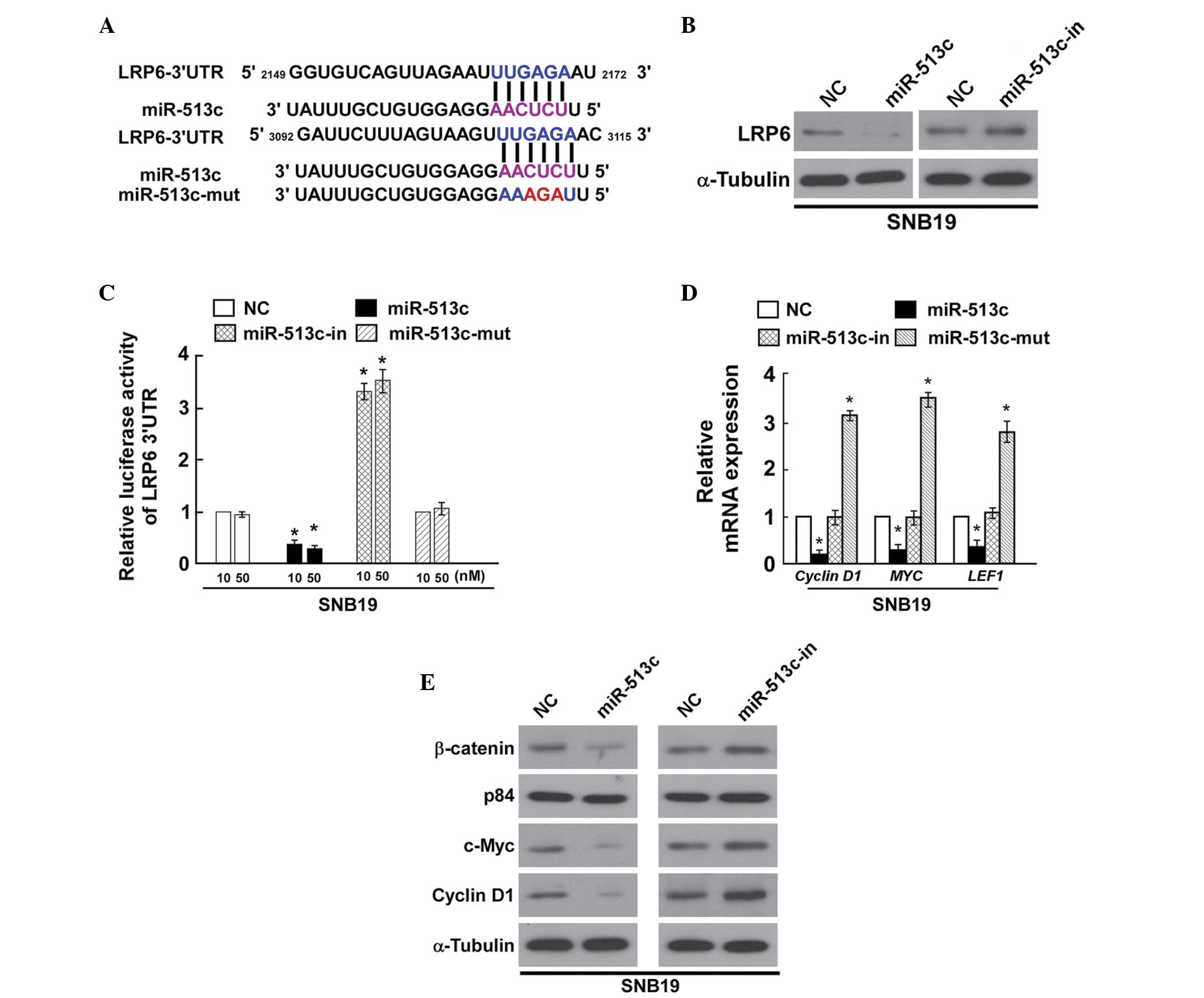
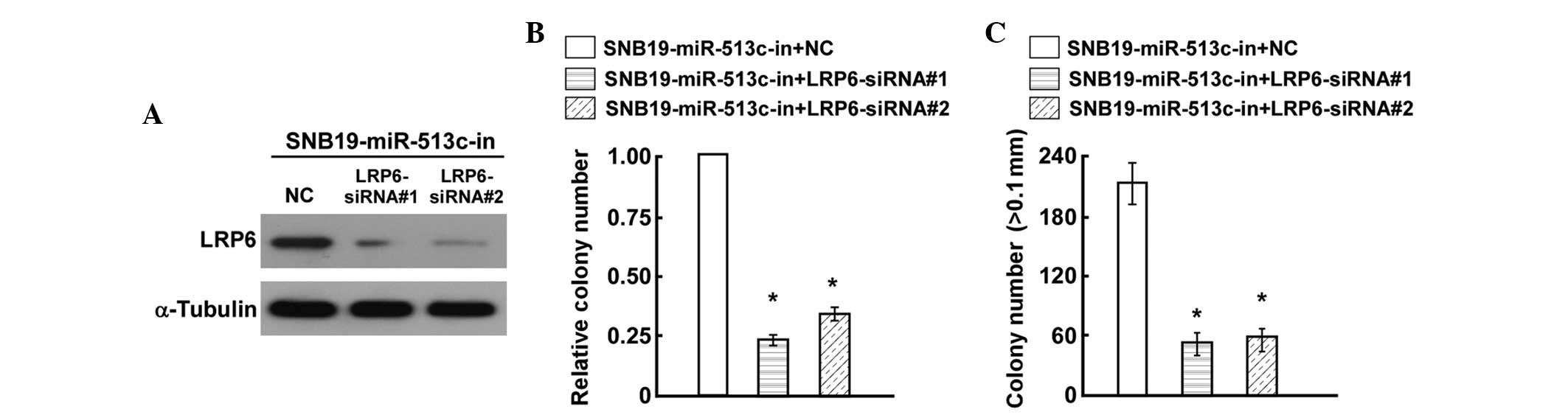
|
1
|
Wen PY and Kesari S: Malignant gliomas in
adults. N Engl J Med. 359:492–507. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Baek D, Villén J, Shin C, Camargo FD, Gygi
SP and Bartel DP: The impact of microRNAs on protein output.
Nature. 455:64–71. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Miska EA: How microRNAs control cell
division, differentiation and death. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
15:563–568. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hsu SY, Kudo M, Chen T, et al: The three
subfamilies of leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled
receptors (LGR): Identification of LGR6 and LGR7 and the signaling
mechanism for LGR7. Mol Endocrinol. 14:1257–1271. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li Y, Lu W, He X, Schwartz AL and Bu G:
LRP6 expression promotes cancer cell proliferation and
tumorigenesis by altering beta-catenin subcellular distribution.
Oncogene. 23:9129–9135. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lu W, Lin C, King TD, Chen H, Reynolds RC
and Li Y: Silibinin inhibits Wnt/beta-catenin signaling by
suppressing Wnt coreceptor LRP6 expression in human prostate and
breast cancer cells. Cell Signal. 24:2291–2296. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Formosa A, Markert EK, Lena AM, et al:
MicroRNAs, miR-154, miR-299-5p, miR-376a, miR-376c, miR-377,
miR-381, miR-487b, miR-485-3p, miR-495 and miR-654-3p, mapped to
the 14q32.31 locus, regulate proliferation, apoptosis, migration
and invasion in metastatic prostate cancer cells. Oncogene.
33:5173–5182. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lehmann U, Streichert T, Otto B, et al:
Identification of differentially expressed microRNAs in human male
breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 10:1092010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gong X, Carmon KS, Lin Q, Thomas A, Yi J
and Liu Q: LGR6 is a high affinity receptor of R-spondins and
potentially functions as a tumor suppressor. PLoS One.
7:e371372012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gray JD, Kholmanskikh S, Castaldo BS, et
al: LRP6 exerts non-canonical effects on Wnt signaling during
neural tube closure. Hum Mol Genet. 22:4267–4281. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Joiner DM, Ke J, Zhong Z, Xu HE and
Williams BO: LRP5 and LRP6 in development and disease. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 24:31–39. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Maletínská L, Blakely EA, Bjornstad KA,
Deen DF, Knoff LJ and Forte TM: Human glioblastoma cell lines:
levels of low-density lipoprotein receptor and low-density
lipoprotein receptor-related protein. Cancer Res. 60:2300–2303.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Semënov MV, Zhang X and He X: DKK1
antagonizes Wnt signaling without promotion of LRP6 internalization
and degradation. J Biol Chem. 283:21427–21432. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ochoa-Hernández AB, Juárez-Vázquez CI,
Rosales-Reynoso MA and Barros-Núñez P: WNT-β-catenin signaling
pathway and its relationship with cancer. Cir Cir. 80:389–398.
2012.In Spanish.
|
|
17
|
Kim KH, Seol HJ, Kim EH, et al:
Wnt/β-catenin signaling is a key downstream mediator of MET
signaling in glioblastoma stem cells. Neuro Oncol. 15:161–171.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Hsieh IS, Chang KC, Tsai YT, et al:
MicroRNA-320 suppresses the stem cell-like characteristics of
prostate cancer cells by downregulating the Wnt/beta-catenin
signaling pathway. Carcinogenesis. 34:530–538. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Fu Y, Zheng S, An N, et al: β-catenin as a
potential key target for tumor suppression. Int J Cancer.
129:1541–1551. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chocarro-Calvo A, García-Martínez JM,
Ardila-González S, De la Vieja A and García-Jiménez C:
Glucose-induced β-catenin acetylation enhances Wnt signaling in
cancer. Mol Cell. 49:474–486. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang D, Wise ML, Li F and Dey M:
Phytochemicals attenuating aberrant activation of β-catenin in
cancer cells. PLoS One. 7:e505082012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
He TC, Sparks AB, Rago C, et al:
Identification of c-MYC as a target of the APC pathway. Science.
281:1509–1512. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kolligs FT, Bommer G and Göke B:
Wnt/beta-catenin/tcf signaling: a critical pathway in
gastrointestinal tumorigenesis. Digestion. 66:131–144. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nagayama M, Iwamoto M, Hargett A, et al:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling regulates cranial base development and
growth. J Dent Res. 87:244–249. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang FI, Chen YL, Chang CN, Yuan RH and
Jeng YM: Hepatocyte growth factor activates Wnt pathway by
transcriptional activation of LEF1 to facilitate tumor invasion.
Carcinogenesis. 33:1142–1148. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Planutiene M, Planutis K and Holcombe RF:
Lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1, a representative of
vertebrate-specific Lef1/Tcf1 sub-family, is a Wnt-beta-catenin
pathway target gene in human endothelial cells which regulates
matrix metal-loproteinase-2 expression and promotes endothelial
cell invasion. Vasc Cell. 3:282011. View Article : Google Scholar
|